Procedures
Staging can be performed using blood testing only. Therapeutic decision-making for AL amyloidosis involves choosing between high-dose chemotherapy and stem cell transplant or bortezomib-based chemotherapy. There are 3 therapies approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for managing ATTR amyloidosis, depending on clinical phenotype.
Therapy
Amyloidosis had been considered to be an incurable disease but during the past one decade several therapeutic approaches have been employed for the amyloidosis patients with diverse pathogenetic backgrounds: intravenous large dose of melphalan accompanied by autologous peripheral blood stem cell transplantation for AL amyloidosis and liver transplantation for …
Nutrition
To treat AL amyloidosis, our doctors usually combine traditional chemotherapy drugs such as melphalan (Alkeran ®) or dexamethasone (Decadron ®, Dexasone ®, Diodex ®, Hexadrol ®, Maxidex ®) with proteasome inhibitors such as bortezomib (Velcade ® ). Proteasome inhibitors block the activity of the proteasome.
What are some potential treatments of amyloidosis?
14 rows · They are so far the most successful models of systemic amyloidosis and have been widely used ...
What is amyloidosis and how is it treated?
Oct 19, 2021 · AL amyloidosis treatment relies on cytoreductive, PC-directed chemotherapy and/or immune-therapy with the goal of achieving rapid and deep hematologic remission to halt progression of end-organ damage.
How to diagnose and treat amyloidosis?
Mar 14, 2020 · Some varieties of amyloidosis may lead to life-threatening organ failure. Treatments may include chemotherapy similar to that used to combat cancer. Your doctor may suggest medications to reduce amyloid production and to control symptoms. Some people may benefit from organ or stem cell transplants. Products & Services
How do I treat amyloidosis?
Medicines used to treat ATTR include: patisiran (Onpattro) – evidence shows that it reduces disability and improves quality of life. It may also stop and... inotersen (Tegsedi) – evidence shows that it slows down progression of the illness

What is the best treatment for amyloidosis?
Recent studies have shown that people with newly diagnosed AL amyloidosis, the four-drug combination of subcutaneous daratumumab, bortezomib, cyclophosphamide, and dexamethasone is safe and effective. This treatment is now considered standard of care for most patients.
What is the latest treatment for amyloidosis?
Diagnoses are often delayed, and approximately 30% of patients die within the first year of diagnosis. The new approval is for subcutaneous daratumumab (Darzalex Faspro), to be used in combination with bortezomib, cyclophosphamide, and dexamethasone.Jan 20, 2021
How long can you live with amyloidosis of the heart?
Amyloidosis has a poor prognosis, and the median survival without treatment is only 13 months. Cardiac involvement has the worst prognosis and results in death in about 6 months after onset of congestive heart failure. Only 5% of the patients with primary amyloidosis survive beyond 10 years.Mar 25, 2020
How long does it take amyloidosis to progress?
How long that takes depends on the patient and the affected organ. Typically, 12 to 18 months will pass before amyloid buildup in the heart becomes fatal, while a patient with an affected kidney could live for 5 to 10 years, he says.Dec 4, 2018
What is systemic amyloidosis?
Systemic amyloidosis is an uncommon disorder in which misfolded protein becomes resistant to the body's catabolic processes and fibrils deposit extracellularly within tissues, leading to organ dysfunction and death.Jul 7, 2020
What foods should I avoid with amyloidosis?
Other dietary changes Also, if you're experiencing bowel symptoms, it's a good idea to refrain from coffee, alcohol, and spices. These can all aggravate a delicate gastrointestinal tract. There are also some studies on the potential neurological impacts of tea on amyloidosis.Aug 20, 2018
Is amyloidosis a terminal illness?
There's no cure for amyloidosis and severe amyloidosis can lead to life-threatening organ failure. But treatments can help you manage your symptoms and limit the production of amyloid protein. Diagnosis as early as possible can help prevent further organ damage caused by the protein buildup.Oct 15, 2019
Is amyloidosis a death sentence?
“A generation ago, a diagnosis of AL amyloidosis often was a death sentence, particularly when it involved the heart, but in the last 10 years treatments have improved by leaps and bounds so we can now give very effective treatments to many patients with the disease,” Witteles says.
Is amyloidosis a terminal of the heart?
Amyloid reduces your heart's ability to fill with blood between heartbeats. Less blood is pumped with each beat, and you may experience shortness of breath. If amyloidosis affects your heart's electrical system, your heart rhythm may be disturbed. Amyloid-related heart problems can become life-threatening.Mar 14, 2020
What organs affect amyloidosis?
The fibrils are then deposited in organs. The most common organs affected are the heart and kidneys. Light chain amyloidosis can also affect the stomach, large intestine, liver, nerves, skin and can cause an enlarged tongue. The condition can cause problems with one or more parts of the body.Jun 2, 2020
Can you live a long life with amyloidosis?
There is no cure for patients with AL amyloidosis but more frequently patients can go into remission with drug therapy. In our experience, the majority of patients surviving the first six months can often start recovering thereafter and can typically live normal or near normal lives for years to come.
What happens if amyloidosis is left untreated?
The build-up of amyloid proteins (deposits) can make it difficult for the organs and tissues to work properly. Without treatment, this can lead to organ failure.
What is used to treat AL amyloidosis?
Chemotherapy. Many of the same types of medicines used to treat some forms of cancer are used in AL amyloidosis to stop the growth of abnormal cells that produce the protein leading to formation of amyloid.
Why is it important to diagnose Amyloidosis early?
Amyloidosis is often overlooked because the signs and symptoms can mimic those of more-common diseases. Early diagnosis can help prevent further organ damage. Precise diagnosis is important because treatment varies greatly, depending on your specific condition.
What is a tracer test?
In this test, tiny amounts of radioactive material (tracers) are injected into a vein. This can reveal early heart damage caused by certain types of amyloidosis. It can also help distinguish between different types of amyloidosis, which can guide treatment decisions.
What is the difference between MRI and nuclear imaging?
These can be used to assess the structure and function of your heart. Nuclear imaging. In this test, tiny amounts of radioactive material (tracers) are injected into a vein.
How do you get autologous stem cells?
Autologous blood stem cell transplant. This procedure involves collecting your own stem cells from your blood through a vein and storing them for a short time while you have high-dose chemotherapy. The stem cells are then returned to your body via a vein . This treatment is most appropriate for people whose disease isn't advanced and whose heart isn't greatly affected.
Is there a cure for amyloidosis?
There's no cure for amyloidosis. But treatment can help manage signs and symptoms and limit further production of amyloid protein. If the amyloidosis has been triggered by another condition, such as rheumatoid arthritis or tuberculosis, treating the underlying condition can be helpful.
What are the different types of amyloidosis?
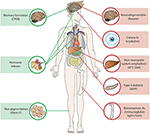
This disorder is classified into four major forms: immunoglobulin light chain-derived (AL), reactive AA, dialysis-related (beta2M) and hereditary transthyretin (ATTR) type . Heart, kidney, gastrointestinal tract and peripheral nerves are commonly affected by amyloid deposition in systemic amyloidosis and histopathological demonstration of amyloid deposits on any of affected organs is the first step leading to the diagnosis of this disease. Immunohistochemical analysis of amyloid protein on tissue amyloid deposits is necessary to make classification of the disease and DNA testing is also useful in a hereditary form. Amyloidosis had been considered to be an incurable disease but during the past one decade several therapeutic approaches have been employed for the amyloidosis patients with diverse pathogenetic backgrounds: intravenous large dose of melphalan accompanied by autologous peripheral blood stem cell transplantation for AL amyloidosis and liver transplantation for hereditary ATTR type amyloidosis. As a result some amyloidosis patients have been rescued and are now enjoying their own social lives. It is likely that recent advance on the research of amyloidosis has changed the concept of this disease.
Which organs are most affected by amyloid deposition?
Heart, kidney, gastrointestinal tract and peripheral nerves are commonly affected by amyloid deposition in systemic amyloidosis and histopathological demonstration of amyloid deposits on any of affected organs is the first step leading to the diagnosis of this disease.
What is systemic amyloidosis?
Systemic Amyloidoses. Systemic amyloidoses are rare. In this group of related diseases, an abnormally folded protein forms a substance called amyloid. It can build up in one or more organs, such as the kidney, heart, or liver. It can also accumulate in nervous system tissue.
How to tell if you have amyloidosis?
Symptoms of systemic amyloidoses can include: 1 weakness or fatigue 2 weight loss 3 heart damage (congestive heart failure) or irregular heart rhythm 4 shortness of breath 5 swelling of the feet or legs due to accumulation of fluid 6 stomach discomfort on the right side 7 abdominal swelling 8 early fullness with eating 9 gastrointestinal bleeding 10 chest pains 11 lightheadedness (due to the lowering of blood pressure during sudden position changes) 12 numbness or tingling in the lower extremities (called peripheral neuropathy)
How many people have AL amyloidosis?
It is also called AL amyloidosis or primary systemic amyloidosis. AL amyloidosis is diagnosed in approximately 3,000 people in the United States each year. However, many experts think it is actually underdiagnosed. They suggest that primary care doctors may not recognize when and how to test for AL amyloidosis.
Is AL amyloidosis rare?
This amyloid prevents the organs from working normally and potentially causes serious damage. AL amyloidosis is rare, but our doctors care for numerous people with the disease. This extensive experience enables them to make an accurate diagnosis and to select the best course of treatment based each patient’s needs.
What is the most common type of amyloid?
The most common type of amyloid is made of immunoglobulins produced by plasma cells in the bone marrow. As amyloid builds up, it can prevent the organs from working properly and eventually cause them to fail. There are four major forms of systemic amyloidoses: AL amyloidosis (or primary systemic amyloidosis)
Is stem cell transplantation safe?
For people who are good candidates for stem cell transplantation, this has proven to be a safe and effective treatment. With this approach, people first receive a high dose of the chemotherapy drug melphalan. They then undergo an autologous stem cell transplant.
What is the test for heart damage?
Imaging tests detect damage to the heart or other organs that may be affected. Other tests include a bone marrow biopsy or a biopsy from an affected organ or part of the body with many blood vessels, such as abdominal fat or the rectum. Back to top.
What causes amyloidosis?
Some varieties are hereditary. Others are caused by outside factors, such as inflammatory diseases or long-term dialysis. Many types affect multiple organs, while others affect only one part of the body.
Where is amyloidosis found?
Amyloid isn't normally found in the body, but it can be formed from several different types of protein. Organs that may be affected include the heart, kidneys, liver, spleen, nervous system and digestive tract. Some varieties of amyloidosis occur in association with other diseases.
What is the most common type of amyloidosis?
The most common type of amyloidosis in developed countries, AL amyloidosis is also called primary a myloidosis. It usually affects the heart, kidneys, liver and nerves. AA amyloidosis. Also known as secondary amyloidosis, this variety is usually triggered by an inflammatory disease, such as rheumatoid arthritis.
How do you know if you have amyloidosis?
Signs and symptoms of amyloidosis may include: Numbness, tingling or pain in your hands or feet, especially pain in your wrist ( carpal tunnel syndrome) Unintentional weight loss of more than 10 pounds (4.5 kilograms) Skin changes, such as thickening or easy bruising, and purplish patches around the eyes.
What does it mean when you lose weight?
Diarrhea, possibly with blood, or constipation. Unintentional weight loss of more than 10 pounds (4.5 kilograms) An enlarged tongue, which sometimes looks rippled around its edge. Skin changes, such as thickening or easy bruising, and purplish patches around the eyes. An irregular heartbeat.
What causes numbness in the toes?
The kidneys' ability to remove waste products from your body is lowered, which may eventually lead to kidney failure and the need for dialysis. Nervous system. You may experience pain, numbness or tingling of your fingers or numbness, lack of feeling or a burning sensation in your toes or the soles of your feet.
Can amyloidosis be treated?
Some varieties of amyloidosis occur in association with other diseases. These types may improve with treatment of the underlying disease. Some varieties of amyloidosis may lead to life-threatening organ failure. Treatments may include chemotherapy similar to that used to combat cancer. Your doctor may suggest medications to reduce amyloid ...
What is the best treatment for ATTR amyloidosis?
inotersen (Tegsedi) – evidence shows that it slows down progression of the illness. Some types of inherited ATTR amyloidosis can be treated with a liver transplant.
What causes AL amyloidosis?
AL amyloidosis is caused by an abnormality in certain cells found in the bone marrow, called plasma cells. The abnormal plasma cells produce abnormal forms of light chain proteins, which enter the bloodstream and can form amyloid deposits. Healthy people have normal light chain proteins in their blood that are part of their natural antibody ...
What is the name of the condition where the body is unable to work properly?
Amyloidosis. Amyloidosis is the name for a group of rare, serious conditions caused by a build-up of an abnormal protein called amyloid in organs and tissues throughout the body. The build-up of amyloid proteins (deposits) can make it difficult for the organs and tissues to work properly. Without treatment, this can lead to organ failure.
What are the symptoms of kidney failure?
Symptoms of kidney failure include: swelling, often in the legs, caused by fluid retention (oedema) tiredness. weakness.
What causes shortness of breath?
Deposits of amyloid in the heart can cause the muscles to become stiffer, making it more difficult to pump blood around the body. This may result in heart failure, which can cause: shortness of breath. oedema. an abnormal heartbeat (arrhythmia)
How do you know if you have a numb hand?
Symptoms can include: feeling lightheaded or fainting, particularly after standing or sitting up. numbness or a tingling feeling in the hands and feet (peripheral neuropathy) nausea, diarrhoea or constipation. numbness, tingling and pain in the wrist, hand and fingers (carpal tunnel syndrome) easy bruising.
Is ATTR amyloidosis hereditary?
Another type of ATTR amyloidosis is not hereditary. This is called wild-type ATTR amyloidosis, or senile systemic amyloidosis. In this condition, the amyloid deposits mainly affect the heart and can also cause carpal tunnel syndrome in some people. Hereditary ATTR amyloidosis may cause symptoms at any age from about 30 years old.
What is localized amyloidosis?
Localized amyloidosis (ALoc) There are many types of localized amyloidoses. Localized amyloid deposits in the airway (trachea or bronchus), eye, or urinary bladder are often caused by local production of immunoglobulin light chains, not originating in the bone marrow.
What causes AA amyloidosis?
AA amyloidosis is caused by a chronic infection or an inflammatory disease such as rheumatoid arthritis, familial Mediterranean fever (FMF), osteomyelitis, or granulomatous ileitis. Infection or inflammation causes elevation of an acute phase protein, SAA, a portion of which deposits as amyloid fibrils. Therefore, it is termed AA amyloidosis. AA amyloidosis usually begins as disease in the kidneys, but other organs can be affected. Medical or surgical treatment of the underlying chronic infection or inflammatory disease can slow down or stop the progression of this type of amyloidosis.
What is the name of the disorder in which a monoclonal immunoglobulin light chain is produced?
AL (immunoglobulin light chain) amyloidosis is an acquired plasma cell disorder in which a monoclonal immunoglobulin light chain is produced in the bone marrow and usually found in the blood or urine. AL amyloidosis occasionally occurs with multiple myeloma, lymphoma, or Waldenstorm’s macroglobulinemia. The amyloid fibrils in this type of amyloidosis are made up of immunoglobulin light chain proteins (kappa or lambda). Symptoms can occur in any organ of the body and include heart failure, protein in the urine or kidney failure, enlarged liver, neuropathy or enlarged tongue. Treatment with chemotherapy including high dose chemotherapy with stem cell transplantation, and other agents, can put the bone marrow disease in remission, leading to improvement in organ dysfunction and protect the target organs. This is one of the most common type of amyloidosis diagnosed in the United States.
Where does AA amyloidosis start?
AA amyloidosis usually begins as disease in the kidneys , but other organs can be affected. Medical or surgical treatment of the underlying chronic infection or inflammatory disease can slow down or stop the progression of this type of amyloidosis.
What are the amyloid fibrils?
The amyloid fibrils in this type of amyloidosis are made up of immunoglobulin light chain proteins (kappa or lambda). Symptoms can occur in any organ of the body and include heart failure, protein in the urine or kidney failure, enlarged liver, neuropathy or enlarged tongue.
What is ATTR mutation?
There are several types of inherited amyloidoses, the most common of which is caused by a mutation in the transthyretin (TTR) gene that produces abnormal transthyretin protein.
What are the symptoms of ATTR amyloidosis?
Symptoms of disease are usually neuropathy and cardiomyopathy and occur in mid to late life. ATTR amyloidosis is found in families of nearly every ethnic background. More than 100 different mutations in transthyretin are known and most cause amyloidosis.
What are the symptoms of AL amyloidosis?
There are other symptoms that are common and may have been present for some time before diagnosis, such as chronic fatigue and weakness. Some patients with AL amyloidosis experience purpura, which is bruising around the eyes or other skin areas.
What biomarkers are used for AL amyloidosis?
The cardiac biomarkers that are used include troponin T or troponin I , and NT-proBNP (which stands for N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide) or BNP (brain natriuretic peptide).
What does it mean when you have a lot of protein in your urine?
Excess protein in the urine may be an indication of kidney involvement. The level of ALP (an enzyme called “alkaline phosphatase”) in your regular blood workup. Blood tests to look for stress and strain on the heart are useful in many forms of heart disease, including AL amyloidosis.
What is the color of amyloid in a tissue biopsy?
A tissue biopsy involves the removal of a small sample of tissue to find evidence of amyloid deposits. Any kind of tissue or organ biopsy must be sent to a lab for microscopic examination, where the tissue is stained with a dye called “Congo-red stain.” After putting it under a microscope, amyloid protein is discovered if it turns an apple-green color, resulting in a diagnosis of amyloidosis. Possible areas for less invasive biopsies include:
What is the FDA approved drug?
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved the use of DARZALEX FASPRO® (daratumumab and hyaluronidase-fihj), a subcutaneous formulation of daratumumab, in combination with bortezomib, cyclophosphamide, and dexamethasone (D-VCd) for the treatment of adult patients with newly diagnosed light chain (AL) amyloidosis.
Why do my fingers feel numb?
For example, patients may have carpal tunnel syndrome, where amyloid deposits in the wrist area can squeeze and irritate the nerve, causing tingling and numbness in the fingers and thumb. Deposits in the tongue may lead to a swollen and enlarged tongue, called “macroglossia.”.
What is the condition where the kidneys are swollen?
Amyloid deposits in the kidneys can affect how they filter toxins and proteins in the blood. This may result in a condition called nephrotic syndrome, where there is excess protein in the urine and the lower legs can become swollen (also called “edema”). Swelling can affect the belly, arms, and lungs as well.
