
Corticosteroids are the most effective antiasthma drugs for patients experiencing exacerbations of asthma. Oral or inhaled corticosteroids are valuable as maintenance pharmacotherapy to prevent disabling wheezing, chest constriction, nocturnal wheezing dyspnea, and other symptoms of ineffectively controlled asthma.
What are corticosteroids for asthma?
In short, corticosteroids lower the inflammation in the body and, specifically for asthmatics, in the lungs. Corticosteroids mimic the hormones that are produced naturally in the body (more specifically the adrenal glands). When the dose is more than what the body naturally makes, it suppresses inflammation. The SET mnemonic for asthma
How effective are inhaled corticosteroids?
They are effective in preventing asthma attacks but require daily use in regularly spaced doses in order to be effective. While not all patients respond similarly to inhaled corticosteroids, they have been found to improve a number of important asthma outcomes such as:
What is the role of corticosteroids in the treatment of hypersensitivity reactions?
Corticosteroids have no effect on the immediate hypersensitivity reaction and have no direct role in bronchial reactivity. By blocking the late reaction, they prevent the increased airway reactivity observed with late bronchial reactions. The limitation of using corticosteroids are their side effects.
What is a corticosteroid?
Corticosteroids, also referred to as oral steroids, are synthetic drugs that mimic the hormone cortisol naturally produced by the adrenal glands. They work by tempering a hyperresponsive immune system, reducing inflammation either locally (in a specific part of the body) or systemically (throughout the entire body).
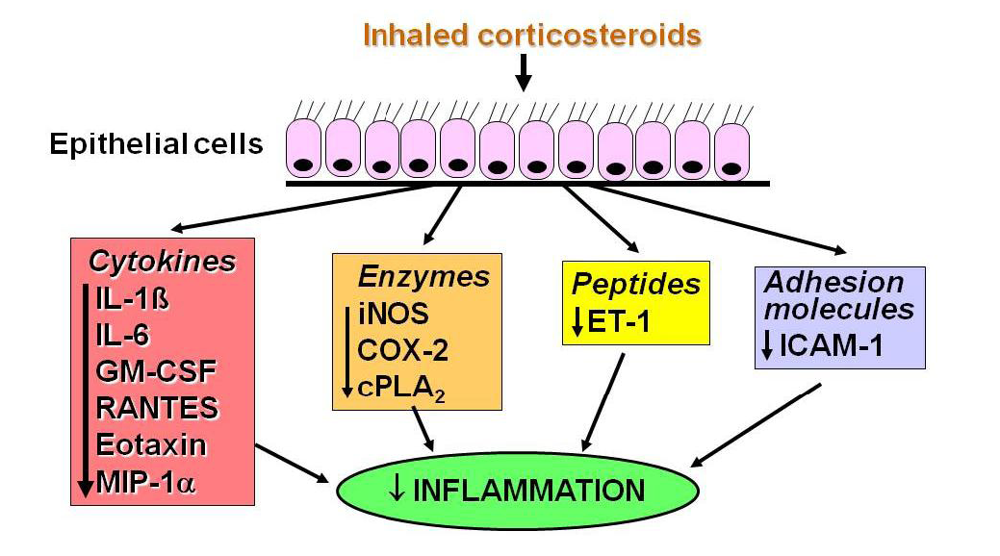
What benefit are corticosteroids in the treatment of asthma?
Corticosteroids are copies of hormones your body produces naturally. Steroids help asthma by calming inflamed airways and stopping inflammation. This helps ease asthma symptoms such as breathlessness and coughing. It will also help prevent your lungs reacting to triggers.
What are the benefits of corticosteroids?
Corticosteroids are mainly used to reduce inflammation and suppress the immune system. They are used to treat conditions such as: asthma. allergic rhinitis and hay fever.
What do corticosteroid inhalers do?
When they're inhaled, steroids reduce swelling (inflammation) in your airways. This can help reduce symptoms of asthma and COPD, such as wheezing and shortness of breath. Steroid inhalers are different to the anabolic steroids that some people use illegally to increase their muscle mass.
What is the action of corticosteroids?
Corticosteroids modify the functions of epidermal and dermal cells and of leukocytes participating in proliferative and inflammatory skin diseases. After passage through the cell membrane corticosteroids react with receptor proteins in the cytoplasm to form a steroid-receptor complex.
How does cortisone work?
However, cortisone itself is not a pain medication. Instead, cortisone is an anti-inflammatory that works by preventing collagen production. The injection shuts down collagen-producing cells in the tendon or joint; this action suppresses inflammation and calms nerves, indirectly reducing pain.
How do corticosteroids reduce inflammation?
Corticosteroids can reduce inflammation in the body and relieve related symptoms, such as body pain, swelling, and stiffness. Corticosteroids reduce inflammation by suppressing the immune system. They are a standard treatment for autoimmune conditions, which often cause inflammation in the body.
How do inhaled corticosteroids reduce inflammation?
Inhaled corticosteroids (ICS) are the most effective controllers of asthma. They suppress inflammation mainly by switching off multiple activated inflammatory genes through reversing histone acetylation via the recruitment of histone deacetylase 2 (HDAC2).
Which inhaled corticosteroid is best for asthma?
Mometasone may be preferred if once-daily dosing is desired. Ciclesonide has been found highly effective in once-daily dose and without side effects even in high doses. Further studies comparing it with other ICSs over longer periods of use will determine its place in treatment of chronic asthma.
What is corticosteroids used for?
Both can be used medicinally to treat a variety of health conditions, including orthopedic conditions like arthritis and inflammation from soft tissue injuries.
How do corticosteroids affect the body?
Glucocorticoids can help to fight inflammation and suppress hypersensitive white blood cell responses to infection and other threats. These corticosteroids also affect blood pressure and skin cell production .
Why are corticosteroids dangerous?
The very reasons they work so well at reducing pain and inflammation are the same reasons they’re dangerous if taken too frequently or in large quantities. Corticosteroids suppress the immune system and the creation of white blood cells, halting immune system “overreactions” that create pain and swelling .
Why do orthopedists inject corticosteroids?
In orthopedics, injectable corticosteroids are often used for their anti-inflammatory properties. For some painful conditions, for example arthritis or a bulging disc, an orthopedist may suggest one or more injections to the joint or the site of injury in order to bring down swelling, inflammation, or pain.
What is the treatment for osteoarthritis?
Aspiration of collected fluid, followed by corticosteroid injection is an option for treatment. Osteoarthritis (OA). Treatment of OA is probably one of the most common uses of corticosteroids in orthopedics. When cartilage wears away, pain and inflammation in the joints is common.
What conditions can be treated with cortisol injections?
Conditions that may benefit from cortisol or hydrocortisone injections include: Bursitis. The fluid-filled bursa, or sac, that acts as a cushion between bones and soft tissue can sometimes become irritated, inflamed, or swollen. Pain and limited motion can result.
Is cortisol a natural glucocorticoid?
Cortisol ( hydrocortisone) is a naturally-occurring glucocorticoid. Prednisone, commonly prescribed for a variety of health issues including asthma and allergies, is an example of a synthetic or human-made glucocorticoid. Mineralocorticoids regulate the balance of water and electrolytes in the kidneys.
How do corticosteroids help with muscle spasms?
Corticosteroids enhance the beta-adrenergic response to relieve the muscle spasm. They also act by reversing the mucosal edema, decreasing vascular permeability by vasoconstriction, and inhibiting the release of LTC4 and LTD4. Corticosteroids reduce the mucus secretion by inhibiting the release of secretagogue from macrophages.
What are the limitations of corticosteroids?
The limitation of using corticosteroids are their side effects. They vary from tolerable to life threatening side effects. Each tissue in the body is a target for corticosteroids. The mechanism of adverse effects have been studied in extensive detail but many questions are yet to be answered.
How do corticosteroids affect mucus secretion?
Corticosteroids reduce the mucus secretion by inhibiting the release of secretagogue from macrophages. Corticosteroids inhibit the late phase reaction by inhibiting the inflammatory response and interfering with chemotaxis. This action may be due to the inhibition of LTB4 release.
Do corticosteroids cause bronchial reactivity?
Corticosteroids have no effect on the immediate hypersensitivity reaction and have no direct role in bronchial reactivity. By blocking the late reaction, they prevent the increased airway reactivity observed with late bronchial reactions. The limitation of using corticosteroids are their side effects.
Do corticosteroids help with asthma?
It is beyond any doubt that CS act on many sites to help reverse the pathologic process of bronchial asthma. Corticosteroids enhance the beta-adrenergic response to relieve the muscle spasm. They also act by reversing the mucosal edema, decreasing vascular permeability by vasoconstriction, and inhibiting the release of LTC4 and LTD4. Corticosteroids reduce the mucus secretion by inhibiting the release of secretagogue from macrophages. Corticosteroids inhibit the late phase reaction by inhibiting the inflammatory response and interfering with chemotaxis. This action may be due to the inhibition of LTB4 release. The eosinopenic effect of corticosteroids may help to prevent the cytotoxic effect of the major basic protein and other inflammatory mediators released from eosinophils. Corticosteroids have no effect on the immediate hypersensitivity reaction and have no direct role in bronchial reactivity. By blocking the late reaction, they prevent the increased airway reactivity observed with late bronchial reactions. The limitation of using corticosteroids are their side effects. They vary from tolerable to life threatening side effects. Each tissue in the body is a target for corticosteroids. The mechanism of adverse effects have been studied in extensive detail but many questions are yet to be answered. Alternate-day therapy and inhalation therapy are meant to minimize these side effects. The expansion of using inhaled steroid therapy and finding some inhaled preparations that have even less systemic side effects seems a reasonable approach to deal with severe asthma.
How do corticosteroids help with asthma?
Inhaled corticosteroids prevent asthma symptoms by reducing inflammation in the bronchial tubes, or airways, that carry oxygen to the lungs. In addition, they reduce the amount of mucus produced by the bronchial tubes.
Which combination of corticosteroids is best for asthma?
3 . Advair (fluticasone*/salmeterol) Aerobid (flunisolide) Alvesco, Omnaris, Zetonna (ciclesonide)
What are the mainstays of asthma treatment?
They are the current mainstay of treatment once a person with asthma needs a higher level of care than a rescue inhaler (bronchodilator). 1 . Inhaled corticosteroids help prevent chronic asthma symptoms such as: Wheezing. Chest tightness.
What is ICS in asthma?
Inhaled corticosteroids (ICS), also known as inhaled steroids, are the most potent anti-inflammatory controller medications available today for asthma control and are used to decrease the frequency and severity of asthma symptoms. They are the current mainstay of treatment once a person with asthma needs a higher level of care than ...
What is the role of steroids in asthma?
This is achieved by blocking the late-phase immune reaction to an allergen, decre asing airway hyperrespons iveness and inflammation, and inhibiting inflammatory cells such as mast cells, eosinophils, and basophils . Inhaled steroids are a key part of asthma control for many.
Can steroids affect your voice?
Dysphonia: Inhaled steroids can affect your voice, a phenomenon known as dysphonia, which impacts 5% to 58% of people taking the medication. 5 It may be prevented by using a spacer and treated by decreasing the ICS dose temporarily and giving your vocal cords a rest.
Do corticosteroids affect the body?
Side Effects. Since inhaled corticosteroids act locally in the airway, minuscule amounts of the medicine make its way into the rest of the body. Therefore, the risk of potentially serious side effects commonly experienced by people taking systemic steroid medications is significantly lower.
What are the best corticosteroids for asthma?
The four oral corticosteroids most commonly used for the treatment of acute or severe asthma are: 1 Prednisone 2 Prednisolone 3 Methylprednisolone 4 Dexamethasone
How do corticosteroids work?
They work by tempering a hyperresponsive immune system, reducing inflammation either locally (in a specific part of the body) or systemically (throughout the entire body).
What is the best medication for asthma?
The four oral corticosteroids most commonly used for the treatment of acute or severe asthma are: Prednisone. Prednisolone. Methylprednisolone. Dexamethasone. Oral steroids can be used in infants, toddlers, adolescents, teens, and adults with severe persistent asthma, albeit at different doses. 1 . Pros and Cons of Corticosteroids.
Why are steroids prescribed?
Because oral steroids are prescribed at higher doses, they are used for specific purposes where the benefits of treatment outweigh the risks. They are most commonly used to treat asthma attacks (a.k.a. acute exacerbations) but can also be used to control asthma in people with advanced disease.
Why do corticosteroids need to be delayed?
Because oral corticosteroids actively suppress the immune system, they may need to be delayed in people with an active bacterial, fungal, viral, or parasitic infection, including tuberculosis, ocular herpes simplex, measles, and chickenpox.
What is oral corticosteroids?
Dosage. Side Effects. Warnings and Interactions. Oral corticosteroids are a type of drug taken by mouth that have their place in the treatment of asthma. They are most often used when a person has a severe asthma attack to rapidly reduce airway inflammation and relieve asthma symptoms.
What is severe persistent asthma?
Severe persistent asthma is a classification of disease with clearly defined diagnostic criteria. If you do not meet it, an oral corticosteroid will likely not be prescribed. To evaluate you for severe persistent asthma, your doctor will perform a series of pulmonary function tests (PFTs).
How do steroids help with asthma?
Steroids and other anti-inflammatory drugs work by reducing inflammation, swelling, and mucus production in the airways of a person with asthma. As a result, the airways are less inflamed and less likely to react to asthma triggers, allowing people with symptoms of asthma to have better control over their condition.
What is the name of the drug that controls the blood cells that trigger asthma?
Mepolizumab ( Nucala) is a biologic therapy that has been found to control the blood cells that often trigger asthma. Nucala targets Interluken-5 (IL-5) which regulates the levels of blood eosinophils (the type of white blood cells that helps trigger asthma).
How do leukotriene modifiers help with asthma?
Leukotriene modifier drugs help control asthma by blocking the actions of leukotrienes in the body. Studies show that these medications are helpful in improving airflow and reducing asthma symptoms. The leukotriene modifiers are taken as pills and have been shown to decrease the need for other asthma medications.
What are the benefits of inhaled steroids?
The benefits of inhaled steroids for better asthma control far exceed their risks, and include: Reduced frequency of asthma attacks. Decreased use of beta-agonist bronchodilators (quick relief or rescue inhalers) Improved lung function. Reduced emergency room visits and hospitalizations for life-threatening asthma.
How long does it take for steroids to work on asthma?
Dosages of inhaled steroids in asthma inhalers vary. Inhaled steroids need to be taken daily for best results. Some improvement in asthma symptoms can be seen in 1 to 3 weeks after starting inhaled ...
What are the best treatments for asthma?
Medically Reviewed by Carol DerSarkissian, MD on August 11, 2019. The key treatments for asthma are steroids and other anti-inflammatory drugs . These asthma drugs both help to control asthma and prevent asthma attacks. Steroids and other anti-inflammatory drugs work by reducing inflammation, swelling, and mucus production in the airways ...
What are the side effects of systemic steroids?
Side effects of systemic steroids can include weakness, acne, weight gain, mood or behavior changes, upset stomach, bone loss, eye changes, and slowing of growth. These side effects rarely occur with short-term use, such as for an acute asthma attack.
What is the best treatment for asthma?
If you have serious worsening of asthma symptoms (an asthma attack), your doctor may prescribe a brief course of oral steroids such as prednisone. Oral steroids may also be prescribed when your asthma symptoms worsen but you do not require hospitalization.
What are the side effects of asthma inhalers?
Unlike the serious side effects of oral steroids, the most common side effects of anti-inflammatory asthma inhalers are hoarseness and thrush, ...
Can you take steroids for asthma?
Steroids, anti-inflammatory drugs such as prednisone, can be used for asthma as well as other lung diseases. Prednisone and other steroids (inhaled, oral, or by injection) help calm airway inflammation in asthma. If you've ever had a serious asthma attack, you may have had high doses of steroids administered intravenously in the hospital.
Should I rinse my mouth after using an asthma inhaler?
As with all asthma inhalers, you should rinse the mouth carefully after using your inhaler. Gargle with water after inhalation to help reduce the risk of oral thrush. For more detail, see WebMD’s Asthma, Steroids & Other Anti-Inflammatory Drugs. Share on Facebook Share on Twitter Share on Pinterest Email Print.
Does prednisone go through the body?
That means that after taking prednisone by mouth (orally), it is absorbed in the body, unlike inhaled steroids (anti-inflammatory asthma inhalers) that go straight to the lungs. Prednisone decreases your immune system's response to reduce symptoms such as swelling and allergic-type reactions. Prednisone and other systemic steroids may be used ...

Types
How They Work
- Inhaled corticosteroids prevent asthma symptoms by reducing inflammation in the bronchial tubes, or airways, that carry oxygen to the lungs. In addition, they reduce the amount of mucus produced by the bronchial tubes. This is achieved by blocking the late-phase immune reaction to an allergen, decreasing airway hyperresponsiveness and inflammation,...
Efficacy
- Generally, inhaled corticosteroids are used for long-term treatment of asthma in people of all ages who require daily management. They are effective in preventing asthma attacks but require daily use in regularly spaced dosesin order to be effective. While not all people respond similarly to inhaled corticosteroids, they have been found to improve a number of important asthma outcom…
Side Effects
- Since inhaled corticosteroids act locally in the airway, minuscule amounts of the medicine make its way into the rest of the body. Therefore, the risk of potentially serious side effects commonly experienced by people taking systemic steroid medications is significantly lower. Overall, the risks associated with inhaled corticosteroids are very low, but there are several things you can do to …
A Word from Verywell
- While inhaled corticosteroids improve asthma control more effectively than any other agent used as a single treatment, it is important to note that these drugs cannot relieve an asthma attack already in progress. A rescue inhaler is still needed for those situations.