What drugs cause damage to 8 cranial nerve?
a chemotherapy that is working but causing ongoing damage to your nerves. The risk of nerve damage is related to the dose of the chemotherapy, the schedule of the chemotherapy, and the total amount of chemotherapy that the patient received. Certain chemotherapy drugs are more likely to cause nerve damage , including: • Cisplatin • Carboplatin
How do you assess the 8th cranial nerve?
- Hearing is first tested in each ear by whispering something while occluding the opposite ear.
- Vestibular function can be evaluated by testing for nystagmus.
- If patients have acute vertigo during the examination, nystagmus is usually apparent during inspection.
What are the symptoms of ulnar nerve damage?
Ulnar Nerve Injury
- Symptoms. Numbness and tingling (commonly referred to as paresthesia) are signs that nerve signals are being disrupted. ...
- Causes. Injuries to the ulnar nerve can occur at multiple points along the course of the nerve. ...
- Diagnosis. ...
- Treatment. ...
How to conduct a cranial nerve examination?
• Ask patient to turn head to one side and push against examiners hand or ask to flex head against resistance, palpate and evaluate strength of sternocleidomastoid muscle. • Evaluate both right and left side, compare for symmetry. CRANIAL NERVES 39 40.
Can the 8th cranial nerve be repaired?
Treatment. If a cranial nerve is completely cut in two, it cannot be repaired. However, if it is stretched or bruised but the nerve remains intact, it can recover. This takes time and can cause a variety of unpleasant symptoms including tingling and pain.
How do you treat cranial nerve damage?
The types of treatment options for cranial nerve disorders include:Medication. ... Microvascular Decompression (MVD) ... Gamma Knife® Perfexion™ Radiosurgery. ... Supra Orbital and Infra Orbital Peripheral Nerve Stimulation. ... Percutaneous Glycerol Rhizotomy. ... Research and Clinical Trials.
What happens when cranial nerve 8 is damaged?
CN VIII pathology can result from direct trauma, congenital malformations, tumor formation, infection, and vascular injury. Presenting symptoms include vertigo, nystagmus, tinnitus, and sensorineural hearing loss.
How long does it take for a cranial nerve to heal?
Expect no noticeable signs of healing before about four to six months after the damage occurs.
How do neurologists treat nerve pain?
Multimodal therapy (including medicines, physical therapy, psychological counseling and sometimes surgery) is usually required to treat neuropathic pain. Medicines commonly prescribed for neuropathic pain include anti-seizure drugs such as: Gabapentin (Neurontin®).
How can I heal my nerves naturally?
Regular exercise can help to combat pain and improve your overall health. Being active can reduce your blood sugar, which, in turn, can reduce or slow down nerve damage. Exercise also increases blood flow to your arms and legs and reduces stress. These are all factors that help to reduce discomfort and pain.
What is the most common cause of damage to cranial nerve VIII?
The most common lesions responsible for damage to VIII are vestibular Schwannomas.
How do you test cranial nerve 8?
Cranial Nerve 8 - Auditory Acuity, Weber & Rinne Tests The cochlear division of CN 8 is tested by screening for auditory acuity. This can be done by the examiner lightly rubbing their fingers by each ear or by using a ticking watch. Compare right versus left.
What cranial nerve causes vertigo?
Labyrinthitis is the inflammation of part of the inner ear called the labyrinth. The eighth cranial nerve (vestibulocochlear nerve) may also be inflamed. The inflammation of these causes a feeling of spinning (vertigo), hearing loss, and other symptoms.
Can nerve damage be repaired?
Sometimes a section of a nerve is cut completely or damaged beyond repair. Your surgeon can remove the damaged section and reconnect healthy nerve ends (nerve repair) or implant a piece of nerve from another part of your body (nerve graft). These procedures can help your nerves regrow.
Can MRI show cranial nerve damage?
An MRI may be able help identify structural lesions that may be pressing against the nerve so the problem can be corrected before permanent nerve damage occurs. Nerve damage can usually be diagnosed based on a neurological examination and can be correlated by MRI scan findings.
Can you repair facial nerve damage?
Facial nerve damage can be repaired in many cases. The success rate depends on the extent and the duration of the nerve damage. The sooner it is identified and treated appropriately, the better the prognosis.
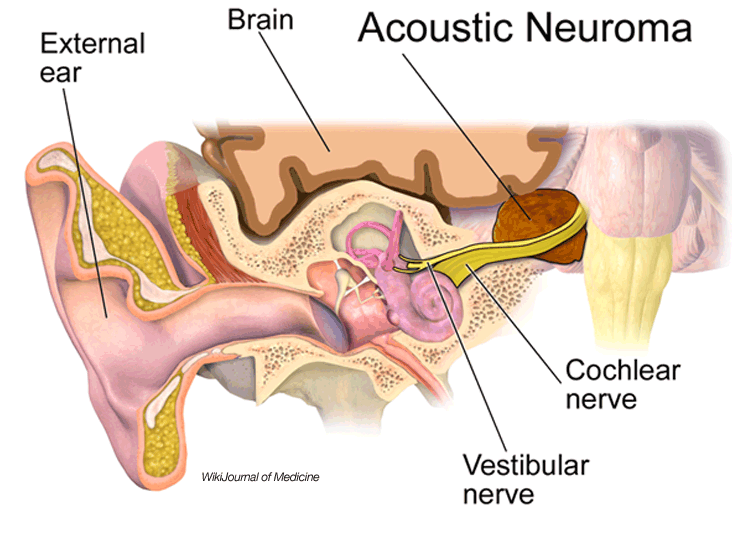
What is the cochlear nerve?
Introduction. The vestibulocochlear nerve, also known as cranial nerve eight (CN VIII), consists of the vestibular and cochlear nerves. Each nerve has distinct nuclei within the brainstem. The vestibular nerve is primarily responsible for maintaining body balance and eye movements, while the cochlear nerve is responsible for hearing.
What is the function of the cochlear nerve?
The cochlear nerve is responsible for transmitting auditory signals from the inner ear to the cochlear nuclei, within the brainstem, and ultimately to the primary auditory cortex, within the temporal lobe.
What is the function of hair cells in the vestibular nerve?
The stimulation of the hair cells results in depolarization and increased calcium (Ca) influx, leading to increased firing of afferent vestibular nerve fibers. Those fibers travel to the vestibular ganglion (Scarpa’s ganglion), located in the IAC. The ganglion is composed of bipolar neurons that send peripheral processes to the vestibular apparatus and central processes that join together to form the vestibular nerve. The ganglion is separated into superior and inferior divisions. The superior division receives input from the utricle and superior and lateral semicircular ducts. The inferior division receives input from the saccule and posterior semicircular duct. [8]
How to treat vestibular schwannomas?
Treatment options for vestibular schwannomas (acoustic neuromas) are microsurgical resection, radiation therapy, and observation. Post-operative mortality rates have decreased dramatically over the last century. Therefore, preserving facial nerve function has become the primary goal of surgery, while removing as much as of the tumor as possible. The three standard surgical approaches are middle fossa, retrosigmoidal, and translabyrinthine. Pre-operative hearing level, tumor size, and tumor location determine which approach is used. [17][18]
What are the three divisions of the cochlear nucleus?
There are three divisions of the cochlear nuclei: anteroventral (AVCN), dorsal (DCN), and posteroventral (PVCN). [1][4][5] Upon entering the brainstem, the cochlear nerve separates from the vestibular nerve and branches into anterior and posterior divisions.
How does the vestibular system help with postural control?
It has also been suggested that the auditory stimuli interact with the vestibu lar system to influence postural control.[9] Additionally, the vestibular system helps control blood pressure, by using sympathetic pathways and the baroreceptors on the carotid and the aortic arch. [10]
What nerve relays information related to motion and position?
The vestibular nerv e relays information related to motion and position. The vestibular system involves coordinated communication between the vestibular apparatus (semicircular canals, saccule, and utricle), ocular muscles, postural muscles, brainstem, and cerebral cortex. [3][8]
Which cranial nerve is involved in clinical medicine?
The eighth cranial nerve is deeply involved in clinical medicine. Hearing is of course central as patients generally hear our questions and we hear their answers. Routine assessment and treatment depend heavily on intact hearing. Some of the most common complaints in general medicine are vestibular (such as dizziness) and auditory (such as tinnitus and hearing impairment). This article covers the essential anatomy and physiology, abnormal clinical signs found in clinical psychiatry, and how to elicit these signs.
What is the cranial nerve VIII?
Cranial nerve VIII brings sound and information about one's position and movement in space into the brain. The auditory and vestibular systems subserve several functions basic to clinical medicine and to psychiatry. This article covers the basics of cranial nerve VIII, hearing and vestibular systems, including common problems with hearing and balance, problems with hearing and balance that tend to be found in psychiatric patients, and some simple assessments of value in clinical practice.
How to test for conductive hearing loss?
If the bad side seems to be softer the damage is probably sensorineural. If the bad side seems to be louder, the damage is probably conductive. If they seem equal, the Weber is inconclusive. The Rinne test is a more accurate test, if conductive hearing loss is suspected. The patient is asked to report which seems louder, as bone and air conduction stimuli are applied. The simplest approach is to hold the tuning fork alternately to the mastoid (lightly but firmly) and about one inch from the ear, each for about two seconds. The tuning fork should be held so that its long axis is perpendicular to the line through the ear canals. If bone conduction is definitely heard better than air conduction (BC>AC), this is strong support for conductive hearing loss.6
When confronted with acute vestibular signs and symptoms in routine psychiatric practice, it is important?
When confronted with acute vestibular signs and symptoms in routine psychiatric practice (nausea, dizziness or vertigo, nystagmus, impaired balance), it is important to think early of intoxication, particularly with ethanol or an anticonvulsant, or withdrawal, particularly from a serotonergic antidepressant.47
Where do vestibular nerve impulses originate?
Vestibular system. As with the acoustic branch, vestibular nerve impulses encoding motion and position originate in hairs within fluid-filled cavities. These cavities, the semicircular canals, utricle and saccule (collectively the labyrinth), are positioned so that any change or rotation is uniquely codified. The vestibular branch of the eigth cranial nerve closely adjoins the auditory. Its neurons synapse in vestibular nuclei, as well as in the rostral medulla. The vestibular nuclei project to many locations with intuitive relevance, including cerebellum, spinal cord, extraocular nuclei (nystagmus), parietal cortex (spatial orientation), vagal nucleus (vomiting), nucleus solitarius (nausea), and reticular formation (pallor, diaphoresis).
How to do a horizontal head impulse test?
The horizontal head impulse test is a quick vestibulo-ocular reflex used to distinguish the more benign peripheral from the more ominous central lesions causing vertigo. Approaching a seated and relaxed patient from the front, grasp the head from both sides and instruct the patient to relax and (the examiner must do the work) fixate on your nose. Starting from about 20 degrees rotation off center, rapidly rotate the head to midline, observing the eyes. An abnormal response occurs when the head is rotated toward a vestibular lesion and consists of a quick corrective saccade (gaze shift) once the head stops moving. Without vestibular input, the patient cannot maintain fixation during the head rotation, requiring the adjustment. A normal result on this test (no corrective saccade seen) is strong evidence of central nervous system (CNS) involvement.48
Microvascular Decompression Surgery for Treating Cranial Nerve Disorders
Microvascular decompression is a minimally invasive surgical procedure using endoscopes to relieve abnormal compression of a cranial nerve.
Other Treatment Options for Cranial Nerve Disorders
In addition to microvascular decompression surgery, UPMC offers treatment options for cranial nerve disorders not always available elsewhere.
Where does the VIII nerve run?
It is an intracranial nerve which runs from the sensory receptors in the internal ear to the brain stem nuclei and finally to the auditory areas: the post-central gyrus and superior temporal auditory cortex. The most common lesions responsible for damage to VIII are vestibular Schwannomas.
What nerve is responsible for hearing and balance?
The vestibulocochlear nerve is responsible for both hearing and balance and brings information from the inner ear to the brain. Problems with the vestibulocochlear nerve can result in vertigo, vomiting, ringing in the ears, a false sense of motion, motion sickness, or even hearing loss.
Which nerve transmits sound and balance to the brain?
The vestibulocochlear nerve (auditory vestibular nerve), known as the eighth cranial nerve, transmits sound and equilibrium (balance) information from the inner ear to the brain.
What are the risks of nerve VIII surgery?
Symptoms may include: Loss of hearing. Tinnitus.
Which nerve is responsible for hearing?
Cochlear Nerve : The cochlear nerve ( auditory nerve ), branches off of CN8, goes to the cochlea (spinal ganglion) and is the nerve specifically for hearing. Vestibular Nerve: This nerve branches off of CN8, connects the vestibule and the semicircular canals; function is balance and orientation.
Which nerve splits to become the vestibular nerve?
After a short distance from the brainstem, the vestibulocochlear nerve splits to become the vestibular nerve, balance nerve, and the cochlear nerve (acoustic nerve), the hearing nerve, as it extends towards the inner ear.
Which organ is sent through the posterior, superior and lateral canals?
Membranous Ampulla (Balance Glands): Body movement is sent through the posterior, superior and lateral canals semicircular canals into the ampullae glands at the end of each canal; information to the vestibular nerve.
Can tumor growth cause cochlear nerve damage?
result in other dangerous compression issues like intracranial pressure (obstructive hydrocephalus) Important to Note: Tumor growth can cause damage to the vestibular nerve branch and potentially not damage the cochlear nerve.
What is the name of the condition that affects the vestibular nerve?
A related syndrome is called vestibular neuritis. It causes similar symptoms. But it doesn't cause hearing problems. It affects only the vestibular part of the labyrinth and nerve.
How to help vestibular symptoms go away?
If your symptoms go away in a few weeks, you likely won’t need other treatment. If you have symptoms that don’t go away, you may need to do certain exercises . These are known as vestibular rehabilitation exercises. They are a form of physical therapy. These exercises may help your brain learn to adjust to the vestibular imbalance.
How long does it take for vertigo to go away?
Symptoms include vertigo, hearing loss, and dizziness. Symptoms may start suddenly and go away in a few weeks. Your healthcare provider will need to rule out other more dangerous causes of vertigo, such as stroke. You might need medicines to treat your symptoms.
What is the downside of a facial nerve surgery?
The downside of this technique is that it results in permanent hearing loss.
How many surgical approaches are there for removing acoustic neuroma?
There are three main surgical approaches for removing an acoustic neuroma:
What is acoustic neuroma?
Acoustic Neuroma Causes. Acoustic Neuroma Treatments. An acoustic neuroma is a noncancerous growth that develops on the eighth cranial nerve. Also known as the vestibulocochlear nerve, it connects the inner ear with the brain and has two different parts. One part is involved in transmitting sound; the other helps send balance information from ...
What part of the brain is responsible for transmitting sound?
One part is involved in transmitting sound; the other helps send balance information from the inner ear to the brain. Acoustic neuromas -- sometimes called vestibular schwannomas or neurilemmoma -- usually grow slowly over a period of years.
Can radiation therapy be used for acoustic neuromas?
Radiation therapy is recommended in some cases for acoustic neuromas. State-of-the-art delivery techniques make it possible to send high doses of radiation to the tumor while limiting expose and damage to surrounding tissue. Radiation therapy for this condition is usually delivered in one of two ways:
What nerve is used for MRI?
MRI has been used to visualize the compression of the 8th cranial nerve. However the role of imaging to diagnose and identify the affected side is not clear, as there is a high rate of vascular compression of the 8th cranial nerve in healthy subjects.
What nerve is involved in vestibular paroxysmia?
It is assumed that vestibular paroxysmia occurs due to compression of the eighth cranial nerve (otherwise known as the vestibulocochlear nerve) by an artery. This nerve supplies the inner ear (which assists with balance) and the cochlea (the organ of hearing). Timothy Hain, MD, notes some controversy regarding the exact cause ...
What is vestibular paroxysmia?
Vestibular paroxysmia is an episodic vestibular disorder which is assumed to be due to compression of the eighth cranial nerve. The exact cause of this nerve compression/irritation is unknown. Diagnosis of this condition is often based on the patient’s symptoms and the frequency and length of attacks. Download PDF.
How long does vertigo last?
Attacks of spinning or non-spinning vertigo lasting a fraction of a second to a minute or more
Does oxcarbazepine help vestibular paroxysmia?
A positive response to these medications helps to support the diagnosis of vestibular paroxysmia. Surgical treatment is not recommended.