
The primary difference between therapy evaluations and therapy treatments is the Clinical Reasoning Skills of the therapist. When Is It Evaluation?
Full Answer
How do we evaluate the efficacy of treatments?
May 02, 2022 · The primary difference between therapy evaluations and therapy treatments is the Clinical Reasoning Skills of the therapist. When Is It Evaluation? The therapy evaluation thought process is a mental set of constant observation and interpretation of patient abilities and behaviors to develop an ever-clearer picture of the patient’s problems and necessary …
Is there a difference between evaluation and research?
Dec 01, 2002 · This document is organized on the basis of two related dimensions for the evaluation of guidelines. The first dimension is treatment efficacy, the systematic and …
What is the difference between assessments and evaluation?
Feb 17, 2016 · Distribution of estimations of the mean in the treatment group for two sample sizes. The horizontal axis is RBC size in femtoliter (fL). Sample size=10,000 (red). Sample …
What is the difference between process evaluation and outcome evaluation?
the difference between evaluation types. There are a variety of evaluation designs, and the type of evaluation should match the development level of the program or program activity …
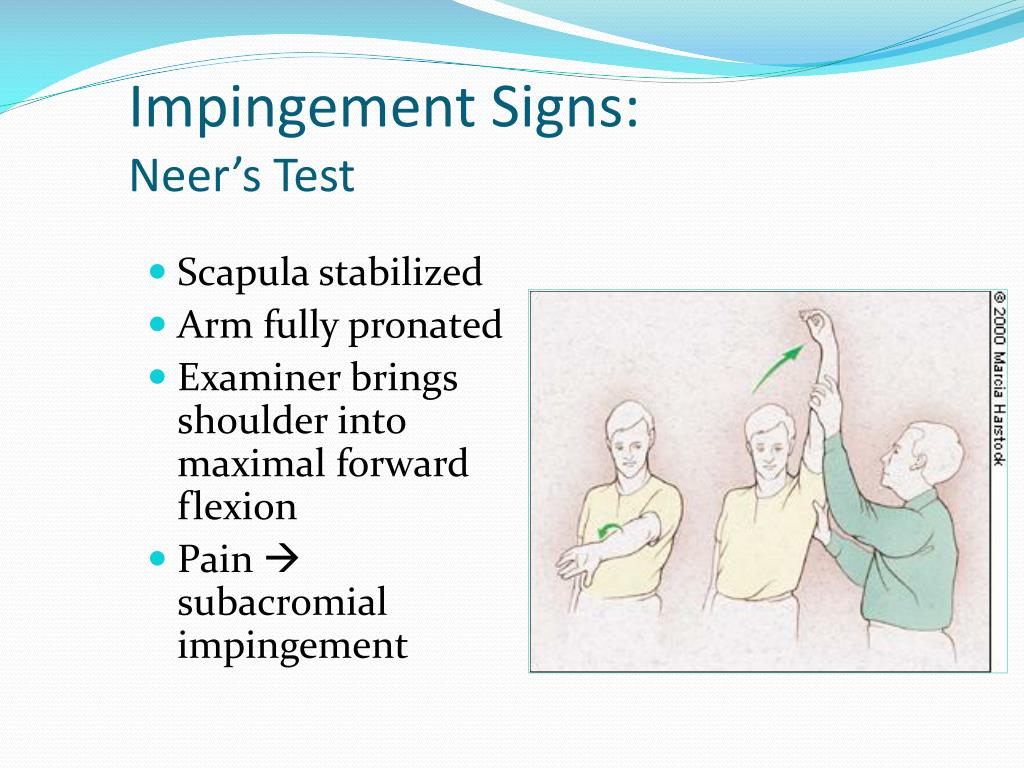
How do you evaluate a treatment?
What are the differences between evaluation and assessment?
What is evaluation in therapy?
Is an assessment a treatment?
Which statement correctly describes a difference between evaluation and assessment?
What are the three most striking differences between assessment and evaluation?
...
The key differences between Assessment and Evaluation.
| Assessment | Evaluation |
|---|---|
| The orientation of assessment is process oriented. | The orientation of evaluation is product oriented. |
| The outcome of assessment is constructive feedback. | The outcome of evaluation is to show shortcomings. |
What are the 3 types of evaluation?
What are methods of evaluation?
What are the steps in evaluation process?
- Plan the program/Collect information.
- Write objectives.
- Decide what, how and when to measure.
- Conduct the program and monitor progress.
- Collect information and interpret findings.
- Use results.
What is treatment plan?
What is an assessment and treatment unit?
How do you write an assessment and treatment plan?
- The patient's personal information, psychological history and demographics.
- A diagnosis of the current mental health problem.
- High-priority treatment goals.
- Measurable objectives.
- A timeline for treatment progress.
How to evaluate efficacy of a treatment?
Methods for evaluating efficacy often begin with health care professionals' judgments and then progress through more highly systematized research strategies. For some treatments, the most accessible source of information on treatment efficacy may be the judgment of health care professionals and patients who have experience with the treatments. It is important to distinguish between the context of discovery of an intervention and the context of verification of its clinical efficacy. Historically, some interventions that were later proven by systematic evaluation to be very powerful have arisen from clinical innovations and case studies. The question of whether particular interventions have beneficial effects is best answered using research methodologies that have been refined over many years to reduce the uncertainties inherent in subjective judgment alone and to increase confidence in the strength of the intervention. The systematic application of these research strategies also promotes the welfare of patients.
What is treatment guidelines?
That is, treatment guidelines are patient directed or patient focused as opposed to practitioner focused, and they tend to be condition or treatment specific (e.g., pediatric immunizations, mammography, depression).
Why is it important to use guidelines in clinical practice?
Another common assumption is that standardizing treatment via guidelines will always be beneficial because it reduces practice variation. However, variation in clinical practice is often based on the needs of individual patients and their responses to specific treatments. When the application of guidelines results in a rigid system that eliminates the ability to respond to individual needs of the patient and the opportunity for self-correction in treatment, this can be detrimental to patient care.
Why should treatment guidelines be open to public scrutiny?
Treatment guidelines have the potential to influence the health care of many patients, and therefore the guidelines and the process used in their development should be open to public scrutiny. Moreover, failure to disclose the scientific justification for a guideline violates a basic principle of science, which requires open scrutiny and debate. Without the disclosure of adequate scientific information, guidelines are mere expressions of opinion.
Why are guidelines important for treatment?
Good guidelines allow for flexibility in treatment selection so as to maximize the range of choices among effective treatment alternatives.
Why are guidelines promulgated?
Guidelines are promulgated to encourage high quality care. Ideally, they are not promulgated as a means of establishing the identity of a particular professional group or specialty, nor are they used to exclude certain persons from practicing in a particular area.
What is a health care guideline?
Generally, health care guidelines are pronouncements, statements, or declarations that suggest or recommend specific professional behavior, endeavor, or conduct in the delivery of health care services. Guidelines are promulgated to encourage high quality care.
Why is it not possible to examine all cases?
The examination of all cases is usually not done for the following reasons: it is difficult to identify all cases, it is resource intensive, and from a statistical point of view it provides little added certainty. Additionally, examination might involve destruction of the biological sample (e.g., estimating the weight of biologic organs on a scale is limited to pathologic specimens removed as warranted by surgery or at autopsy). For these reasons, the researcher is likely to use a sample in order to estimate values related to the greater population. In order to assure an accurate estimation, that sample must be representative of the population.
What is inferential statistics?
When using inferential statistics, the researcher is attempting to predict an unknown value (e.g., the mean) that applies to all such patients. The true value for the entire group of all such patients is initially unknown and remains unknown. The nature of inferential statistics is the calculation of an estimate and qualification of the estimate in terms of its accuracy.
Is the SD of the estimates of the mean normal?
The SD of the estimates of the mean is referred to as the SEM.
Can you assign iron supplements to one group at random?
For example, in assigning two groups at random it may occur by chance alone that there is some important difference between the two groups that could be associated with differences in the measurement of interest. A disproportionate (chance) assignment of patients taking iron supplements to one group might alter estimates of the MCV, because total body iron may impact the MCV (5).
Why do physical therapists use muscle weakness?
Physical and occupational therapists often use the underlying impairment of muscle weakness for a treatment diagnosis because muscle weakness causes many functional deficits and impacts every aspect of the physical and occupational therapy plan of treatment.
What is part A in Medicare?
Part A: All disciplines use the facility selected primary medical diagnostic code (s) that will be used to bill Medicare for the SNF services. Should clearly relate to the identified functional limitations the resident is presenting with that was identified during the evaluation process.
Why do physical therapists use muscle weakness?
Physical and occupational therapists often use the underlying impairment of muscle weakness for a treatment diagnosis because muscle weakness causes many functional deficits and impacts every aspect of the physical and occupational therapy plan of treatment.
What is part A in Medicare?
Part A: All disciplines use the facility selected primary medical diagnostic code (s) that will be used to bill Medicare for the SNF services. Should clearly relate to the identified functional limitations the resident is presenting with that was identified during the evaluation process.
What is evaluation criteria?
Evaluation criteria are set and agreed upon by all instructors before implementing educational activities. Students must know in advance when to expect evaluation and what criteria will be evaluated. Through evaluation the instructor determines the effectiveness of the educational activities.
What is the difference between assess and evaluate?
When assessing students, instructors gather, summarize, and interpret data to determine which strategies to implement to further enhance the learning experience.
When evaluating students, what do instructors gather, summarize, and interpret data to determine?
When evaluating students, instructors gather, summarize, and interpret data to determine the student’s mastery of content and the effectiveness of the teaching strategies. They evaluate students’ understanding of new concepts, ability to perform certain skills and the evolution of values.
What is assessment in education?
Through assessment, the instructor understands the cognitive, psychomotor and affective learning needs of the student in order to determine the next educational steps.
What is the difference between research and evaluation?
Research is about being empirical. Evaluation is about drawing evaluative conclusions about quality, merit or worth. Research that is not evaluation involves factual description without judgements about quality – for example, census data, interview data which collects descriptions.
Why is evaluation research different from other research?
If I need to explain how evaluation research is different from other research that people may be familiar with, I would say that it's different from purely theoretical work because the purpose of evaluation is to provide the best possible information to improve whatever is being evaluated.
What is not research evaluation?
Evaluation that is not research involves making evaluative judgements without systematic collection of data – for example a connoisseur evaluator who produces a judgement without carefully gathering data.
What are the different types of evaluation?
There are many different types of evaluation needed for effective organisations and programs, including product evaluation, personnel evaluation, as well as program and policy evaluation.
What are the challenges of evaluation?
One of the challenges of working in evaluation is that important terms (like ‘evaluation’, ‘impact’, ‘indicators’, ‘monitoring’ and so on ) are defined and used in very different ways by different people. Sometimes the same word is used but to mean quite different things; other times different words are used to mean the same thing. And, most importantly, many people are simply unaware that other people use these words in these different ways.
Why is better evaluation important?
Since BetterEvaluation seeks to support discussion and learning across organisational, sectoral, and disciplinary boundaries, it is important for us to find ways to understand each other.
When planning an evaluation, it can be useful to think of research as a subset of evaluation?
When planning an evaluation, it can be useful to think of research as a subset of evaluation so that attention is paid to the processes of framing and managing an evaluation as well the specific research methods used to gather and analyse data. The BetterEvaluation Rainbow framework explicitly tries to bring issues about these wider tasks in evaluation into the planning for evaluations.
