Medication
Treatment methods above for Stage A apply. All patients should take an angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor (ACE inhibitor) and beta-blocker. Diuretics (water pills) and digoxin may be ...
Procedures
· This may be achieved with: atenolol (Tenormin) bisoprolol (Zebeta) carvedilol (Coreg) esmolol (Brevibloc) metoprolol (Lopressor) nadolol (Corgard) nebivolol (Bystolic)
Nutrition
· Take medications as directed and see their doctor for regular checkups to stay on top of the disease. Get cardiac rehabilitation early and exercise regularly thereafter. Exercise has clearly been shown to decrease symptoms, optimize physical conditioning around an imperfect heart and prolong life.
What medications is prescribed to treat CHF?
· In the initial evaluation of patients with heart failure, physicians should locate structural and functional cardiac abnormalities and identify disorders and behaviors that could cause the disease...
What is life expectancy for Real with CHF?
What are examples of diuretics used in CHF therapy? Furosemide (Lasix) Hydrochlorothiazide First line therapy for both systolic and diastolic failure. Used in treatment of heart failure before digitalis and other drugs are considered. What drug classes are used to improve symptoms in heart failure? Cardiac glycosides Dopamine antagonists
What are the differences between COPD vs CHF?
The goal of drug therapy in patients with diastolic dysfunction is to control symptoms by reducing ventricular filling pressure without reducing cardiac output. Diuretic drugs and nitrates are the drugs of choice for symptomatic patients. Calcium channel blockers, β-blockers and ACE inhibitors may be of benefit.
What to expect as end stage CHF?
· These include: 7 ACE inhibitors: Lotensin (benazepril), Valsotec (enalapril), and others Beta blockers: Monocor (bisoprolol), Toprol-XL (metoprolol succinate), and Coreg (carvedilol) Angiotensin receptor blockers: Diovan (valsartan), Avapro (irbesartan), and others Aldactone (spironolactone) BiDil ...
What are 1st line pharmacological treatments for heart failure?
First-line therapies for heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) ACE inhibitors (ACEIs), ARBs, beta-blockers, MRAs and diuretics form the basis of first-line pharmacological management of left ventricular systolic heart failure (HFrEF).
What is the primary treatment for heart failure?
Doctors usually treat heart failure with a combination of medications. Depending on your symptoms, you might take one or more medications, including: Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors. These drugs relax blood vessels to lower blood pressure, improve blood flow and decrease the strain on the heart.
Which treatment is used for CHF?
According to Jones, the types of medications typically prescribed include these: Vasodilators expand blood vessels, ease blood flow, and reduce blood pressure. Diuretics correct fluid retention. Aldosterone inhibitors help with fluid retention and improve chances of living longer.
What are the four stages of CHF?
There are four heart failure stages (Stage A, B, C and D)....There are many possible symptoms of heart failure. The most common are:Shortness of breath.Feeling tired (fatigue).Less able to exercise.Weak legs.Waking up to urinate.Swollen feet, ankles, lower legs and abdomen (edema).
Why are ACE inhibitors used in heart failure?
Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors are widely used in the treatment of heart failure. These agents decrease the formation of angiotensin II, thereby decreasing both arteriolar and venous resistance.
Stage A
Stage A is considered the first stage of CHF. Technically, people in this stage are considered “pre-heart failure.” 1 This means that you are at higher risk of developing CHF because of your family history, personal health history, and lifestyle choices.
Stage B
Stage B is the second stage of heart failure, but it’s still considered pre-heart failure. You don’t have symptoms of heart failure, but you may have been diagnosed with systolic left ventricular dysfunction, which is reduced power in the left ventricle of your heart.
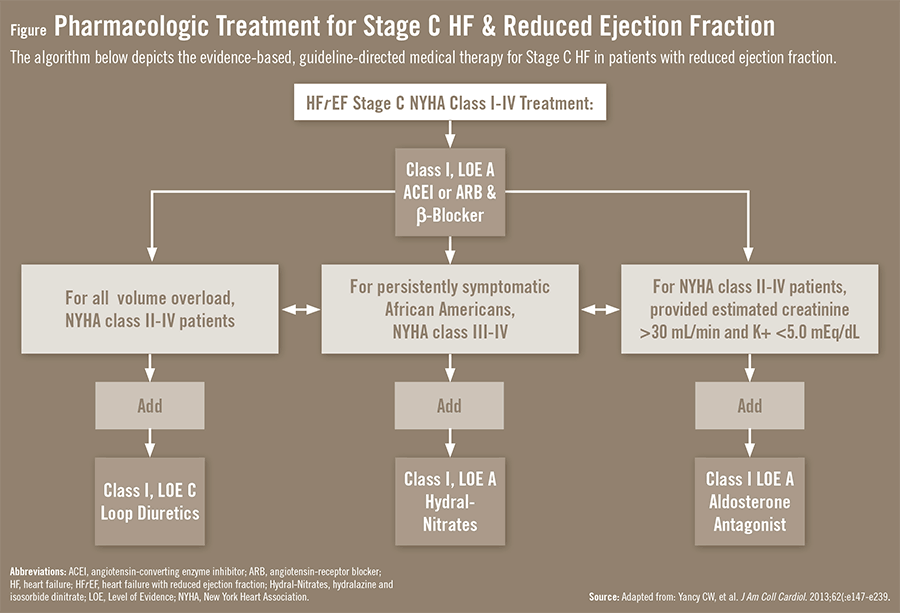
Stage C
Stage C is the first significant stage of heart failure in terms of how you feel. At this stage, you have been officially diagnosed with heart failure and have or had symptoms. Symptoms in this stage include: 2
Stage D
Stage D is advanced or severe heart failure. At this point, medications and other treatments don’t offer much relief from symptoms. Your symptoms are similar to those in stage C, but more severe. It may be difficult to do much physically without becoming severely tired or out of breath. 1
Prevention
Heart failure is a chronic, progressive disease. Once you have reached a certain stage, you may be able to slow its progression, but you can’t undo damage that has already been done to the heart. For this reason, prevention is a key strategy, especially for people with risk factors of CHF.
Frequently Asked Questions
In the end stages of heart failure, most physical activities will become difficult. You will likely require frequent or prolonged hospitalization or need home health or skilled nursing care. You may also need to wear oxygen or receive intravenous medications.
Summary
Congestive heart failure is a chronic condition that can progress. The stages range from pre-heart failure to advanced heart failure. Once you move on to the next stage, you can’t go back even with treatment.
What is the best treatment for high cholesterol?
Treat high cholesterol. Discontinue alcohol or illegal drug use . An angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor ( ACE inhibitor) or angiotensin II receptor blocker (ARB) may be prescribed if you've had a previous heart attack or if you have diabetes, high blood pressure, or other vascular or cardiac conditions.
What is stage B heart disease?
Stage B. People who have developed structural heart disease that is strongly associated with the development of heart failure (such as those with a history of heart attack, those with a low ejection fraction, valve disease with no symptoms) but without signs and symptoms of heart failure. Treatment methods above for Stage A apply.
How to tell if a child has heart failure?
excessive sweating. difficulty breathing. These symptoms can easily be misunderstood as colic or a respiratory infection. Poor growth and low blood pressure can also be signs of heart failure in children.
What is the term for the condition where the heart pumping fluid?
Congestive heart failure (CHF) is a chronic progressive condition that affects the pumping power of your heart muscle. While often referred to simply as heart failure, CHF specifically refers to the stage in which fluid builds up within the heart and causes it to pump inefficiently. You have four heart chambers.
What is the term for the condition where fluid builds up in the heart?
Congestive Heart Failure (CHF) Congestive heart failure (CHF) is a chronic progressive condition that affects the pumping power of your heart muscle. While often referred to simply as heart failure, CHF specifically refers to the stage in which fluid builds up within the heart and causes it to pump inefficiently.
How many chambers does the heart have?
You have four heart chambers. The upper half of your heart is made up of two atria, and the lower half of your heart is made up of two ventricles. The ventricles pump blood to your body’s organs and tissues, and the atria receive blood from your body as it circulates back from the rest of your body. CHF develops when your ventricles can’t pump ...
What are the symptoms of a heart attack?
Symptoms that indicate a severe heart condition. fatigue. irregular heartbeat. chest pain that radiates through the upper body. swelling in your ankles, feet, and legs. a cough that develops from congested lungs. rapid breathing.
What does it mean when you feel a heart attack?
shortness of breath, which may indicate pulmonary edema. fainting. Chest pain that radiates through the upper body can also be a sign of a heart attack. If you experience this or any other symptoms that may point to a severe heart condition, seek immediate medical attention.
Can beta blockers slow heart rate?
Beta-blockers. Beta-blockers decrease the work the heart has to do and can reduce blood pressure and slow a rapid heart rhythm. This may be achieved with: Beta-blockers should be taken with caution with the following medications, as they may cause an adverse reaction: Medications that slow the heart rate.
How to diagnose CHF?
The first step in diagnosing CHF is to see your provider for a careful health history and a physical exam. Physicians have a number of tests that they may order to diagnose this condition. The most common are blood tests, electrocardiogram (EKG), chest X-rays, stress tests, and, most importantly, an echocardiogram.
Can you breathe with CHF?
People with CHF can experience shortness of breath with exertion while lying down or even while doing simple daily activities. People may awaken at night breathless and require pillows to prop themselves up to avoid trouble breathing.
How many people are diagnosed with CHF?
In the United States: 1 It’s estimated that 450,000 new cases of CHF are diagnosed annually. 2 There are 4.6 million Americans currently diagnosed and living with CHF. 3 CHF is the single largest volume diagnosis in the Medicare-age population in this country. 4 The disease is the most likely diagnosis that leads to readmission to the hospital after initial treatment.
Does congestive heart failure mean death?
Despite the ominous-sounding name, congestive heart failure doesn’t mean sudden death or that the heart suddenly stops working. CHF can be a gradual disease. As the heart muscle weakens, the heart has to work harder to adequately meet the demands of the body.
How many classes of medication are there for heart failure?
There are at least five classes of medication that have clearly been shown to decrease symptoms of heart failure, improve the heart’s pumping function (ejection fraction) and increase survival rates.
Can a pacemaker help with heart failure?
Adequate blood flow to the heart can be restored. Certain pacemakers can help improve heart function, and implantable defibrillators can treat potentially dangerous heart rhythms that can accompany a weakened heart muscle and congestive heart failure.
How to reduce heart disease symptoms?
Exercise has clearly been shown to decrease symptoms, optimize physical conditioning around an imperfect heart and prolong life. Lose weight, maintain an optimal weight and maintain a healthy diet and lifestyle. All are critically important to long-term symptom relief and survival.
What is the best treatment for myocardial infarction?
ACE inhibitors and beta blockers are recommended for all patients with a history of myocardial infarction regardless of EF or heart failure symptoms. Beta blockers also are indicated in patients with a reduced LVEF but no history of myocardial infarction or symptoms of heart failure.
What should be the first step in the evaluation of a patient with heart failure?
In the initial evaluation of patients with heart failure, physicians should locate structural and functional cardiac abnormalities and identify disorders and behaviors that could cause the disease or accelerate its progression. Physicians then should focus on clinical assessment to identify symptoms and determine their effects on function. An ongoing review of symptoms and function is critical to treatment selection.
What are the stages of heart failure?
Heart failure is a clinical syndrome characterized by specific symptoms (e.g., dyspnea, fatigue) and signs (e.g., edema, rales). The development of heart failure has been divided into four stages ( Figure 1): A—high risk of heart failure but no structural disease or symptoms; B—structural heart disease but no signs or symptoms;
What is the best diagnostic tool for heart failure?
The most useful diagnostic tool for evaluating patients with heart failure is two-dimensional echocardiography with Doppler to assess left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF), LV size, ventricular compliance, wall thickness, and valve function. This should be performed during the initial evaluation. Comprehensive evaluation is important because there often is more than one contributing cardiac abnormality, and the test also can be useful as a baseline for comparison.
Can ACE inhibitors be used for heart failure?
ACE inhibitors can alleviate symptoms, improve clinical status, enhance well-being, and reduce the risks of death and hospitalization in patients with heart failure. All patients with current or prior symptoms of heart failure and reduced LVEF should receive ACE inhibitors unless contraindicated.
Can beta blockers help with heart failure?
Long-term beta-blocker therapy can reduce heart failure symptoms, improve clinical status, and reduce the risks of death and hospitalization. Beta blockers should be initiated at very low dosages as soon as LV dysfunction is diagnosed, even when symptoms are mild or have responded to other treatments.
Is CAD a causative factor?
Although myocardial disorders often are responsible for cardiomyopathy, there typically is no identifiable causative factor.
What should a patient with chronic heart failure undergo?
Patients presenting with chronic heart failure and those patients with acute heart failure in whom the cause was not established during the stabilization period should undergo diagnostic testing to determine the etiology.
Can you be admitted to the hospital for acute heart failure?
Patients presenting with acute heart failure usually should be admitted to the hospital. Initial diagnostic testing for patients with acute heart failure should be limited to those tests necessary to exclude etiologies requiring special therapeutic procedures. Further diagnostic testing generally can be deferred until hemodynamic stability and improvement have been attained.
What is the clinical presentation of acute heart failure?
The clinical presentation of acute heart failure ranges from the sudden appearance of dyspnea to frank cardiogenic shock. The management of acute heart failure differs for the various patient groups residing within the clinical spectrum of this condition; thus, this topic is approached by separately discussing the management of each of the major clinical groups.
What are the endogenous hormones that are activated in patients with heart failure?
The sympathetic nervous system is activated early in the disease process, and its activity may be increased even in patients with asymptomatic left ventricular dysfunction. The renin–angiotensin system appears to be activated later in the disease process (once diuretic therapy has been initiated), and its activity is markedly enhanced in patients with advanced symptoms (particularly those with renal hypoperfusion). Other vasoconstrictor hormonal factors that appear to be increased in heart failure include endothelin and vasopressin. In addition to the activation of the vasoconstrictor hormonal system, the activity of several hormonal systems with vasodilator activity is also altered in patients with chronic heart failure.
Can alcohol cause heart failure?
Factors aggravating or precipitating heart failure should be corrected (eg, anemia, infections, hypertension, obesity). Alcohol can produce cardiomyopathy, and excessive intake can cause hypertension. Restriction of intake or abstinence should be encouraged.
Is sodium restriction good for heart failure?
Sodium restriction is a critical strategy in the treatment of patients with heart failure. Calcium channel blockers are not of proven benefit for patients with systolic heart failure and may be harmful. Such risks may not accompany the use of amlodipine, which is undergoing further evaluation.
What is the most common cause of heart failure in children?
However, the most common cause of “heart failure” in infants and children is ventricular septal defect, in which myocardial function is frequently normal.
Is there a cure for CHF?
There is no specific cure for CHF, so treatment relies on taking on the underlying conditions that have caused it. Therapy for this type of heart disease can include: Heart-healthy lifestyle changes: Adjusting exercise levels, diet, and other aspects of health can combat the conditions underlying CHF to help manage it.
What does CHF mean?
CHF is a medical abbreviation for congestive heart failure (sometimes referred to simply as “heart failure”), in which the heart is unable to properly circulate blood. 1 In these cases, the heart hasn’t actually stopped functioning altogether, rather its muscles are failing to keep up with the body’s needs.
How does CHF affect the heart?
Primarily, the damaging effects of CHF have to do with “congestion,” or the improper pooling of blood due to the failure of healthy circulation. Over time, problems get worse as the body attempts to compensate for this issue, leading to: Enlarged heart as cardiac muscles pump harder and grow.
Can CAD cause heart problems?
Notably, CAD can lead to angina (chest pains), heart attack, and other issues. Hypertension (high blood pressure): Elevated blood pressure over the long-term can also cause plaque buildup and weaken the heart.
What causes plaque buildup in the heart?
Hypertension (high blood pressure): Elevated blood pressure over the long-term can also cause plaque buildup and weaken the heart. Type 2 diabetes: Chronic cases of this disease, in which the body is unable to effectively utilize sugar (glucose) for energy, can also impact cardiac activity and output.
How common is CHF?
A sub-type of a broader category of heart failure that also includes right and left-sided heart failure, CHF is quite common, with almost 5 million living with it in the U.S. 3 As such, you’ll most likely hear CHF used when your primary care physician or a cardiologist suspect the condition, or when the other types of heart failure have been ruled out.
What causes CHF?
CHF most often arises as a result of other heart conditions, though it can also occur on its own. As such, it’ll be screened for when other conditions, such as coronary artery disease (CAD), type 2 diabetes, irregular heartbeat, or high blood pressure, are present.
What are the stages of HF?
The ACCF/AHA also defines four stages of HF:3 1 Stage A: At high risk for HF but without structural heart disease or symptoms of HF 2 Stage B: Structural heart disease but without signs or symptoms of HF 3 Stage C: Structural heart disease with prior or current symptoms of HF 4 Stage D: Refractory HF requiring specialized interventions
What are the different types of HF?
In addition to HF type, patients can be assigned a class and/or stage of HF. The New York Heart Association (NYHA) defines four classes of HF:3 1 Class I: No physical limitation; ordinary physical activity does not cause HF symptoms 2 Class II: No symptoms at rest, but ordinary physical activities cause HF symptoms 3 Class III: No symptoms at rest, but less-than-ordinary physical activities cause HF symptoms 4 Class IV: Symptoms of HF at rest
How does ACE inhibitor work?
ACE inhibitors decrease peripheral resistance and reduce the load on the failing myocardium by inhibiting the conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II, thus preventing vasoconstriction and causing relaxation of the vasculature. The efficacy of ACE inhibitors has been proven over several decades.
Why are ARBs used?
The 2016 ACCF/AHA/HFSA guidelines recommend that ARBs be used to reduce morbidity and mortality in patients who are intolerant of ACE inhibitors because of cough or angioedema or in patients who are tolerating ARBs for another indication.
What are the adverse effects of diuretics?
Adverse effects of diuretics include fluid depletion, hypotension, azotemia, and depletion of sodium, potassium, magnesium, chloride, and calcium. Typical monitoring parameters for these agents include daily weight and blood pressure measurements, and periodic monitoring of renal function.
Does thiazide increase uric acid?
Because loop and thiazide diuretics may increase uric acid, patients utilizing these agents should be monitored for changes in uric acid levels as well as signs and symptoms of gout. The presence of orthopnea and B-type natriuretic peptide levels should be followed daily if possible during inpatient admissions.43.
What is the role of digoxin in myocardial contraction?
It inhibits the sodium–potassium ATPase pump, causing positive inotropy (increasing force and velocity of myocardial contraction) and deactivating neurohormonal effects (decreasing sympathetic and RAAS responses).48.
Stage A
Stage B
Stage C
Stage D
Specialist to consult
Prevention
Summary
- Stage B is the second stage of heart failure, but it’s still considered pre-heart failure. You don’t have symptoms of heart failure, but you may have been diagnosed with systolic left ventricular dysfunction, which is reduced power in the left ventricle of your heart. The left ventricle is the chamber of the heart that sends oxygen-rich blood out to other parts of your body. People at sta…
Frequently Asked Questions
- Stage C is the first significant stage of heart failure in terms of how you feel. At this stage, you have been officially diagnosed with heart failure and have or had symptoms. Symptoms in this stage include:2 1. Noticeable limitations of physical activity 2. Shortness of breath with activity 3. A low tolerance for activity, easily tired 4. Heart palpitationsor chest pain 5. Most comfortable w…