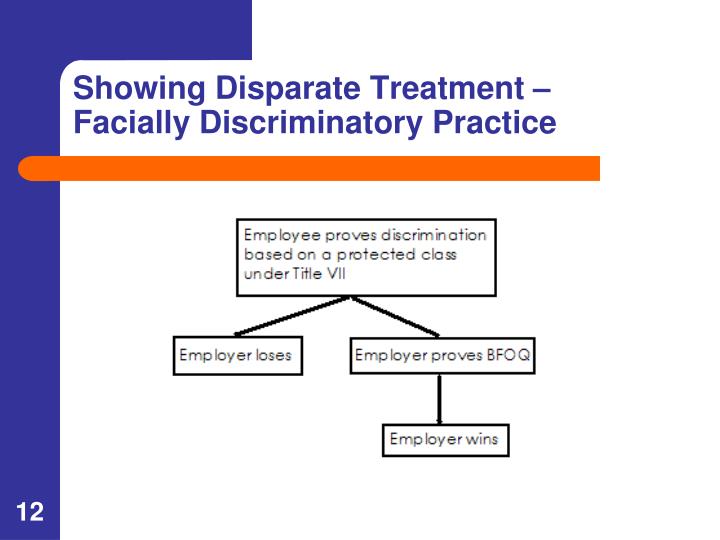
To support a disparate treatment claim, you need to establish four elements:
- The individual is a member of a protected class;
- The employer knows of the individual’s protected class;
- A harmful act occurred; and
- Other similarly situated individuals were treated more favorably or not subjected to the same treatment.
Full Answer
Can You claim for disparate treatment?
What is a disparate impact claim?
What is a disparate treatment discrimination case?
A disparate treatment claim is made by those employees who felt that they were treated differently from their co-workers regardless of being in the same position in the hierarchy. To …
What is an example of disparate treatment and impact?
Disparate treatment is when an employer regards a specific applicant or an employee differently than others, solely because they are a woman, minority, or member of another protected …

What is disparate treatment?
Disparate treatment is a way to prove illegal employment discrimination. An employee who makes a disparate treatment claim alleges that he or she was treated differently than other employees who were similarly situated, and that the difference was based on a protected characteristic. In other words, the employee alleges ...
How to prove a disparate treatment claim?
To prove a disparate treatment claim, an employee must first present enough evidence to allow the judge or jury to infer that discrimination took place.
What is prima facie case?
The Prima Facie Case. The type of evidence an employee has to present to prove a prima facie case of disparate treatment discrimination depends on the facts. If there is direct evidence of discrimination, that's enough. For example, if an employer hires only female bartenders or has said it will not promote African Americans to management ...
What does discrimination mean in employment?
The term means that an employee was treated differently than other employees similarly situated, though in a legal sense, the different treatment must be based on the individual’s inclusion in a protected class. Discrimination is prohibited by the U.S. Constitution, and as such, the wronged person may take his case before the employment board, ...
What is disparate treatment?
Disparate treatment is a claim of discrimination in which an individual complains to have been treated differently than other people in a similar situation, but who don’t share the individual’s protected class. Disparate treatment is a common element of proving employment discrimination, but it occurs in other areas of life as well, ...
What is protected class?
What is a Protected Class. Federal anti-discrimination laws make it unlawful to discriminate against anyone on the basis of certain characteristics. Because these characteristics are protected by law, people having these trait s or qualities are considered to be in a protected class.
How can a person be treated differently?
There are two ways in which a person may be treated differently, or “disparately,” for purposes of discrimination actions: (1) disparate treatment, and (2) disparate impact. The difference between the two has to do with intent and effect.
What is disparate discrimination?
The EEO defines this type of discrimination as: “Inconsistent application of rules and policies to one group of people over another.” In 1977, the U.S. Supreme Court defined disparate treatment as discriminatory acts in which “ [t]he employer simply treats some people less favorably than others because of their race, color, religion, sex, or national origin.” Proving disparate treatment often involves proving that the employer’s decision was motivated by the employee’s protected trait.
What is after acquired evidence?
After-acquired evidence is evidence of an employee’s wrongdoing or misconduct, gathered by the employer only after the employee’s discharge and claim of discrimination. Over the years, there has been some debate as to whether after-acquired evidence could prevent a plaintiff from winning his discrimination, or disparate treatment, lawsuit. In general, the courts have held that after-acquired evidence of misconduct unrelated to the grounds for termination can only prevent a plaintiff from being awarded reinstatement, injunctive relief, and front pay, if accepted at all.
What is a civil lawsuit?
Civil Lawsuit – A lawsuit brought about in court when one person claims to have suffered a loss due to the actions of another person. Defendant – A party against whom a lawsuit has been filed in civil court, or who has been accused of, or charged with, a crime or offense.
What is disparate treatment?
A claim of disparate treatment must be supported by evidence. The employee must prove that he/she was addressed differently from all workers who did not possess the protected trait.
Proving a claim of disparate treatment
An employee must first provide adequate details to enable a jury or judge to conclude the case with verdict. This is known as introducing a “ prima facie ” case since it seems to be biased at first glance. However, the significance of the proof depends on the details.
The prima facie case
It purely relies on the facts, whenever it comes to proving a prima facie with the kind of evidence an employee provides. However, it is sufficient enough to win the claim when there is clear evidence of discrimination.
Proving pretext
Soon after the employer has given a legitimate rationale for the action. The employee must illustrate that the employer’s claimed reason for the action is a pretext for discrimination. However, this does not imply that the employee must derive absolute evidence of bad intentions.
What is Disparate Treatment?
Disparate treatment is when an employer regards a specific applicant or an employee differently than others, solely because they are a woman, minority, or member of another protected class. Disparate treatment is illegal to ensure employers don’t act with discriminatory intent against an applicant or employee.
What Is the Difference Between Disparate Impact and Disparate Treatment Discrimination?
The main difference between disparate impact (also called disparate effect) and disparate treatment is:
How Are Disparate Impact and Disparate Treatment Proven?
Note that both disparate impact and disparate treatment are illegal discrimination unless an employer can prove the policies, procedures, and practices are necessary and related directly to the job position.
What Is a Protected Class?
A protected class is a group of individuals who are legally protected by Title VII of the Civil Rights Act of 1964 from employment discrimination based on:
What happens if you treat someone with disparate treatment?
Disparate treatment can cause serious issues inside your organization. Not only can it lead to legal action, it can also cause your organization to lack diversity , which can dramatically impact your bottom line.
What is disparate treatment?
In summary, disparate treatment is a claim an employee can make against an organization that states that the company has treated them differently in a discriminatory way. In other words, disparate treatment is proof that an organization is discriminating against employees based on their race, religion, gender, sexuality, or other 'difference.'.
Is disparate treatment intentional?
Unlike adverse impact, which can spring up even if your intentions are pure, disparate treatment is intentional, meaning that it can be stopped before it starts by ensuring that your managers, hiring team, and other employees are not motivated to treat those in protected classes differently.
What is disparate treatment?
A disparate treatment claim argues that the individual suffered less favorable treatment than similarly situated individuals. The basis for the less favorable treatment may be due to the individual’s race, religion, sex, color, or national origin. In disparate treatment claims, the employer’s intent is the matter at issue.
What are the federal protections for discrimination?
There are federal protections that protect individuals from discrimination in the workplace. Your employer, or potential employer, has an obligation to prevent and address discrimination against employees. Multiple federal and state protections ensure that if discrimination occurs, victims may file a claim for this treatment.
What is the Civil Rights Act of 1964?
Title VII of the Civil Rights Act of 1964 prohibits employers from discriminating against individuals based on race, color, religion, sex, or national origin . Title VII prohibits an employer from discriminating with regard to any term, condition, or privilege of employment.
What is a Title VII employer?
Title VII prohibits an employer from discriminating with regard to any term, condition, or privilege of employment. Common employer practices such as hiring, terminating, disciplining, recruiting, assigning, evaluating, and training fall under Title VII. Apprenticeship programs.
What is Title VII?
Title VII prohibits an employer from discriminating with regard to any term, condition, or privilege of employment. Common employer practices such as hiring, terminating, disciplining, recruiting, assigning, evaluating, and training fall under Title VII. Under Title VII, the parties covered include the following:
What is the age discrimination in employment act?
The Age Discrimination in Employment Act (ADEA) protects employees or potential hires 40 years of age or older. The ADEA protections extend to workplace practices involving hiring, promotion, discharge, compensation, or terms, conditions, or privileges of employment. The ADEA is enforced by the Equal Employment Opportunity Commission.
Who enforces the ADEA?
The ADEA is enforced by the Equal Employment Opportunity Commission.
What Is Disparate Treatment Discrimination?
The difference between racial discrimination and disparate treatment is subtle. In disparate treatment lawsuits, an employee is not claiming that he or she was deliberately singled out by an employer because of his or her race.
How Do You Prove a Disparate Treatment Claim?
In order to successfully prove a disparate treatment claim, an employee needs to demonstrate enough evidence for a judge or jury to infer that discrimination actually took place. This is known as presenting a “prima facie” case.
What West Coast Employment Lawyers Can Do For You?
If you have made up your mind to take action, it is important to work with an attorney that specializes in cases like yours. The racial discrimination lawyers at West Coast Employment Lawyers have extensive experience handling racial discrimination cases.
What is disparate treatment discrimination?
Disparate treatment occurs when a worker is treated differently than employees who do not have the same protected characteristics. These types of lawsuits normally involve arguments about the treatment of similarly situated employees differed from the plaintiffs’.
Proving a disparate treatment claim
In order to prove a claim of disparate treatment, you will need to be able to show enough evidence for the court to infer that discrimination occurred. This process is called establishing a prima facie case of discrimination.
What is a prima facie case?
Presenting a prima facie case will depend on the facts of what happened. If you have direct evidence of discrimination, you will have enough. In many cases, however, you will need to rely on circumstantial evidence. The Supreme Court of the United States has defined a four-part test for disparate treatment claims, including the following:
Proving pretext
After your employer presents evidence supporting a legitimate reason for his or her decision, you will then have to prove that the reason was a pretext for discrimination. You will need to present evidence that questions the employer’s reason.
What is disparate impact?
Disparate impact is unintentional discrimination, such as when a company’s policies are neutral but inadvertently result in discrimination against people in a protected class. On the other hand, disparate treatment is intentional discrimination and more obvious.
What is prima facie case?
1. Prima Facie Case. To prove disparate treatment, the employee (plaintiff) must first present a “prima facie” case, meaning that he must present evidence that discrimination has occurred. This evidence can be either direct evidence or indirect (circumstantial) evidence.
Is disparate treatment illegal?
If you think you are a victim of disparate treatment, it is important to understand your legal rights. Disparate treatment is illegal, but it takes a skilled employment law attorney to prove it. Contact us today to ensure that your rights are protected.

Definition of Disparate Treatment
What Is Disparate Treatment
- Disparate treatment is a claim of discrimination in which an individual complains to have been treated differently than other people in a similar situation, but who don’t share the individual’s protected class. Disparate treatment is a common element of proving employment discrimination, but it occurs in other areas of life as well, such as loan ap...
Disparate Treatment vs. Disparate Impact
- There are two ways in which a person may be treated differently, or “disparately,” for purposes of discrimination actions: (1) disparate treatment, and (2) disparate impact. The difference between the two has to do with intent and effect.
Proving A Disparate Treatment Complaint
- Proving a claim of disparate treatment does not require proof beyond doubt. Rather, it requires the individual complaining of discrimination (the “plaintiff”) to make a prima facie case, which means he has to provide sufficient evidence to the court that there is at least the appearanceof discrimination. The employer must then defend its actions, providing evidence of a reasonable, …
Disparate Treatment Example in Firefighter Promotions
- In 2003, the New Haven Connecticut Fire Department needed to fill 15 management positions, having 7 openings for Captain, and 8 openings for Lieutenant. Like most civil service organizations, hiring is done by a “Rule of Three,” in which a civil service examination is given, after which the department chooses from the three highest-scoring applicants on the list. The Ci…
Related Legal Terms and Issues
- Civil Lawsuit– A lawsuit brought about in court when one person claims to have suffered a loss due to the actions of another person.
- Defendant– A party against whom a lawsuit has been filed in civil court, or who has been accused of, or charged with, a crime or offense.
- Discrimination– The practice of unfairly treating different categories of people, especially on …
- Civil Lawsuit– A lawsuit brought about in court when one person claims to have suffered a loss due to the actions of another person.
- Defendant– A party against whom a lawsuit has been filed in civil court, or who has been accused of, or charged with, a crime or offense.
- Discrimination– The practice of unfairly treating different categories of people, especially on the grounds of ethnicity, national origin, gender, race, religion, and sexual orientation.
- Front Pay– Employment compensation for the period between judgement ordering reinstatement, and actual reinstatement. Front pay is, like back pay, an award of lost earnings.