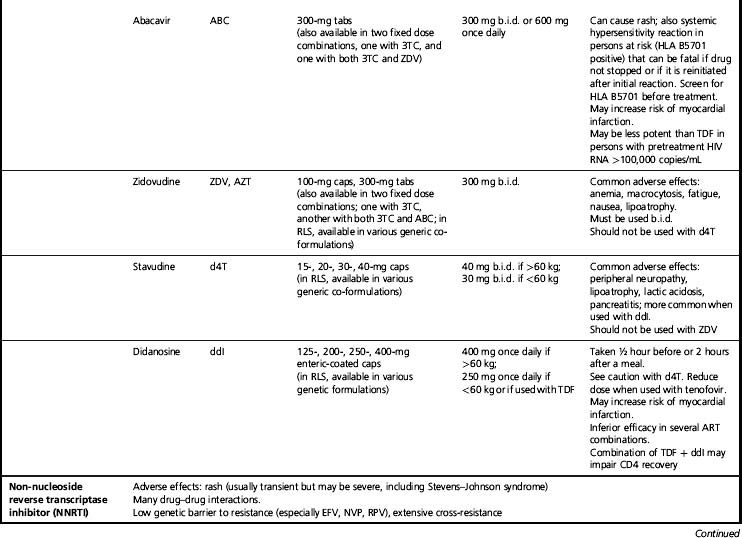
Antiretroviral Drug Abbreviations
| Abbreviation | Full Name |
| 3TC | lamivudine |
| ABC | abacavir |
| ATV | atazanavir |
| BIC | bictegravir |
What are antiretrovirals and how do they work?
What is the abbreviation for Antiretroviral Treatment? Antiretroviral Treatment is abbreviated as ART (also ARV or ARVT)
What are antiretroviral drugs?
antiretroviral therapy. ARV. antiretroviral (drug) AST. aspartate aminotransferase. ATV. atazanavir. AUC. area under curve. AZT. zidovudine (also known as ZDV) BAL. bronchoalveolar lavage. BCG. bacille Calmette – Guérin (vaccine) BSA. body surface area. CD4+ T-lymphocyte bearing CD4 receptor %CD4+ percent CD4+ CDC. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. …
What is the abbreviation for tenofovir?
Jul 23, 2014 · ART are medications that treat HIV. The drugs do not kill or cure the virus. However, when taken in combination they can prevent the growth of the virus. When the virus is slowed down, so is HIV disease. Antiretroviral drugs are referred to as ARV. Combination ARV therapy (cART) is referred to as highly active ART(HAART).
What is the acronym for HIV?
Antiretroviral Therapy for HIV Infection in Adults and Adolescents: Recommendations for a Public Health Approach: 2010 Revision. ... International Treatment Preparedness coalition. LPV. lopinavir. LPV/r. ... ACRONYMS AND ABBREVIATIONS - Antiretroviral Therapy for HIV Infection in Adults and Adolescents. Your browsing activity is empty.
What do the acronyms ARVs?
What does AZT stand for?
What are the 3 antiretroviral therapy?
- bictegravir/tenofovir alafenamide/emtricitabine (Biktarvy)
- dolutegravir (Tivicay) plus tenofovir/emtricitabine (Truvada)
What is art and HAART?
What is TDF FTC?
What is ADCO zidovudine syrup?
What are the 6 classes of antiretroviral drugs?
Which are the 5 antiretroviral drugs?
- Atazanavir or ATV (Reyataz)
- Darunavir or DRV (Prezista)
- Fosamprenavir or FPV (Lexiva)
- Indinavir or IDV (Crixivan)
- Lopinavir + ritonavir, or LPV/r (Kaletra)
- Nelfinavir or NFV (Viracept)
- Ritonavir or RTV (Norvir)
How is antiretroviral therapy given?
What is HAART?
Is HAART the same as cART?
What are the 3 active antiretrovirals comprised of?
What Is Antiretroviral Therapy?
Antiretroviral therapy (ART) involves using two or more antiretroviral drugs to suppress the virus to undetectable levels in the blood. This treatment can slow the progression of the disease to a point at which you can live a long, healthy life. 4
How It Works
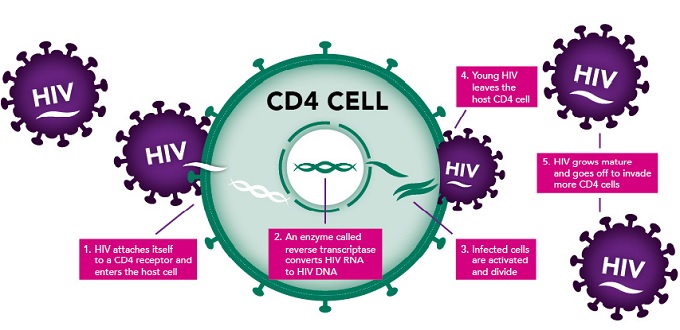
Antiretroviral drugs do not kill HIV. Rather, they prevent the virus from making copies of itself by blocking stages in the virus's life cycle (also known as the replication cycle ). Antiretrovirals are so named because HIV is a type of virus known as a retrovirus. 4
Side Effects
While all drugs can cause side effects, current antiretrovirals tend to cause far fewer side effects than drugs of the past. Even so, side effects can occur and, in rare cases, be severe.
Tests
Once you have been diagnosed with HIV, your doctor will advise to you start treatment immediately to bring the virus under control. You will not only be counseled on how to take your drugs correctly (including dietary restrictions) but also advised on ways to maintain optimal adherence .
Other Treatments
There are no other medications other than antiretrovirals that can control HIV.
Talk to Your Doctor
The choice of ART relies heavily on the results of a genetic resistance test that helps determine which antiretrovirals work best based on your virus's genetic profile. But it is not the sole factor involved in the selection of ART. 17
Summary
Antiretroviral therapy is used to control HIV. It relies on drugs that inhibit points of the viral replication cycle so the virus cannot make copies of itself and infect immune system cells. Antiretroviral drugs are usually given daily in the form of a pill, which may contain a combination of drugs. These medications may have side effects.
What is an ARV drug?
ARV drugs are chosen on the basis of treatment guidelines, HIV drug resistance, your health (for example, kidney or liver disease) and lifestyle factors. While ARV regimens are usually well tolerated, each ARV drug can have side effects. Some may be serious. Refer to the fact sheet for each individual drug.
How do HIV entry inhibitors work?
Entry inhibitors prevent HIV from entering a cell by blocking step 2 of the life cycle. Two drugs of this type have been approved: HIV integrase inhibitors prevent HIV from inserting its genetic code into the human cell's code in step 5 of the life cycle. The two drugs of this type are:
How does HIV work?
1. Free virus circulates in the bloodstream. 2. HIV attaches to a cell. 3. HIV empties its contents into the cell. 4. The HIV genetic material (RNA) is used by the reverse transcriptase enzyme to build HIV DNA. 5.
What is the difference between ART and ARV?
However, when taken in combination they can prevent the growth of the virus. When the virus is slowed down, so is HIV disease. Antiretroviral drugs are referred to as ARV. Combination ARV therapy (cART) is referred to as highly active ART (HAART).
Why is it important to adhere to ARVs?
Adherence to ARVs is very important for treatment to work. The viral load test is used to see if ARV drugs are working.
Do ARVs reduce viral load?
ARVs reduce the viral load, the amount of virus in your bloodstream, but are not a cure. A blood test measures the viral load. People with undetectable viral loads stay healthier longer. They are also less likely to transmit HIV infection to others.
Can you use ARV with two drugs?
If only one or two ARV drugs are used, it is easy for the virus to develop resistance. For this reason, using just one or two drugs is not recommended .
How do antiretrovirals work?
How Antiretrovirals Works. Antiretroviral drugs do not kill HIV; rather, they block different stages in the virus's life cycle —from the time it attaches to a cell to the time it creates new copies of itself to infect other cells.
How much is antiretroviral therapy reduced?
Moreover, when antiretroviral therapy is started early, the risk of severe HIV-associated diseases and non-HIV-associated illnesses (like cancers and heart disease) is reduced by as much as 72% , according to research published in the New England Journal of Medicine. 11 .
What does HAART mean?
Drug Classes. Benefits. HAART is the acronym for "highly active antiretroviral therapy," a term coined in the late 1990s to describe the effectiveness of combination drug therapies used to treat HIV. The term is less commonly used today given that modern antiretrovirals are more than just "highly active" but able to afford people ...
How does treatment as prevention work?
The strategy, known as treatment as prevention, aims to reduce the "community viral load" within a population, making it more difficult to spread infection. 9
What is PREP in HIV?
The strategy, known as pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP), is currently recommended for people at high risk of infection, including serodiscordant (mixed-status) couples, injecting drug users, and those who engage in protected anal or vaginal sex. 13 . High vs. Low Risk Activities for HIV Transmission.
What happens if one drug is unable to suppress a certain viral type?
By keeping the viral population fully suppressed ( undetectable ), there are fewer circulating viruses in the bloodstream and fewer opportunities for the virus to mutate into a drug-resistant variant.
Can you take antiretrovirals with HIV?
The benefits extended not only to people with HIV but to others around them. Today, antiretrovirals can even be used in non-infected people to further reduce their risk of infection. By taking one pill a day, an HIV-negative person can reduce their risk of getting the virus by as much as 99%. 12 .

What Is Antiretroviral Therapy?
- Antiretroviral therapy (ART) involves using two or more antiretroviral drugs to suppress the virus to undetectable levels in the blood. This treatment can slow the progression of the disease to a point at which you can live a long, healthy life.4 The benefits of an undetectable viral loadare threefold: 1. With early ART, a person with HIV can expec...
How It Works
- Antiretroviral drugs do not kill HIV. Rather, they prevent the virus from making copies of itself by blocking stages in the virus's life cycle (also known as the replication cycle). Antiretrovirals are so named because HIV is a type of virus known as a retrovirus.4 The different classes of antiretrovirals are named after the specific stage of the replication cycle they inhibit (block). Th…
Side Effects
- While all drugs can cause side effects, current antiretrovirals tend to cause far fewer side effects than drugs of the past. Even so, side effects can occur and, in rare cases, be severe. Short-term side effects may include headache, fatigue, nausea, diarrhea, insomnia, and even a mild rash. These tend to resolve within a few weeks as your body adapts to treatment.4 Other side effects …
Tests
- Once you have been diagnosed with HIV, your doctor will advise to you start treatment immediately to bring the virus under control. You will not only be counseled on how to take your drugs correctly (including dietary restrictions) but also advised on ways to maintain optimal adherence. You will also be given baseline blood tests, called a CD4 count and viral load, agains…
Other Treatments
- There are no other medications other than antiretrovirals that can control HIV. Even so, there are drugs a doctor may prescribe along with ART if you are at risk of an opportunistic infection. These preventive medications, referred to a prophylactics, are commonly prescribed when your CD4 count is below 200 or 100.18 These may include daily oral antibiotics to prevent severe infection…
Talk to Your Doctor
- The choice of ART relies heavily on the results of a genetic resistance testthat helps determine which antiretrovirals work best based on your virus's genetic profile. But it is not the sole factor involved in the selection of ART.17 As you will be the one taking the pills every day, you will want medications with the greatest tolerability and the greatest ease of use. Both help improve adher…
Summary
- Antiretroviral therapy is used to control HIV. It relies on drugs that inhibit points of the viral replication cycle so the virus cannot make copies of itself and infect immune system cells. Antiretroviral drugs are usually given daily in the form of a pill, which may contain a combination of drugs. These medications may have side effects. The drugs used in antiretroviral therapy are …
A Word from Verywell
- Antiretroviral therapy has advanced to where people living with HIV enjoy long, healthy lives with minimal side effects or impact on lifestyle. With that said, the drugs only work if you take them, and that is where many people fall short. According to the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS), fewer than 60% of people living with HIV in the United States achieve and sustai…