
Treatment
- Antiviral medications. Hepatitis C infection is treated with antiviral medications intended to clear the virus from your body.
- Liver transplantation. If you have developed serious complications from chronic hepatitis C infection, liver transplantation may be an option.
- Vaccinations. ...
How do direct-acting antiviral drugs (DAA) treat hepatitis C?
There are 3 targets on the hepatitis C virus (HCV) that currently recommended direct-acting antiviral (DAA) medications attack to destroy the virus. Each DAA medication attacks one of these targets; combination DAA tablets attack more than one target.
Are the new hepatitis C Daas effective?
These all new hepatitis C DAAs – the brands of which sport tongue twisting names such as Epclusa, Harvoni, Marivet and Zepatir – are highly effective and have significant benefits and improvements compared to the old interferon/ribavirin treatment. Are the DAAs an actual cure for hep C? For starters, the DAAs are a cure.
What is the DAA medication class (es) for hepatitis C (HCV)?
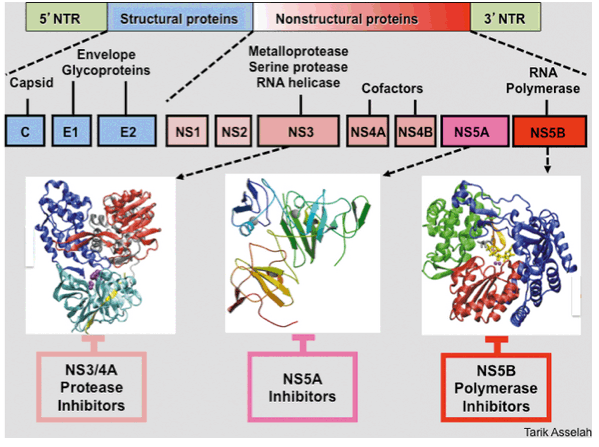
Recognizing the DAA medication class (es) becomes particularly important when retreating a patient for HCV who has been previously treated with a DAA-based therapy. There are 3 classes of currently recommended DAA medications: NS3/4A protease inhibitors. NS5A polymerase inhibitors. NS5B polymerase inhibitors.
What are the treatments for hepatitis C?
Here’s an overview of the past, present, and future treatments for hepatitis C, starting where it all began. The first treatment for hepatitis C came in the 1980s, by way of a series of protein-based injections called recombinant interferon-alfa (IFNa).
What is a DAA treatment?
Direct-acting antivirals (DAA) are drugs used to treat hepatitis C infections. They are a combination of antiviral drugs that target stages of the hepatitis C virus reproductive cycle. They are more effective than older treatments such as ribavirin and interferon.
What is hepatitis DAA?
Direct-acting antiviral (DAA) agents are medications that doctors use to treat hepatitis C. DAA agents contain a combination of drugs to destroy the hepatitis C virus (HCV).
How long is DAA treatment?
Under existing guidelines, most patients are prescribed 12 weeks of DAA therapy, a treatment duration that has shown high rates of sustained virological response (SVR) across various viral and host characteristics.
What is the newest treatment for hep C?
Recent advances in antiviral treatment have led to the development of new highly effective drugs for the treatment of all types of hepatitis C. The new hepatitis C treatments are sofosbuvir with ledipasvir (Harvoni); sofosbuvir (Sovaldi); daclatasvir (Daklinza); and ribavirin (Ibavyr).
Is Harvoni a DAA?
Harvoni is a type of drug called a direct-acting antiviral (DAA). It was approved by the FDA in 2014 to treat several different genotypes, or forms, of hepatitis C.
Is Ribavirin a DAA?
DAA therapies were: sofosbuvir (SOF) + ribavirin (RBV) in 10 patients; SOF + simeprevir (SMV) ± RBV in 73; SOF + pegylated interferon (PEG-IFN) + RBV in 6; SOF + daclatasvir (DCV) ± RBV in 51, SOF + ledipasvir (LDV) ± RBV in 61, and par-itaprevir/ritonavir + ombitasvir + dasabuvir (PTVr/OBV/DSV) ± RBV in 18 patients.
Will I feel better after hep C treatment?
Since hepatitis C doesn't always cause any symptoms, you may not feel any different after being cured. If you were experiencing symptoms — fatigue is the common one — you should start to feel stronger and more energetic, which should continue to improve after you finish treatment, says Massoud.
How long do you have to be clean to get hep C treatment?
Researchers studied Medicaid programs in the United States from 2017 to 2020. They found that many states require a 6-month to 1-year period of sobriety before someone can start HCV treatment.
Does hep C go away after treatment?
Hepatitis C infection is cured if the virus is undetectable 12 weeks after the completion of a course of direct-acting antiviral treatment. This is known as a sustained virologic response (SVR).
Is hep C curable 2021?
Today, chronic HCV is usually curable with oral medications taken every day for two to six months. Still, about half of people with HCV don't know they're infected, mainly because they have no symptoms, which can take decades to appear.
What is the success rate of hep C treatment?
Hepatitis C treatment can cure more than 90 percent of hepatitis C cases, but testing is a critical first step. It's estimated 40 percent of people with hepatitis C in the U.S. from 2015-2018 were unaware of their infection.
Can you live a normal life with hep C?
If the disease is caught early and treated, people with hepatitis C can live a normal life. Approximately 3 to 5 million people in the United States are living with chronic hepatitis C, an infection that causes inflammation and scarring in the liver.
What to do if you have hepatitis C?
If you receive a diagnosis of hepatitis C, your doctor will likely recommend certain lifestyle changes. These measures will help keep you healthy longer and protect the health of others as well:
How long does it take to cure hepatitis C?
As a result, people experience better outcomes, fewer side effects and shorter treatment times — some as short as eight weeks.
How old do you have to be to get tested for hepatitis C?
The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommends that all adults ages 18 to 79 years be screened for hepatitis C, even those without symptoms or known liver disease. Screening for HCV is especially important if you're at high risk of exposure, including: Anyone who has ever injected or inhaled illicit drugs.
How long does it take for hepatitis C to clear?
The goal of treatment is to have no hepatitis C virus detected in your body at least 12 weeks after you complete treatment.
How to prevent liver damage?
Avoid medications that may cause liver damage. Review your medications with your doctor, including over-the-counter medications you take as well as herbal preparations and dietary supplements. Your doctor may recommend avoiding certain medications. Help prevent others from coming in contact with your blood.
How to prepare for a liver appointment?
Because appointments can be brief and because there's often a lot to discuss, it's a good idea to be well prepared. To prepare, try to: Review your medical record. This is particularly important if you are seeing a liver specialist (hepatologist) for the first time after finding out you have hepatitis C.
What is the test that measures the speed of the liver's dispersal through the liver?
Transient elastography. Another noninvasive test, transient elastography is a type of ultrasound that transmits vibrations into the liver and measures the speed of their dispersal through liver tissue to estimate its stiffness.
Why do people stop hepatitis C treatment?
Some people stop therapy because of side effects. Since hepatitis C can lead to liver damage, cirrhosis, and liver cancer if not treated, it’s vital to stick with a treatment plan.
How long does it take to cure hepatitis C?
The latest medications for hepatitis C are taken by mouth, in pill form. Treatment generally lasts between 8 weeks to 6 months, depending on the medication. Overall, new drugs cure the hepatitis C infection in 90 to 100 percent. Trusted Source.
Why do people stop taking hepatitis C?
Some people stop therapy because of side effects. Since hepatitis C can lead to liver damage, cirrhosis, and liver cancer if not treated , it’s vital to stick with a treatment plan. Newer drugs have fewer severe side effects than pegylated interferon and ribavirin.
What is the best medication for genotype 1 and 4?
Depending on the genotype, it’s used in combination with either peginterferon and ribavirin, or with just ribavirin. Zepatier (elbasvir/grazoprevir) is approved for genotypes 1 and 4. It’s important to take medication as directed.
Why don't people seek treatment for hepatitis C?
Many people don’t seek treatment for chronic hepatitis C infection because they don’t know they have the virus. It’s only years later, when hepatitis C leads to serious health issues, that many people seek medical attention. Early intervention is important because it may help keep people healthy longer.
Can you get hep C without treatment?
Hepatitis C (hep C) infection used to be a lifelong condition for most people. Only about 15 to 25 percent. of people clear the hepatitis C virus (HCV) from their body without treatment. For everyone else, the infection becomes chronic. With advances in hep C treatment, most people can now be cured of HCV.
Is Zepatier a daily pill?
Zepatier is a once-daily pill approved for genotypes 1 and 4.
What drugs were used to treat hepatitis C?
The results were two protease inhibitors (PIs) called boceprevir (Victrelis) and telaprevir (Incivek). With precision, these drugs directly targeted hepatitis C and worked to stop the virus from spreading.
What antiviral pill is used for hepatitis C?
In 2014 and 2015, hepatitis C genotype-specific drugs were created that could target particular types of hepatitis C. These included: Sofosbuvir/ledipasvir (Harvoni). This antiviral pill fights hepatitis C genotypes 1 and 3 at different stages during its life cycle by blocking proteins that cause the virus.
How long does glecaprevir last?
This treatment is for adults with chronic hepatitis C genotypes 1 through 6, and treatment duration can be as little as eight weeks. Results from early trials showed that 92 to 100 percent had no evidence of infection after treatment.
When was hepatitis C first discovered?
Those who will develop this disease may take some comfort in knowing that today’s hepatitis C treatments differ extremely from what was available when it was first discovered in 1989.
When was Sofosbuvir approved?
In July 2017 , sofosbuvir/velpatasvir/voxilaprevir (Vosevi) was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to treat chronic hepatitis C of all genotypes. This fixed-dose combination pill prohibits the development of the specific protein NS5A.
Is hepatitis C 100 percent curable?
Regardless of your genotype, there are now more treatment options than ever. More exciting is the possibility that eventually most genotypes of hepatitis C will be 100 percent curable. Last medically reviewed on March 9, 2018.
How does hepatitis C therapy help?
Proper adherence to Hepatitis C therapy will increase your chance of being cured and decrease the long-term complications of Hepatitis C. Adhering to other aspects of your treatment plan is also important.
How long does it take to get cured of hepatitis C?
Sustained virologic response (SVR): You are considered cured if the Hepatitis C virus is not detected when measured with a blood test three months after you’ve completed treatment. This is called a sustained virologic response and data suggest that you will stay virus free indefinitely.
How long does it take for hepatitis C to clear?
Your doctor may recommend one medication or a combination of two to three medications to be taken for 12 – 24 weeks or longer. Blood tests and doctor visits are necessary during this time so that your response to treatment can be carefully monitored and evaluated.
What to do if you think you have hepatitis C?
If you think you are at risk of having Hepatitis C, talk to your current healthcare provider about getting tested. Once you’ve been diagnosed with Hepatitis C infection, you may want to see a specialist. Specialists who work with people with Hepatitis C include the following healthcare providers:
What is CAM in hepatitis?
Some people seek out complementary or alternative ways to treat their Hepatitis C. Complementary and alternative medicine, known as CAM, includes a variety of interventions. Some common complementary therapies include the following:
Is it important to know about hepatitis C?
Many hepatitis C medications have important considerations that you should be aware of before starting a course of treatment for your HCV infection. Some considerations are specific to a particular drug, while others are more general in nature.
Can you change your medication before hepatitis C treatment?
If available, your Hepatitis C provider will select a treatment option with no interactions. If not available , he or she can talk to your other healthcare providers about the possibility of changing your current medicines before Hepatitis C treatment begins.
What are the new hepatitis C DAAs?
These all new hepatitis C DAAs – the brands of which sport tongue twisting names such as Epclusa, Harvoni, Marivet and Zepatir – are highly effective and have significant benefits and improvements compared to the old interferon/ribavirin treatment.
What are the side effects of the new Hep C treatment?
It was rare for anyone to make it through the regimen without some nausea, or tiredness, or even their hair falling out. For many, the treatment was dubbed “worse than the disease”. While some people were willing to go through interferon/ribavirin, many elected not to – unless advancing liver disease, caused by their hep C, forced them to give it a go.
What is a genotype in hepatitis C?
A “genotype” is a variation within the hepatitis C virus, and there are several common variants: genotype 1, genotype 2, and so on. Depending on a person’s genotype, the interferon/ribavirin treatment, was not suitable for everyone. That has changed with the Direct Acting Anti-virals.#N#While DAAs were initially only effective on certain genotypes during their first year of availability in Australia, newer DAA versions are “pangenotypic” – able to be used with all genotypes of the virus. This is great news for everyone, regardless of their genotype.
How does DAA work?
Instead of trying to force the body’s immune system to kill the virus (which is how interferon/ribavirin was used), the DAAs stop the hepatitis C virus from reproducing within liver cells. This works in over 95% of cases. Following an SVR test, twelve weeks after the end of their DAA treatment, ...
Can you get hepatitis C DAAs in Australia?
When the hepatitis C DAAs were listed on the PBS, access to them came with virtually no strings attached. Essentially, anyone in Australia living with hepatitis C who is over the age of 18 and who has a Medicare number can be treated (and retreated). They do not need to have liver fibrosis or cirrhosis; they can be treated if they are in prison; they can be treated if they are a person who injects drugs; 18 or 108+ years of age; they can be treated. This degree of equal access was greatly welcomed; it meant that people were not excluded from lifesaving treatment.
Is hepatitis C worse than DAA?
By comparison, hepatitis C DAA treatment is now – for over 95% of people – completely, or almost completely, ...
Is a liver biopsy used for hep C?
It’s worth mentioning at this point that liver biopsies, an unpleasant medical procedure once part of hep C treatment, is no longer used either. In almost all instances, a device known as a fibroscan – similar to an ultrascan – is now used to assess the liver for any fibrosis or cirrhosis prior to treatment.
What is the DAA for HCV?
In 2011, new medications named direct acting antivirals (DAA) were developed, which represents a major advancement in the treatment of HCV that achieved a virological response exceeding 90% in most genotypes. There is a very rapid progress in the development of DAAs that limits the ability to overwhelm the pharmacological details of each DAA. This review is a trial to give an overview of the pharmacology of most DAAs.
What is the direct acting antiviral therapy?
The direct acting antiviral therapy was started when the first-wave, first-generation HCV NS3-4A protease inhibitors boceprevir and telaprevir were approved in combination with PegIFN-alpha and ribavirin for the treatment of chronic HCV genotype 1 infection in 2011.[7] However, these drugs have been reported to have several drug-drug interactions, and are largely replaced with newer DAA including Simeprevir, Paritaprevir, Daclatasvir, Ledipasvir, Ombitasvir, Sofosbuvir and Dasabuvir. Table 3summarizes the pharmacokinetics of all approved DAA with special reference to the sites of drug-drug interaction. Clinical pharmacology of the newer DAA will be discussed in the next section.
What is a DAA?
Chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection is a leading cause of chronic liver disease. The introduction of direct acting antiviral agents (DAAs) for its treatment represents a major advance in terms of sustained virologic response (SVR) rates and adverse effect profiles. Mechanistically, DAAs inhibit specific HCV non-structural proteins (NS) that are vital for its replication. Boceprevir, telaprevir, simeprevir, asunaprevir, grazoprevir and paritaprevir are NS3/4A inhibitors. Ombitasvir, ledipasvir, daclatasvir, elbasvir and velpatasvir are NS5A inhibitors. Sofosbuvir and dasabuvir are NS5B inhibitors. Currently, a combination of two or more DAAs is the corner stone for the treatment of HCV infection. However, the success of DAA therapy is facing several challenges, including the potential of drug-drug interactions and resistant variance. Moreover, the shortage of relevant clinical pharmacological data and drug interaction regarding DAA is a clinical concern. The present review discusses the clinical pharmacology of DAAs with special emphasis on drug-drug interaction.
How many people are infected with hepatitis C?
Globally, the chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) is a leading cause of liver diseases such as liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. It affects approximately 180 million people worldwide; about 3% of the world population.[1] Three to four million persons are newly infected each year, with the predominant prevalence being infection with genotype 1, followed by genotypes 2 and 3. The other genotypes, 4, 5, and 6, have specific geographical distribution. The infection with HCV occurs as the result of percutaneous transmission via infectious blood (blood-to-blood). Less than 20% of those acutely infected clear the virus; the rest (70-80%) become chronically infected for decades, a significant fraction of whom die of HCV-related illnesses. [2]
How long does DAA last?
N.B.: The duration of therapy of DAA ranges from 12 to 24 weeks. It depends on several factors including the presence of cirrhosis, genotype and previous failure of therapy.
Is Daclatasvir approved for use with Sofosbuvir?
Daclatasvir was approved to beused with sofosbuvir.
How long does it take to cure hepatitis C?
Treatments are available that can cure most people with hepatitis C in 8 to 12 weeks.
How long does it take for hepatitis C to clear?
For reasons that are not known, less than half of people who get hepatitis C are able to clear, or get rid of, the virus without treatment in the first 6 months after infection.
What is hepatitis?
Hepatitis means inflammation of the liver. The liver is a vital organ that processes nutrients, filters the blood, and fights infections. When the liver is inflamed or damaged, its function can be affected. Heavy alcohol use, toxins, some medications, and certain medical conditions can cause hepatitis.
How does hepatitis C spread?
The hepatitis C virus is usually spread when someone comes into contact with blood from an infected person. This can happen through: ► Sharing drug-injection equipment. Today, most people become infected with hepatitis C by sharing needles, syringes, or any other equipment used to prepare and inject drugs. ► Birth.
What happens if you get hepatitis C?
Left untreated, chronic hepatitis C can cause serious health problems including liver disease, liver failure, liver cancer, and even death.
How old do you have to be to get tested for hepatitis C?
CDC recommends you get tested for hepatitis C if you: Are 18 years of age and older. Are pregnant (get tested during each pregnancy) Currently inject drugs (get tested regularly) Have ever injected drugs, even if it was just once or many years ago. Have HIV.
What are the most common types of hepatitis?
In the United States, the most common types of viral hepatitis are hepatitis A, hepatitis B, and hepatitis C . Although all types of viral hepatitis can cause similar symptoms, they are spread in different ways, have different treatments, and some are more serious than others.
What is the role of post cure care for hepatitis C?
Equally important aspects of postcure care are the prevention of liver disease progression and the management of complications in patients who have significant fibrosis at the time of achieving cure. Patients with advanced fibrosis need to remain under surveillance for liver complications, including hepatocellular carcinoma. All patients are potentially at risk for liver disease progression if other factors causing liver injury are present, such as harmful levels of alcohol use or risk factors for fatty liver including obesity, diabetes, and other metabolic comorbidities. Fatty liver is a particular threat to the long-term well-being of patients after HCV cure due to the high prevalence of its risk factors in this population. Strong counseling messages and ongoing monitoring are key.
What is the goal of HCV management?
The goals are 2-fold: to prevent reinfection and to prevent and treat complications of liver disease. Critical to appropriate triage of patients is accurate staging of liver fibrosis prior to cure. Patients with cirrhosis may develop HCC and other liver-related complications postcure, although the rates are significantly reduced by clearance of HCV. Specialists play a key role in educating nonspecialists regarding appropriate follow-up postcure and in caring for patients with advanced fibrosis and liver-related complications.
Why is it important to keep cured patients under the care of a specialist?
The rationale for keeping cured patients under the care of a specialist is to prevent and manage the complications of liver disease that can occur in spite of cure. The patients at highest risk for liver-related complications are those with cirrhosis at the time of cure. Longitudinal studies of DAA-treated patients with cirrhosis show a significant reduction in the risk of liver-related mortality for decompensation and HCC,27,28but risk persists. Patients with decompensated cirrhosis are at a higher risk of future liver complications than those with compensated cirrhosis. For patients with decompensated cirrhosis who achieve cure, approximately 75% will experience an improvement in MELD and Child-Pugh scores, but only 25% will improve to compensated cirrhosis.29Thus, most patients with decompensated cirrhosis remain at risk for liver complications and need close monitoring. Consideration of liver transplantation in appropriate patients is critical.
Is alcohol safe for HCV?
The achievement of HCV cure substantially reduces the risk of liver disease progression, but some patients remain at risk. Moreover, liver injury can occur from other causes before and after cure, specifically related to alcohol use or superimposed metabolic fatty liver. Thus, it is important to provide counseling messages to patients for lifelong liver health.16While safe levels of alcohol intake for otherwise healthy men and women are fewer than 4 and 2 drinks per day, respectively, these levels were defined in persons without known preexisting liver disease.17Thus, for patients with HCV infection who have underlying fibrosis, these levels cannot be considered safe, and abstinence is recommended.4For patients with no or minimal fibrosis, counseling messages should stress safe levels of alcohol use (≤2 drinks per day for men and ≤1 drink per day for women18), although a recent study suggests that even lower limits should be adopted.19Marijuana may also have profibrogenic potential in patients with fibrosis, so daily use is not recommended.20Fatty liver from metabolic causes (obesity, diabetes) is a major concern given the epidemic of these comorbidities in the population. Aiming for the ideal body weight and for control of metabolic cofactors is very important for maintenance of liver health after cure. Finally, avoidance of potentially hepatotoxic medications, herbal products, or over-the-counter medications should be mentioned to patients. Safe levels of acetaminophen are 2 g or less.
Can fibrosis progress after HCV cure?
Although the majority of patients, especially those without cirrhosis at baseline, will show evidence of fibrosis regression as time increases from HCV cure, some patients can progress. This may be related to concurrent alcohol use or the presence of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Alternatively, genetic or immunologic factors may contribute to the risk of liver complications after cure.26Given this possibility, counseling patients on measures for maintaining good liver health is important (Table). Additionally, periodic assessment of fibrosis severity using elastography may be beneficial. Post-SVR, the absolute value for liver stiffness is difficult to interpret and should not be relied upon to provide accurate staging information, although trends in liver stiffness values are helpful. For example, liver stiffness values that are stable or decreasing would be indicative of stable or reduced fibrosis, whereas an increase in liver stiffness values may reflect increased necroinflammation or fibrosis and promote further investigation into the cause. Importantly, even if post-SVR elastography measures show reversal of advanced fibrosis to levels indicative of F2 or less, this should not lead to a discontinuation of surveillance for HCC.4,5

Diagnosis
Treatment
- Antiviral medications
Hepatitis C infection is treated with antiviral medications intended to clear the virus from your body. The goal of treatment is to have no hepatitis C virus detected in your body at least 12 weeks after you complete treatment. Researchers have recently made significant advances in treatmen… - Liver transplantation
If you have developed serious complications from chronic hepatitis C infection, liver transplantation may be an option. During liver transplantation, the surgeon removes your damaged liver and replaces it with a healthy liver. Most transplanted livers come from decease…
Clinical Trials
- Explore Mayo Clinic studiestesting new treatments, interventions and tests as a means to prevent, detect, treat or manage this condition.
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
- If you receive a diagnosis of hepatitis C, your doctor will likely recommend certain lifestyle changes. These measures will help keep you healthy longer and protect the health of others as well: 1. Stop drinking alcohol.Alcohol speeds the progression of liver disease. 2. Avoid medications that may cause liver damage.Review your medications with your doctor, including o…
Preparing For Your Appointment
- If you think you may have a risk of hepatitis C, see your family doctor. Once you've been diagnosed with a hepatitis C infection, your doctor may refer you to a specialist in liver diseases (hepatologist) or infectious diseases.