
Medication
Options include: Curettage and electrodesiccation (electrosurgery) Mohs surgery Excisional surgery Radiation therapy Photodynamic therapy Cryosurgery Laser surgery Topical medications Medications for advanced BCC
Procedures
May 18, 2021 · Basal cell carcinoma treatment The type of treatment depends on many things including the size of the cancer, location, depth of growth, rate of... Your dermatologist will discuss these factors with you and decide on the appropriate treatment together. Continue to practice prevention strategies: ...
Nutrition
It is usually applied once a day or every other day for six weeks or longer. 5-Fluorouracil (5-FU) This is a chemotherapeutic medication that is usually applied twice daily for three to six weeks. Both imiquimod and 5-FU act to destroy cancer cells, so you will most likely feel effects where they have been applied.
Can basal cell carcinoma heal on its own?
Dec 31, 2021 · How Dermatologists Treat Basal Cell Carcinoma Freezing: The procedure is called cryotherapy , and it can be performed during an office visit. Cryotherapy involves... Light therapy: The medical name for this procedure is . Its a two-part procedure. First, a …
How to cure basal cell easy?
Oct 17, 2018 · Study: Best Treatments for Basal Cell Carcinoma When treating low-risk primary basal cell carcinoma (BCC), surgery and external beam radiation yield a better chance of a cure and a lower recurrence rate compared with other treatment modalities. This is the finding of a recent meta-analysis published in the Annals of Internal Medicine.
Which pills are used to treat basal cell carcinoma?
Nevertheless, surgery is the cornerstone of treatment of BCC on the nose and a wide variety of techniques have been developed to combine complete 3D tumour removal with good aesthetic and functional outcome.
How quickly should basal cell carcinoma be removed?
Dec 16, 2021 · Surgery is the preferred method of treatment for basal cell cancer. Radiation is an alternative when surgery is not desirable because of cosmetic concerns or medical reasons.
See more
Oct 01, 2021 · To reduce your risk of basal cell carcinoma you can: Avoid the sun during the middle of the day. In many places, the sun's rays are strongest between about 10 a.m. and 4 p.m. Wear sunscreen year-round. Use a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30, even on cloudy days. Apply... Wear ...
How do you get rid of basal cell carcinoma without surgery?
Radiation therapy is often a good option for treating patients who aren't able to have surgery and for treating tumors on the eyelids, nose, or ears – areas that can be hard to treat surgically – especially in older patients where cure may not be as important as control over the long term.Feb 10, 2021
How long does it take for basal cell carcinoma to spread?
The tumors enlarge very slowly, sometimes so slowly that they go unnoticed as new growths. However, the growth rate varies greatly from tumor to tumor, with some growing as much as ½ inch (about 1 centimeter) in a year.
Can basal cell carcinoma go away on its own?
Basal cell carcinomas may appear to heal on their own but inevitably will recur. Common symptoms of basal cell carcinoma include: Round, dome-shaped or flat scaling bumps.
What happens if I don't treat basal cell carcinoma?
However, left untreated, BCCs can grow deeper into the skin and damage surrounding skin, tissue, and bone. Occasionally, a BCC can become aggressive, spreading to other parts of the body and even becoming life threatening.
What is considered a large BCC?
A size larger than 3 cm has been described as a high-risk feature [13]. Notwithstanding the foregoing, this risk factor has been more accurately defined as 1 cm for head and neck tumors and more than 2 cm in other body areas [11].Feb 3, 2015
What is the average size of a basal cell carcinoma?
Santiago et al. researched 306 cases of BCC with an average size of 5.7 mm (range: 5-6 mm).Jul 15, 2020
What is Mohs surgery for basal cell carcinoma?
Mohs surgery is a precise surgical technique used to treat skin cancer. During Mohs surgery, thin layers of cancer-containing skin are progressively removed and examined until only cancer-free tissue remains. Mohs surgery is also known as Mohs micrographic surgery.
What cream is used for basal cell carcinoma?
The creams used to treat basal cell skin cancer are imiquimod and 5-FU (fluorouracil). They contain powerful medicines that cause a painful irritation in the treated area. The skin gets inflamed and crusts over as it heals. You apply the cream every day or two for several weeks.
Does basal cell carcinoma grow deep?
BCCs grow slowly and the prognosis is typically excellent. If left untreated, the basal cell carcinoma will continue to grow deeper and wider into the skin and may involve the nerves, muscle, or bone underneath the skin. When basal cell carcinomas have grown significantly, they will cause disfigurement.
What is the survival rate for basal cell carcinoma?
The 5-year relative survival for BCC is 100%. This means that, on average, all of the people diagnosed with BCC are just as likely to live at least 5 years after their diagnosis as people in the general population. The 5-year relative survival for SCC is slightly less at 95%.
Is Mohs surgery necessary for basal cell carcinoma?
Mohs surgery. Mohs surgery might be recommended if your basal cell carcinoma has a higher risk of recurring, such as if it's larger, extends deeper in the skin or is located on your face.Oct 1, 2021
What is Stage 4 basal cell carcinoma?
Stage 4. The cancer can be any size and may have spread to nearby lymph nodes. It has also spread to areas outside the skin, such as to distant organs like the brain or lungs, or has invaded the skeleton (axial or appendicular) or perineural invasion of skull base.
What is the cure rate for BCC?
It is especially useful for patients with bleeding disorders or problems tolerating anesthesia. The cure rate is between 85 and 90 percent. This technique is used less commonly for invasive BCC because it may miss deeper portions of the tumor, and because scar tissue at the site can make a recurrence harder to detect.
What is cemiplimab used for?
Cemiplimab is used to treat patients with advanced basal cell carcinoma (BCC) previously treated with a hedgehog pathway inhibitor (HHI) or for whom an HHI is not appropriate. Full approval was granted for patients with locally advanced BCC and accelerated approval was granted for patients with metastatic BCC.
Can basal cell carcinoma be cured?
When detected early, most basal cell carcinomas (BCCs) can be treated and cured. Prompt treatment is vital, because as the tumor grows, it becomes more dangerous and potentially disfiguring, requiring more extensive treatment. Certain rare, aggressive forms can be fatal if not treated promptly.
How does scalpel surgery work?
How it works. Using a scalpel, the surgeon removes the entire tumor along with a “safety margin” of surrounding tissue and sends it to an off-site lab for analysis. The margin of skin removed depends on the thickness and location of the tumor.
Can a cancer wound heal on its own?
The doctor repeats this process until there is no evidence of cancer. Then the wound may be closed or, in some cases, allowed to heal on its own.
What is Vismodegib used for?
Vismodegib is used for the extraordinarily rare cases of metastatic BCC or locally advanced BCC (tumors that have penetrated the skin deeply or frequently recurred) that either recur after surgery or radiation, or cannot be treated with surgery or radiation and have become dangerous or life-threatening.
Can BCC be treated with oral medications?
Two oral medications are FDA-approved for treating adults with very rare cases of advanced BCC that are large or have penetrated the skin deeply, spread to other parts of the body or resisted multiple treatments and recurred.
What is the best treatment for basal cell carcinoma?
C and E might be an option for treating small basal cell carcinomas that are less likely to recur, such as those that form on the back, chest, hands and feet. Radiation therapy . Radiation therapy uses high-energy beams, such as X-rays and protons, to kill cancer cells.
What is the goal of basal cell carcinoma treatment?
The goal of treatment for basal cell carcinoma is to remove the cancer completely. Which treatment is best for you depends on the type, location and size of your cancer, as well as your preferences and ability to do follow-up visits. Treatment selection can also depend on whether this is a first-time or a recurring basal cell carcinoma.
How to remove basal cell carcinoma?
Basal cell carcinoma is most often treated with surgery to remove all of the cancer and some of the healthy tissue around it. Options might include: Surgical excision. In this procedure, your doctor cuts out the cancerous lesion and a surrounding margin of healthy skin.
Can basal cell carcinoma spread to lymph nodes?
Very rarely, basal cell carcinoma may spread (metastasize) to nearby lymph nodes and other areas of the body. Additional treatment options in this situation include: Targeted drug therapy. Targeted drug treatments focus on specific weaknesses present within cancer cells.
What is the treatment for skin cancer?
Photodynamic therapy. Photodynamic therapy combines photosensitizing drugs and light to treat superficial skin cancers. During photodynamic therapy , a liquid drug that makes the cancer cells sensitive to light is applied to the skin. Later, a light that destroys the skin cancer cells is shined on the area.
Can you have Mohs surgery on your face?
Mohs surgery might be recommended if your basal cell carcinoma has a higher risk of recurring, such as if it's larger, extends deeper in the skin or is located on your face.
How to treat basal cell carcinoma?
Basal cell carcinoma treatment 1 The type of treatment depends on many things including the size of the cancer, location, depth of growth, rate of growth, your age, health, and other risk factors. 2 Your dermatologist will discuss these factors with you and decide on the appropriate treatment together. 3 Continue to practice prevention strategies: Avoid the sun and tanning beds, wear sunscreen, wear protective clothing, seek the shade, regularly examine your skin, see your dermatologist annually.
Where are basal cells located?
Basal cells are in the lower part of the epidermis, or basal cell layer. These cells form new cells to replace squamous cells near the skin’s surface. Occurs when DNA damage from UV exposure or indoor tanning triggers changes in basal cells in the epidermis. Usually starts as a nonhealing spot that bleeds easily.
Why is it important to wear sunscreen?
Exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light is the biggest culprit for both BCC and SCC, so it’s important to wear a good SPF sunscreen and limit your time in the sun. Most skin cancers typically start in the top layer of skin (the epidermis), where these cells turn cancerous and begin to grow out of control.
What does it mean when a sore doesn't heal?
An open sore that does not heal or appears to heal and come back. Signs for concern – any spot that looks red and scabby or bleeds, oozes, or crusts over. A small pink growth with raised or rolled edges and crusty, an indentation in center. A reddish patch or irritated area on your face, arm, chest, shoulder, leg.
How many cases of cancer are there in the US?
Most common cancer worldwide. More than 3 million cases annually in the U.S. BCC and SCC are on the rise, but death from these cancers is rare. Growth often occurs on sun-exposed skin, including face, head, and neck.
When is skin cancer awareness month?
May is Skin Cancer Awareness Month and a great time to schedule a skin cancer screening. You should review the risk factors for all skin cancers, know what to look for, and get a game plan for the summer days ahead. Your skin has to carry you through the decades.
What does it mean when you have a bump on your arm?
A reddish patch or irritated area on your face, arm, chest, shoulder, leg. A shiny bump or growth that looks pearly or clear, pink or red, and may resemble a mole. A spot that is flat with a white or waxy appearance or skin that appears shiny and taut with poorly defined borders.
What is the procedure to freeze a BCC tumor?
This procedure involves applying a cold substance, such as liquid nitrogen, to the tumor and freezing it off. It may be considered for low-risk BCC when more effective therapies are either not advised or impractical. It can also be considered in individuals with conditions that cause them to form large numbers of tumors.
What is the treatment for cancer?
Light (Photodynamic) Therapy. This treatment uses light-activated radiotherapy. It’s a two-part process: A solution (called a photosensitizer) that makes your skin sensitive to light is applied to the cancer and a portion of surrounding skin.
What is the procedure to remove cancer from the skin?
A dermatologist (or specialized surgeon) cuts out the cancer and an area around the tumor. Removing an extra part of skin (a wide margin) assures that s/he got all the cancer. If there is a big enough margin of normal skin around the cancer cells, your treatment is complete. If not, your doctor may need to go back and take more.
How long does it take for 5-FU to work?
5-Fluorouracil (5-FU) This is a chemotherapeutic medication that is usually applied twice daily for three to six weeks. Both imiquimod and 5-FU act to destroy cancer cells, so you will most likely feel effects where they have been applied. These include skin redness, swelling, sores, crusting, itching, and tingling.
When is radiation therapy given?
Radiation therapy is used if you can’t receive surgery or if you really don’t want it. Or in some cases, radiation is given for people who have aggressive BCC as a follow-up treatment to surgery to help destroy any remaining cancer cells so that the cancer does not come back ( adjuvant therapy ). The radiation therapy is given at a hospital or treatment center over a period of several weeks. Radiation is typically only used in people 60 years of age or older.
Can skin cancer be removed?
It is done at a hospital only rarely, when surgery will be extensive. The surgeon removes the skin cancer that can be seen. Then a thin layer of surrounding skin is cut away and examined under a microscope. If cancer cells are found in that additional layer, the process will be repeated until no cancer cells can be seen.
What is adjuvant treatment for squamous cell skin cancer?
For squamous cell skin cancer, the primary treatment is usually surgery. Adjuvant therapy may include chemotherapy, radiation therapy, hormone therapy, targeted therapy, biological therapy, or immunotherapy.
What is the most common non-melanoma skin cancer?
Basal cell carcinoma (BCC) is the most common non-melanoma skin cancer. In Germany about 115,000 new cases are seen each year. The incidence has been calculated as 130 per 100,000 inhabitants and year.[1] About 80% of all BCC occur on the face, of these tumours 25% to 30% are found on the nose.
Where does BCC occur?
About 80% of all BCC occur on the face, of these tumours 25% to 30% are found on the nose. BCC is the most common non-melanoma skin cancer of this region.[2] . The nose has a 2.5 times higher risk of recurrence of BCC after surgical excision.[3] .
What is primary closure?
Primary closure is the simplest type of defect repair. Primary closure on the nose is possible for tumours with small tissue defects. It is most suitable at nasal root where skin is mobile. Another option for primary closure is the medial part of the nasal bridge after fusiform excision.
What nerves are involved in motor innervation?
Motoric innervation is by the nasal branches of the trigeminal nerve. Arterial supply of the lateral parts of the nose originates from external carotid, ophthalmic and infraorbital arteries. Anterior ethmoidal and angular arteries are the major vessels of the nose.
What is basal cell carcinoma?
Overview. Basal cell carcinoma is a type of skin cancer that most often develops on areas of skin exposed to the sun. This photograph shows a basal cell carcinoma that affects the skin on the lower eyelid. Basal cell carcinoma is a type of skin cancer.
Where does basal cell carcinoma develop?
Basal cell carcinoma usually develops on sun-exposed parts of your body, especially your head and neck. Less often, basal cell carcinoma can develop on parts of your body usually protected from the sun, such as the genitals.
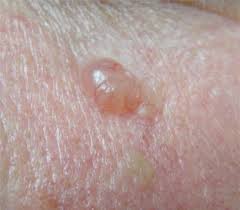
What is a pink bump on the skin?
Basal cell carcinoma appears as a change in the skin, such as a growth or a sore that won't heal. These changes in the skin (lesions) usually have one of the following characteristics: A pearly white, skin-colored or pink bump that is translucent, meaning you can see a bit through the surface.
Where does skin cancer begin?
Skin cancer begins in the cells that make up the outer layer (epidermis) of your skin. One type of skin cancer called basal cell carcinoma begins in the basal cells, which make skin cells that continuously push older cells toward the surface.
Is basal cell carcinoma more common in older people?
The risk of basal cell carcinoma is higher among people who freckle or burn easily or who have very light skin, red or blond hair, or light-colored eyes. Increasing age. Because basal cell carcinoma often takes decades to develop, the majority of basal cell carcinomas occur in older adults.
Does basal cell carcinoma cause skin cancer?
An increased risk of other types of skin cancer. A history of basal cell carcinoma may also increase the chance of developing other types of skin cancer, such as squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer that spreads beyond the skin.
Where are basal cells located?
Basal cells are found at the bottom of the epidermis — the outermost layer of skin. Basal cells produce new skin cells. As new skin cells are produced, they push older cells toward the skin's surface, where the old cells die and are sloughed off. The process of creating new skin cells is controlled by a basal cell's DNA.
