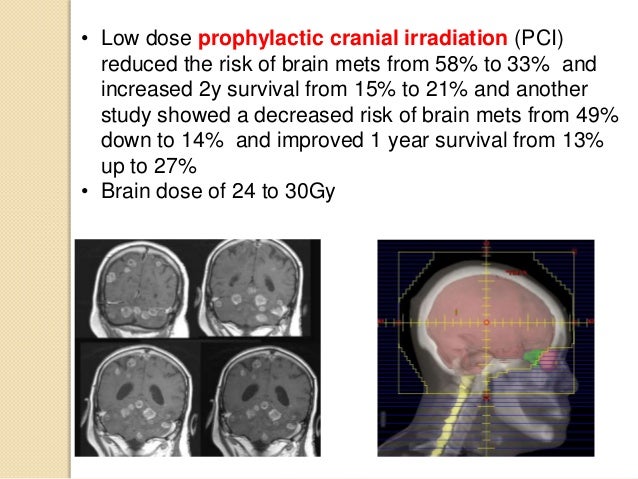
Prophylactic cranial irradiation (PCI) is a type of radiation therapy used to prevent the spread (metastasis) of lung cancer from the lungs to the brain. The brain is among the most common site of metastases in people with advanced lung cancer, along with the liver, bones, adrenal glands, and other parts of the lung. 1
What to expect of radiation therapy?
Radiation therapy sessions. Your radiation oncologist leads a team of technicians and nurses. The team will work with you at each radiation therapy session. What should I expect? During each session, you will lie on a special table. You may be asked to hold your breath while the radiation is given.
What does prophylactic therapy mean?
Prophylactic therapy, also known as prophylactic treatment or preventative therapy, is any type of therapy or treatment designed to improve or maintain a person’s health. The most common types of preventative therapy include physical, antibiotic, surgical, and immunization therapies. Prophylaxis can be primary or secondary.
What are the contraindications of radiation therapy?
Contraindications. Irradiation of the eyes. Exposure of the eyes can be avoided by having the patient wear UV-opaque goggles throughout treatment and by having the therapist wear UV-opaque goggles when at risk of irradiation, such as when turning the UV lamp on or off. Patients taking UV-sensitizing drugs, such as psoralens, should continue to ...
Are there specialists for radiation therapy?
Several types of specialized medical professions use radiation to perform health tests and treat patients. People who work with radiation are protected by laws that limit the amount of radiation exposure they can have each year. Specialists in radiation science are called health physicists.
What are the side effects of prophylactic cranial irradiation?
Cranial irradiation can be related to both acute and long-term toxicity. Acute adverse effects associated with PCI are fatigue, alopecia, scalp erythema, headaches, and low-grade nausea, all of which usually are self-limited, whereas long-term toxicity, especially neurocognitive impairment, is a potential concern.
What are the four types of radiation therapies?
There are several types of brachytherapy characterized by different methods of placing radiation inside the body: interstitial brachytherapy, intracavitary brachytherapy, intraluminal radiation therapy, and radioactively tagged molecules given intravenously.
Does palliative radiotherapy prolong life?
Palliative radiotherapy aims at symptom alleviation and improvement of quality of life. It may be effective in conferring a reasonable quantum of local control, as well as possibly prolonging survival on the short term.
How many sessions of radiation is normal?
Most people have 5 treatments each week (1 treatment a day from Monday to Friday, with a break at the weekend). But sometimes treatment may be given more than once a day or over the weekend.
Is radiation worse than chemo?
The radiation beams change the DNA makeup of the tumor, causing it to shrink or die. This type of cancer treatment has fewer side effects than chemotherapy since it only targets one area of the body.
Do tumors grow back after radiation?
Normal cells close to the cancer can also become damaged by radiation, but most recover and go back to working normally. If radiotherapy doesn't kill all of the cancer cells, they will regrow at some point in the future.
What is the difference between radiation and palliative radiation?
Radiation therapy uses high energy xrays to treat cancer. Palliative treatment means treatment to shrink a cancer, slow down its growth, or control symptoms caused by the cancer.
What is the difference between radiotherapy and palliative radiotherapy?
Radiotherapy to relieve symptoms is also known as palliative radiotherapy. Palliative radiotherapy aims to shrink cancer, slow down its growth or control symptoms. It doesn't aim to cure cancer. Depending on the type of cancer you have, and where it has spread to, you might have external or internal radiotherapy.
What is life expectancy after radiation therapy?
Median follow-up time for this report was 41 months (range=14.6-59.0). Following treatment with stereotactic radiation, more than eight in ten patients (84%) survived at least 1 year, and four in ten (43%) survived 5 years or longer. The median overall survival (OS) time was 42.3 months.
What time of day is best for radiation therapy?
New research from Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center, to be presented at the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) Annual Meeting 2019 in Atlanta, reports that administering radiation treatments in the morning as opposed to later in the day can significantly reduce severity of mucositis and its related ...
What is the success rate of radiation therapy?
“When patients are treated with modern external-beam radiation therapy, the overall cure rate was 93.3% with a metastasis-free survival rate at 5 years of 96.9%.
Can I drive myself to radiation treatments?
Unless you feel ill, you can typically drive yourself to treatment. In fact, many patients are able to work full-time during their treatment.
Why do people have PCR after chemo?
If the cancer has not spread to other parts of the body ( limited-stage SCLC ), they may have PCR after chemoradiation. If the cancer has spread further ( extensive-stage SCLC ), they may have PCR and also radiotherapy to the chest. PCR treats the whole brain. It is given because chemotherapy is not good at treating cancer cells ...
What is a PCR?
Prophylactic cranial radiotherapy (PCR) Prophylactic cranial radiotherapy ( PCR) is treatment to prevent or reduce the risk of cancer cells spreading to the brain.
What is PCR radiotherapy?
What is prophylactic cranial radiotherapy (PCR)? PCR is also sometimes called prophylactic cranial irradiation (PCI). It is used to prevent or reduce the risk of cancer cells spreading to the brain. Prophylactic means preventive, and cranial means the head.
Why is PCR used for cancer?
PCR treats the whole brain. It is given because chemotherapy is not good at treating cancer cells that may have spread to the brain. This is because the brain is protected by a membrane called the blood-brain barrier. This stops a lot of chemotherapy drugs from getting to the brain.
How long does radiotherapy last?
Each treatment lasts for a few minutes. You usually have treatment every day from Monday to Friday, with a rest at weekends. Your doctor or nurse will tell you how many treatments you will have. Your radiotherapy is carefully planned to make sure it works as well as possible.
How long does it take for a person to get tired after radiotherapy?
Somnolence is an extreme tiredness some people get after radiotherapy to the brain. It happens about 4 to 8 weeks after treatment finishes.
Why do you wear a radiographer?
You wear this during your treatment. It helps keep your head still so the treatment is effective. You can breathe through it and it should not be uncomfortable. At the beginning of each session of radiotherapy, the radiographer positions you carefully on the couch and makes sure you are comfortable.
What is the treatment for SCLC?
Using Prophylactic Cranial Irradiation (PCI) To Treat SCLC. New treatment options for small cell lung cancer (SCLC) are of the utmost importance. Although medications have not changed much for SCLC over the years, other treatment options, like radiation, are on the rise. 1. SCLC makes up about 15 percent of all lung cancers, ...
Why is PCI called prophylactic?
PCI is called prophylactic because it is preventative. It is used to help prevent spread to the brain before it actually happens. 2. Since it can help prevent cancer rather than treat an existing tumor, ...
What are the side effects of PCI?
The most common side effects of PCI include: 1,2. Rash or redness around the face or head (where the radiation is given) Fatigue or tiredness. Nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, or weight loss. Hair loss. Headache. Confusion or memory issues. Many of these side effects will improve after PCI treatment is over.
How long does a PCI last?
Most people will undergo PCI for a few minutes each session, 5 days a week. PCI also lasts for a shorter amount of time than traditional radiation. Most people will not undergo PCI for more than 3 weeks. PCI is not painful. 2.
How does SCLC affect the body?
SCLC makes up about 15 percent of all lung cancers, and many will be treated with chemotherapy, radiation, or both. 1 SCLC can spread throughout the body (metastasize). One of the places it tends to spread to is the brain. This can cause many serious issues that can impact a person’s quality of life, including seizures.
Does PCI help with lung cancer?
Some have suggested that PCI decreases the risk of lung cancer’s spread to the brain and improves overall survival time. Others have suggested that these benefits may only be found in those who have more limited-stage SCLC (cancer that is detected early and has not spread to other parts of the body). 2,3.
Is PCI recommended for lung cancer?
PCI may be recommended in a variety of different situations. Often, it is for people whose lung cancer has responded to chemotherapy and other radiation. Your doctor can help you determine if PCI is right for your specific case.
Why are prophylactic antibiotics not given?
Prophylactic antibiotics are avoided whenever possible in health care, as the overuse of antibiotics has led to antibiotic resistance, and provides no benefit to the patient. There may be individual instances where the use of antibiotics prior to surgery is deemed to be appropriate, or when a patient is sick enough to warrant the use of antibiotics before blood cultures or other lab results confirm the presence of infection. In these cases, the potential benefit outweighs the risk of harm, and the physician chooses to utilize antibiotics.
What is a prophylactic dental cleaning?
Prophylactic Health Care. In medicine, the term prophylactic is used to describe surgeries, dental cleanings, vaccines, birth control and many other types of procedures and treatments that prevent something from happening. A prophylactic hepatitis vaccine prevents the patient from getting hepatitis, while a prophylactic dental cleaning prevents ...
What is prophylactic care?
Types of Prophylactic Care. Preventative care takes many forms and continues even after a disease process has been identified. Generally speaking, prophylaxis doesn't just mean preventing disease, it can also mean preventing a worsening of disease, minimizing the severity of disease, and preventing over-treatment.
What does prophylaxis mean?
Updated on January 31, 2020. The term prophylaxis means preventative, or to prevent. Greek in origin, from the word "phylax", meaning "to guard" and "watching", prophylactic treatment is frequently used in health care to minimize illness and disease. Caiaimage / Sam Edwards / Getty Images.
What is tertiary prophylaxis?
Tertiary Prophylaxis: Measures taken to reduce the impact of a chronic, ongoing disease or injury that is likely to produce long-lasting effects , such as stroke rehab programs or disease management programs for heart failure.
Do you need antibiotics for joint replacement?
There is no longer a recommendation that individuals with joint replacements receive antibiotic prophylaxis prior to dental procedures. If you have had a procedure that makes prophylactic antibiotics a good idea, your surgeon will make you aware of this.
When to use antibiotics before surgery?
There may be individual instances where the use of antibiotics prior to surgery is deemed to be appropriate, or when a patient is sick enough to warrant the use of antibiotics before blood cultures or other lab results confirm the presence of infection.
What is SBRT treatment?
This allows each treatment to be given over just a few minutes. Stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) also known as stereotactic ablative radiotherapy (SABR), is most often used to treat early-stage SCLC when surgery isn’t an option due to a person’s health or in people who don’t want surgery.
What is the best treatment for SCLC?
Types of radiation therapy. The type of radiation therapy most often used to treat SCLC is called external beam radiation therapy (EBRT). A machine outside the body focuses radiation at the cancer. Treatment is much like getting an x-ray, but the radiation dose is stronger.
How long does a cranial radiation treatment last?
Radiation to relieve symptoms and prophylactic cranial radiation are given for shorter periods of time, typically less than 3 weeks. Newer EBRT techniques have been shown to help doctors treat lung cancers more accurately while lessening the radiation exposure to nearby healthy tissues.
What is IMRT radiation?
Intensity modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) is an advanced form of 3D therapy.
How does a linear accelerator work?
In another version, a linear accelerator (a machine that creates radiation) that is controlled by a computer moves around your head to deliver radiation to the tumor from many different angles. These treatments can be repeated if needed.
What is the purpose of a lung shrink?
To shrink tumors to relieve (palliate) symptoms of lung cancer such as pain, bleeding, trouble swallowing, cough, shortness of breath, and problems caused by spread to other organs such as the brain or bone.
Why do people need cranial irradiation?
This is sometimes done for patients with extensive stage disease, or it can be used for people with limited stage disease who cannot tolerate getting chemotherapy and radiation at the same time. To help lower the chances of cancer spreading to the brain. This is called prophylactic cranial irradiation. This is used most often to treat people ...
What is palliative radiation?
Radiation is the use of high energy x-rays to damage the DNA of cells, which leads to the death of cancer cells. Palliative radiation is the use of radiation to treat a specific area, and in some cases to reduce side effects such as pain and bleeding. Palliative radiation is done to improve the quality of life of the patient.
What are the side effects associated with palliative radiation?
Although you will only receive a few treatments, you could have side effects. These are often short-term side effects, lasting 1-4 weeks after your treatment has ended. The side effects you have are in relation to the part of the body being treated. Side effects can include:
When should I contact my provider?
You should call your provider if you have any new or worsening side effects such as:
What is protons radiation?
Radiation therapy using X-rays has long been used to treat cancers and noncancerous (benign) tumors. Proton therapy is a newer type of radiation therapy that uses energy from positively charged particles called protons .
What is proton therapy?
Proton therapy is used as a treatment for cancer and some noncancerous tumors. Proton therapy may be used as the only treatment for your condition. Or it may be used in conjunction with other treatments, such as surgery and chemotherapy. Proton therapy is sometimes used to treat: Brain tumors. Breast cancer.
What is radiation simulation?
During radiation simulation, your radiation therapy team works to find a comfortable position for you during treatment. It's imperative that you lie still during treatment, so finding a comfortable position is vital. To do this, you'll be positioned on a table that will be used during your treatment.
How long does proton therapy take?
You typically undergo proton therapy five days a week for several weeks. However, in some cases, you may undergo only one or only a few treatments, depending on your condition. The actual proton therapy treatment may take only a minute or so, but expect to spend 30 to 45 minutes preparing before each treatment session.
How to prepare for proton therapy?
Before you undergo proton therapy, your health care team guides you through a planning process to ensure that the proton beam reaches the precise spot in your body where it's needed. Planning typically includes: Determining the best position for you during treatment.
What imaging is used to determine the area of the body to be treated?
Your radiation therapy team may have you undergo magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or computerized tomography (CT) scans to determine the area of your body to be treated and how best to reach it with the proton beams.
What are the different types of cancer?
Head and neck cancers. Liver cancer. Lung cancer. Pituitary gland tumors. Prostate cancer. Sarcoma. Tumors affecting the spine. Tumors in the base of the skull. Clinical trials are investigation proton therapy as a treatment for a number of other types of cancer.
Purpose of The Procedure
Risks and Contraindications
- Prophylactic cranial irradiation can play an important role in the prevention of brain metastases by killing metastatic cancer cells in the brain. The radiation dose is far lower than that used to cure solid tumors but significantly higher than that used for imaging tests like computed tomography (CT) scans. The repeated exposure to radiation of this level can lead to neurotoxicity in which br…
Before The Procedure
- The decision to use prophylactic cranial irradiation is a very personal one. Due to the increased risk of neurotoxicity and neurocognitive impairment, the benefits and risks need to be carefully weighed in tandem with your long-term prognosis. In addition, your healthcare provider will need to assess your performance status—usually rated on a scale of 0 (completely active) to 4 (comp…
Simulation
- Before your first treatment is scheduled, you will need to attend a planning session called a simulation. This is used to calculate the correct radiation dose and map the treatment area with both the radiation oncologist and radiation therapist. To ensure your head is in the correct position for each and every treatment, a mold of your face will be created using a grid-like therm…
During The Procedure
- On the day of the procedure, arrive at least 15 minutes beforehand to register and settle in. PCI is typically overseen by the radiation therapist with the aid of a radiology nurse.
Follow-Up
- Because prophylactic cranial radiation is preventive, the only measure of success is the absence of brain metastases on imaging studies. Your oncologist will schedule routine CT, MRI, or positron emission tomography (PET)scans to monitor for any signs of metastasis, not only in the brain but also in other organs and your bones. Your healthcare provider will also monitor for any neurocog…
What Is PCI?
- PCI involves delivering radiation to the brain. A machine sends this radiation in doses stronger than normal x-rays. This is much like the radiation that can be given to the chest to treat the original site of a person’s lung cancer. PCI is called prophylactic because it is preventative. It is used to help prevent spread to the brain before it actu...
When Is PCI used?
- In many cases, a person will get a brain scan (MRI) before getting PCI to make sure there is no visible cancer. PCI can kill cancer cells that are just starting to spread to the brain before they are detected on scans. This can be helpful in preventing or slowing spread to the brain. PCI may be recommended in a variety of different situations. Often, it is for people whose lung cancer has re…
What Are The Side Effects of PCI?
- The most common side effects of PCI include:1,2 1. Rash or redness around the face or head (where the radiation is given) 2. Fatigueor tiredness 3. Nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, or weight loss 4. Hair loss 5. Headache 6. Confusion or memory issues Many of these side effects will improve after PCI treatment is over. However, some after effects, especially those involving …
What Does The Research Say?
- Research on PCI for preventing brain metastasis in lung cancer is mixed. Some have suggested that PCI decreases the risk of lung cancer’s spread to the brain and improves overall survival time. Others have suggested that these benefits may only be found in those who have more limited-stage SCLC (cancer that is detected early and has not spread to other parts of the body).2,3 Lik…