
Gas Nitriding
- Nitriding and Metallurgical Behavior. Gas nitriding is a form of steel heat treatment in which one uses heat to diffuse nitrogen-rich gas onto the surface of the metal with the ...
- Gas vs. Liquid Nitriding. ...
- Nitriding vs. Carburizing. ...
- Advantages of Gas Nitriding. Low-cost compared with other case applications. ...
What are the main purposes of nitriding treatment?
The main purposes of nitriding treatment are: To get high hardness on the surface. Hardness achieved in nitriding is usually higher than carburizing method. To increase the wear resistance. To improve fatigue life and other fatigue-related properties. To improve the corrosion resistance of the material.
What are other hardening heat treatments competitive with nitriding?
Other hardening heat treatments competitive with nitriding are carburizing, nitrocarburizing and ferritic nitrocarburizing (FNC). Have You Seen These 18 Heat Treat Technical Resources?
What is the thermodynamics of nitriding?
A great deal of research has taken place in the last few decades to understand the thermodynamics and kinetics of the reactions taking place. Nitriding is a heat treating process that diffuses nitrogen into the surface of a metal to create a case hardened surface.
What is nitride hardening and how does it work?
The nitride hardening process integrates into the bulk material, allowing the portion of metal below the surface layer to remain soft. Ammonia is the most commonly used gas and it separates into nitrogen and hydrogen when it comes into contact with the metal.
What is the purpose of nitriding?
The main objectives of nitriding are to increase the surface hardness of the material, as well as its wear resistance, fatigue life, and corrosion resistance [30], which are achieved by the presence of the nitrided layer.
What type of process is nitriding?
Nitriding is a heat-treating process that diffuses nitrogen into the surface of a metal to create a case-hardened surface.
How is nitriding done?
Nitriding is usually done by heating steel objects in gaseous ammonia (NH3) at temperatures between 500 and 550 °C (950 and 1,050 °F) for periods of 5 to 100 hours, depending upon the desired depth of diffusion of the nitrogen.
What are the advantages of nitriding?
Advantages of Nitriding ProcessQuick processing time.Low-temperature process.Clean pollution-free operation.Economic and energy-efficient operation.Lower friction coefficient.Improved fatigue properties.Uniform surface.High surface hardness.More items...
Which gas is used in nitriding?
Gas nitriding uses ammonia or ammonia–hydrogen mixtures to enhance the nitrogen activity. Ammonia easily dissociates into gaseous nitrogen and hydrogen according to the chemical equilibrium.
What materials can be nitrided?
Aluminum, chromium, molybdenum, titanium, tungsten, and vanadium easily combine with nitrogen at high temperatures to form nitrides of the respective metals. Low-carbon alloys of steel containing these metals are typically good candidates for nitriding. The primary steel alloys used for nitriding include: -SAE 4130.
Why is nitriding done at low temperatures?
Low temperature nitriding (550°C) increases the fatigue strength of a titanium alloy due to the formation of the nitrogen diffusion layer without nitrogen compounds.
What is nitriding depth?
Typical nitrided case depths for steel are 0.010-0.020 inches (0.25-0.50 mm). Shallower or deeper case depths are possible. Significantly longer cycles are required for case depths about 0.020 inch due to the slow diffusion rate of nitrogen into steel.
Why Carburising is done?
Carburizing increases strength and wear resistance by diffusing carbon into the surface of the steel creating a case while retaining a substantially lesser hardness in the core. This treatment is applied to low carbon steels after machining.
What are advantages and limitations of nitriding process?
1) This process produce greater surface finish. 2) In nitriding process produces higher fatigue strength under corrosion condition. 3) Endurance limit is high under bending stresses. 4) In nitriding process hardness is better at elevated temperatures.
What does nitriding do to a metal?
Nitriding is a heat treating process that diffuses nitrogen into the surface of a metal to create a case-hardened surface. These processes are most commonly used on low-alloy steels.
Does nitriding add thickness?
During nitriding the volume of the component increases by 3% of the layer thickness.
What is nitriding heat treatment?
Nitriding heat treatment is one of several surface hardening heat treat processes. Nitriding diffuses nitrogen into the surface of certain metals creating a hard surface more resistant to wear and corrosion.
Who is the host of Heat Treat Radio?
Heat Treat Radio. Heat Treat Radio host, Doug Glenn, an interview that Doug Glenn conducted with Mark Hemsath, director of nitriding and special vacuum furnaces with SECO/Vacuum Technologies, where he oversees nitriding, including ferritic nitrocarburizing (FNC), and also other surface engineering such as carburizing.
What is nitriding furnace?
A modern computerised nitriding furnace. Nitriding is a heat treating process that diffuses nitrogen into the surface of a metal to create a case-hardened surface. These processes are most commonly used on low-alloy steels. They are also used on titanium, aluminium and molybdenum.
What is plasma nitriding?
Plasma nitriding, also known as ion nitriding, plasma ion nitriding or glow-discharge nitriding, is an industrial surface hardening treatment for metallic materials. In plasma nitriding, the reactivity of the nitriding media is not due to the temperature but to the gas ionized state.
What are some examples of nitridable steels?
Examples of easily nitridable steels include the SAE 4100, 4300, 5100, 6100, 8600, 8700, 9300 and 9800 series , UK aircraft quality steel grades BS 4S 106, BS 3S 132, 905M39 (EN41B), stainless steels, some tool steels (H13 and P20 for example) and certain cast irons. Ideally, steels for nitriding should be in the hardened and tempered condition, requiring nitriding to take place at a lower temperature than the last tempering temperature. A fine-turned or ground surface finish is best. Minimal amounts of material should be removed post nitriding to preserve the surface hardness.
What temperature does plasma nitriding work at?
Plasma nitriding can thus be performed in a broad temperature range, from 260 °C to more than 600 °C.
What is the donor gas in nitriding?
In gas nitriding the donor is a nitrogen-rich gas, usually ammonia (NH 3 ), which is why it is sometimes known as ammonia nitriding. When ammonia comes into contact with the heated work piece it dissociates into nitrogen and hydrogen. The nitrogen then diffuses onto the surface of the material creating a nitride layer.
What gas is used to clean nitrided parts?
Other gasses like hydrogen or Argon are also used. Indeed, Argon and H 2 can be used before the nitriding process during the heating of the parts to clean the surfaces to be nitrided. This cleaning procedure effectively removes the oxide layer from surfaces and may remove fine layers of solvents that could remain.
What is the best way to nitride steel?
Ideally, steels for nitriding should be in the hardened and tempered condition, requiring nitriding to take place at a lower temperature than the last tempering temperature. A fine-turned or ground surface finish is best. Minimal amounts of material should be removed post nitriding to preserve the surface hardness.
How does nitriding work?
Nitriding - How it works? Nitriding is a case hardening processthat depends on the absorption of nitrogen into the steel. All machining, stress relieving, as well as hardening and tempering are normally carried out before nitriding. The parts are heated in a special container through which ammonia gas is allowed to pass.
What is nitriding in metal?
Nitriding | Metallurgy for Dummies. Nitriding is a case hardening process that depends on the absorption of nitrogen into the steel. All machining, stress relieving, as well as hardening and tempering are normally carried out before nitriding. The parts are heated in a special container through which ammonia gas is allowed to pass.
What temperature does plasma nitriding work at?
Plasma nitriding can thus be performed in a broad temperature range, from 260°C to more than 600°C.
What is the difference between ammonia and nitride?
The ammonia splits into hydrogen and nitrogen and the nitrogen reacts with the steel penetrating the surface to form nitrides. Nitriding steels offer many advantages: a much higher surface hardness is obtainable when compared with case-hardening steels; they are extremely resistant to abrasion and have a high fatigue strength.
What are the advantages of gas nitriding?
The advantages of gas nitriding over the other variants are: All round nitriding effect (can be a disadvantage in some cases, compared with plasma nitriding) Large batch sizes possible - the limiting factor being furnace size and gas flow.
What gas is used in plasma nitriding?
In plasma nitriding processes nitrogen gas (N2) is usually the nitrogen carrying gas. Other gasses like hydrogen or Argon are also used. Indeed, Argon and H2 can be used before the nitriding process during the heating up of the parts in order to clean the surfaces to be nitrided.
What is salt bath nitriding?
Salt Bath Nitriding. Nitriding is a heat treating process that diffuses nitrogen into the surface of a metal to create a case hardened surface. It is predominantly used on steel, but also titanium, ...
What is nitriding in metals?
Nitriding is a heat-treating process that diffuses nitrogen into the surface of a metal to create a case-hardened surface.
Does nitriding affect core properties?
Core properties are not affected by the nitriding process provided the final tempering temperature for the product was higher than the nitriding process temperature. Nitride surfaces are highly wear resistant and provide anti-galling properties.
How does nitriding work?
Gas nitriding disperses gas to the metal via heat in a furnace or sealed atmosphere. Liquid nitriding uses a cyanide salt mixture in a bath. The heat requirements for liquid are lower than for the gas technique, and the hardened compound on the surface of the component is thicker.
What is nitriding metal?
Gas nitriding is a form of steel heat treatment in which one uses heat to diffuse nitrogen-rich gas onto the surface of the metal with the intention of hardening it. The nitride hardening process integrates into the bulk material, allowing the portion of metal below the surface layer to remain soft.
Why is nitride hardening used in construction?
The nitride hardening process is used on the main components of construction machinery because of the sliding properties it provides, preventing scuffs and dents. Refining the process by understanding the kinetics involved has resulted in achieving a thicker hardened layer and exploring a broader range of use applications.
What is the process of hardening nitride?
The nitride hardening process integrates into the bulk material, allowing the portion of metal below the surface layer to remain soft. Ammonia is the most commonly used gas and it separates into nitrogen and hydrogen when it comes into contact with the metal. Only the nitrogen diffuses onto the surface to form the nitride layer.
When was nitriding first used?
The United States began developing nitriding processes in the early 1900’s , but there was little interest for industrial uses until after World War II. In applications that require improved fatigue strength and precision, such as in extrusion screws and precision gears, gas nitriding is most appropriate.
Does nitrogen diffuse onto the surface?
Only the nitrogen diffuses onto the surface to form the nitride layer. Quenching methods (such as oil quenching) is not required, and the metal’s core properties are not affected.
What is nitriding surface treatment?
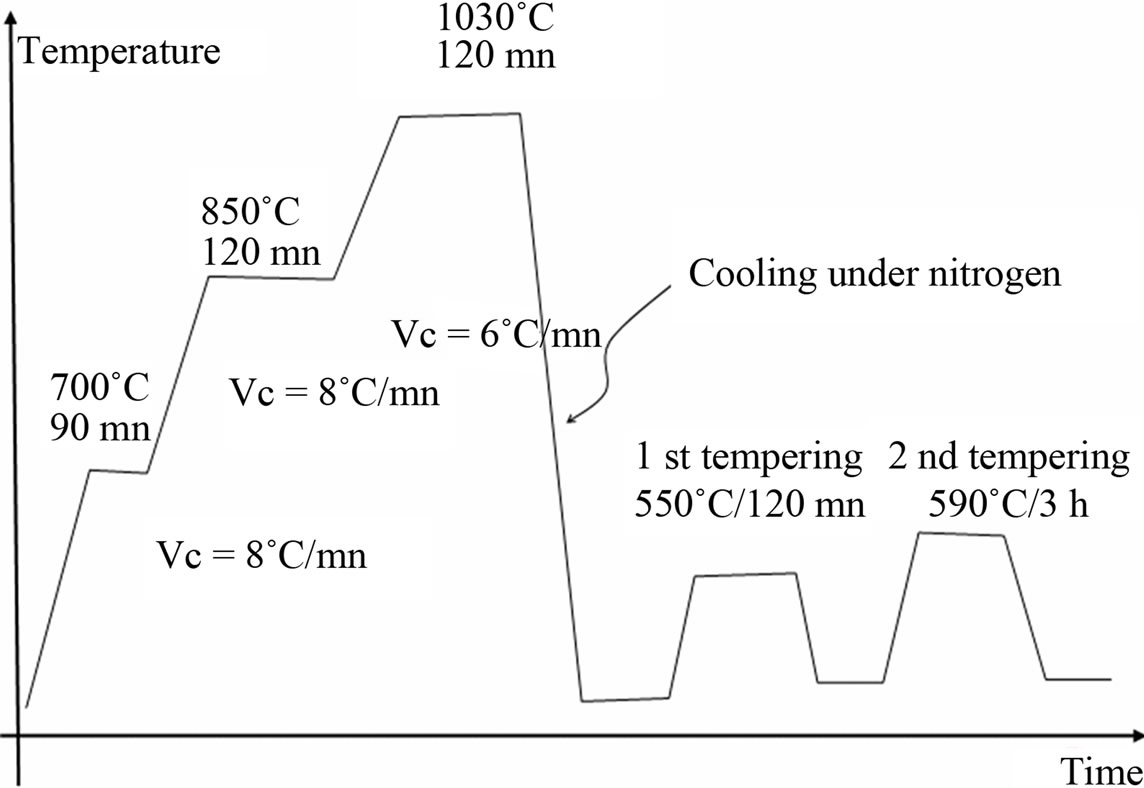
Nitriding is a diffusion-related surface treatment (Fig. 3) with the objective to increase surface hardness (among other properties) by the creation of a case on the surface of the part (Fig. 4).#N#One of the appeals of this process is that rapid quenching is not required. Therefore, dimensional changes are kept to a minimum. It is not suitable for all applications. For example, one of its limitations is that the extremely high surface-hardness case is more brittle than that produced by the carburizing process.#N#A typical manufacturing sequence for gas nitriding (Fig. 5) consists of several heat-treatment steps, including pre-treatments and (optionally) stress relief between machining steps.#N#Nitriding creates a component that has the following properties: 1 High surface hardness (typically > 67 HRC) 2 Resistance to wear 3 Anti-galling properties (for applications in poor lubrication conditions) 4 A minimum of distortion and deformation (less than, for example, carburizing/hardening) 5 Resistance to tempering (that is, resistant to softening) 6 Stability of the nitrided case 7 Improved fatigue life and other fatigue-related properties 8 Reduction in notch sensitivity 9 Resistance to corrosion (except for 300- series stainless steels) 10 Small volumetric changes (some growth does occur)
What is nitriding in stainless steel?
Nitriding is a (relatively) low-temperature process compared to other case-hardening processes (Fig. 2).
What color is nitrided ammonia?
Parts gas nitrided in ammonia should have a dull, matte-gray color (Fig. 11). Structure of the Nitrided Case. In the nitriding process, the nitrogen that diffuses into the steel reacts with the nitride-forming elements present in solid solution. The hardening results from the reaction.
What is the process of nitrogen being introduced into the surface of a ferrous alloy?
Nitriding is a case-hardening process in which nitrogen is introduced into the surface of a ferrous alloy such as steel by holding the metal at a temperature below that at which the crystal structure begins to transform to austenite on heating as defined by the Iron-Carbon Phase Diagram.
Why should steel be hardened before nitriding?
First, the steel should be hardened, quenched and tempered prior to nitriding so as to possess a uniform structure. Tempering temperature has an influence on the hardness of the case as well as the depth of nitriding (Fig. 9).
What does it mean when nitrided parts are shiny?
If nitrided parts exhibit a shiny-gray surface after their removal from the furnace, the results should be viewed with suspicion. Invariably, the case will be shallow and below hardness. The parts should have a matte-gray appearance, although a slight discoloration does not indicate faulty nitriding.
What temperature should steel be before nitriding?
All hardenable steels must be hardened and tempered before being nitrided. The minimum tempering temperature is usually at least 50°F higher than the maximum temperature to be used in nitriding. Typical tempers range from 1150-1350°F (620-730°C).
What is nitriding used for?
Nitriding is generally employed to Steel parts which are moving like engine parts such a cylinder, crankshaft, etc. 6. Cyaniding: Cyaniding is also a surface hardening process in which the heated parts to be surface hardened are immersed in a bath of molten sodium or potassium cyanide.
Why is heat treatment important?
It is very important manufacturing process that can not only help the manufacturing process but can also improve the product, its performance, and its characteristics in many ways. By Heat Treatment process, Example: The plain carbon steel. The following changes may be achieved: The hardness of Steel may be increased or decreased.
What is the purpose of hardening steel?
Hardening is carried to accomplish the following: To reduce the grain size. Obtain maximum hardness.
What is recrystallization in steel?
This causes complete recrystallization in steel to form New grain structure. This will release the internal stresses previously the strip in the steel and improve the machinability.
What is normalizing carried for accomplishing?
Normalizing carried for accomplishing one or more of the following: To refine the grain size. Reduce or remove internal stresses. Improve the machinability of low carbon steel. Increase the strength of medium carbon steel. And also To improve the mechanical properties of the medium Carbon Steel.
What is normalizing steel?
Normalizing is a heat treatment process similar to annealing in which the Steel is heated to about 50 degree Celsius above the upper critical temperature followed by air cooling. This results in a softer state which will be lesser soft than that produced by annealing.
What happens when ammonia is in contact with steel?
During this process, when Ammonia comes in contact with steel is diffuses into nascent hydrogen and nascent nitrogen. This nascent nitrogen so produced diffuses into the surface of the workpiece forming hard nitrites which increase surface hardness.
Overview
Processes
The processes are named after the medium used to donate. The three main methods used are: gas nitriding, salt bath nitriding, and plasma nitriding.
In gas nitriding the donor is a nitrogen-rich gas, usually ammonia (NH3), which is why it is sometimes known as ammonia nitriding. When ammonia comes into contact with the heated work piece it dissociates into nitrogen and hydrogen. The nitrogen then diffuses onto the surfac…
Materials for nitriding
Examples of easily nitridable steels include the SAE 4100, 4300, 5100, 6100, 8600, 8700, 9300 and 9800 series, UK aircraft quality steel grades BS 4S 106, BS 3S 132, 905M39 (EN41B), stainless steels, some tool steels (H13 and P20 for example) and certain cast irons. Ideally, steels for nitriding should be in the hardened and tempered condition, requiring nitriding to take place at a lower temperature than the last tempering temperature. A fine-turned or ground surface finish i…
History
Systematic investigation into the effect of nitrogen on the surface properties of steel began in the 1920s. Investigation into gas nitriding began independently in both Germany and America. The process was greeted with enthusiasm in Germany and several steel grades were developed with nitriding in mind: the so-called nitriding steels. The reception in America was less impressive. With so little demand the process was largely forgotten in the US. After WWII the process was reintro…
See also
• Boriding
• Carburization
• Carbonitriding
• Ferritic nitrocarburizing
• Surface finishing
Further reading
• Chatterjee-Fischer, Ruth (1995). Wärmebehandlung von Eisenwerkstoffen: Nitrieren und Nitrocarburieren [Heat treatment of ferrous materials: nitriding and nitrocarburising] (in German) (2nd ed.). Expert-Verlag. ISBN 3-8169-1092-0.
• Chattopadhyay, Ramnarayan (2004). "Plasma Nitriding". Advanced Thermally Assisted Surface Engineering Processes. Berlin: Springer. pp. 90–94. ISBN 1-4020-7696-7.
External links
• "MIL-S-6090A, Military Specification: Process for Steels Used In Aircraft Carburizing and Nitriding". United States Department of Defense. 7 Jun 1971. Archived from the original on 29 August 2019. Retrieved 20 June 2012.
• An Introduction to Nitriding
1. ^ Pye, David. "The Heat Treatment Library". pye-d.com. Archived from the original on 2017-01-11…