
Medication
Mar 23, 2019 · Clinical manifestations of psoriasis. (A,B) Psoriasis vulgaris presents with erythematous scaly plaques on the trunk and extensor surfaces of the limbs.(C) Generalized pustular psoriasis.(D) Pustular psoriasis localized to the soles of the feet.This variant typically affects the palms of the hands as well; hence, psoriasis pustulosa palmoplantaris.
Therapy
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune skin disease that speeds up the growth cycle of skin cells. How is psoriasis diagnosed and treated? Psoriasis often has a typical appearance that a primary care doctor can recognize, but it can be confused with other skin diseases (like eczema), so a dermatologist (skin doctor) is often the best doctor to diagnose it. The treatment of psoriasis …
Nutrition
Dec 15, 2021 · What is the treatment for Psoriasis? The goal of psoriasis treatment is to stop the skin cells from growing rapidly and to remove the scales. There are several treatment options for psoriasis. The type of treatment done for you depends on how severe is psoriasis, and how responsive it has been to a previous treatment.
What are the topical therapies used to treat psoriasis?
Finding the right treatment for psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis (PsA) can be complicated. You can find that treatment with the help of your health care provider, whether it’s your primary care physician or a specialist such as a dermatologist or a rheumatologist. You can also contact our Patient Navigation Center for help in finding a provider.
Which is the best treatment for psorisis?
Nov 19, 2021 · Psoriasis is an immune-mediated disease that causes raised, scaly patches on the skin due to systemic inflammation. Psoriasis symptoms vary from mild to severe. Systemic inflammation of psoriasis increases risk for diabetes, depression, metabolic disease, etc.
How to cure psoriasis permanently?
Apr 21, 2022 · Researchers today understand that psoriasis is more than just a skin disease. It is a chronic autoimmune disorder that causes systemic inflammation. This newer understanding has helped shape modern...
How to find the best doctor for your psoriasis?
Treatments for moderate to severe psoriasis include: Light therapy. A doctor shines ultraviolet light on your skin to slow the growth of skin cells. PUVA …
What is the best treatment of psoriasis?
Steroid creams or ointments (topical corticosteroids) are commonly used to treat mild to moderate psoriasis in most areas of the body. The treatment works by reducing inflammation. This slows the production of skin cells and reduces itching. Topical corticosteroids range in strength from mild to very strong.
What is the main cause of psoriasis?
Common psoriasis triggers include: Infections, such as strep throat or skin infections. Weather, especially cold, dry conditions. Injury to the skin, such as a cut or scrape, a bug bite, or a severe sunburn.2 May 2020
What is the fastest treatment for psoriasis?
Humira. Humira is generally considered the fastest of the biologic treatments for psoriasis. Humira was previously approved for psoriatic arthritis at a dose of one injection every other week.8 Oct 2020
Is psoriasis a serious disease?
Psoriasis is not generally considered life-threatening, except in cases of erythrodermic psoriasis. This rare type of psoriasis can affect the entire body. Erythrodermic psoriasis can cause shivering and fluid retention, and may increase the risk of pneumonia and heart failure.29 Jun 2021
Can psoriasis go away?
Even without treatment, psoriasis may disappear. Spontaneous remission, or remission that occurs without treatment, is also possible. In that case, it's likely your immune system turned off its attack on your body. This allows the symptoms to fade.
How long can psoriasis last?
At times, treatment can lead to clear skin and no psoriasis symptoms. The medical term for this is “remission.” A remission can last for months or years; however, most last from 1 to 12 months. Psoriasis is notoriously unpredictable, so it's impossible to know who will have a remission and how long it will last.
How do you stop psoriasis from spreading?
Still, you can do a lot on your own to help control and prevent flare-ups.Use Moisturizing Lotions. ... Take Care of Your Skin and Scalp. ... Avoid Dry, Cold Weather. ... Use a Humidifier. ... Avoid Medications That Cause Flare-Ups. ... Avoid Scrapes, Cuts, Bumps, and Infections. ... Get Some Sun, But Not Too Much. ... Zap Stress.More items...•14 Sept 2020
Is psoriasis a fungus?
Both conditions cause red, scaly, and itchy plaques to form on the skin. While ringworm is a temporary rash caused by a fungus, psoriasis is an autoimmune condition that lasts for a lifetime, although the symptoms can be treated.27 Sept 2021
What organs can be affected by psoriasis?
Living with psoriasis can be difficult enough, but new research suggests sufferers may be at a higher risk for other serious diseases affecting vital organs like the heart, lungs and kidneys.7 Aug 2013
Can psoriasis patient get married?
It is possible to enjoy a normal married life with the correct treatments for psoriasis if you still take precautions in managing the disease.28 Apr 2021
How many miRNAs are aberrantly expressed in psoriatic skin?
Most of the studies of miRNAs in association with psoriasis address the plaque-type variant (see Table 1 ), and so far, more than 250 miRNAs are aberrantly expressed in psoriatic skin [ 132, 133, 134, 135 ].
What is the most common type of psoriasis?
The dermatologic manifestations of psoriasis are varied; psoriasis vulgaris is also called plaque-type psoriasis, and is the most prevalent type. The terms psoriasis and psoriasis vulgaris are used interchangeably in the scientific literature; nonetheless, there are important distinctions among the different clinical subtypes (See Figure 1 ).
What is the pathogenesis of psoriasis?
In the past 15 years, breakthroughs in the understanding of the pathogenesis of psoriasis have been translated into targeted and highly effective therapies providing fundamental insights into the pathogenesis of chronic inflammatory diseases with a dominant IL-23/Th17 axis. This review discusses the mechanisms involved in the initiation and development of the disease, as well as the therapeutic options that have arisen from the dissection of the inflammatory psoriatic pathways. Our discussion begins by addressing the inflammatory pathways and key cell types initiating and perpetuating psoriatic inflammation. Next, we describe the role of genetics, associated epigenetic mechanisms, and the interaction of the skin flora in the pathophysiology of psoriasis. Finally, we include a comprehensive review of well-established widely available therapies and novel targeted drugs.
What are some examples of epigenetic modifications?
Epigenetic mechanisms modify gene expression without changing the genomic sequence; some examples include: long noncoding RNA (lncRNA), microRNA (miRNA) silencing, and cytosine and guanine (CpG) methylation.
What is pustulosa palmoplantaris?
Pustular psoriasis can be localized or generalized. Two distinct localized phenotypes have been described: psoriasis pustulosa palmoplantaris (PPP) and acrodermatitis continua of Hallopeau. Both of them affect the hands and feet; PPP is restricted to the palms and soles, and ACS is more distally located at the tips of fingers and toes, and affects the nail apparatus. Generalized pustular psoriasis presents with an acute and rapidly progressive course characterized by diffuse redness and subcorneal pustules, and is often accompanied by systemic symptoms [ 10 ].
What is guttate psoriasis?
Guttate psoriasis is a variant with an acute onset of small erythematous plaques. It usually affects children or adolescents, and is often triggered by group-A streptococcal infections of tonsils. About one-third of patients with guttate psoriasis will develop plaque psoriasis throughout their adult life [ 8, 9 ].
What are AMPs in psoriasis?
Among the most studied psoriasis-associated AMPs are LL37, β-defensins, and S100 proteins [56].
What is the treatment for psoriatic arthritis?
The treatment of psoriatic arthritis usually involves the use of drugs (such as methotrexate). Psoriatic disease (when a person has psoriasis or psoriatic arthritis) may be treated with drugs (such as methotrexate) or a combination of drugs and creams or ointments.
What is the name of the disease that speeds up the growth cycle of skin cells?
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune skin disease that speeds up the growth cycle of skin cells.
How many people had psoriasis in 2013?
A recent analysis of NHANES data estimates that 7.4 million adults had psoriasis in 2013.
What are the health problems associated with psoriasis?
Many people who have psoriasis also have serious health conditions such as diabetes, heart disease, and depression. Some people with psoriasis also have an inflammatory condition which affects their joints, called psoriatic arthritis.
Is psoriatic arthritis the same as osteoarthritis?
It is different from more common types of arthritis (such as osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis) and is thought to be related to the underlying problem of psoriasis. Psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis are sometimes considered together as psoriatic disease.
What is the most common type of psoriasis?
Plaque psoriasis is the most common type of psoriasis. It usually causes dry, red skin lesions (plaques) covered with silvery scales. Guttate psoriasis, more common in children and adults younger than 30, appears as small, water-drop-shaped lesions on the trunk, arms, legs and scalp.
What causes red patches on the scalp?
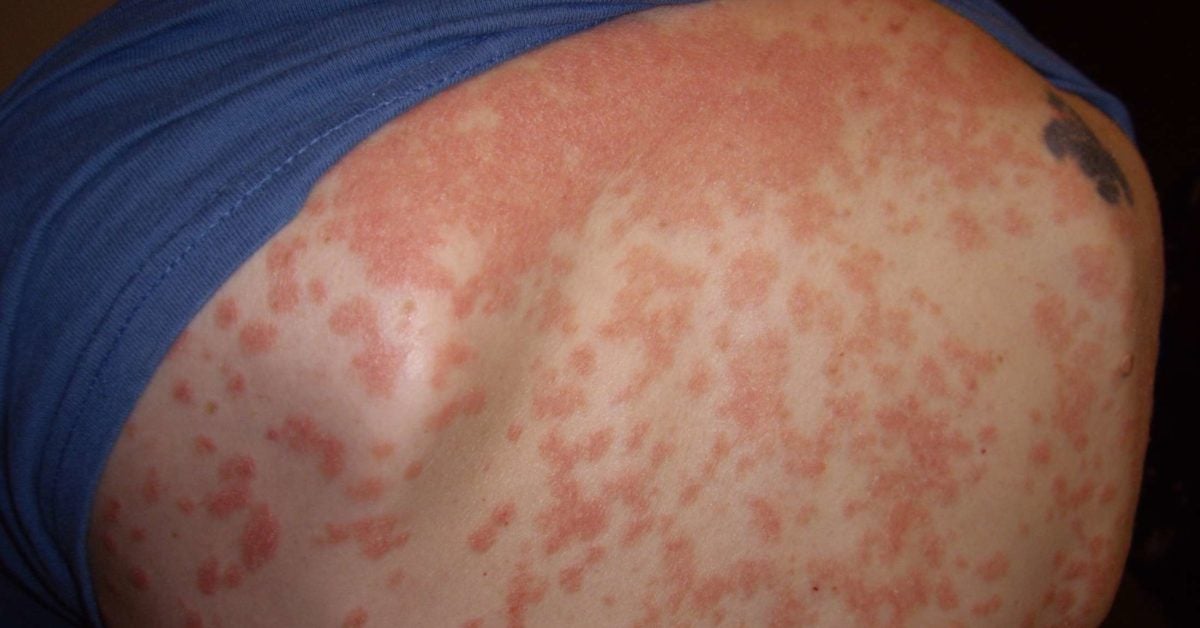
Psoriasis is a skin disease that causes red, itchy scaly patches, most commonly on the knees, elbows, trunk and scalp. Psoriasis is a common, long-term (chronic) disease with no cure. It tends to go through cycles, flaring for a few weeks or months, then subsiding for a while or going into remission. Treatments are available to help you manage ...
What is the name of the small water drop shaped lesions on the trunk, arms, legs and scalp?
Guttate psoriasis, more common in children and adults younger than 30, appears as small, water-drop-shaped lesions on the trunk, arms, legs and scalp. The lesions are typically covered by a fine scale. Scalp psoriasis. Open pop-up dialog box. Close.
What causes red spots on the back of the head?
Plaque psoriasis. The most common form, plaque psoriasis causes dry, raised, red skin patches (lesions) covered with silvery scales. The plaques might be itchy or tender, and there may be few or many. They usually appear on elbows, knees, lower back and scalp. Nail psoriasis.
Why does my skin turn red?
Causes. Psoriasis is thought to be an immune system problem that causes the skin to regenerate at faster than normal rates. In the most common type of psoriasis, known as plaque psoriasis, this rapid turnover of cells results in scales and red patches.
Where is psoriasis most commonly found?
The most commonly affected areas are the lower back, elbows, knees, legs, soles of the feet, scalp, face and palms.
What happens if you have psoriasis?
Also, talk to your doctor if your psoriasis: Becomes severe or widespread. Causes you discomfort and pain. Causes you concern about the appearance of your skin. Leads to joint problems, such as pain, swelling or inability to perform daily tasks.
What is the meaning of Psoriasis?
Psoriasis is a chronic (long-term) skin disorder causing red, itchy, scaly patches usually covered by silvery or white scales. This condition is most often seen in the elbows, knees, lower back, legs, soles of the feet, palms, and scalp region.m Psoriasis usually begins in early adulthood, although it can start later in life as well.
What are the causes of Psoriasis?
Psoriasis is an immune system (disease-fighting system of the body) problem.
What are the risk factors for Psoriasis?
Some factors may trigger the risk of developing psoriasis. These factors include:
What are the symptoms of Psoriasis?
Psoriasis commonly affects the elbows, knees, legs, lower back, palms, soles of the feet, scalp, and face.
How to diagnose Psoriasis?
Physical examination: Psoriasis can usually be diagnosed by the doctor by physical examination. The doctor will examine your scalp, skin, and nails. The patient’s symptoms are noted, along with the medical history and family history of the patient.
What is the treatment for Psoriasis?
The goal of psoriasis treatment is to stop the skin cells from growing rapidly and to remove the scales.
What are the complications of Psoriasis?
Other autoimmune diseases like celiac disease (immune reaction triggered on eating gluten) and sclerosis (nerve damage disrupting the communication between the brain and the body)
Why do skin cells fall off?
This occurs because the overactive immune system speeds up skin cell growth. Normal skin cells completely grow and shed (fall off) in a month. With psoriasis, skin cells do this in only three or four days. Instead of shedding, the skin cells pile up on the surface of the skin.
What is psoriasis mediated?
What Is Psoriasis? Psoriasis is an immune-mediated disease* (a disease with an unclear cause that is characterized by inflammation caused by dysfunction of the immune system) that causes inflammation in the body.
How does psoriasis affect your life?
Psoriasis may affect your emotional health, your relationships, and how you handle stress. It could even affect areas of your life that you wouldn’t expect, such as the clothes that you choose to wear.
How many types of psoriasis are there?
There are five types of psoriasis. It’s possible to have more than one type of psoriasis at one time and more than one type in a lifetime. Treatments may vary depending on the type and location of the psoriasis. Locations and Types.
Where do psoriasis plaques appear?
Plaques and scales may appear on any part of the body, although they are commonly found on the elbows, knees, and scalp.
Can psoriasis cause inflammation?
Inflammation caused by psoriasis can impact other organs and tissues in the body. People with psoriasis may also experience other health conditions. One in three people with psoriasis may also develop psoriatic arthritis. Signs of PsA include swelling, stiffness and pain in the joints and areas surrounding the joints.
When does psoriasis start?
However, it’s important to treat PsA early on to help avoid permanent joint damage. Symptoms often start between ages 15 and 25 , but can start at any age. Men, women, and children of all skin colors can get psoriasis.
Why do my sheets turn red?
Erythrodermic psoriasis, which causes fiery redness of the skin and shedding of scales in sheets. It's triggered by severe sunburn, infections, certain medications, and stopping some kinds of psoriasis treatment. It needs to be treated immediately because it can lead to severe illness.
What is the best treatment for psoriasis?
Retinoid creams. Treatments for moderate to severe psoriasis include: Light therapy. A doctor shines ultraviolet light on your skin to slow the growth of skin cells. PUVA is a treatment that combines a medicine called psoralen with a special form of ultraviolet light. Methotrexate.
How to treat a rash on the face?
Common treatments include: Steroid creams. Moisturizers for dry skin.
How often do new skin cells grow?
No one knows the exact cause of psoriasis, but experts believe that it’s a combination of things. Something wrong with the immune systemcauses inflammation, triggering new skin cells to form too quickly. Normally, skin cells are replaced every 10 to 30 days. With psoriasis, new cells grow every 3 to 4 days.
What causes red spots on the palms of the hands?
Other types of psoriasisinclude: Pustular psoriasis, which causes red and scaly skinwith tiny pustules on the palms of the hands and soles of the feet. Guttate psoriasis, which often starts in childhood or young adulthood, causes small, red spots, mainly on the torso and limbs.
How do you know if you have psoriasis?
Some common symptoms for plaque psoriasis-- the most common variety of the condition -- include: . Plaques of red skin, often covered with silver-colored scales. These plaques may be itchy and painful, and they sometimes crack and bleed.
What causes bumps on the back of the head?
What Is Psoriasis? Psoriasisis a skin disorder that causes skin cells to multiply up to 10 times faster than normal. This makes the skinbuild up into bumpy red patches covered with white scales. They can grow anywhere, but most appear on the scalp, elbows, knees, and lower back.

Topical Therapy
Oral Or Injected Medications
Treatment Considerations
Alternative Medicine