Discitis
Discitis, or diskitis, is an infection in the intervertebral disc space that affects different age groups. In adults, it can lead to severe consequences, such as sepsis or epidural abscess, but it can also spontaneously resolve, especially in children under 8 years of age. Discitis occurs post-surgically in approximately 1-2 percent of patients after spinal surgery.
Do antibiotics during diskography reduce the rate of diskitis?
Sharma et al reported on the severe complication of diskitis following diskography.They found that the available clinical evidence did not conclusively demonstrate that IV or intradiskal antibiotics during diskography decreased the rate of diskitis in comparison with sterile technique alone.
What kind of medication can I take for discitis?
In some cases, they may also prescribe steroids to help relieve severe or chronic cases of discitis. They may recommend nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, such as ibuprofen, to help relieve pain. Your doctor may also recommend the following:
How long does it take for antibiotics to work for discitis?
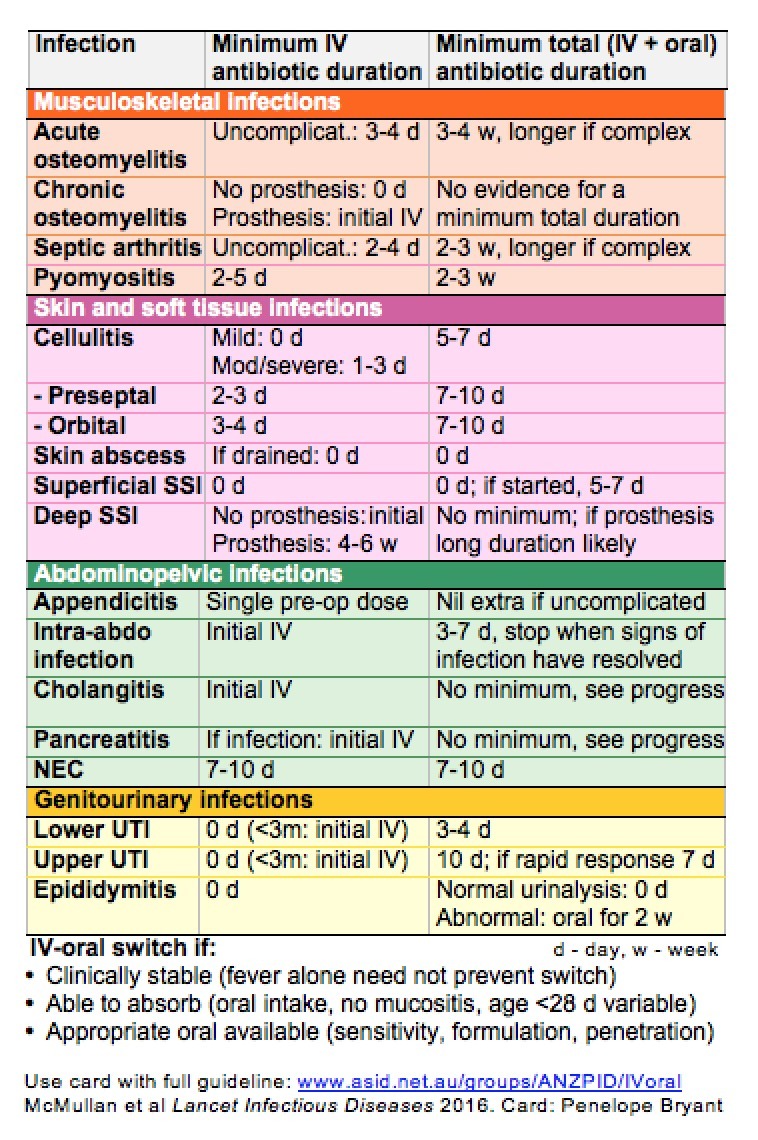
Treating discitis can be a challenge, given how discs don’t have a good blood supply, and antibiotics travel via the bloodstream. Discitis is treatable, though, and it’s typically done so with a 6- to 8-week course of antibiotics given intravenously (IV).
Can discitis be prevented?
Infection prevention is vital in diabetics and the immune-compromised, especially, as the disease is most prevalent in these populations. Pearls and Other Issues Discitis is a serious but uncommon cause of back pain It is more common in children than adults, has a male predilection, and targets diabetics, and immune-compromised patients
What is the treatment for discitis?
Discitis is treatable and usually results in an uncomplicated cure. However, it takes a very long course of antibiotic therapy that is usually given intravenously every day at an infusion center. The standard therapy requires six to eight weeks of this intravenous antibiotic therapy.
What is the most common cause of discitis?
Discitis is usually caused by an infection that develops in one of the spine's vertebral bones and/or intervertebral discs. Often, discitis is a bacterial infection, but it may be viral.
How do you treat an infection in your spine?
Nonsurgical Treatment Spinal infections often require long-term intravenous antibiotic or antifungal therapy and can equate to extended hospitalization time for the patient. Immobilization may be recommended when there is significant pain or the potential for spine instability.
Can discitis go away on its own?
The outlook for most people who have discitis is good. If you have a viral infection, it may heal on its own. If you have a bacterial infection, it will likely resolve with antibiotics.
Can you get discitis twice?
Back pain and ESR/CRP elevation are the most consistent abnormalities seen in cases of discitis [3, 4, 7, 8]. Blood cultures are positive in only one third to one half of cases, and recurrence of infection occurs in 2–8% of patients [3, 9].
What causes discitis in the spine?
Often the cause of the infection is staphylococcus, or a bacterial or viral infection. The discs in the lumbar and thoracic section of the spine are usually the ones affected by discitis. Discitis is rare, but it affects children under 10 more often.
What antibiotics treat spinal infection?
For cryptogenic infection (ie, no identified primary source), a suggested regimen is ampicillin plus cefotaxime plus metronidazole. Ampicillin must be administered to cover L monocytogenes. For hematogenous spread, the choice of antibiotics obviously depends on the primary source of infection.
How do you reduce inflammation in the spine?
Your doctor may recommend physical therapy, exercise, posture training, and/or lifestyle modifications to provide improved mobility and sustainable pain management for your spinal inflammatory arthritis. These nonsurgical treatments may also help prevent serious arthritis-related spinal complications.
How long does it take to cure a spinal infection?
With treatment, you may recover from vertebral osteomyelitis in a month to six weeks. However, it might take up to six months for you to feel fully recovered. Without treatment, you may develop severe spine damage or septicemia (blood poisoning from bacteria).
How serious is an infection in the spine?
If left untreated, spine infection can lead to paralysis or even fatality. Signs of spine infection include back pain, fever and a stiff back as well as possible swelling or inflammation of the spine, sensory deficit or numb, motor weakness or paralysis. Prof.
Can CT diagnose discitis?
Computed tomography CT has the ability to detect diskitis earlier than plain radiography does. Findings include hypodensity of the intervertebral disk and destruction of the adjacent endplate and bone (see the image below), with edematous surrounding tissues.
What does discitis look like on MRI?
The most reliable MRI findings in discitis are hyperintensity of the disc on T2-weighted imaging (sensitivity 93%); the presence of paraspinous or epidural inflammation/abscess, (sensitivity 98%); and contrast enhancement of the disc and adjacent bone marrow (sensitivity 95%).
What is the treatment for discitis?
[3][7][8]Most commonly, the treatment of discitis includes antibiotics and less commonly surgery.
What is a diskitis?
Diskitis - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf. Discitis is a serious but uncommon medical diagnosis. It is an infection of the intervertebral disc space. The role of the intervertebral discs is to separate and cushion the spinal segments from each other. An infection, and thus inflammation of these discs can cause much pain and discomfort.
What is discitis in medical terms?
Introduction. Discitis is a serious but uncommon medical diagnosis. It is an infection of the intervertebral disc space. The role of the intervertebral discs is to separate and cushion the spinal segments from each other. An infection, and thus inflammation of these discs can cause much pain and discomfort. What makes the condition uncommon is also ...
What is discitis in the spine?
Discitis is a serious but uncommon medical diagnosis. It is an infection of the intervertebral disc space. The role of the intervertebral discs is to separate and cushion the spinal segments from each other. An infection, and thus inflammation of these discs can cause much pain and discomfort.
Why is discitis more common in children than adults?
Overall, the frequency of discitis is more common in pediatric patients than in the adult population, which is thought to be due to the vascular supply of the intervertebral discs, which diminish later in life.[4] However, there is a bimodal distribution of ages, as it again increased in incidence around age 50.[3]
How long does it take for discitis to show up after surgery?
Postoperatively, symptoms typically occur 1 to 16 weeks after surgery.
Which spinal region is most commonly involved in discitis?
The lumbar spinal region is most commonly involved, followed by the cervical spine and then the thoracic spine. [1][2][3] Epidemiology. The incidence of discitis in the United States is around 0.4 to 2.4 per 100000 people each year.[3]
What is gentamicin used for?
Used in conjunction with gentamicin for prophylaxis in patients who are allergic to penicillin and are undergoing gastrointestinal or genitourinary procedures. Initial therapy for suspected penicillin-G–resistant streptococcal or staphylococcal infections. Use parenteral therapy initially for severe infections.
When to use CrCL for vancomycin?
To avoid toxicity, the current recommendation is to assay vancomycin trough levels after the third dose is drawn and a half an hour prior to the next dose. Use CrCl to adjust the dosage in patients diagnosed with renal impairment.
What is an empiric antimicrobial?
Empiric antimicrobial therapy must be comprehensive and should cover all likely pathogens in the context of the clinical setting. Vancomycin (Lyphocin, Vancocin, Vancoled) View full drug information. Potent antibiotic that is directed against gram-positive organisms and is active against Enterococcus species.
How long does it take to cure discitis?
However, it takes a very long course of antibiotic therapy that is usually given intravenously every day at an infusion center. The standard therapy requires six to eight weeks of this intravenous antibiotic therapy.
What are the causes of discitis?
Causes. There are two types of discitis. One is the result of an intervention at the site of the infection by a surgical, diagnostic or therapeutic procedure. For example, surgery on the back or a needle placed in the back for a diagnostic or treatment can introduce pathogens.
Is discitis a symptom of discitis?
Symptoms. Severe, almost unbearable back pain is usually the major symptom. Because, as mentioned at the outset, back pain is common and has a great number of causes, discitis is often misdiagnosed and that means it is late to be appropriately treated and the back pain remains.
Can a spinal disc infection cause debilitation?
As we age, one of the rare problems that can occur after a systemic infection is localized and very painful spinal infection of the disc. This is a debilitation and often late-diagnosed problem that requires immediate antibiotic treatment to get the cure that usually does come, but painfully long into the disease.
Is discitis a disease?
Discitis. Discitis is a disease, as the "itis" would indicate, of infection of the discs between the vertebra of the spine. Like appendicitis, discitis is usually a bacterial infection but may be viral. The purpose of the disc is to allow some movement and shock absorption of the vertebra that the discs separate in the spinal column.
What is the inflammation of the discs?
Discitis, or diskitis, is inflammation that develops between the intervertebral discs of your spine. These discs are located between your vertebrae. The spaces between them are called intervertebral disc spaces. Swelling in these spaces can put pressure on the discs, leading to pain. Discitis is relatively uncommon.
How do you know if you have discitis?
If you have discitis, you’ll likely have significant pain in part of your spine. Your lower and upper back may be affected. Other symptoms can include: changes in your posture. stiffness in your back. difficulty performing regular mobility tasks. abdominal pain or discomfort. fever.
What tests can be done to see if you have a spine infection?
Your doctor may also order radiological imagining tests, such as an X-ray or MRI. These tests can create pictures of your spine and surrounding tissues. Infection and inflammation can potentially move from one area to another.
Can a virus cause discitis?
Viral or bacterial infections can cause discitis. An autoimmune disorder can also cause it. The infection or autoimmune response leads to swelling and inflammation, which results in pain and other symptoms.
Can discitis cause back pain?
Chronic back pain is a rare complication associated with discitis. You might also experience unpleasant side effects from the medications that you take to treat it. If your pain levels increase or return after your initial treatment, make an appointment with your doctor. You may need additional treatments.
Can a doctor order blood work for discitis?
Your doctor may order blood tests to help diagnose discitis. They’ll collect a sample of your blood to send to a laboratory for analysis. Lab technicians can use a variety of tests to check for signs of infection.
Can you have surgery for discitis?
In some cases of discitis, your doctor may recommend more invasive treatments. In rare cases, you may need surgery to resolve problems stemming from discitis and osteomyelitis. Your doctor may need to reconstruct areas of your spine to improve its function and your mobility.
What is the cause of vertebral osteomyelitis?
Vertebral osteomyelitis most often occurs as a result of hematogenous seeding of one or more vertebral bodies from a distant focus [ 1 ]. Infection may also involve the adjacent intervertebral disc space, which has no direct blood supply in adults. Infection can also arise following surgery or injection of the disc space or via contiguous spread ...
What is pyogenic spondylitis?
The term pyogenic spondylitis refers to either vertebral osteomyelitis or discitis. The diagnosis and management of these two entities are similar in most patients. Issues related to vertebral osteomyelitis will be reviewed here.
Is vertebral osteomyelitis a disease?
EPIDEMIOLOGY. Vertebral osteomyelitis is primarily a disease of adults; most cases occur in patients >50 years old [ 2 ]. The incidence increases with age. Men are affected approximately twice as often as women in most case series; the reason for this is not fully understood.
How long does it take to get rid of discitis?
Discitis is treatable, though, and it’s typically done so with a 6- to 8-week course of antibiotics given intravenously (IV).
What is discitis in the spine?
Discitis is a Spinal Disc Infection and Inflammation. Written by Stewart G. Eidelson, MD. Discitis is usually caused by an infection that develops in one of the spine’s vertebral bones and/or intervertebral discs.
Why do people have discitis?
Because discitis is typically caused by infections that first developed elsewhere in the body, people with certain medical conditions are at higher risk for developing discitis. These conditions include diabetes, AIDS, cancer, and chronic kidney disease.
What is it called when a disc is infected?
When the infection begins elsewhere and travels to the disc, it is called transient bacteremia (short-lived bacteria in the blood stream). Ear infections and skin infections are examples of infections that could lead to transient bacteremia and possibly discitis. Once a disc becomes infected, it's difficult for the body to fight the infection.
Where does discitis occur?
Discitis most often occurs in the lumbar (low back) region of the spine, followed by the cervical (neck) spine, and then in the thoracic (mid-back) spine. Discitis often accompanies vertebral osteomyelitis, and both types of spinal infections share many of the same characteristics.
What is the most accurate test for discitis?
Though blood tests may be considered during diagnosis, the most accurate and commonly used diagnostic tool to confirm discitis is magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), which will show an infection if it exists.
What causes discitis?
There are 2 recognized causes of discitis. The rarer of the 2 causes is from a previous surgical or diagnostic procedure (when a needle or other device transfers the infection). The other cause—which is more common—is known as spontaneous discitis. This means the infection developed from a bacterial or viral organism that traveled to ...