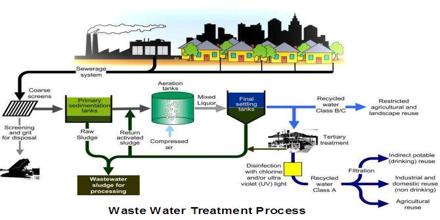
What is sewage treatment explain?
Sewage Treatment refers to the process of removing contaminants, micro-organisms and other types of pollutants from wastewater. Wastewater, or raw sewage, is water that drains from toilets, sinks, showers, baths, dishwashers, washing machines and liquid industrial waste.
What are the 3 stages of sewage treatment?
There are three main stages of the wastewater treatment process, aptly known as primary, secondary and tertiary water treatment.
What is the main treatment of sewage?
Primary treatment of sewage basically involves the physical removal of large and small particles, through filtration and sedimentation. This is done in many stages. Initially, floating debris is removed by sequential filtration and then the grit i.e. soil and small pebbles, is removed by sedimentation.
What are the 4 steps of sewage treatment?
4 Steps of Community Water TreatmentCoagulation and Flocculation. ... Sedimentation. ... Filtration. ... Disinfection.
What is sewage treatment class 12?
Sewage treatment is carried out in two stages: Primary treatment: This step involves physical removal of particles from sewage through filtration and sedimentation. Floating debris is removed by sequential filtration. Grit is removed by sedimentation. All solids that settle form the primary sludge.
What is called sludge?
The residue that accumulates in sewage treatment plants is called sludge (or biosolids). Sewage sludge is the solid, semisolid, or slurry residual material that is produced as a by-product of wastewater treatment processes. This residue is commonly classified as primary and secondary sludge.
What is sewage treatment class 8?
Answer: Sewage treatment involves three processes, namely physical, chemical and biological. They remove physical, chemical and biological contaminants present in the wastewater.
What are the types of sewage?
Types of sewage There are three types of wastewater, or sewage: domestic sewage, industrial sewage, and storm sewage. Domestic sewage carries used water from houses and apartments; it is also called sanitary sewage. Industrial sewage is used water from manufacturing or chemical processes.
Why is sewage treatment necessary?
So, when sewage is discharged untreated into rivers or seas, it becomes dangerous for aquatic plants and animals. Therefore, it is necessary to treat sewage before disposing it off in a water body as it can cause harm to human and aquatic life.
What bacteria is used in sewage treatment?
Anaerobic bacteria are used in wastewater treatment on a normal basis. The main role of these bacteria in sewage treatment is to reduce the volume of sludge and produce methane gas from it.
What is the first step of sewage treatment?
Treatment StepsStep 1: Screening and Pumping. ... Step 2: Grit Removal. ... Step 3: Primary Settling. ... Step 4: Aeration / Activated Sludge. ... Step 5: Secondary Settling. ... Step 6: Filtration. ... Step 7: Disinfection. ... Step 8: Oxygen Uptake.
How sludge is removed?
Digested sludge is put through large centrifuges that work in the same fashion as a washing machine spin cycle. The spinning centrifuge produces a force that separates the majority of the water from the sludge solid, creating a biosolid substance.
What are the stages of STP?
The 3 Main Stages of Sewage Treatment DesignThe Primary Stage. The first stage in the sewage treatment is the primary sedimentation stage. ... The Secondary Stage. ... The Tertiary Stage.
What is the first stage in sewage treatment process?
Primary treatment in sewage treatment involves physical removal of particles (large and small) from the sewage through filtration and sedimentation. Initially floating debris is removed by sequential filtration. Then the grit (soil and small pebbles) are removed by sedimentation.
What is staging in STP?
The Sewage Treatment Process essentially includes three stages. The three stages can be divided into primary, secondary, and Tertiary. In each step, water is purified to the next level to access clean water for humans and the environment.
What is the last stage in the treatment of sewage?
If disinfection is practiced, it is always the final process. It is also called "effluent polishing".
What is sewage treatment?
Sewage treatment is the process that removes the majority of the contaminants from waste-water or sewage and produces both a liquid effluent suitable for disposal to the natural environment and a sludge.
Who Will Lead the Global Surveillance of Antimicrobial Resistance Via Sewage?
Feb. 11, 2020 — A professor calls for someone to carry on a global surveillance of antimicrobial resistance and infectious diseases via ...
What is sewage water?
Sewage water is wastewater from people living in a community. It is the water released from households after use for various purposes like washing dishes, laundry, and flushing the toilet, thus the name wastewater. The used water moves from the houses through pipes installed during plumbing. The sewage water then moves into sewers, ...
How does sewage pollution affect aquatic life?
Further, there is subsequent death of aquatic life due to the release of harmful toxins that interfere with the normal activities of sea life. For instance, the release of ammonia is toxic to plants. They easily oxidize with the oxygen present in water leading to deprivation of oxygen to aquatic life.
How does wastewater get mixed?
The wastewater is mixed with the microbes and aeration is facilitated. Like in the filters, the microbes feed on the organic molecules and form the activated sludge. The wastewater now flows into an aeration tank where more aeration of the sludge is done.
What are some examples of sewer pollution?
These waste materials then result in the clogging of water ways further along sewer lines. For example, plastics such as soap wrappings clog rivers and prevent further flow due to stagnation. As a result, it harbors harmful organisms and bacteria. The blockages also lead to air pollution caused by the spread of the foul smell from the sewer. Generally, sewer treatment plants face a lot of hardship due to blockages and the foreign material present in the wastewater thereby causing sewage pollution.
Why do sewers overflow?
Sewers are built to accommodate a certain volume of wastewater. Nevertheless, there are various reasons why sewers overflow. For starters, there are contractors who on construction of buildings end up connecting the sewage system of the new building to the existing sewer made for another residential building.
Why are toilets considered fixtures?
Toilets are designated as fixtures for relieving nature calls . Sadly, careless people have turned toilets into deposit banks for waste materials such as papers, sanitary products and some even go to the extent of flushing plastics. These waste materials are the causes of blockages of sewage ways in most buildings.
What happens when sewage is high in a pipe?
3. Overcapacity of wastewater.
What is chemical sewage treatment?
The preliminary chamber is equipped with coarse and fine mesh of screen as filters to remove large solid particles from getting into the system. In many designs it stay set at the top of the primary chamber with flow measurement device recording and filtering waste water inlet at the same time.
What is sewage treatment plant?
A sewage treatment plant is designed to treat and process raw sewage over different steps involving breaking, filtering, settling, controlled aerobic decomposition and chemical treatment. One of the most common things that come in our mind regarding human waste; is to dump it to the sewers and let the government take care of it.
How long does it take to remove the smell of chlorine from a water tank?
This is done by adding a 5 % solution of chlorine to kill of bacteria within a period of 30 minutes. Further chemical treatment is done to remove the smell and get rid of the pale colour.
What is the process used to break down sewage into small parts?
The process used to systematically break the sewage into small parts; using biological and chemical method is known as sewage treatment.
How many crews are required to have a sewage treatment plant?
The law requires all ships and water vessels above 4000 Gross tonnage dead weight or carrying more than 15 crew / personal in international waters is required to have dedicated sewage treatment plant or sludge tank to hold sewage for appropriate time.
Why is activated carbon added to sewage?
It get on to absorb all the organic molecules associated with the smell and distinct colour. In many design the activated carbon sets are filled just after the settling chamber; thus allowing waste water to be treated before moved to next chamber.
Where is raw water stored?
The raw waste water originating from toilet, wash basins and bathrooms; with a concentration of 0.1% solid waste by weight is stored in the primary chamber. The sewage is fed into the chamber with special macerator pumps that reduce human waste to slurry using blending and grinding techniques.
What is the purpose of screening wastewater?
Screening the wastewater. First, we remove large objects that may block or damage equipment or pollute our rivers. This includes items that should never have been put down the drain in the first place, such as nappies, wet wipes, sanitary items and cotton buds, and sometimes even things like bricks, bottles and rags.
What is the name of the tank where sewage is put into?
At our larger sewage treatment works, we put the wastewater into rectangular tanks called ‘aeration lanes’ , which pump air into the water. This encourages the useful bacteria to break down and eat ...
How do we separate waste from water?
We separate the waste from the water by putting it into large settlement tanks, where solids sink to the bottom. We call the settled solids ‘sludge’. Large arms or scrapers help to push the sludge towards the centre, where it’s then pumped away for further treatment.
Why do we treat sludge?
We treat the sludge we collect at the start of the process so that we can put it to good use. We recycle most of it to agricultural land for farmers to use as fertiliser, but we also use it to generate energy. We do this in several different ways:
What is the process of drying sludge into blocks called?
2. Thermal destruction: We dry the sludge into blocks called ‘cake’ , which are then burned to generate heat. We capture this heat and turn it into electricity.
How to make biogas from sludge?
1. Combined heat and power: We treat the sludge using a process called ‘anaerobic digestion’. This heats the sludge up to high temperatures, encouraging the bacteria inside to break down the waste. This creates biogas that we can then burn to create heat, which in turn creates electricity. 2.
Who regulates the quality of wastewater?
The Environment Agency strictly regulates the quality of the cleaned wastewater, and we test it to make sure that it meets their high-quality standards.
Why does wastewater treatment matter?
Why does it matter? The overall wastewater treatment process has to clean the water of chemicals, food particles, and grit. It also has to remove human waste, which is where sewage treatment comes in.
What are the components of wastewater treatment?
Here are the different things that are treated during wastewater and sewage treatments. Inorganic Materials: Inorganic materials include metals and minerals.
How does wastewater enter a treatment plant?
Wastewater comes into a treatment plant through sewer lines or at a septage acceptance plant. If the wastewater is being trucked in, septic trucks drive up to the septage acceptance plant and unload the materials pumped from septic systems into the facility. Pretreatment occurs as wastewater enters the treatment plant.
How is black water handled?
How Black Water is Handled at a Wastewater Treatment Plant. The sludge that’s removed from clarification tanks goes through sewage treatment. Anaerobic digesters break down the sludge, and carbon dioxide and methane are removed and captured during that process. That biogas can be used to provide electricity and heat.
How long does wastewater sit in a clarification tank?
From the grit chamber, wastewater goes to a clarification tank to start primary treatment. The wastewater sits for several hours to allow solids to sink to the bottom of the tank. Grease floats to the top, where it’s skimmed away.
Why is oxygen added to wastewater?
Oxygen is added to the leftover water to help stir it up and get oxygen to begin breaking down any particles of waste or organic materials that didn’t sink to the bottom. Again, the wastewater moves to a clarification tank to allow the remaining sludge to settle, get scraped to pumps, where it goes to sewage treatment.
What is wastewater made of?
Wastewater is made up of black water and gray water. These two types of wastewater go to the same facility for treatment, but they’re different and require different steps. Start by understanding the differences between gra y water and black water.
What is municipal sewage?
Municipal wastewater, or sewage, refers to water that has been used in urban and suburban area homes or businesses for washing, bathing, and flushing toilets. Municipal wastewater also may include water from industrial sources.
What is biosolids in sewage?
The term "biosolids" also helps to distinguish sewage sludge from industrial sludge by emphasizing that the former is produced by a biological process.
How much sewage sludge does Pennsylvania produce?
This means that Pennsylvania's POTWs generate approximately 300,000 tons of sewage sludge (dry weight basis) each year.
What is biosolids in wastewater treatment?
The industry defines biosolids as sewage sludge that has undergone sufficient treatment for stabilization and pathogen reduction, and that is of sufficiently high quality to be land applied. The term is intended to distinguish high-quality, treated sewage sludge from raw sewage sludge and from sewage sludge that contains large quantities of environmental pollutants. The term "biosolids" also helps to distinguish sewage sludge from industrial sludge by emphasizing that the former is produced by a biological process. The term has been criticized by some as an attempt to disguise the real nature of sewage sludge, thereby making land application of this material less objectionable to the general public. Although "biosolids" undoubtedly does not conjure up the same negative images as does "sewage sludge" or simply "sludge," it is a legitimate and functional term when correctly used to make the distinction described above. In this document, "sewage sludge" will be used to refer to wastewater treatment solids generally, and "biosolids" will be used to refer specifically to material that is suitable for land application.
How are sludge solids concentrated?
Sludge solids are concentrated either by settling due to gravity or by introducing air, which causes sludge solids to float.
How long does it take for a sludge to increase pH?
Sufficient alkaline material, most commonly lime (CaO), is added to the sludge to increase its pH to at least 12 for 2 hours. The pH must remain above 11.5 for an additional 22 hours.
How long does sludge stay in the air?
One of the most widely used methods for sludge treatment. Sludge is held in the absence of air for 15 to 60 days at temperatures of 68 to 131°F. Anaerobic bacteria feed on the sludge, producing methane and carbon dioxide. In some treatment plants, the methane is collected and burned to maintain the treatment temperature.
