Nutrition
Treatment. TB is a treatable and curable disease. Active, drug-susceptible TB disease is treated with a standard 6-month course of 4 antimicrobial drugs that are provided with information and support to the patient by a health worker or trained volunteer. Without such support, treatment adherence is more difficult.
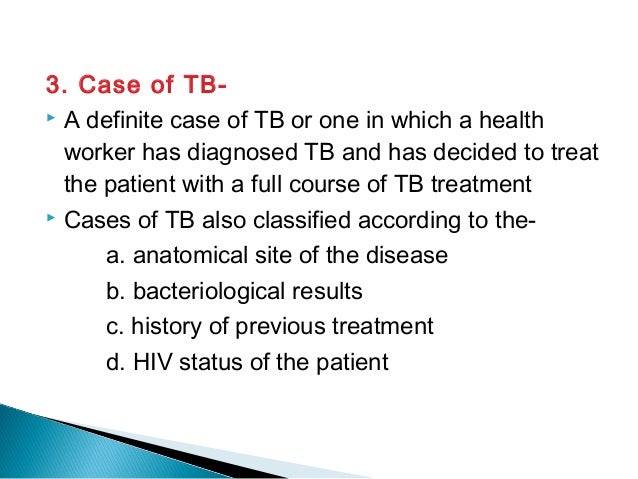
What is TB and how it is treated?
The following are the stages of TB:
- Exposure. This happens when a person has been in contact with, or exposed to, another person who has TB. ...
- Latent TB infection. This happens when a person has TB bacteria in his or her body, but does not have symptoms of the disease. ...
- TB disease. This describes the person who has signs and symptoms of an active infection. ...
What are the phases of TB treatment?
What is the treatment for TB?
- The following medications are commonly used to treat TB:
- Isoniazid. Each small white tablet contains 100mg of Isoniazid and the adult dose is 300mg daily. ...
- Rifampicin. The capsules come in two strengths, 150mg or 300mg. The colours vary with the different brands and strengths.
What medications are used to treat TB?
Treatment
- Most common TB drugs. If you have latent tuberculosis, you might need to take only one or two types of TB drugs. ...
- Medication side effects. Serious side effects of TB drugs aren't common but can be dangerous when they do occur. ...
- Completing treatment is essential. After a few weeks, you won't be contagious and you might start to feel better. ...
What are the side effects of TB treatment?
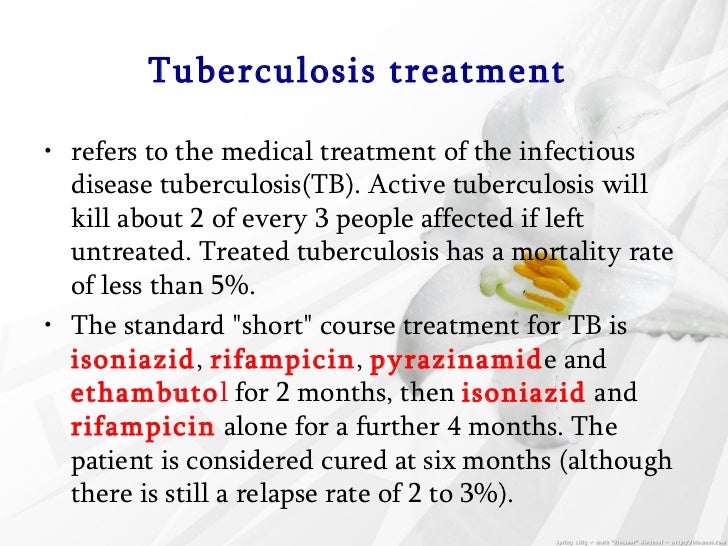
How is TB treated today?
If you have an active TB disease you will probably be treated with a combination of antibacterial medications for a period of six to 12 months. The most common treatment for active TB is isoniazid INH in combination with three other drugs—rifampin, pyrazinamide and ethambutol.
Can the TB be completely cured?
With treatment, TB can almost always be cured. A course of antibiotics will usually need to be taken for 6 months. Several different antibiotics are used because some forms of TB are resistant to certain antibiotics.
What is the fastest way to cure TB?
The most common medications used to treat TB disease are isoniazid, rifampin, ethambutol, and pyrazinamide. Be sure to take your medicine exactly as prescribed, for as long as it's prescribed. If you stop, or don't take it as ordered, you can get sick again.
Is TB treatment difficult?
Tuberculosis treatment is a combination of antibiotics taken for half a year or more—a major drawback, because patients often quit therapy prematurely, increasing the risk of drug-resistant strains emerging.
How long can a TB patient live?
The overall mortality rate was 12.3% (249 cases) and the mean age at death was 74 years; 17.3% (43 cases) of all TB deaths were TB-related. Most of the TB-related deaths occurred early (median survival: 20 days), and the patient died of septic shock.
What are the 3 stages of TB?
There are 3 stages of TB—exposure, latent, and active disease. A TB skin test or a TB blood test can diagnose the disease. Treatment exactly as recommended is necessary to cure the disease and prevent its spread to other people.
How do u know if u have TB?
Signs and symptoms of active TB include: Coughing for three or more weeks. Coughing up blood or mucus. Chest pain, or pain with breathing or coughing.
What food should be avoided in TB?
Foods To Avoid Limit intake of refined carbs such as maida and sugar-laden foods as they offer only empty calories devoid of nutrients. Deep-fried foods and junk foods packed with saturated fats and trans-fat would worsen symptoms associated with TB such as diarrhoea, abdominal cramps, and fatigue.
What are the main cause of TB?
Tuberculosis (TB) is caused by a type of bacterium called Mycobacterium tuberculosis. It's spread when a person with active TB disease in their lungs coughs or sneezes and someone else inhales the expelled droplets, which contain TB bacteria.
How long is TB recovery?
After taking TB medicine for several weeks, a doctor will be able to tell TB patients when they are no longer able to spread TB germs to others. Most people with TB disease will need to take TB medicine for at least 6 months to be cured.
Does TB treatment make you sick?
Pyrazinamide has a strong action against the Tuberculosis bacteria in the early stages of treatment. Common side effects include loss of appetite, nausea and flushing. Some people experience pain in their joints.
How long does TB treatment take?
RIPE regimens for treating TB disease have an intensive phase of 2 months, followed by a continuation phase of either 4 or 7 months (total of 6 to 9 months for treatment).
How long does it take to treat TB?
TB disease can be treated by taking several drugs for 6 to 9 months. There are 10 drugs currently approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for treating TB. Of the approved drugs, the first-line anti-TB agents that form the core of treatment regimens are: isoniazid (INH) rifampin (RIF)
What is it called when TB bacteria multiply?
When TB bacteria become active (multiplying in the body) and the immune system can’t stop the bacteria from growing, this is called TB disease. TB disease will make a person sick. People with TB disease may spread the bacteria to people with whom they spend many hours.
What is XDR TB?
Extensively drug-resistant TB (XDR TB) is a rare type of MDR TB that is resistant to isoniazid and rifampin, plus any fluoroquinolone and at least one of three injectable second-line drugs (i.e., amikacin, kanamycin, or capreomycin). Treating and curing drug-resistant TB is complicated.
Can TB be treated?
It is very important that people who have TB disease are treated, finish the medicine, and take the drugs exactly as prescribed. If they stop taking the drugs too soon, they can become sick again; if they do not take the drugs correctly, the TB bacteria that are still alive may become resistant to those drugs.
How long does TB treatment last?
For new patients with presumed drug susceptible pulmonary TB, the World Health Organisation (WHO) recommends that they should have six months of treatment. This consists of a two month intensive phase followed by a four month continuation phase.
What are the best drugs for TB?
The drugs that a patient should take depends on whether the patient has ever had TB treatment before. If the patient has never had treatment before then it can be assumed that the bacteria in the patient's body will respond, and be sensitive to all the TB drugs. So the patient can then be given the following drugs: 1 Isoniazid 2 Rifampicin 3 Pyyrazinamide 4 & Ethambutol.
Why does TB treatment fail?
It is often suggested that TB treatment fails because a patient doesn’t take their TB drugs correctly. However there can be a number of different reasons for TB treatment failure. It is certainly true that if a patient doesn’t take their TB drugs properly that this can lead to the development of drug resistant TB.
What is the responsibility of a doctor for TB?
A patient must take their drugs properly. But it is also the responsibility of the doctor to make sure that the patient has the correct drugs. The doctor must also explain to the patient how to take the drugs correctly. In many countries there are "alternative" medicines available.
How many drugs are there for TB?
There are more than twenty drugs available for TB treatment. Which ones have to be taken depends on the circumstances of the patient. If you are having TB treatment (sometimes known as antitubercular treatment or ATT), then this should always be supervised by an experienced doctor or other health person.
What happens if you take only one or two TB drugs?
If only one or two TB drugs are taken then only some of the bacteria may be killed. They may then become resistant to the TB drugs which then don't work. If the person becomes sick again then different TB drugs called second line drugs may be needed.
How often should I take isoniazid?
Isoniazid. plus rifampicin. for the continuation treatment phase. It is recommended that patients take the TB drugs every day for six months. Taking the drugs three times a week used to be considered satisfactory but is no longer recommended by the WHO. It is essential that all the recommended TB drugs are taken.
How long does it take to cure TB?
TB treatment takes at least six months, patients need to take many tablets each day and side effects are common. This can be very difficult for people to manage, but it’s crucial that they take their treatment as prescribed and complete the course, to ensure they are completely cured and prevent them developing drug-resistant TB.
What is drug resistant TB?
Drug-resistant TB requires a longer course of treatment, with different combinations of drugs that can have more side effects. A patient will be tested to find out the exact course of treatment that should work for them.
Can TB go away?
With any medication, it is possible to experience side effects. Most are nothing to worry about and will go away. The TB nurse or doctor should advise patients of these before they start treatment.
Can latent TB be treated?
Most cases of latent TB are not considered for treatment, as 90% of people with latent TB do not go on to become ill with active TB. Treatment is recommended for people whose immune systems are weaker as they are more likely to go on to develop an active infection. This includes children and people living with HIV.
How to get rid of tuberculosis in the first week?
Don't go to work or school or sleep in a room with other people during the first few weeks of treatment. Ventilate the room. Tuberculosis germs spread more easily in small closed spaces where air doesn't move. If it's not too cold outdoors, open the windows and use a fan to blow indoor air outside.
Why is TB a killer?
Tuberculosis also remains a major killer because of the increase in drug-resistant strains. Over time, some TB germs have developed the ability to survive despite medications. This is partly because people don't take their drugs as directed or don't complete the course of treatment.
How is tuberculosis spread?
The bacteria that cause tuberculosis are spread from person to person through tiny droplets released into the air via coughs and sneezes.
What is the cause of tuberculosis?
Tuberculosis is caused by bacteria that spread from person to person through microscopic droplets released into the air. This can happen when someone with the untreated, active form of tuberculosis coughs, speaks, sneezes, spits, laughs or sings.
Why did tuberculosis start increasing in 1985?
Once rare in developed countries, tuberculosis infections began increasing in 1985, partly because of the emergence of HIV, the virus that causes AIDS. HIV weakens a person's immune system, so it can't fight the TB germs.
What are the complications of tuberculosis?
Back pain and stiffness are common complications of tuberculosis. Joint damage. Arthritis that results from tuberculosis (tuberculous arthritis) usually affects the hips and knees. Swelling of the membranes that cover your brain (meningitis).
What are the symptoms of TB outside the lungs?
Chest pain, or pain with breathing or coughing. Unintentional weight loss. Fatigue. Fever. Night sweats. Chills. Loss of appetite. Tuberculosis can also affect other parts of your body, including the kidneys, spine or brain. When TB occurs outside your lungs, signs and symptoms vary according to the organs involved.