
Maintenance ECT involves getting treatments every two weeks to every month, usually for a period of six months to a year. But patients have gone on maintenance ECT for up to three years, depending on their response.
How long does it take for ECT to work?
Apr 10, 2022 · Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) is most often used in cases of severe, intractable, hard to treat (treatment-resistant) depression. Generally, ECT is a short-term treatment where the patient receives 6-12 treatments over the course of 2-4 weeks. However, in some cases, continuation ECT or maintenance ECT is used.
How often is ECT given?
Mar 02, 2022 · You may lose your memory for 1 to 3 weeks, and some memories may be lost forever. You may also get a headache after an ECT treatment. These headaches usually only last a short time. If you have a headache after ECT, ask …
What is maintenance electroconvulsive therapy (ECT)?
May 12, 2020 · When you awaken, you may experience a period of disorientation lasting from a few minutes to several hours. Headaches, jaw pain, and muscle soreness may occur. ECT requires a series of treatments, often initiated two to three times a week for a few weeks and then the frequency is tapered down.
How long does it take for confusion to go away after ECT?
Abortive or brief seizures including procedures for identifying aborted or brief seizures (typically, less than 15 seconds of ictal motor activity), specifying the length of time before restimulation can occur (usually longer than 45 seconds), and determining the adequacy of treatment.

How do you feel after first ECT treatment?
After the Procedure When you awaken, you may experience a period of disorientation lasting from a few minutes to several hours. Headaches, jaw pain, and muscle soreness may occur. ECT requires a series of treatments, often initiated two to three times a week for a few weeks and then the frequency is tapered down.May 12, 2020
Does ECT work immediately?
ECT can often work quickly, but 50% or more of the people who receive this treatment will relapse within several months if there is no subsequent treatment (for example, medicines) to prevent relapse.Sep 8, 2020
How long does ECT procedure take?
An ECT session takes about one hour total. There is time for patient assessments before treatment, receiving treatment (20 minutes), resting in the recovery area (20 minutes), and getting transferred back to a unit (inpatient) or to the driver's vehicle (outpatient).
What is the average number of ECT treatments?
HOW MANY TIMES WILL I NEED TO BE TREATED? People undergoing ECT need multiple treatments. The number needed to successfully treat severe depression can range from 4 to 20, but most people need a total of 6 to 12 treatments. The treatments are usually given three times a week — Monday, Wednesday, and Friday.Apr 7, 2021
Does ECT damage the brain?
Despite many scientific and governmental authorities having concluded that ECT does not cause brain damage, there is significant evidence that ECT has indeed caused brain damage in some patients, both historically and recently, and evidence that it always causes some form or degree of brain damage.
Does ECT wear off?
The duration of improvement (how long recovery lasts). The benefits of ECT may last for years or they may disappear in a matter of weeks. After a series of ECT treatments, your doctor may prescribe medication to help prevent symptomsfrom returning.
Who is ECT Not recommended for?
ECT is not recommended for ongoing management of schizophrenia, or as a routine treatment for mild to moderate depression. You can read full guidelines on the NICE website for using ECT to treat catatonia, mania or schizophrenia, and as one of the treatments for moderate or severe depression.
What happens if ECT doesn't work?
If nothing else has helped, including ECT, and you are still severely depressed, you may be offered neurosurgery for mental disorder (NMD), deep brain stimulation (DBS) or vagus nerve stimulation (VNS).
Is ECT treatment painful?
Freeman and R. E. Kendell of the University of Edinburgh found that 68 percent reported that the experience was no more upsetting than a visit to the dentist. For the others, ECT was more unpleasant than dentistry, but it was not painful. Still, the treatment is not hazard-free.
Does ECT reset the brain?
ECT has been referred to as a “reset button for the brain,” which not only directly improves depressive symptoms, but also allows current medications to work more effectively.
Does ECT change personality?
ECT does not change a person's personality, nor is it designed to treat those with just primary “personality disorders.” ECT can cause transient short-term memory — or new learning — impairment during a course of ECT, which fully reverses usually within one to four weeks after an acute course is stopped.
Does ECT increase serotonin?
Conclusion. Altogether, our results showed that serum serotonin levels significantly increase following ECT in MDD patients.
What is ECT in medical terms?
Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) is a procedure, done under general anesthesia, in which small electric currents are passed through the brain, intentionally triggering a brief seizure. ECT seems to cause changes in brain chemistry that can quickly reverse symptoms of certain mental health conditions.
Why is electroconvulsive therapy used?
Why it's done. Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) can provide rapid, significant improvements in severe symptoms of several mental health conditions. ECT is used to treat: Severe depression, particularly when accompanied by detachment from reality (psychosis), a desire to commit suicide or refusal to eat. Treatment-resistant depression, ...
How often do you get ECT?
In the United States, ECT treatments are generally given two to three times weekly for three to four weeks — for a total of six to 12 treatments. Some doctors use a newer technique called right unilateral ultrabrief pulse electroconvulsive therapy that's done daily on weekdays.
What is ECT used for?
ECT is used to treat: Severe depression, particularly when accompanied by detachment from reality (psychosis), a desire to commit suicide or refusal to eat. Treatment-resistant depression, a severe depression that doesn't improve with medications or other treatments. Severe mania, a state of intense euphoria, agitation or hyperactivity ...
How long after ECT can you drive?
However, some people may be advised not to return to work, make important decisions, or drive until one to two weeks after the last ECT in a series, or for at least 24 hours after a single treatment during maintenance therapy.
What is a blood pressure cuff?
A blood pressure cuff placed around one ankle stops the muscle relaxant medication from entering your foot and affecting the muscles there. When the procedure begins, your doctor can monitor seizure activity by watching for movement in that foot.
What is the term for a lack of movement, fast or strange movements, lack of speech, and other symptoms?
Catatonia, characterized by lack of movement, fast or strange movements, lack of speech, and other symptoms. It's associated with schizophrenia and certain other psychiatric disorders. In some cases, catatonia is caused by a medical illness.
How long does ECT last?
Generally, ECT is a short-term treatment where the patient receives 6-12 treatments over the course of 2-4 weeks. However, in some cases, continuation ECT or maintenance ECT is used. These two therapies continue ECT beyond the initial 6-12 sessions used in acute treatment.
What is maintenance ECT?
Maintenance ECT consists of ECT treatments given infrequently over a long period of time after the index series and continuation ECT. The goal of maintenance ECT is to prevent the reoccurrence of the mental illness.
Why do people need ECT?
Maintenance ECT: Why Some People Need Continuation ECT. Electroconvulsive therapy, once known as shock therapy, is a safe and effective treatment for depression and other mental illnesses. Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) is most often used in cases of severe, intractable, hard to treat (treatment-resistant) depression.
Is ECT effective for relapse?
Relapse after a positive response to ECT is common. Most frequently, prevention of relapse is accomplished through the use of medication but continuation ECT has also been shown effective for the prevention of illness relapse.
How long does an ECT procedure last?
How long is an ECT procedure? A single ECT session usually lasts one hour. This includes the time the patient will be in the treatment room (approximately 15-20 minutes) and the time spent in the recovery room (approximately 20-30 minutes). Typically, ECT (whether inpatient or outpatient) is given two to three times a week for a total ...
How long does it take to drive after ECT?
Usually this takes about 20 to 25 minutes. Patients who are given ECT on an outpatient basis must have someone drive them home after the procedure and stay with them until they go to sleep at night. People should not drive in the 24 hours following ECT.
How does ECT work?
Why does ECT work? No one is sure how ECT helps certain psychiatric disorders. It may promote changes in how brain cells communicate with each other at synapses and it may stimulate the development of new brain cells. ECT may flood the brain with neurotransmitters such as serotonin and dopamine, which are known to be involved in conditions like ...
How long does it take to sleep before ECT?
During the procedure, the patient receives a short acting anesthetic agent which puts the patient to sleep for approximately 5-10 minutes.
How can families help with ECT?
Families can help by providing a gentle reminder of the day and date and that feeling confused is to be expected. Family members should inform the nurse of any concern they have about their loved one. View a Powerpoint Presentation for Families about ECT.
Can memories be lost after ECT?
Memories formed closer to the time of ECT are at greater risk of being lost while those formed long before ECT are at less risk of being lost. The ability to form new memories is also impaired after a course of ECT treatments but this ability usually makes a full recovery in the weeks and months following the last treatment.
Can you take ECT if you have schizophrenia?
ECT may also be prescribed when antidepressant medications have not worked . It can be useful for older patients who are unable to tolerate antidepressants and for pregnant women in whom medication might damage the fetus. People suffering from bipolar disorder and schizophrenia may also benefit from ECT.
What is ECT therapy?
WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW: Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) is a treatment that sends a small electric current to your brain to cause a seizure. The seizure affects the chemicals in your brain, which may make your brain cells work better.
How long does it take for ECT to go away?
ECT may cause memory loss and confusion. Your confusion may go away in a short time, such as 1 hour after your treatment. You may lose your memory for 1 to 3 weeks, and some memories may be lost forever.
What does it mean when you have a fever?
You have a fever. You have a severe headache that does not get better, even after you take medicine to treat it. You have a stiff neck or trouble thinking clearly. You have feelings of guilt or hopelessness, or thoughts of hurting or killing yourself or others.
How to help depression?
Antidepressants: You may be given this medicine to help decrease or prevent symptoms of depression. Take your medicine as directed. Contact your healthcare provider if you think your medicine is not helping or if you have side effects. Tell him of her if you are allergic to any medicine.
Can you fall after ECT?
If more ECT treatments are planned for you, ask the healthcare provider to give you medicine before the treatments to help prevent headaches. There is a greater chance that you will fall after ECT treatments . Ask someone to help you when you want to stand up or walk.
What are the guidelines for ECT?
Guidelines: Providers should assure review of medical conditions that may substantially increase risk during the delivery of ECT. A medical history and physical examination are essential before prescribing of ECT to determine risk factors and minimize risks.
What should providers identify for ECT?
Guidelines: Providers should identify principal diagnostic indications and other diagnostic indications for the use of ECT. When identifying persons for possible ECT, a current psychiatric evaluation and diagnosis should be part of the required procedures.
How many seizures should a provider treat per week?
Guidelines: Providers should address the following: Frequency of treatments, including the usual number of weekly treatments (generally, 3 per week), variations in frequency, and review of frequency, based on patient response. In general, the use of more than one adequate seizure per treatment session is discouraged.
Does ECT diminish with age?
The efficacy of treatment does not diminish with advancing age. ECT may have a lower risk of complications than some forms of pharmacotherapy in the elderly. Pregnant women and nursing mothers may receive ECT during all trimesters of pregnancy, puerperium and nursing.
Is ECT a primary or secondary treatment?
ECT may be considered as a primary treatment (or first-line treatment) for persons exhibiting syndromes such as: severe major depression, acute mania, mood disorders with psychotic features, and catatonia.
Does an ECT psychiatrist administer anesthesia?
Since the Office of Mental Health advocates that the ECT psychiatrist not administer both anesthesia and ECT, the facility should develop an ECT administration plan which clearly describes the process. The plan should be sent to OMH ’s Chief Medical Officer for review and approval.
What does the speed of response tell us about the mechanisms of action of ECT?
What does the speed of response tell us about the mechanisms of action of ECT? Clearly, in certain patients, the neurobiological changes induced by ECT include almost immediate alterations in brain systems that regulate mood and affect. Perhaps a “switch” mechanism (similar to that seen in bipolar patients) occurs; however, there is no evidence to suggest that very rapid improvement with ECT is associated with bipolar rather than unipolar depression. There is evidence to demonstrate that, overall, bipolar patients require fewer ECT sessions than unipolar patients. 11 Investigation of the rapid antidepressant action of the intravenous anesthetic ketamine may lead to elucidation of related mechanisms of recovery from severe affective illness. 12
How long does it take for depression to go away?
There is considerable variability in the trajectories, but most commonly there is progressive symptomatic improvement within the first week and complete remission within 3 to 4 weeks.
Is electroconvulsive therapy effective?
The overall effectiveness of electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) is well known, but its speed of action is much less talked about. Here I review what is known about the time course of action of ECT in depression. Most patients who are referred for ECT have been ill with severe mood disorders for many months, some even for years.
Do patients look good after ECT?
Unfortunately, patients who have considerable symptom improvement after the first ECT session and who would be expected to do very well, never look as good as they did after that first treatment. The reasons underlying such a trajectory of symptom persistence are not yet understood.
Do bipolar patients need ECT?
There is evidence to demonstrate that, overall, bipolar patients require fewer ECT sessions than unipolar patients. 11 Investigation of the rapid antidepressant action of the intravenous anesthetic ketamine may lead to elucidation of related mechanisms of recovery from severe affective illness. 12.
What to do if you are considering ECT?
If you are considering ECT for mental health treatment, you should discuss the risks and benefits of ECT treatment with your psychiatrist. If you are considering ECT for depression treatment, you should also be aware of the potential non-medication treatment alternatives available to you.
How does ECT work?
ECT is accomplished by connecting electrodes to the scalp, running electric current into the brain and causing a small, controlled seiz ure. Though the exact mechanism of how ECT works is unclear, researchers know that ECT creates large-scale and small-scale physiologic changes that help reset the structure and functioning of the brain’s neurons.
What is electroconvulsive therapy?
Electroconvulsive therapy is usually reserved for situations where medication or psychotherapy have been unable to adequately treat a mental health condition. Certain mental health conditions are particularly responsive to ECT, and ECT is approved by the Food and Drug Administration to treat the following: Major depressive disorder.
What is the treatment team for ECT?
An ECT treatment team usually consists of a psychiatrist, an anesthesiologist and either a nurse or physician assistant. Treatment begins by placing electrodes at specific locations on a person’s scalp. The patient is given general anesthesia and a muscle relaxant.
What are the side effects of ECT?
As with all other medical procedures, ECT treatment does have potential risks and side effects. It is important to talk with a psychiatrist about ECT risks. Common ECT side effects are: 1 Nausea 2 Lightheadedness 3 Headache 4 Fatigue 5 Confusion 6 Memory loss
What is the purpose of an ECG before ECT?
Since the heart is also governed by an electric current, an electrocardiogram (ECG) is performed to ensure that the heart is healthy enough for the procedure.
How long does a seizure last after anesthesia?
This creates a small, controlled seizure that lasts for about one minute. Patients wake up from the procedure within minutes and can go home if someone else is driving.
2 patient evaluations for Bilateral Electroconvulsive Therapy ECT
Advice & Tips: I like the fact that I have no more suicidal thoughts, but I hate that fact that I have no personality and I still have depression. The last 2 times I've had it done, I end up in depression. I'm not happy about anything. I've taken more time off of work to work through the depression and find myself. I feel like a walking zombie.
Sep 6, 2010 (Started May 25, 2010)
Advice & Tips: I like the fact that I have no more suicidal thoughts, but I hate that fact that I have no personality and I still have depression. The last 2 times I've had it done, I end up in depression. I'm not happy about anything. I've taken more time off of work to work through the depression and find myself. I feel like a walking zombie.
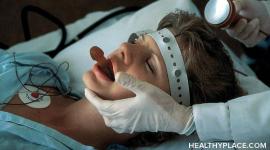
Overview
- Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) is a procedure, done under general anesthesia, in which small electric currents are passed through the brain, intentionally triggering a brief seizure. ECT seems to cause changes in brain chemistry that can quickly reverse symptoms of certain mental health conditions. ECT often works when other treatments are unsuccessful and when the full course …
Why It's Done
- Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) can provide rapid, significant improvements in severe symptoms of several mental health conditions. ECT is used to treat: 1. Severe depression,particularly when accompanied by detachment from reality (psychosis), a desire to commit suicide or refusal to eat. 2. Treatment-resistant depression,a severe depression that doesn't improve with medications o…
Risks
- Although ECT is generally safe, risks and side effects may include: 1. Confusion.Immediately after treatment, you may experience confusion, which can last from a few minutes to several hours. You may not know where you are or why you're there. Rarely, confusion may last several days or longer. Confusion is generally more noticeable in older adults. 2. Memory loss.Some people hav…
How You Prepare
- Before having your first ECT treatment, you'll need a full evaluation, which usually includes: 1. Medical history 2. Complete physical exam 3. Psychiatric assessment 4. Basic blood tests 5. Electrocardiogram (ECG) to check your heart health 6. Discussion of the risks of anesthesia These exams help make sure that ECT is safe for you.
What You Can Expect
- The ECT procedure takes about five to 10 minutes, with added time for preparation and recovery. ECT can be done while you're hospitalized or as an outpatient procedure.
Results
- Many people begin to notice an improvement in their symptoms after about six treatments with electroconvulsive therapy. Full improvement may take longer, though ECT may not work for everyone. Response to antidepressant medications, in comparison, can take several weeks or more. No one knows for certain how ECT helps treat severe depression and other mental illness…