
What are the benefits of life-prolonging treatments?
Benefits of life-prolonging treatments The benefits of a life-prolonging treatment might include living longer and improving the quality of your life. But everyone is different and the likelihood of success will depend on your particular medical circumstances. Potential burdens of life-prolonging treatments
What is a life-prolonging procedure?
Life Prolonging Procedure. Any medical procedure, treatment, or intervention which. (1) Uses mechanical or other artificial means to sustain, restore, or supplant a spontaneous vital function, or which affords no reasonable expectation of recovery from a terminal condition and.
What is Life-Sustaining Treatment?
Your health care provider may tell you that these organs will not repair themselves. Medical care to prolong life can keep you alive when these organs stop working well. The treatments extend your life, but do not cure your illness. These are called life-sustaining treatments.
What are some treatments that can help you live longer?
Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) to try to restart your heart. The decision to receive treatments that may help you live longer is a personal one. You may want your doctor to do everything possible to keep you alive, even when your chance for recovery is small.

What does prolonging life mean?
Your health care provider may tell you that these organs will not repair themselves. Medical care to prolong life can keep you alive when these organs stop working well. The treatments may extend your life, but do not cure your illness. These are called life-sustaining treatments.
What happen if life sustaining treatments are continued?
What happens if life-sustaining treatments are continued? These treatments can help extend your life. But they will not cure your illness. If you are near the end of your life, you may find it hard to handle the side effects and problems that can occur with these treatments.
When do doctors stop life support?
If they are not taking in any fluids, they will usually die within several days of a feeding tube removal, though they may survive for as long as a week or two. When someone is unconscious or not of sound mind, doctors and family members decide when life support measures should stop.
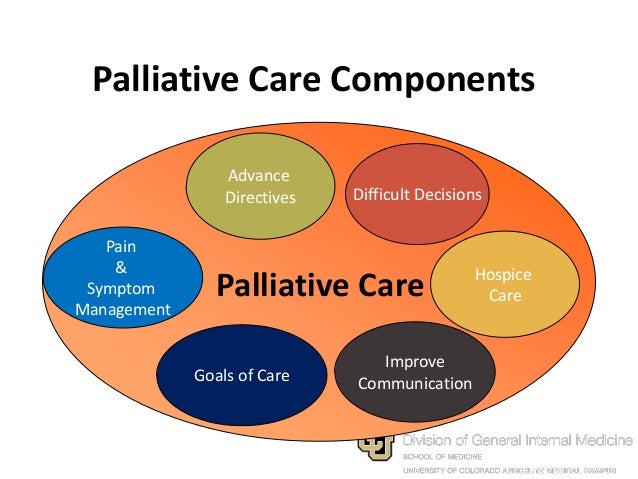
How is palliative care given?
Palliative care is most often given to the patient in the home as an outpatient, or during a short-term hospital admission. Even though the palliative care team is often based in a hospital or clinic, it's becoming more common for it to be based in the outpatient setting.
What are examples of life-sustaining treatments?
Patients may consider many life-sustaining treatments; in addition to cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR), options include elective intubation, mechanical ventilation, surgery, dialysis, blood transfusions, artificial nutrition and hydration, diagnostic tests, antibiotics, other medications and treatments, as well as ...
Can a patient request life-sustaining treatment?
As contentious as this case was, however, certain principles were reinforced: patients have the right to refuse life‐sustaining medical treatment, even if incapacitated; and if a patient has expressed those wishes clearly, then a guardian may act according to those wishes.
Can someone on life support hear you?
They do hear you, so speak clearly and lovingly to your loved one. Patients from Critical Care Units frequently report clearly remembering hearing loved one's talking to them during their hospitalization in the Critical Care Unit while on "life support" or ventilators.
Is ventilator life support?
It is also used to support breathing during surgery. Ventilators, also known as life-support machines, won't cure an illness, but they can keep patients alive while they fight an infection or their body heals from an injury.
What is the final stage of dying?
Active dying is the final phase of the dying process. While the pre-active stage lasts for about three weeks, the active stage of dying lasts roughly three days. By definition, actively dying patients are very close to death, and exhibit many signs and symptoms of near-death.
Does palliative care mean end of life?
Does Palliative Care Mean You are Dying? No, palliative care does not mean death. However, palliative care does serve many people with life-threatening or terminal illnesses. But, palliative care also helps patients stay on track with their health care goals.
What are the 5 stages of palliative care?
Palliative Care: Includes, prevention, early identification, comprehensive assessment, and management of physical issues, including pain and other distressing symptoms, psychological distress, spiritual distress, and social needs. Whenever possible, these interventions must be evidence based.
Why do doctors recommend palliative care?
It provides relief from the symptoms and stress of a serious illness. The goal is to improve quality of life for both the patient and the family. Palliative care is provided by a specially-trained team who work together with your other doctors to provide an extra layer of support.
What happens if you stop treatment?
If these don't work, then you might think about stopping treatment. If you stop treatment, you will still receive care that focuses on pain relief and comfort.
What is the purpose of antibiotics?
Antibiotics to treat serious infections, such as pneumonia.
Why do we need antibiotics?
Medicines to slow the progress of certain diseases, such as heart disease, diabetes, cancer, AIDS, or Alzheimer's disease. Antibiotics to treat serious infections, such as pneumonia.
Is your chance of surviving your illness low?
Your chance of surviving your illness is very low. You have tried all possible treatments for your illness, but they have not helped. You can no longer deal with the side effects of treatment. You have already met the goals you set out to achieve in your life.
Can you stop treatment that keeps you alive?
A decision to stop treatment that keeps you alive does not have to be permanent. You can always change your mind if your health starts to improve. Even though treatment focuses on helping you live longer, it may cause side effects that can greatly affect your quality of life.
Can you cure an illness?
There is a good chance that your illness can be cured or managed. You think you can manage the possible side effects of treatment. You don't think treatment will get in the way of your quality of life. You have personal goals that you still want to pursue and achieve.
What to do when you are near the end of your life?
Making the Decision for Yourself. If you are near the end of your life or you have an illness that will not improve, you can choose what kind of treatment you want to receive. You should know that the illness or the injury is the main cause of the end of life, not the removal of life support equipment. Talk to your providers to learn about life ...
What happens to the organs after injury?
Sometimes after injury or a long illness, the main organs of the body no longer work properly without support. Your health care provider may tell you that these organs will not repair themselves.
Can you cancel an advanced care directive?
As your life or health changes, you may also change your health care decisions. You can change or cancel an advanced care directive at any time.
What is aggressive medical treatment?
Aggressive Medical Treatment: A range of treatments which use complex, invasive methods to prolong a person’s life, such as CPR, ventilation, or dialysis. Commonly asked in end of life situations: “Shall we continue aggressive treatments or shall we change to comfort care?”
What do people need to know about the end of life?
In order to make good decisions, people nearing the end of life and their families need to know what their choices are. Many of the ideas and terms explained here might be new to you but are very common in medical settings and are important for you to know. There are some difficult issues involved in making end-of-life decisions.
How long after CPR can you stop?
For this reason, many doctors believe that after 30 minutes without a positive response, CPR should be stopped. In Hawaii, if you do not want CPR at the end of life: Discuss your wishes with your doctor and family and document them in your advance directive.
What is comfort care?
The goal of comfort care is to give the best quality of life for the person and family during the time of illness, dying, and grieving. Other terms for comfort care that you may have heard are “ palliative care ,” “ hospice care ,” or “supportive care.”.
When is CPR useful?
When cardiac arrest occurs in young or otherwise healthy people, CPR is often life saving. CPR is thought to be useful when the chance of getting better is very good.
Does modern medicine have limits?
Although modern medicine helps many people lead longer and healthier lives, it has limits . Many of us may fear that medical technology could help us to live longer but leave us dependent on others, unable to think or make decisions for ourselves, and in great pain.
Who brings different viewpoints to end of life decisions?
Last, but not least, family, friends, and spiritual leaders all bring important but different viewpoints to end-of-life decisions.
What is life prolonging treatment?
What is life-prolonging treatment? There are many kinds of treatment that can help you live longer. These may be needed for only a short time until your illness improves. Or you may use them over the long term to help keep you alive.
What are some ways to slow the progression of a disease?
Medicines to slow the progress of certain diseases, such as heart disease, diabetes, cancer, AIDS, or Alzheimer's disease. Antibiotics to treat serious infections, such as pneumonia. Dialysis to clean your blood if your kidneys stop working. A breathing machine to help you breathe if you can't breathe on your own.
What does "health encyclopedia" mean?
Your use of this information means that you agree to the Terms of Use and Privacy Policy. The Health Encyclopedia contains general health information. Not all treatments or services described are covered benefits for Kaiser Permanente members or offered as services by Kaiser Permanente.
What happens if you stop treatment?
If these don't work, then you might think about stopping treatment. If you stop treatment, you will still receive care that focuses on pain relief and comfort.
Can you cure an illness?
There is a good chance that your illness can be cured or managed. You think you can manage the possible side effects of treatment. You don't think treatment will get in the way of your quality of life. You have personal goals that you still want to pursue and achieve.
Can you stop treatment that keeps you alive?
A decision to stop treatment that keeps you alive does not have to be permanent. You can always change your mind if your health starts to improve. Even though treatment focuses on helping you live longer, it may cause side effects that can greatly affect your quality of life.
Is your chance of surviving your illness low?
Your chance of surviving your illness is very low. You have tried all possible treatments for your illness, but they have not helped. You can no longer deal with the side effects of treatment. You have already met the goals you set out to achieve in your life.
What is the best outcome we can expect for a patient?
If the best outcome we can expect for a patient is to be bedridden, institutionalized and dependent for all activities , we need to be certain that that is an outcome acceptable to that person . The important priority is the patient’s values and preferences; the simple objective of survival is not a sufficient goal.
How long do syringes stay in purgatory?
They are often consigned for weeks or even months to a sort of medical purgatory, attached by tubes in their tracheas to ventilators, with catheters protruding from their necks, chests, abdomens or bladders.
Do intensivists rotate in and out of service?
Unfortunately, intensivists who rotate in and out of service on a weekly basis only to be confronted with a critically ill patient on a ventilator and other forms of life support do not have this understanding about the patient or the relationships that we have developed.
Do we need to consider the patient's quality of life when making decisions about ongoing care in desperately ill patients?
You are quite right in that we must consider the patient’s quality of life when making decisions about ongoing care in desperately ill patients. This highlights the need to understand the patient’s as well as family’s wishes in these difficult circumstances.
Can an ICU practitioner duplicate a relationship with a patient?
The ICU practitioner by definition can’t duplicate the type of relationship that a patient may have with their surgeon — relationships that in some cases go back decades — and thus knows the patient less well as a person. In fact we often depend on the surgeon, as well as the patient’s family, to help us understand the patient’s goals and values, to understand what they were like before they became critically ill and unable to speak for themselves.
What is life sustaining treatment?
These are called life-sustaining treatments. They include: dialysis – where a machine takes over the kidneys' functions. Eventually, with terminal illness, there may come a time when it's clear there's no prospect of recovery and that life-sustaining treatments are prolonging the dying process.
Can terminal illness be cured?
Eventually, with terminal illness, there may come a time when it's clear there's no prospect of recovery and that life-sustaining treatments are prolonging the dying process.
When should a physician elicit patient goals of care?
Physicians should elicit patient goals of care and preferences regarding life-sustaining interventions early in the course of care, including the patient’s surrogate in that discussion whenever possible.
What is the best professional judgment of a surrogate?
In the physician’s best professional judgment a decision by the patient’s surrogate clearly violates the patient’s previously expressed values, goals for care, or treatment preferences, or is not in the patient’s medical interest.
Is there an ethical difference between withholding and withdrawing treatment?
While there may be an emotional difference between not initiating an intervention at all and discontinuing it later in the course of care, there is no ethical difference between withholding and withdrawing treatment.
Is it ethical to withhold life sustaining interventions?
Decisions to withhold or withdraw life-sustaining interventions can be ethically and emotionally challenging to all involved. However, a patient who has decision-making capacity appropriate to the decision at hand has the right to decline any medical intervention or ask that an intervention be stopped, even when that decision is expected to lead ...
Questions
What Is Comfort Care?
Medical Conditions
Medical Technologies
What About The Costs?
What Is CPR?
- Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) is the use of life-saving measures when the person stops breathing. CPR can involve applying strong pressure to the chest and mouth-to-mouth resuscitation to someone who is having a cardiac or respiratory arrest. CPR may also include airway intubation, mechanical ventilation, electric shock (defibrillation), and ...
What Is Tube-Feeding?