
Medication
The Top 10 Asthma Medicines
- Anti-inflammatory drugs (mast cell mediators) Cromolyn and Tilade, were more popular years ago, as asthma management drugs but the are no longer used.
- Long-acting beta-adrenoceptor agonists (LABAs) These help asthmatics control bronchospasm long term. ...
- Combination inhalers. ...
- Oral steroids. ...
- Oral bronchodilators. ...
- Immunomodulators. ...
Procedures
Types of asthma medications
- Inhaled corticosteroids
- Leukotriene modifiers
- Long-acting beta agonists (LABAs)
- Theophylline
- Combination inhalers that contain both a corticosteroid and a LABA
Self-care
- Reslizumab ( Cinqair) is an immunomodulator maintenance medication. ...
- Mepolizumab ( Nucala) targets the levels of blood eosinophils. ...
- Omalizumab ( Xolair) is an antibody that blocks immunoglobulin E (IgE) and is used as an asthma maintenance medication. ...
Nutrition
Atectura Breezhaler
- It is a single daily dose regime due to the long lasting effects of the two medicines it contains: mometasone and indacaterol
- It is delivered by the Breezhaler device which may be a new device for people with asthma. ...
- The Breezhaler device requires the preparation of a capsule inside the device, which may be new for people with asthma
See more
What is the most common medication for asthma?
What are the common inhalers and medicines for asthma?
What drugs treat asthma?
What is the newest asthma medication?

Which drug is used in the prophylactic treatment of asthma?
In addition, judicious and preserving use of pharmaceuticals may be employed for prophylaxis in childhood asthma. These include cromolyn sodium by inhalation, beclomethasone dipropionate aerosols, round-the-clock methylxanthines and beta 2 adrenergic bronchodilator agents. Their application is discussed.
Why steroid therapy is used as prophylactic in asthma treatment?
Steroids and other anti-inflammatory drugs work by reducing inflammation, swelling, and mucus production in the airways of a person with asthma. As a result, the airways are less inflamed and less likely to react to asthma triggers, allowing people with symptoms of asthma to have better control over their condition.
What are 4 treatments for asthma?
Quick-relief (rescue) medications are used as needed for rapid, short-term symptom relief during an asthma attack. They may also be used before exercise if your doctor recommends it....MedicationsInhaled corticosteroids. ... Leukotriene modifiers. ... Combination inhalers. ... Theophylline.
What is the first-line treatment for asthma?
Thus, inhaled corticosteroids are recommended as first-line therapy in all patients with persistent asthma.
What are 5 treatments for asthma?
These are the most common long-term control medications for asthma. These anti-inflammatory drugs include fluticasone (Flovent HFA), budesonide (Pulmicort Flexhaler), beclomethasone (Qvar RediHaler), ciclesonide (Alvesco, Omnaris) and mometasone (Asmanex HFA).
What happens when you stop taking steroid inhaler?
When you stop your treatment, you usually need to reduce your dose gradually. This can help avoid unpleasant side effects (withdrawal symptoms), such as severe tiredness, joint pain, being sick and dizziness.
Which treatment is best for asthma?
Long-term control medications such as inhaled corticosteroids are the most important medications used to keep asthma under control. These preventive medications treat the airway inflammation that leads to asthma symptoms. Used on a daily basis, these medications can reduce or eliminate asthma flare-ups.
What is the best treatment for asthmatic patient?
Short-acting beta-agonists are the first choice for quick relief of asthma symptoms. They include albuterol (ProAir HFA, Proventil HFA, Ventolin HFA), epinephrine (Asthmanefrin, Primatene Mist), and levalbuterol (Xopenex HFA).
What are the 3 types of asthma?
Types of asthmaDifficult to control asthma.Severe asthma.Occupational asthma.
What is the gold standard for asthma treatment?
The gold standard in asthma therapy is still a low-dose ICS as a controller together with an on-demand Short-acting beta-2-agonist (SABA). An LTRA (Leucotriene-receptor antagonist) can be tried as a second choice.
What are the 4 categories of asthma?
Ideally, asthma severity is determined before initiating therapy. The EPR-3 guideline classification divides asthma severity into four groups: intermittent, persistent-mild, persistent-moderate, and persistent-severe.
What is the latest treatment for asthma?
THURSDAY, Dec. 23, 2021 (HealthDay News) -- People who struggle with severe asthma now have a new treatment to get some relief. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration has approved an injectable drug called Tezspire (tezepelumab-ekko), which would be administered every four weeks by a health care professional.
Common Symptoms of Asthma
Symptoms of asthma include: 1. Wheezing (a whistling sound when exhaling (a common sign of asthma in children) 2. Usually begins suddenly 3. Comes...
Should I See A Doctor About My Asthma?
Call for an appointment with your health care provider if you or your child experience mild asthma symptoms (to discuss treatment options). Call yo...
Emergency Symptoms of Asthma
1. Extreme difficulty breathing 2. Breathing temporarily stops 3. Bluish color to the lips and face 4. Severe anxiety due to shortness of breath 5....
Long-Term Control Medications
Long-term control medications are used on a regular basis to prevent attacks. These are not appropriate as treatment during an acute asthma attack....
How to help asthma?
Regular exercise can strengthen your heart and lungs, which helps relieve asthma symptoms. If you exercise in cold temperatures, wear a face mask to warm the air you breathe. Maintain a healthy weight. Being overweight can worsen asthma symptoms, and it puts you at higher risk of other health problems.
How to stop asthma attacks?
Treatment. Prevention and long-term control are key to stopping asthma attacks before they start. Treatment usually involves learning to recognize your triggers, taking steps to avoid triggers and tracking your breathing to make sure your medications are keeping symptoms under control.
How is asthma classified?
How asthma is classified. To classify your asthma severity, your doctor will consider how often you have signs and symptoms and how severe they are. Your doctor will also consider the results of your physical exam and diagnostic tests. Determining your asthma severity helps your doctor choose the best treatment.
What test is used to diagnose asthma?
Other tests to diagnose asthma include: Methacholine challenge. Methacholine is a known asthma trigger. When inhaled, it will cause your airways to narrow slightly. If you react to the methacholine , you likely have asthma. This test may be used even if your initial lung function test is normal. Imaging tests.
How to reduce asthma triggers?
Taking steps to reduce your exposure to asthma triggers is a key part of asthma control. To reduce your exposure, you should: Use your air conditioner. Air conditioning reduces the amount of airborne pollen from trees, grasses and weeds that finds its way indoors.
What is the best bronchodilator for asthma?
Like other bronchodilators, ipratropium (Atrovent HFA) and tiotropium (Spiriva, Spiriva Respimat) act quickly to immediately relax your airways, making it easier to breathe. They're mostly used for emphysema and chronic bronchitis, but can be used to treat asthma. Oral and intravenous corticosteroids.
What is the test for lung function?
Lung function tests often are done before and after taking a medication to open your airways called a bronchodilator (brong-koh-DIE-lay-tur), such as albuterol. If your lung function improves with use of a bronchodilator, it's likely you have asthma.
What is the purpose of asthma medication?
Purpose. Types. Long-term asthma control medications. Taken regularly to control chronic symptoms and prevent asthma attacks — the most important type of treatment for most people with asthma. Inhaled corticosteroids.
How to keep asthma under control?
Making the most of your asthma medications. Tracking symptoms and side effects and adjusting your treatment accordingly is key to keeping your asthma symptoms under control. With your doctor or other health care providers, write a detailed plan for taking long-term control medications and for managing an asthma attack.
What is a long acting beta agonist?
Long-acting beta agonists (LABAs) These bronchodilator (brong-koh-DIE-lay-tur) medications open airways and reduce swelling for at least 12 hours. They're used on a regular schedule to control moderate to severe asthma and to prevent nighttime symptoms.
What is omalizumab used for?
Omalizumab (Xolair) is sometimes used to treat asthma triggered by airborne allergens. If you have allergies, your immune system produces allergy-causing antibodies to attack substances that generally cause no harm, such as pollen, dust mites and pet dander.
How often do you get asthma shots?
You generally receive injections once a week for a few months, and then once a month for three to five years.
What is ipratropium used for?
Ipratropium (Atrovent) Oral and intravenous corticosteroids (for serious asthma attacks) Medications for allergy-induced asthma. Taken regularly or as needed to reduce your body's sensitivity to a particular allergy-causing substance (allergen) Allergy shots (immunotherapy) Allergy medications. Biologics.
How long do you need to take corticosteroids for asthma?
They reduce swelling and tightening in your airways. You may need to use these medications for several months before you get their maximum benefit.
How do corticosteroids help with asthma?
Inhaled corticosteroids help to decrease inflammation and narrowing of the airways. These agents must be used regularly to get maximum benefit, and are recommended to help prevent asthma symptoms, reduce the need for rescue inhalers, and decrease the risk of serious attacks, and improve the quality of life.
What are the common allergens in asthma?
Common allergens include pet dander, dust mites, cockroach allergens, molds, and pollens. Common respiratory irritants include tobacco smoke, pollution, and fumes from burning wood or gas.
What is the effect of leukotriene modifiers on asthma?
The release of leukotrienes causes airway constriction, increased mucus production, swelling and inflammation in the lungs resulting in the characteristic wheezing and shortness of breath in asthma.
What happens when you have asthma?
When an asthma attack occurs, the muscles surrounding the airways become tight and the lining of the air passages swell and narrow. This reduces the amount of air that can pass through the airways and can lead to wheezing sounds, coughing, chest tightness and shortness of breath .
What does it mean when you wheeze when you exhale?
Wheezing (a whistling sound when exhaling (a common sign of asthma in children) Usually begins suddenly. Comes in episodes. May be worse at night and interfere with sleep; may worsen in early morning. Gets worse with cold air, exercise, and heartburn.
How is asthma medicine delivered?
Medication for asthma is either delivered by inhalation, orally or parenterally (by injection). Inhalation is the preferred route of administration as this allows the drug to be delivered directly into the airways in smaller doses. This causes fewer side effects than if given orally or by injection.
How long does asthma last?
Asthma attacks can last from minutes to days and can become dangerous if the airflow becomes severely restricted. In sensitive individuals, asthma symptoms can be triggered by breathing in allergy-causing substances (called allergens or triggers). Identifying triggers and avoiding them are essential to asthma control.
Drugs used to treat Asthma
The following list of medications are in some way related to, or used in the treatment of this condition.
Alternative treatments for Asthma
The following products are considered to be alternative treatments or natural remedies for Asthma. Their efficacy may not have been scientifically tested to the same degree as the drugs listed in the table above. However there may be historical, cultural or anecdotal evidence linking their use to the treatment of Asthma.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
What is the best treatment for asthma?
Inhalers, which are devices that let you breathe in medicine, are the main treatment. Tablets and other treatments may also be needed if your asthma is severe. You'll usually create a personal action plan with a doctor or asthma nurse.
Why do you need a preventer inhaler?
You use a preventer inhaler every day to reduce the inflammation and sensitivity of your airways, which stops your symptoms occurring. It's important to use it even when you do not have symptoms. Speak to a GP or asthma nurse if you continue to have symptoms while using a preventer inhaler.
Why do people use combination inhalers?
Combination inhalers are used every day to help stop symptoms occurring and provide long-lasting relief if they do occur. It's important to use it regularly, even if you do not have symptoms. Side effects of combination inhalers are similar to those of reliever and preventer inhalers. Asthma UK: combination inhalers.
How to prevent throat soreness?
You can help prevent these side effects by using a spacer, which is a hollow plastic tube you attach to your inhaler, as well as by rinsing your mouth after using your inhaler. Asthma UK: preventer inhalers.
Can a reliever inhaler cause a fast heartbeat?
They may suggest additional treatment, such as a preventer inhaler. Reliever inhalers have few side effects, but they can sometimes cause shaking or a fast heartbeat for a few minutes after they're used. Asthma UK: reliever inhalers.
Is bronchial thermoplasty safe?
A procedure called bronchial thermoplasty may be offered as a treatment for severe asthma. It works well and there are no serious concerns about its safety. You will be sedated or put to sleep using a general anaesthetic during a bronchial thermoplasty.
Can breathing exercises help with asthma?
There's little evidence to suggest many of these treatments help. There's some evidence that breathing exercises can improve symptoms and reduce the need for reliever medicines in some people, but they should not be used instead of your medicine. Asthma UK: complementary therapies for asthma.
What is asthma therapy?
The current concept of asthma therapy is based on a stepwise approach, depending on disease severity, and the aim is to reduce the symptoms that result from airway obstruction and inflammation, to prevent exacerbations and to maintain normal lung function.
What are the two main classes of asthma drugs?
The established treatment of asthma primarily comprises two classes of drug, bronchodilators and anti-inflammatory/immunosuppressive drugs. By far the most effective bronchodilators in asthma are β 2 ‐adrenoceptoragonists.
How is asthma severity classified?
To date, asthma severity has been classified according to the frequency of symptoms in combination with lung function parameters such as forced expiratory volume in one second and peak expiratory flow; this classification forms the basis of a stepwise approach to asthma therapy.
Why does asthma cause a narrowing of the airway?
Asthma symptoms are mainly caused by recurrent episodes of acute airway narrowing that are believed to result from airway hyperresponsiveness and inflammation irrespective of whether the origin of the disease is allergic or nonallergic. The underlying mechanisms of airway hyperresponsiveness are still far from being completely understood.
What is the best treatment for airway obstruction?
β 2 ‐Adrenoceptor agonists and glucocorticoids are at present the most effective drugs for the treatment of airway obstruction and inflammation, with theophylline, leukotriene receptor antagonists and anticholinergics as second- or third-line therapy.
What is the underlying mechanism of airway hyperresponsiveness?
In allergic asthma, it is assumed that the early-phase reaction is based on an immunoglobulin (Ig)‐E mediated reaction with antigen cross-linking of Ig‐E molecules bound to specific receptors on mast cells.
What is the future of asthma?
In future, it will be important to develop preventive and, possibly, curative therapeutic approaches, which are based on an improved understanding of the pathogenesis and pathophysiology of asthma. Current treatment strategies advocate a stepwise approach to treatment, which depends on the severity of the disease 1.
How to manage asthma?
Many people with exercise-induced asthma play sports, enjoy a range of activities and live an active lifestyle. People of all fitness levels, including Olympic athletes and marathon runners, manage asthma and excel at their sports. If you or your child has EIB, be sure to include a warmup routine before exercise. Keep an eye on pollen counts and air quality before you head outside. Talk to your provider about medications that can help you breathe easier. With lifestyle changes and prior planning, you can stay active and exercise safely.
What to do if your child has asthma?
If you or your child has symptoms of exercise or sports-induced asthma, call your provider. Several conditions have symptoms that are similar to EIB. It’s essential to get evaluated. If you or your child has severe shortness of breath or trouble breathing, seek immediate medical attention.
How long does it take for asthma symptoms to show after exercise?
Symptoms can range from mild to severe. They can appear a few minutes after you start exercising or after you finish a workout. Symptoms usually start to improve after about 30 minutes of rest. Sometimes, exercise-induced asthma can return up to 12 hours after you’ve finished exercising.
What is the cause of shortness of breath and coughing?
Exercise-Induced Asthma. Exercise-induced asthma, or sports-induced asthma, happens when airways constrict during physical activity. This causes coughing, wheezing and shortness of breath. These symptoms appear during or after exercise and may come back after rest. With medications and good exercise choices you can manage exercise-induced asthma ...
Why is asthma worse when you exercise?
When you exercise, you breathe in through your mouth more often, and the air coming in remains cold and dry. If you have asthma, the bands of muscle around your airways react to the cold, dry air by constricting (becoming narrow). Exercise-induced asthma is worse when: Air is cold and dry. Pollen counts are high.
How to protect your airways from pollen?
If pollution and pollen levels are high, you may want to stay indoors. Cover your mouth and nose: Use a mask, scarf or gaiter to protect your airways from cold, dry air.
Is exercise induced asthma common?
Is exercise-induced asthma common? Yes. Exercise-induced asthma, sometimes called exercise-induced bronchospasm or sports-induced asthma, is common. About 90% of people with asthma have symptoms of asthma during or after exercise.
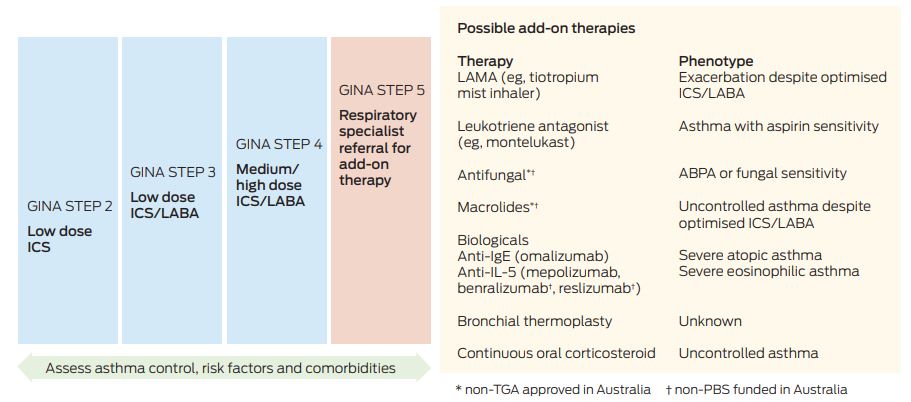
Diagnosis
Treatment
Clinical Trials
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Specialist to consult
Alternative Medicine
- Asthmais an inflammatory disease that affects a person’s respiratory system, inflaming the airways, and causing symptoms including wheezing, coughing, shortness of breath, and tightness in the chest. Prophylactic asthma medications have a two-fold purpose: control or maintain symptoms, and prevent occurrences or recurrences of attacks. Unlike rescu...
Coping and Support
Preparing For Your Appointment