
Explore
Jun 09, 2021 · However, not all treatments for invasive breast cancer may be optimal for DCIS, Gupta says. His study suggests that in most cases of DCIS, the side effects of hormone therapy may outweigh its benefits. The CUIMC Newsroom spoke with Gupta to learn how the study’s findings can help providers and their patients navigate treatment for DCIS.
What is DCIS, and how is it treated?
Surgery for DCIS Surgery is the first step to treat DCIS. It removes the abnormal tissue from the breast. Depending on how far the DCIS has spread within the milk ducts, surgery can be mastectomy or lumpectomy. If DCIS is spread throughout the ducts, affecting a large part of the breast, a total (simple) mastectomy will be done.
How should DCIS be treated?
What is the treatment for DCIS? Lumpectomy with radiation. The standard treatment is breast-preserving surgery (a lumpectomy) with radiation therapy, which results in successful outcomes for most patients. Cancers can be larger than expected, so about 20% of the time, patients need a re-excision lumpectomy — another surgery — to remove all of the cancer.
Is no treatment the best treatment for DCIS breast cancer?
Jan 21, 2022 · Most women with DCIS or breast cancer that can be treated with surgery have three surgery choices. lumpectomy or other breast-sparing surgery, such as partial mastectomy segmental mastectomy mastectomy mastectomy with reconstruction Lumpectomy or other breast-sparing surgery, followed by radiation therapy
How should we treat DCIS?

Is hormone therapy necessary for DCIS?
Hormonal therapy is recommended for some women with DCIS to help prevent breast cancer from developing and to prevent DCIS from returning after it has been surgically removed. It is only effective for women whose DCIS is “estrogen receptor positive”, which DCIS usually is.Feb 16, 2018
How long does it take for DCIS to become invasive?
'' DCIS rarely leads to death from breast cancer – approximately 11 out of 100 women treated by lumpectomy only go on to develop invasive cancer within eight years of the initial diagnosis of DCIS, and only 1 to 2 percent of women die of breast cancer within 10 years of diagnosis.Apr 28, 2010
What is the survival rate of DCIS?
Generally, patients diagnosed with DCIS have an excellent long-term breast-cancer-specific survival of around 98% after 10 years of follow-up24–27 and a normal life expectancy.Jul 9, 2019
Does DCIS ever go away?
Clusters of abnormal cells like D.C.I.S. can sometimes disappear, stop growing or simply remain in place and never cause a problem. The suspicion is that the abnormal cells may be harmless and may not require treatment.Aug 20, 2015
Is DCIS slow growing?
Grade 1 DCIS is almost always ER and PR positive and is a very slow growing form of cancer. It can take years, even decades, to see progression of the disease. In some cases, it may take such a long time to spread beyond the breast duct that it is not an event that will happen during a person's lifetime.Sep 30, 2016
Should I have a mastectomy for DCIS?
If the DCIS is large, a mastectomy may be recommended. Removing the opposite breast usually isn't recommended; chemotherapy usually isn't recommended either. Hormonal therapy may be recommended if the DCIS is hormone-receptor-positive. DCIS is NOT invasive cancer.Apr 10, 2009
Is DCIS 100 curable?
But DCIS is nearly 100 percent curable. Typically, the treatment is a small operation called lumpectomy, often but not always followed by radiation to the area.Aug 5, 2013
What is considered a large DCIS?
Small DCIS tumors (<1.0 cm) with negative margins carry a low risk of local failure and can be treated conservatively with lumpectomy. Large DCIS tumors (⩾2.5 cm) pose a particular risk of residual disease regardless of margin status, and additional adjuvant therapy may be necessary.
How serious is DCIS?
DCIS is non-invasive because it hasn't spread beyond the milk ducts into other healthy tissue. DCIS isn't life-threatening, but if you're diagnosed with DCIS, you have a higher-than-average risk of developing invasive breast cancer later in life.Feb 4, 2022
Can DCIS spread after lumpectomy?
Will DCIS return or spread? Since DCIS is a noninvasive form of cancer, it does not spread throughout the body (metastasize). For patients having a lumpectomy with radiation, the risk of local recurrence ranges from 5% to 15%. For those having mastectomy, the risk of local recurrence is less than 2%.
Can you get DCIS twice?
Although mortality rates are very low, DCIS can recur and around half of recurrences are invasive cancers.Mar 21, 2018
Can DCIS spread to lungs?
They die the conventional way from breast cancer — because it spreads to the bones, liver and lungs. The women who die of DCIS died because their breast cancer already spread by the time they received treatment,” says Narod.Aug 20, 2015
How long does it take to survive DCIS?
It’s important to understand that radiation and hormone treatments do not change survival—the 10-year survival rate for women diagnosed with DCIS is 98% regardless of whether they receive either treatment. These treatments instead reduce the risk of breast cancer down the road.
What is DCIS in mammography?
Before the advent of routine mammography, DCIS (ductal carcinoma in situ) was rarely detected. But today, DCIS accounts for 20% of breast cancer diagnoses and would be the fifth most common cancer in women if classified independently. Apar Gupta. Often called “stage zero breast cancer,” DCIS growths are confined to the inside ...
What is stage zero breast cancer?
Apar Gupta. Often called “stage zero breast cancer,” DCIS growths are confined to the inside of the breast’s milk ducts, and many never develop into invasive cancers. Several treatment options are available, and opinions about the optimal treatment for DCIS vary widely among doctors.
Can hormone therapy be used for DCIS?
However, not all treatments for invasive breast cancer may be optimal for DCIS, Gupta says. His study suggests that in most cases of DCIS, the side effects of hormone therapy may outweigh its benefits. The CUIMC Newsroom spoke with Gupta to learn how the study’s findings can help providers and their patients navigate treatment for DCIS.
Is DCIS a pre-invasive cancer?
“DCIS is considered a pre-invasive cancer, but the current standard of care is to treat it like an early-stage invasive breast cancer,” says Apar Gupta, MD, ...
Can DCIS be overtreated?
Since treatment of DCIS after surgery doesn’t improve survival, there is a growing concern that DCIS may be overtreated if the benefit of these treatments is outweighed by their impact on quality of life.
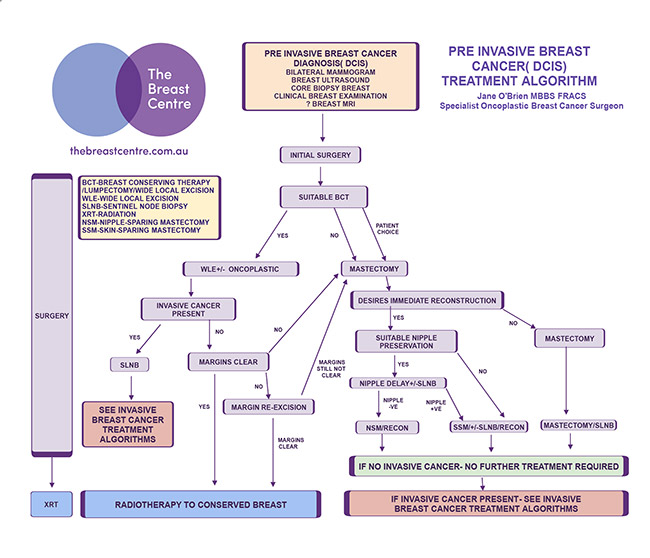
What is the treatment for DCIS?
In most people, treatment options for DCIS include: Breast-conserving surgery (lumpectomy) and radiation therapy. Breast-removing surgery (mastectomy) In some cases, treatment options may include: Lumpectomy only.
What is DCIS on a mammogram?
DCIS is most often discovered during a mammogram used to screen for breast cancer. If your mammogram shows suspicious areas such as bright white specks (microcalcifications) that are in a cluster and have irregular shapes or sizes, your radiologist likely will recommend additional breast imaging. You may have a diagnostic mammogram, which takes ...
What is radiation therapy after lumpectomy?
Radiation therapy after lumpectomy reduces the chance that DCIS will come back (recur) or that it will progress to invasive cancer.
What is a calcification on a mammogram?
Calcifications are small calcium deposits in the breast that show up as white spots on a mammogram. Large, round or well-defined calcifications (shown left) are more likely to be noncancerous (benign). Tight clusters of tiny, irregularly shaped calcifications (shown right) may indicate cancer.
What is lumpectomy surgery?
A lumpectomy involves removing the cancer and some of the healthy tissue that surrounds it. This illustration shows one possible incision that can be used for this procedure, though your surgeon will determine the approach that's best for your particular situation.
What is clinical trial?
Clinical trials are studying new strategies for managing DCIS, such as close monitoring rather than surgery after diagnosis. Whether you're eligible to participate in a clinical trial depends on your specific situation. Talk with your doctor about your options.
Can alternative medicine cure DCIS?
Alternative medicine. No alternative medicine treatments have been found to cure DCIS or to reduce the risk of being diagnosed with an invasive breast cancer. Instead, complementary and alternative medicine treatments may help you cope with your diagnosis and the side effects of your treatment, such as distress.
How to treat DCIS?
Surgery is the first step to treat DCIS. It removes the abnormal tissue from the breast. Depending on how far the DCIS has spread within the milk ducts, surgery can be mastectomy or lumpectomy. If DCIS is spread throughout the ducts, affecting a large part of the breast, a total (simple) mastectomy will be done.
What is a Lumpectomy for DCIS?
Lumpectomy for DCIS is usually followed by whole breast radiation therapy to lower the risk of [ 6-13 ]: DCIS recurrence (a return of DCIS) in the treated breast. Invasive breast cancer in the treated breast.
What is sentinel node biopsy?
A sentinel node biopsy is a procedure used to check whether or not invasive breast cancer has spread to the lymph nodes in the underarm area (axillary nodes). The surgeon removes 1-5 nodes.
Why is DCIS called in situ?
It’s called “in situ” (which means “in place”) because the cells have not left the milk ducts to invade nearby breast tissue. DCIS is also called intraductal (within the milk ducts) carcinoma. You may hear the terms “pre-invasive” or “pre-cancerous” to describe DCIS. DCIS is treated to try to prevent the development of invasive breast cancer.
How do pathologists determine the hormone receptor status of a DCIS tumor?
A pathologist determines the hormone receptor status of the DCIS by testing the tissue removed during a biopsy. Hormone receptor-positive (estrogen receptor-positive/progesterone receptor-positive) DCIS tumors express hormone receptors. This means they have a lot of hormone receptors..
Can you have a sentinel node biopsy after a mastectomy?
Once a mastectomy has been done, a person can’t have a sentinel node biopsy. If it turns out there’s invasive breast cancer (along with DCIS) in the tissue removed during the mastectomy, a sentinel node biopsy will have already been done.
Can a lumpectomy be done with DCIS?
If there’s little spread of DCIS within the ducts, a choice can be made between mastectomy or lumpectomy. With lumpectomy, the surgeon removes only the abnormal tissue in the breast and a small rim of normal tissue around it. The rest of the breast is left intact.
How is DCIS diagnosed?
If a doctor sees the calcifications on your mammogram, he or she will recommend more tests, which could include a breast biopsy. During the biopsy, a doctor or other health care provider takes samples of cells or tissues from your body. The cells are examined by a pathologist — a doctor who checks for signs of disease in body tissues.
What is the treatment for DCIS?
Lumpectomy with radiation. The standard treatment is breast-preserving surgery (a lumpectomy) with radiation therapy, which results in successful outcomes for most patients. Cancers can be larger than expected, so about 20% of the time, patients need a re-excision lumpectomy — another surgery — to remove all of the cancer.
What should I expect after a DCIS diagnosis?
The outlook after DCIS diagnosis, Sun says, is encouraging. “With continued, rigorous monitoring, the prognosis for DCIS is excellent,” she explains. “Your doctor will recommend a regular screening schedule to guard against recurrence in the original breast, and to monitor the other breast for any signs of malignancy.
What are the three choices for breast cancer?
Most women with DCIS or breast cancer that can be treated with surgery have three surgery choices. Surgery Choices: Cindy, Theresa, Paula. Three women describe the type of surgery that they chose to treat their breast cancer.
What is the treatment for breast cancer?
Partial mastectomy. Breast-conserving surgery. Segmental mastectomy. After breast-sparing surgery, most women also receive radiation therapy. The main goal of this treatment is to keep cancer from coming back in the same breast. Some women will also need chemotherapy, hormone therapy, and/or targeted therapy.
What is breast surgery?
Breast-sparing surgery means the surgeon removes only the DCIS or cancer and some normal tissue around it. If you have cancer, the surgeon will also remove one or more lymph nodes from under your arm. Breast-sparing surgery usually keeps your breast looking much like it did before surgery. Other words for breast-sparing surgery include:
How to do breast reconstruction?
The first step is called tissue expansion. This is when the plastic surgeon places a balloon expander under the chest muscle. Over many weeks, saline (salt water) will be added to the expander to stretch the chest muscle and the skin on top of it.
What is a mastectomy?
In a mastectomy, the surgeon removes the whole breast that contains the DCIS or cancer. There are two main types of mastectomy. They are: Total mastectomy. The surgeon removes your whole breast. Sometimes, the surgeon also takes out one or more of the lymph nodes under your arm. Also called simple mastectomy.
What type of breast surgery is needed to remove cancer?
If so, you may be able to choose which type of breast surgery to have. Often, your choice is between breast-sparing surgery (surgery that takes out the cancer and leaves most of the breast) and a mastectomy (surgery that removes the whole breast). Once you are diagnosed, treatment will usually not begin right away.
How long does radiation therapy last after breast sparing surgery?
If you chose to have breast sparing surgery, you will usually need radiation therapy. Radiation treatments are usually given 5 days a week for 5 to 8 weeks. If you have a mastectomy, you may still need radiation therapy. No matter which surgery you choose, you might need: Chemotherapy. Hormone therapy.
Diagnosis
- Breast imaging
DCIS is most often discovered during a mammogram used to screen for breast cancer. If your mammogram shows suspicious areas such as bright white specks (microcalcifications) that are in a cluster and have irregular shapes or sizes, your radiologist likely will recommend additional … - Removing breast tissue samples for testing
During a core needle biopsy, a radiologist or surgeon uses a hollow needle to remove tissue samples from the suspicious area, sometimes guided by ultrasound (ultrasound-guided breast biopsy) or by X-ray (stereotactic breast biopsy). The tissue samples are sent to a lab for analysis…
Treatment
- Treatment of DCIS has a high likelihood of success, in most instances removing the tumor and preventing any recurrence. In most people, treatment options for DCIS include: 1. Breast-conserving surgery (lumpectomy) and radiation therapy 2. Breast-removing surgery (mastectomy) In some cases, treatment options may include: 1. Lumpectomy only 2. Lumpectomy and hormon…
Clinical Trials
- Explore Mayo Clinic studiestesting new treatments, interventions and tests as a means to prevent, detect, treat or manage this condition.
Alternative Medicine
- No alternative medicine treatments have been found to cure DCIS or to reduce the risk of being diagnosed with an invasive breast cancer. Instead, complementary and alternative medicine treatments may help you cope with your diagnosis and the side effects of your treatment, such as distress. If you're distressed, you may have difficulty sleeping and find yourself constantly thinki…
Coping and Support
- A diagnosis of DCIS can be overwhelming and frightening. To better cope with your diagnosis, it may be helpful to: 1. Learn enough about DCIS to make decisions about your care. Ask your doctor questions about your diagnosis and your pathology results. Use this information to research your treatment options. Look to reputable sources of information, such as the Nationa…
Preparing For Your Appointment
- Make an appointment with your doctor if you notice a lump or any other unusual changes in your breasts. If you have already had a breast abnormality evaluated by one doctor and are making an appointment for a second opinion, bring your original diagnostic mammogram images and biopsy results to your new appointment. These should include your mammography images, ultrasound …