What are the side effects of stereotactic radiotherapy?
Dec 10, 2019 · Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy (SBRT) • A precise, high-dose radiation therapy that treats cancer more quickly than traditional radiation • For cancer patients who have small, clearly delineated tumors • SBRT is a noninvasive treatment • Involves interventional radiology, gamma knife center, smilow interventional oncology program Overview
What to expect with stereotactic radiosurgery?
Stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) is a technological advancement in the field of radiation therapy. It’s different from conventional radiation therapy because it delivers very concentrated radiation over a short period of time (days, not weeks). SBRT is used to treat small cancers that haven’t spread to other organs.
What are the risks of stereotactic radiosurgery?
Stereotactic radiosurgery/body radiation therapy (SRS/SBRT) is a specialized type of external beam radiation therapy that uses focused radiation beams targeting a well-defined tumor to deliver the highest possible radiation dose with pinpoint accuracy.
What is SBRT therapy?
Stereotactic body radiation therapy, or SBRT, is a cancer treatment that delivers extremely precise, very intense doses of radiation to cancer cells while minimizing damage to healthy tissue. SBRT involves the use of sophisticated image guidance that pinpoints the exact three-dimensional location of a tumor so that the radiation can be more precisely delivered to cancer …
How effective is stereotactic radiation therapy?
What are the side effects of stereotactic radiation?
- fatigue.
- nausea.
- headache.
- bleeding.
- pain and infection at the pin-sites of the head frame.
- vertigo.
How long does it take for stereotactic radiation to work?
What is the difference between radiotherapy and stereotactic radiotherapy?
Do you lose your hair with stereotactic radiosurgery?
Can I drive after stereotactic radiosurgery?
Do tumors grow back after radiation?
How long does it take for tumor to shrink after radiation?
Who is a candidate for SBRT?
What does the word stereotactic mean?
: involving, being, utilizing, or used in a surgical technique for precisely directing the tip of a delicate instrument (such as a needle) or beam of radiation in three planes using coordinates provided by medical imaging in order to reach a specific locus in the body.
What cancers are treated with SBRT?
Can you have stereotactic radiosurgery twice?
Is SBRT more effective than conventional radiation?
That makes SBRT, which also has fewer side effects than conventional radiation, more effective. At Yale Medicine, our doctors see a very high volume of patients and serve as a referral center for a wide variety of cases.
What is SBRT surgery?
Although "surgery” is a part of the acronym, SBRT is a noninvasive treatment. During the procedure, doctors simply ask that a patient lie quietly and breathe normally. The first part of treatment involves a consultation with one of our radiation oncologists, followed by a discussion of treatment options. Yale Medicine takes a multidisciplinary ...
How does stereotactic radiosurgery work?
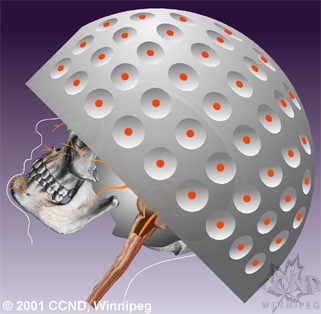
All types of stereotactic radiosurgery and radiotherapy work in a similar manner. The specialized equipment focuses beams of radiation on a tumor or other target. Each beam has very little effect on the tissue it passes through, but a targeted dose of radiation is delivered to the site where all the beams intersect.
Is stereotactic radiosurgery safer than neurosurgery?
Around 50 years ago, stereotactic radiosurgery was pioneered as a less invasive and safer alternative to standard brain surgery (neurosurgery), which requires incisions in the skin, skull, membranes surrounding the brain and brain tissue.
What is SRS in medical terms?
Stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) is a type of radiotherapy. When it's performed on the body rather than the brain, this procedure is sometimes called stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) or stereotactic ablative radiotherapy (SABR). The procedure uses many precisely focused radiation beams to treat tumors and other problems all over the body.
What is SBRT used for?
SBRT is used to treat tumors in the lungs, spine, liver, neck, lymph node or other soft tissues. Because there's no incision, SBRT isn't a traditional type of surgery. Instead, SBRT uses 3D imaging to target high doses of radiation to the affected area.
How does SBRT work?
Instead, SBRT uses 3D imaging to target high doses of radiation to the affected area. This means there's very little damage to the surrounding healthy tissue. Like other forms of radiation, stereotactic radiosurgery works by damaging the DNA of the targeted cells.
What is proton beam?
Proton beam (charged particle) is the newest type of stereotactic radiotherapy and is available in only a few research centers in the U.S., although the number of centers offering proton beam therapy has greatly increased in the last few years. It can use fractionated stereotactic radiotherapy to treat body tumors over several sessions.
What is a fiducial marker?
The fiducial marker is about the size of a grain of rice. The marker is usually in a cylinder, coil or sphere shape and is often made out of gold.
What is SBRT radiation?
SBRT uses several radiation beams of various intensities aimed at the tumor from different angles. This requires one or more sessions of treatment planning. During these sessions, the patient will undergo a CT, MRI and/or other advanced imaging techniques.
What is SBRT used for?
SBRT is used to treat smaller tumors. Among these are many types of primary tumors, often prostate cancer, lung cancer and kidney cancer. In addition, doctors use SBRT to treat tumors that have spread, or metastasized, from another site. This includes oligometastatic disease, in which a patient has just a few metastatic spots.
What are the side effects of SBRT?
One common side effect of SBRT is fatigue. Other possible side effects depend on the tumor’s location. For example, a patient with an abdominal tumor may have SBRT-related gastrointestinal problems. A patient with a tumor near a bone could experience bone damage.
How long does SBRT last?
Sessions take place either once a day or once every other day. Most sessions last about one hour.
What is radiation oncology?
Radiation oncologists are highly trained, board certified and licensed physicaians who use radiation therapy in its various forms to care for patients with cancer and other conditions, and who oversee the care of each person undergoing stereotactic radiation.
What is SRS in medical terms?
Stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) is used to treat conditions involving the brain or spine including: Cancers that recur in the brain (gliomas and other primary brain tumors). Cancers that spread to the brain (brain metastases). Benign tumors arising from the membranes covering the brain (meningiomas).
What is a small lung cancer?
Small lung cancers. Cancers that started elsewhere and spread to the lung (lung metastases). Cancers that start in or spread to the liver (liver metastases). These lists cover commonly treated conditions but cannot include every possibility.
What are the side effects of radiation therapy?
Depending on the site of the treatment, side effects of stereotactic radiation therapy include: 1 Urination problems 2 Skin irritation 3 Fatigue 4 Nausea 5 Sexual impotence 6 Impaired bowel function
How long do side effects last after cancer treatment?
Most side effects usually go away after treatment ends. But you may feel very tired for four to six weeks after your last treatment. Talk to your doctor about ways to treat the side effects. At Northwell Health Cancer Institute, your team of specialists is highly focused on preventing and managing side effects throughout and after your treatment.
What is Northwell Health Cancer Institute?
Northwell Health Cancer Institute is considered a pioneering leader in the use of stereotactic radiation therapy and was the first cancer center in Suffolk County, Long Island, to use the CyberKnife Robotic Radiosurgery System. We have been treating patients with this technology since 2008. Our radiation oncologists have years of experience and hold additional certification in the use of CyberKnife and other stereotactic radiosurgery devices.
What is SBRT radiation?
Stereotactic body radiation therapy, or SBRT, is a cancer treatment that delivers extremely precise, very intense doses of radiation to cancer cells while minimizing damage to healthy tissue.
What is SBRT treatment?
Stereotactic body radiation therapy, or SBRT, is a cancer treatment that delivers extremely precise, very intense doses of radiation to cancer cells while minimizing damage to healthy tissue. SBRT involves the use of sophisticated image guidance that pinpoints the exact three-dimensional location of a tumor so that the radiation can be more ...
What is SBRT imaging?
SBRT involves the use of sophisticated image guidance that pinpoints the exact three-dimensional location of a tumor so that the radiation can be more precisely delivered to cancer cells. Here are answers to some of the common questions our SBRT experts hear from patients.
What is SBRT used for?
SBRT is typically used to treat small, early-stage lung cancer and pancreatic cancer, or cancers that have spread to the lung, liver, adrenal gland, or spine. 2.
How long does SBRT take?
You will be awake during the procedure, which usually takes between 30 minutes and an hour. Back to top. 3.
How often is radiation given?
Conventional radiation is typically delivered in relatively small doses each day over several weeks. This can delay or interfere with other cancer treatments, such as chemotherapy. By contrast, SBRT can usually be given in five or fewer daily sessions and requires no anesthesia.
Do you have to wear a mask at MSK?
Masks Are Still Required at MSK. Patients and visitors must continue to wear masks while at MSK, including people who are fully vaccinated. MSK is offering COVID-19 vaccines to all patients age 12 and over. To schedule or learn more, read this. For Adult Patients /.

Why It's Done
Risks
- Stereotactic radiosurgery doesn't involve surgical incisions, so it's generally less risky than traditional surgery. In traditional surgery, you may have risks of complications with anesthesia, bleeding and infection. Early complications or side effectsare usually temporary. They may include: 1. Fatigue. Tiredness and fatigue may occur for the first few days after SBRT. 2. Swellin…
How You Prepare
- Preparation for SRS and SBRTmay vary depending on the condition and body area being treated but usually involves the following steps:
What You Can Expect
- Stereotactic body radiotherapy is most commonly delivered as an outpatient and takes between 20 to 60 minutes for each treatment. While not common, your doctor will advise you if a family member or friend will need to accompany you for the treatment.
Results
- The treatment effect of stereotactic radiosurgery occurs gradually, depending on the condition being treated: 1. Benign tumors (including vestibular schwannoma).Following stereotactic radiosurgery, the tumor may shrink over a period of 18 months to two years, but the main goal of treatment for benign tumors is to prevent any future tumor growth. 2. Malignant tumors.Cancero…