What does NIDDM stand for?
1. Guava...
2. Apples...
3. Cherries...
4. Grapefruit...
5. Gokhru...
6. Avocado...
7. Strawberries...
8. Oranges...
Learn More...What is the initial management of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM)?
Meaning of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM) medical term. What does non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM) mean? Non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM) | definition of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM) by Medical dictionary
What is the treatment for Type 1 diabetes mellitus (DM)?
The initial management of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM) should include patient education, dietary counselling and, when feasible, individualised physical activity. It is only when such measures fail that drug therapy should be considered.
What is insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM)?
Patients with type 1 DM, unless they have had a pancreatic transplant, require insulin to live; intensive therapy with insulin to limit hyperglycemia (“tight control”) is more effective than conventional therapy in preventing the progression of serious microvascular complications such as kidney and retinal diseases.

What is the drug of choice for NIDDM?
Most widely used oral combination is sulphonylurea with metformin.
Is NIDDM the same as type 2 diabetes?
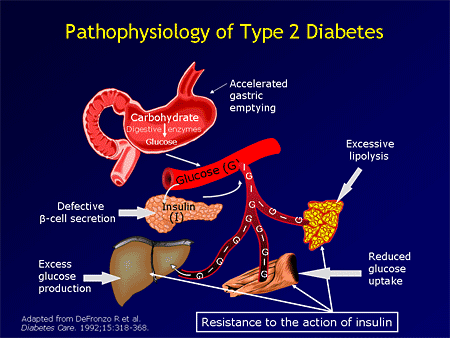
Non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM), also known as type II diabetes, is characterized by abnormal glucose homeostasis, resulting in hyperglycemia, and is associated with microvascular, macrovascular, and neuropathic complications. NIDDM is a complex disease with many causes.
What is the main treatment for type 2 diabetes?
Metformin (Fortamet, Glumetza, others) is generally the first medication prescribed for type 2 diabetes. It works primarily by lowering glucose production in the liver and improving your body's sensitivity to insulin so that your body uses insulin more effectively.
What NIDDM means?
Type II (Non-Insulin Dependent) Diabetes (NIDDM)
What causes NIDDM?
Abstract. Non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM) results from an imbalance between insulin sensitivity and insulin secretion. Both longitudinal and cross-sectional studies have demonstrated that the earliest detectable abnormality in NIDDM is an impairment in the body's ability to respond to insulin.
Is NIDDM genetic?
The latter can be identified because there is a strong genetic determinant for NIDDM; the offspring of two diabetic parents have a markedly increased incidence of the disease. In addition to genetic factors, environmental components contribute to the multifactorial etiology of NIDDM.
What is better than metformin for type 2 diabetes?
Insulin remains the most effective therapy to lower glucose, particularly in comparison to most oral medicines for type 2 (including metformin).
What is the best insulin for type 2 diabetes?
According to the ADA/EASD algorithm for the management of type 2 diabetes, insulin could be initiated with either once-daily NPH insulin or a long-acting insulin analog (5). For several reasons, we consider NPH insulin the preferred option.
How can type 2 diabetes be cured permanently?
According to recent research, type 2 diabetes cannot be cured, but individuals can have glucose levels that return to non-diabetes range, (complete remission) or pre-diabetes glucose level (partial remission) The primary means by which people with type 2 diabetes achieve remission is by losing significant amounts of ...
Which type diabetes is worse 1 or 2?
Type 2 diabetes is often milder than type 1. But it can still cause major health complications, especially in the tiny blood vessels in your kidneys, nerves, and eyes. Type 2 also raises your risk of heart disease and stroke.
What are the basic differences between IDDM and NIDDM?
In the NIDDM, hyperglycemia arises from the loss of normal tissue sensitivity to insulin (also known as insulin resistance). In IDDM, hyperglycemia arises from insufficient production of insulin from pancreatic cells due to autoimmunity. The two types differ also in the management of the disease and its complications.
What is the difference between type1 and type2 diabetes?
People with type 1 diabetes don't produce insulin. You can think of it as not having a key. People with type 2 diabetes don't respond to insulin as well as they should and later in the disease often don't make enough insulin. You can think of it as having a broken key.
What is the treatment for NIDDM?
Oral drug therapies used in NIDDM include sulphonylurea derivatives, which are a first-line treatment in patients who are not grossly obese, metformin, which is the treatment of choice for obese patients, and alpha-glucosidase inhibitors such as acarbose, which are used mainly to reduce postprandial blood glucose peaks.
What is the initial management of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus?
The initial management of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM) should include patient education, dietary counselling and, when feasible, individualised physical activity. It is only when such measures fail that drug therapy should be considered. Dietary management of NIDDM includes a restriction in calories, ...
What is the diet for NIDDM?
Dietary management of NIDDM includes a restriction in calories, and these should be appropriately distributed as carbohydrates, lipids and proteins. Supplementation of the diet with soluble fibre and supplementation with magnesium salts if hypomagnesaemia is demonstrated, is recommended .
What is the immune system in diabetes?
In Type I diabetes, the immune system, the body's defense system against infection, is believed to be triggered by a virus or another microorganism that destroys cells in the pancreas that produce insulin. In Type II diabetes, age, obesity, and family history of diabetes play a role.
What is brittle diabetic?
Brittle diabetics are a subgroup of Type I where patients have frequent and rapid swings of blood sugar levels between hyperglycemia (a condition where there is too much glucose or sugar in the blood) and hypoglycemia (a condition where there are abnormally low levels of glucose or sugar in the blood).
Why does diabetes mellitus cause visual disturbance?
Another manifestation of diabetes mellitus is visual disturbance due to increased osmolarity of the blood and accumulation of fluid in the eyeball, which changes its shape. Once the diabetes is under control, visual problems should abate.
What is the term for a condition in which the pancreas no longer produces enough insulin?
Definition. Diabetes mellitus is a condition in which the pancreas no longer produces enough insulin or cells stop responding to the insulin that is produced, so that glucose in the blood cannot be absorbed into the cells of the body. Symptoms include frequent urination, lethargy, excessive thirst, and hunger.
What are the risks of diabetes mellitus?
Individuals who are at high risk of developing Type II diabetes mellitus include people who: 1 are obese (more than 20% above their ideal body weight) 2 have a relative with diabetes mellitus 3 belong to a high-risk ethnic population (African-American, Native American, Hispanic, or Native Hawaiian) 4 have been diagnosed with gestational diabetes or have delivered a baby weighing more than 9 lbs (4 kg) 5 have high blood pressure (140/90 mmHg or above) 6 have a high density lipoprotein cholesterol level less than or equal to 35 mg/dL and/or a triglyceride level greater than or equal to 250 mg/dL 7 have had impaired glucose tolerance or impaired fasting glucose on previous testing
How much did gestational diabetes increase in 2004?
In 2004, incidence of gestational diabetes were reported to have increased 35% in 10 years. Children of women with gestational diabetes are more likely to be born prematurely, have hypoglycemia, or have severe jaundice at birth. The condition usually is treated by diet, however, insulin injections may be required.
What medications cause diabetes?
Other medications that can cause diabetes symptoms include isoniazid, nicotinic acid, cimetidine, and heparin. A 2004 study found that low levels of the essential mineral chromium in the body may be linked to increased risk for diseases associated with insulin resistance.
How is Type 1 diabetes treated?
Type 1 is treated by insulin while Type 2 can be controlled with a healthy lifestyle or maybe insulin in some cases. 4. People who have Type 1 diabetes are usually thin or have normal weight while people having. Type 2 diabetes are usually overweight. 5.
What is the function of insulin in diabetes mellitus?
Insulin helps lower blood glucose levels.
What is the difference between Type 1 diabetes and Type 2 diabetes?
In Type 1 diabetes, previously called insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM for short) and juvenile-onset diabetes, the body may either produce insulin in very small amounts or it may not produce insulin at all. While in Type 2 diabetes, formerly known as non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM for short) and adult-onset diabetes, ...
Why is insulin important for diabetes?
Insulin helps lower blood glucose levels. When the blood glucose increases, insulin is released from the pancreas to normalize the glucose level. In patients with diabetes, the absence or inadequate production of insulin gives rise to hyperglycemia. Diabetes is considered to be a chronic medical condition; it simply means ...
What happens if you have Type 1 diabetes?
Type 1 diabetes can result in diabetic coma, a state of unconsciousness caused by extremely high levels of glucose in the blood, or even death. In both Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes, complications may include blindness, kidney failure, and heart disease. Diabetes mellitus is classified into two different types.
What are the symptoms of diabetes type 2?
Symptoms characteristic of Type 2 diabetes include those found in Type 1 diabetes as well as repeated infections or skin sores that heal slowly or not at all, generalized tiredness, and tingling or numbness in the hands or feet. Symptoms of Type 2 diabetes usually develop much more slowly and may be subtle or absent.
What are the factors that contribute to the development of diabetes?
Environmental factors, such as certain viruses, may also contribute to the development of the disease specifically in people who already have a genetic predisposition for the disease. Type 1 diabetes may also result from surgical removal of the pancreas.
