
Explore
Medication: You may need to take one or more drugs as part of your treatment. Common heart failure medications for diastolic heart failure include: Diuretics, which help ease swelling
How can you treat diastolic heart failure with medication?
Your provider might prescribe medications specifically for diastolic heart failure that include: Diuretics to help your body get rid of excess sodium and water. Mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists to help your body get rid of extra sodium while keeping potassium. Medications to lower blood pressure. Is there a cure for diastolic heart failure?
What is the best medication for diastolic dysfunction?
Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF), often referred to as diastolic heart failure, remains one of the more challenging forms of heart failure to treat. This is a condition in which patients may or may not have signs and symptoms of heart failure, and retain a left ventricular ejection fraction greater than 50%.
How to treat Grade 1 diastolic dysfunction?
Apr 27, 2021 · There is currently no cure for any kind of heart failure. However, a person can improve their symptoms and outlook with the right treatment. Behavioral changes A person can take up heart-healthy...
Is diastolic heart failure new?
Diastolic heart failure isn't really new. It's just that doctors now have tools that let them see how this form of heart failure differs from "regular" (systolic) heart failure. At least half of the people who develop heart failure each year have diastolic heart failure.
Is ejection fraction normal in diastolic heart failure?
Ejection fraction, a key measure of the heart's pumping ability, is normal in diastolic heart failure and low in systolic heart failure. As researchers search for the best treatments for diastolic heart failure, controlling blood pressure and fluid in the body are key strategies; heart-protecting drugs may be helpful.
What are the two phases of heartbeat?
Every heartbeat has two distinct phases. During systole (SIS-tuh-lee), cardiac muscle fibers contract in unison. This makes the heart twist a bit and close in on itself, propelling blood to the lungs and the body. During diastole (die-AS-tuh-lee), the muscle fibers relax and stretch.
What happens during systole?
During systole (SIS-tuh-lee), cardiac muscle fibers contract in unison. This makes the heart twist a bit and close in on itself, propelling blood to the lungs and the body. During diastole (die-AS-tuh-lee), the muscle fibers relax and stretch.
Does aging cause stiffness in the heart?
Aging takes some of the spring out of the muscles in the heart. High blood pressure, cholesterol-clogged coronary arteries, a malfunctioning heart valve, diabetes, and other problems can also stiffen heart muscle and bulk up the muscle inside the left ventricle. Diastolic heart failure looks and feels just like systolic heart failure.
Why is relaxation important?
Relaxation is every bit as important for your heart as it is for the rest of you. If for some reason the heart has trouble relaxing between beats, then it can't fill completely. Less blood pumped with each contraction sets the stage for a type of heart failure that goes by many names: diastolic heart failure, heart failure with normal ejection ...
How to tell if you have heart failure?
Common signs of heart failure can include: 1 Shortness of breath 2 Tiredness, weakness 3 Swelling in your feet, ankles, legs, or abdomen 4 Lasting cough or wheezing 5 Fast or irregular heartbeat 6 Dizziness, confusion 7 Having to pee more often at night 8 Nausea, lack of appetite
Why does my heart get stiff?
Other than normal aging, the most common causes are: High blood pressure: If you have it, your heart has to work harder to pump more blood through your body. Thanks to that extra work, your heart muscle may get thicker or larger, and it eventually gets stiff. Learn more about the symptoms of high blood pressure.
What is diastolic heart failure?
Diastolic heart failure happens when the heart does not relax properly between beats. This means it is unable to pump blood throughout the body the way it should and has to function at a higher pressure, which can cause symptoms.
What is the difference between systolic and diastolic heart failure?
Systolic heart failure happens when the pumps of the heart are not strong enough to move blood around the body effectively. Diastolic heart failure means the heart does not relax correctly between beats. A person can experience systolic and diastolic heart failure at the same time. Learn about systolic vs. diastolic heart failure here.
What does it mean when your heart is diastolic?
Diastolic heart failure happens when the heart does not relax properly between beats. This means it is unable to pump blood throughout the body the way it should and has to function at a higher pressure, which can cause symptoms.
What does it mean when your heart is not pumping blood?
Diastolic heart failure happens when the heart does not relax properly between beats. This means it is unable to pump blood throughout the body the way it should and has to function at a higher pressure, which can cause symptoms. If the heart pumps less blood, it means that less oxygen goes to vital organs and tissues.
What are the symptoms of congestive heart failure?
tiredness. shortness of breath. swelling in the legs. swelling in the abdomen. exercise intolerance. A person may notice that any kind of physical exertion, including day-to-day activities, become much more difficult due to fatigue and shortness of breath. Learn about symptoms of congestive heart failure here.
Is heart disease a sign of cardiovascular disease?
A person is at risk of heart disease, but there are no signs of cardiovascular disease. The person has no symptoms and can carry out their usual physical activities with no difficulty. B. A person is at risk of heart disease. The person has no symptoms.
What causes a stiff left ventricle?
Diastolic heart failure involves the left side of the heart. It causes a stiff left ventricle that prevents the heart from relaxing between beats. This means that the heart can’t pump an adequate amount of blood throughout the body or has to pump with increased pressure.
Why is diastolic heart failure important?
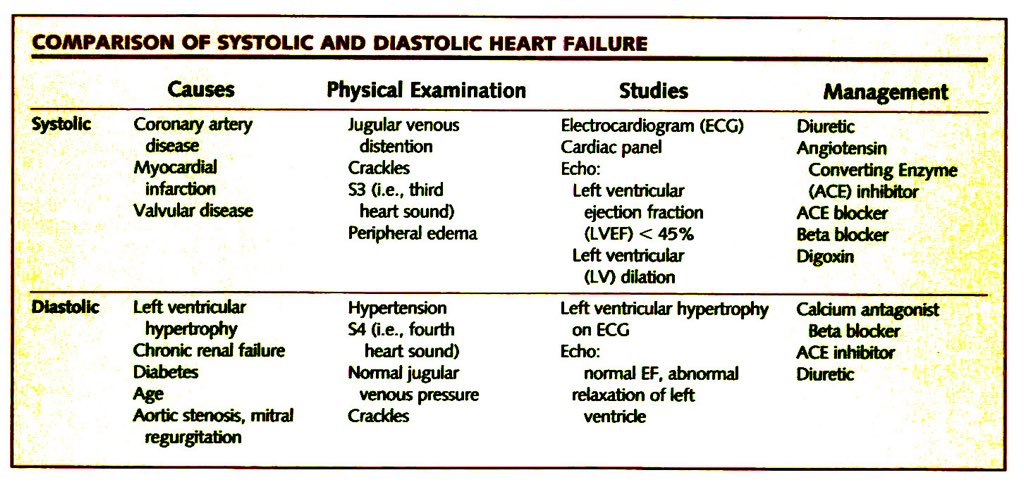
Distinguishing diastolic from systolic heart failure is essential because the optimal therapy for one may aggravate the other. Although diastolic heart failure is clinically and radiographically indistinguishable from systolic heart failure, normal ejection fraction and abnormal diastolic function in the presence of symptoms and signs ...
What is diastolic heart failure?
Diastolic heart failure is defined as a condition caused by increased resistance to the filling of one or both ventricles; this leads to symptoms of congestion from the inappropriate upward shift of the diastolic pressure-volume relation. 7 Although this definition describes the principal pathophysiologic mechanism of diastolic heart failure, it is not clinically applicable. A more practical definition for use in clinical practice is: a condition that includes classic CHF findings and abnormal diastolic and normal systolic function at rest. 8, 9 A study group 7 proposed that physicians combine clinical and echocardiographic information to categorize patients with diastolic heart failure according to the degree of diagnostic certainty ( Table 1 10).
Does heart failure increase with age?
The incidence of diastolic heart failure increases with age; therefore, 50 percent of older patients with heart failure may have isolated diastolic dysfunction. With early diagnosis and proper management the prognosis of diastolic dysfunction is more favorable than that of systolic dysfunction. Distinguishing diastolic from systolic heart failure ...
Does beta blocker help with heart failure?
In addition to slowing heart rate, beta blockers have proven benefits in reducing blood pressure and myocardial ischemia, promoting regression of left ventricular hypertrophy, and antagonizing the excessive adrenergic stimulation during heart failure .
Does aldosterone cause diastolic stiffness?
The hormone aldosterone promotes fibrosis in the heart and contributes to diastolic stiffness. The aldosterone antagonist spironolactone (Aldactone) has been studied in a large clinical trial of systolic heart failure, 29 which showed a reduction in mortality related to heart failure.
What is the process of the heart returning to its relaxed state?
Diastole is the process by which the heart returns to its relaxed state. During this period, the cardiac muscle is perfused. Conventionally, diastole can be divided into four phases: isovolumetric relaxation, caused by closure of the aortic valve to the mitral valve opening; early rapid ventricular filling located after the mitral valve opening; diastasis, a period of low flow during mid-diastole; and late rapid filling during atrial contraction. 16 Broadly defined, isolated diastolic dysfunction is the impairment of isovolumetric ventricular relaxation and decreased compliance of the left ventricle. With diastolic dysfunction, the heart is able to meet the body’s metabolic needs, whether at rest or during exercise, but at a higher filling pressure. Transmission of higher end-diastolic pressure to the pulmonary circulation may cause pulmonary congestion, which leads to dyspnea and subsequent right-sided heart failure. With mild dysfunction, late filling increases until the ventricular end-diastolic volume returns to normal. In severe cases, the ventricle becomes so stiff that the atrial muscle fails and end-diastolic volume cannot be normalized with elevated filling pressure. This process reduces stroke volume and cardiac output, causing effort intolerance. Figure 1 17 summarizes the pathophysiology of diastolic heart failure.
What is the best treatment for heart failure?
Depending on your symptoms, you might take one or more medications, including: Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors. These drugs relax blood vessels to lower blood pressure, improve blood flow and decrease the strain on the heart.
How to manage heart failure?
These steps may help you manage heart failure: Keep track of the medications you take. Make a list of all the medications you take, carry it with you and share it with your doctors. Don't stop taking any medications without first talking to your doctor.
What is the best test to check for heart disease?
Blood tests are done to look for signs of diseases that can affect the heart. Chest X-ray. X-ray images can show the condition of the lungs and heart. Electrocardiogram (ECG). This quick and painless test records the electrical signals in the heart. It can show the timing and length of the heartbeats. Echocardiogram.
Is heart failure a chronic disease?
Heart failure is a chronic disease needing lifelong management. However, with treatment, signs and symptoms of heart failure can improve, and the heart sometimes becomes stronger. Treatment may help you live longer and reduce your chance of dying suddenly.
Can heart failure be reversed?
Although many cases of heart failure can't be reversed, treatment can sometimes improve symptoms and help you live longer . You and your doctor can work together to help make your life more comfortable. Pay attention to your body and how you feel, and tell your doctor when you're feeling better or worse. This way, your doctor will know what treatment works best for you. Don't be afraid to ask your doctor questions about living with heart failure.
What to do if you think you have heart failure?
If you think you may have heart failure or you are worried about your heart failure risk because of other underlying conditions, make an appointment with your family doctor. If heart failure is found early, your treatment may be easier and more effective.
What is the purpose of an echocardiogram?
An echocardiogram can be used to measure ejection fraction, which shows how well the heart is pumping and helps classify heart failure and guides treatment. Stress test.
What is diastolic dysfunction?
When the filling of the heart is abnormal, cardiologists call this diastolic dysfunction. This can lead to diastolic heart failure, or heart failure with preserved ejection fraction, a leading cause of morbidity and mortality. There are no current therapies effective in improving outcomes for these patients.
Does Omega 3 help with heart failure?
Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (omega 3-PUFAs) seem to favorably affect cardiac hemodynamics and may benefit the clinical course of heart failure patients. The role of omega 3-PUFAs supplementation on the left and right ventricular function of patients with heart failure was studied. 205 patients with heart failure were enrolled.
Is diastole energy or energy?
Doctors have long understood that contraction of the heart, known as systole, is an energy-requiring process. The filling of the heart with oxygenated blood returning from the lungs, known as diastole, was thought to be passive (not requiring energy).

Causes
Pathophysiology
- Aging takes some of the spring out of the muscles in the heart. High blood pressure, cholesterol-clogged coronary arteries, muscle damage from a heart attack, a malfunctioning heart valve, diabetes, anemia, an overactive thyroid gland, and other problems can also stiffen heart muscle and bulk up the muscle inside the left ventricle.
Symptoms
- Diastolic heart failure looks and feels just like systolic heart failure. Its hallmarks are shortness of breath with exertion or when lying down; swelling in the legs, ankles, or abdomen; unexplained fatigue; or a bulging jugular vein. The main way to distinguish one type from the other is with an echocardiogram. It can show the size and shape of the left ventricle and gauge how it is functio…
Terminology
- A low ejection fraction (under 35% or so) with symptoms equals systolic heart failure; a normal ejection fraction with symptoms equals diastolic heart failure.
Treatment
- The big problem with diastolic heart failure is that doctors don't yet know the best way to treat it. Therapies proven to work for systolic heart failure (characterized by a thin, flabby left ventricle) don't necessarily work for diastolic heart failure (characterized by a thick, stiff left ventricle). Scores of clinical trials investigating possib...
Contraindications
- In the meantime, the American Heart Association and American College of Cardiology recommend controlling: