Induction chemotherapy is a first-line treatment for cancer in which a patient is given doses of chemotherapy first. These doses may be high, with the goal of attempting to quickly attack the cancer, and after induction chemotherapy, additional treatment options can be explored.
What are the reasons for needing chemotherapy?
Apr 18, 2022 · Induction chemotherapy is a first-line treatment for cancer in which a patient is given doses of chemotherapy first. These doses may be high, with the goal of attempting to quickly attack the cancer, and after induction chemotherapy, …
What are the stages of chemotherapy?
Induction chemotherapy, the delivery of chemotherapy before definitive surgery or radiation therapy, is an approach based on the recognition that systemic chemotherapy is most active in previously untreated patients.
What can interfere with chemotherapy?
Induction chemotherapy. Induction chemotherapy is the first-line treatment of cancer with a chemotherapeutic drug. The goal of induction chemotherapy is to cure the cancer. It may be contrasted with neoadjuvant therapy, with consolidation chemotherapy (intended to kill any cancer cells that survived the initial treatment), and with maintenance chemotherapy given at …
What is the average chemotherapy cycle?
Jul 06, 2003 · Induction therapy typically consists of conventional doses of chemotherapy administered in an attempt to reduce the amount of cancer in a patient’s body prior to high-dose therapy. Patients often have their stem cells collected following induction therapy.

What does induction mean in chemotherapy?
How long is chemotherapy induction?
What is the purpose of induction therapy?
What is induction in drug treatment?
What happens after induction therapy?
What is the difference between induction and consolidation chemotherapy?
What is induction vs maintenance therapy?
What is azacitidine used to treat?
Can chemo treatments affect your legs?
Some chemotherapy drugs can damage the nerves that send signals between the central nervous system and the arms and legs. This is called peripheral neuropathy. Symptoms include tingling (“pins and needles”), numbness or pain in your hands and feet, and muscle weakness in your legs.
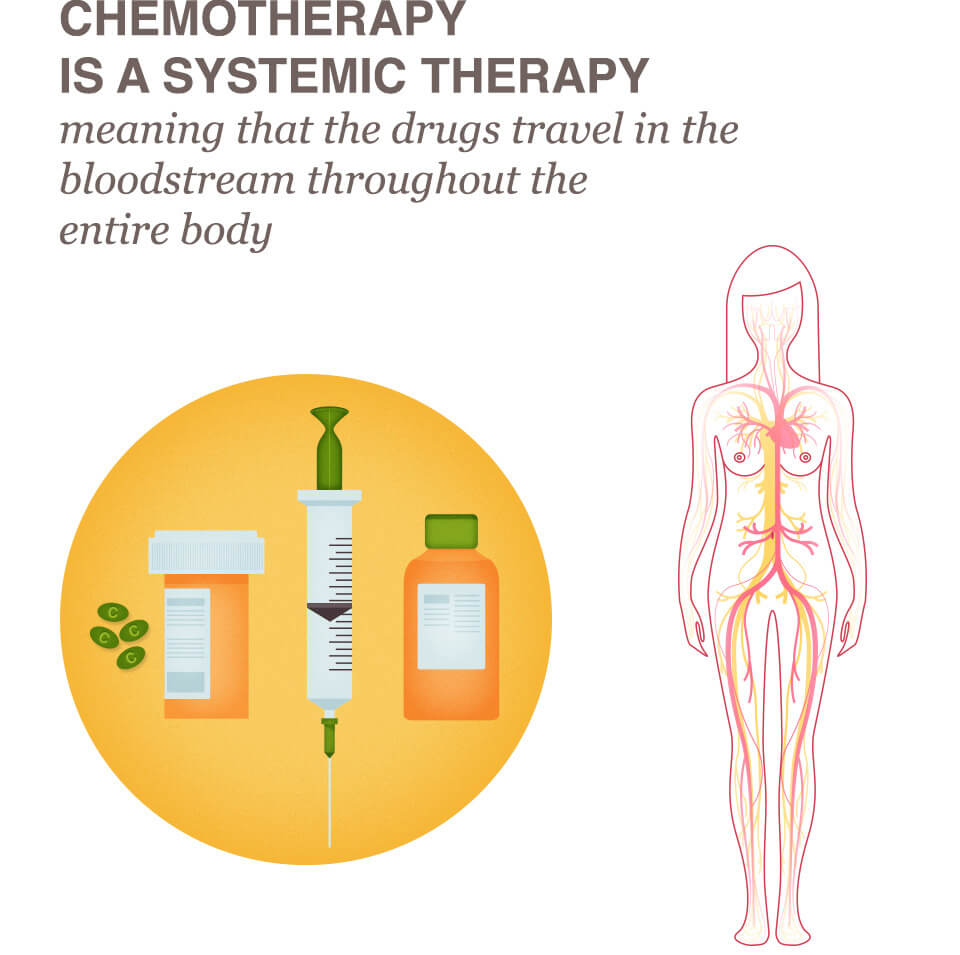
What are 3 ways a person can receive chemotherapy treatments?
- Chemotherapy infusions. Chemotherapy is most often given as an infusion into a vein (intravenously). ...
- Chemotherapy pills. ...
- Chemotherapy shots. ...
- Chemotherapy creams. ...
- Chemotherapy drugs used to treat one area of the body. ...
- Chemotherapy given directly to the cancer.
What does induction phase mean?
What is induction end?
What is induction chemotherapy?
Induction chemotherapy, the delivery of chemotherapy before definitive surgery or radiation therapy, is an approach based on the recognition that systemic chemotherapy is most active in previously untreated patients.
Does induction chemotherapy work for lymphoma?
Only for malignant lymphomas does induction chemotherapy seem to be beneficial in terms of local tumor control. For example, for diffuse large cell lymphomas that are less than 3.5 cm in their greatest dimension, induction chemotherapy that produces a complete response coupled with subsequent irradiation can lead to successful local control at a low total dose of radiation (e.g., 30 Gy). However, tumors 10 cm in diameter or larger that respond completely to induction chemotherapy nonetheless require substantially higher total doses (at least 45 Gy) than do smaller tumors.52
Can chemotherapy be combined with radiation?
The toxicity associated with combining chemotherapy and radiation therapy can be minimized by separating them in time, another feature that can make induction chemotherapy more attractive. Occasionally, induction chemotherapy can even increase the protection of normal tissues.
How does chemotherapy affect survival?
Chemotherapy leads destruction of tumor at a constant fraction rather than a constant number of cancer cells and results in a fractional tumor decrease that is not larger than 1-2 log, leading to exponential survival curves.
What is the response rate of chemotherapy?
Combination chemotherapy regimens with drugs such as fluorouracil and cisplatin can produce response rates of 80% to 90% , which are clinically complete in up to 40% of these patients.127 Although the responses are temporary, the use of chemotherapy as the initial treatment modality is an attractive model and has the potential to maximize the benefit of the chemotherapy while both reducing the magnitude and improving the outcomes of the locoregional therapy.
What is LABC in cancer?
LABC has always included a heterogeneous group of presentations. Technically, LABC can include a patient with a clinically apparent internal mammary or paraclavicular node as well as the more commonly accepted presentations, including a primary breast cancer larger than 5 cm, disease fixed to the chest wall or involving the skin, or bulky palpable disease in the axillae. Inflammatory breast cancer also can be called LABC, but is discussed later in this chapter in the section Inflammatory Disease. The approach to LABC has evolved considerably over the years. Surgery and radiation therapy were initially the only treatments available, but multimodality approaches that emphasize systemic therapy have become the standard of treatment. This approach includes delivery of systemic therapy early in treatment to attempt to reduce subclinical micrometastatic disease, reduce local and regional tumor bulk, and increase the likelihood of successful surgical resection. In addition, the appropriateness of the systemic agents chosen can be assessed by following the patient's locoregional clinical response.
First-line Induction Therapy
Naturally, the hope for all patients and their doctors is that induction therapy succeed, and perhaps cure the patient of his or her cancer (this result is more common in early stage cancers, and more common in lymphoid cancers such as lymphomas and leukemias).
Induction Therapy in Lymphomas
Induction therapy for some of the more common subtypes of lymphoma are as follows:
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is the main induction treatment for AML. Most regimens are built around the drug cytarabine (Cytosar, Ara-C) and daunorubicin (Cerubidine), which may be combined with other drugs or agents.
Targeted therapy
Targeted therapy is treatment that uses drugs or other substances to target specific molecules (usually proteins) involved in cancer cell growth while limiting harm to normal cells.
Central nervous system treatment
The central nervous system (CNS) is the brain and spinal cord. If the leukemia has spread to the CNS, treatment may include chemotherapy given directly into the spinal fluid (called intrathecal chemotherapy). The drug used in intrathecal chemotherapy is methotrexate or cytarabine. It is given during a
Supportive therapy
Supportive therapy is important during every phase of treatment for AML. It is used to treat the complications that usually happen with treatments for AML and the disease itself.
Clinical trials
You may be asked if you want to join a clinical trial for AML. Find out more about clinical trials.
Can chemo be used to treat bladder cancer?
Drugs put into the bladder also can’t reach cancer cells in the kidneys, ureters, and urethra, or those that have spread to other parts of the body. One dose of intravesical chemotherapy might be the only treatment needed for non-invasive cancers. Low-risk non-invasive (low-grade) bladder cancers grow slowly.
How long after a turbt can you get a tumor?
After TURBT. Intravesical therapy is commonly used after transurethral resection of bladder tumor (TURBT). It's often done within 24 hours of the TURBT procedure. Some experts say it should be done within 6 hours. The goal is to kill any cancer cells that may be left in the bladder.
How long does a drug stay in your bladder?
The drug is put in through a soft catheter that's put into your bladder through your urethra. The drug stays in your bladder for up to 2 hours. This way, the drug can affect the cells lining the inside ...
What is non invasive bladder cancer?
They may be called non-invasive (stage 0), or minimally invasive (stage I) bladder cancers. They have not spread into deeper layers on the bladder wall muscles or to other parts of the body.
How long does bladder cancer treatment last?
This is called induction therapy. After a 4- to 6-week break, maintenance treatments are then done for at least 1 year. High-risk non-invasive bladder cancers might be fast-growing (high-grade), big, or there may be more than 1 tumor.
What is the best treatment for bladder cancer?
Immunotherapy causes the body’s own immune system to attack the cancer cells. Bacillus Calmette-Guerin or BCG is the most common intravesical immunotherapy for treating early-stage bladder cancer. It's used to help keep the cancer from growing and to help keep it from coming back.
Can bladder cancer spread to other parts of the body?
These cancers are only in the lining of the bladder. They may be called non-invasive (stage 0), or minimally invasive (stage I) bladder cancers. They have not spread into deeper layers on the bladder wall muscles or to other parts of the body. Intravesical chemotherapy is used for these early-stage cancers because drugs given this way mainly affect the cells lining the inside of the bladder. They have little to no effect on cells elsewhere. This means that any cancer cells outside of the bladder lining, including those that have grown deeply into the bladder wall, are not treated by intravesical therapy. Drugs put into the bladder also can’t reach cancer cells in the kidneys, ureters, and urethra, or those that have spread to other parts of the body.