What are the disadvantages of water fluoridation?
Sodium fluoride: a dry salt additive, typically used in small water systems, dissolved into a solution before being added to water. Sources of Fluoride Additives Most fluoride additives used in the United States are produced from phosphorite rock.
What is the primary reason for fluoridation of water?
Water fluoridation is the process of adding fluoride to the water supply so the level reaches approximately 0.7 ppm, or 0.7 milligrams of fluoride per liter of water; this is the optimal level for preventing tooth decay ( 1 ).
What happens when you add fluoride to water?
Fluoridationis the process of adjusting the concentration of fluoride in public water supplies for the prevention of dental decay. Fluoride has been added to drinking water in the United States since about 1945 and it has been estimated to reduce tooth decay by 25% in children and adults. Fluorosis and Other Problems.
Why do they put fluoride in water?
May 21, 2021 · Water fluoridation is the water adjustment process that rises or reduces the natural fluoride concentration in drinking water to an optimum level that’s effective for reducing tooth decay and promoting good dental health.

What is the fluoridation process?
What is water fluoridation? Water fluoridation is the process of adding fluoride to the water supply so the level reaches approximately 0.7 ppm, or 0.7 milligrams of fluoride per liter of water; this is the optimal level for preventing tooth decay (1).May 15, 2017
What causes fluoridation?
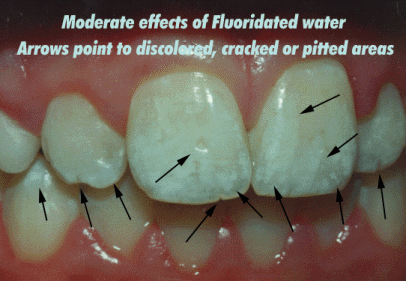
Dental fluorosis is caused by taking in too much fluoride over a long period when the teeth are forming under the gums. Only children aged 8 years and younger are at risk because this is when permanent teeth are developing; children older than 8 years, adolescents, and adults cannot develop dental fluorosis.
Why is fluoridation of water important?
Drinking fluoridated water keeps teeth strong and reduces cavities (also called tooth decay) by about 25% in children and adults. By preventing cavities, community water fluoridation has been shown to save money both for families and for the US health care system.
What does fluoridation remove from water?
It effectively absorbs fluoride and other contaminants from water, which is why the EPA recommends it as a viable option for purifying drinking water. These alumina filters only work on water with a pH less than 8.5. For fluoride removal, the water pH should be between 5 and 6.Feb 6, 2020
What is Amelogenesis imperfecta?
Amelogenesis imperfecta is a disorder of tooth development. This condition causes teeth to be unusually small , discolored, pitted or grooved, and prone to rapid wear and breakage. Other dental abnormalities are also possible.
What are the symptoms of too much fluoride?
7 Side Effects of Consuming Fluoride You Should Know AboutTooth Discoloration. Consumption of too much of fluoride leads to yellowed or browned teeth. ... Tooth Decay. High intake fluoridated water can lead to the weakening of enamel. ... Skeletal Weakness. ... Neurological Problems. ... High Blood Pressure. ... Acne. ... Seizures.
What is community water fluoridation?
Community water fluoridation is the process of adjusting the amount of fluoride in drinking water to a level recommended for preventing tooth decay.
What is fluoridation in dentistry?
The process involves painting a varnish containing high levels of fluoride onto the surface of the tooth every 6 months to prevent decay. It works by strengthening tooth enamel, making it more resistant to decay.
What happens when you stop using fluoride?
What happens if you stop using fluoride? The study's authors warn that in the absence of optimal fluoride levels in drinking water and saliva, teeth may develop with thinner enamel and a reduced ability to remineralize early symptoms of decay.Mar 31, 2018
Which filter is best for drinking water?
That's where water filters come in.Best Overall: Big Berkey Gravity-Fed Water Filter.Best Budget: Brita Standard Everyday Water Pitcher.Best Reverse Water Osmosis: APEC Water System Reverse Osmosis Filter System.Best for Easy Installation: Waterdrop RO Reverse Osmosis Water Filtration System.More items...•Jan 6, 2022
Do fridge filters remove fluoride?
However fluoride cannot be filtered via fridge water filters. Instead, a reverse osmosis filter system is one of the most common ways people remove fluoride from their drinking supply.
Does reverse osmosis remove Pfas?
High-pressure membranes, such as nanofiltration or reverse osmosis, have been extremely effective at removing PFAS. Reverse osmosis membranes are tighter than nanofiltration membranes. This technology depends on membrane permeability.Aug 23, 2018
What is fluoride, and where is it found?
Fluoride is the name given to a group of compounds that are composed of the naturally occurring element fluorine and one or more other elements....
What is water fluoridation?
Water fluoridation is the process of adding fluoride to the water supply so the level reaches approximately 0.7 ppm, or 0.7 milligrams of fluorid...
When did water fluoridation begin in the United States?
In 1945, Grand Rapids, Michigan, adjusted the fluoride content of its water supply to 1.0 ppm and thus became the first city to implement community...
Can fluoridated water cause cancer?
A possible relationship between fluoridated water and cancer risk has been debated for years. The debate resurfaced in 1990 when a study by the Nat...
Where can people find additional information on fluoridated water?
The CDC has information at https://www.cdc.gov/fluoridation/index.html on standards for and surveillance of current fluoridated water supplies in...
What is the AWWA standard for fluoride?
The AWWA standards for fluoride additives are ANSI/AWWA B701 (sodium fluoride), ANSI/AWWA B702 (sodium fluorosilicate), and AN SI/AWWA B703 (FSA). AWWA’s standards are prepared by its Fluoride Standards Committee, with oversight by the Standards Council, concurrence by the AWWA Board of Directors, and concurrence by ANSI.
What are the sources of fluoride?
According to the American Water Works Association Standards Committee on Fluorides, the sources of fluoride products used for water fluoridation in the United States are as follows: 1 Approximately 90% are produced during the process of extracting phosphate from phosphoric ore. 2 Approximately 5% come from the production of hydrogen fluoride or sodium fluoride. 3 Approximately 5% come from the purification of high-quality quartz.
What is the EPA's authority?
The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has authority over safe community drinking water, as specified in the Safe Drinking Water Act. On the basis of the scientific study of potential harmful health effects from contaminated water, the EPA sets a Maximum Contaminant Level (MCL) concentration allowed for various organisms or substances.
Does the FDA regulate bottled water?
141, July 20, 1979), they do regulate the intentional addition of fluoride to bottled water and require labeling identifying the additive used.
What is NSF 60?
The NSF/ANSI Standard 60 limits a chemical or product’s contribution of contaminants to drinking water applications. Standard 60 provides for product purity and safety assurance that aim to prevent adding harmful levels of contaminants from chemicals and water treatment additives. It includes a detailed audit of the production of the additive products, validation testing of quality, and auditing of all locations for logistic handling. There are also specific criteria for imported products from other countries, and in conjunction with NSF/ANSI Standard 223, there is conformity in quality controls regardless of where certification occurs or which entity performs the certification.
Is calcium fluoride better than sodium fluoride?
Some consumers have questioned whether fluoride from natural groundwater sources, such as calcium fluoride, is better than fluorides added “artificially,” such as FSA or sodium fluoride. Two recent scientific studies, listed below, demonstrate that the same fluoride ion is present in naturally occurring fluoride or in fluoride drinking water additives and that no intermediates or other products were observed at pH levels as low as 3.5. In addition, the metabolism of fluoride does not differ depending on the chemical compound used or whether the fluoride is present naturally or added to the water supply.
Does the FDA regulate fluoride?
FDA Regulatory Criteria for Fluoride. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) does not regulate additives used for community drinking water (i.e., tap water), because its regulatory reach concerns the safety and efficacy of food, drugs, or cosmetic-related products.
What is fluoride made of?
Fluoride is the name given to a group of compounds that are composed of the naturally occurring element fluorine and one or more other elements. Fluorides are present naturally in water and soil at varying levels. In the 1940s, scientists discovered that people who lived where drinking water supplies had naturally occurring fluoride levels ...
How much fluoride is needed for tooth decay?
Water fluoridation is the process of adding fluoride to the water supply so the level reaches approximately 0.7 ppm, or 0.7 milligrams of fluoride per liter of water; this is the optimal level for preventing tooth decay ( 1 ).
Does fluoride help with tooth decay?
It was subsequently found that fluoride can prevent and even reverse tooth decay by inhibiting bacteria that produce acid in the mouth and by enhancing remineralization, the process through which tooth enamel is “rebuilt after it begins to decay ( 1, 2 ). In addition to building up in teeth, ingested fluoride accumulates in bones.
What is the purpose of fluoride in water?
Fluoridation is the process of adjusting the concentration of fluoride in public water supplies for the prevention of dental decay. Fluoride has been added to drinking water in the United States since about 1945 and it has been estimated to reduce tooth decay by 25% in children and adults.
How much fluoride is needed for drinking water?
In fluoridation, we also set an optimal fluoride concentration, which is about 1 ppm in drinking water. However, fluoridation has a different goal from chlorination and from other instances of chemical addition in water treatment.
How to determine fluoride level?
Adjusting the fluoride level in a water supply to an optimal level is accomplished by adding the proper concentration of a fluoride chemical at a consistent rate. To calculate the fluoride feed rate for any fluoridation feeder in terms of pounds of fluoride to be fed per day, it is necessary to determine: 1 Dosage 2 Maximum pumping rate (capacity) 3 Chemical purity 4 Available fluoride ion concentration
Why is fluoride important?
Purpose of Fluoridation. Fluoride in water has been proven to protect teeth from decay. Bacteria in the mouth produce acid when a person eats sugary foods. This acid eats away minerals from the tooth's surface, making the tooth weaker and increasing the chance of developing cavities. Fluoride helps to rebuild and strengthen the tooth's surface, ...
Does chlorine react with water?
In chlorination, the chlorine must react with substances in the water, so the optimal chlorine concentration depends primarily on water characteristics. Fluoride, in contrast, is not meant to react with substances in water.
What is the best concentration of fluoride in water?
The optimal concentration of fluoride in drinking water is approximately 1 ppm, with the exact amount depending on a region's average daily temperature.
Is sodium fluoride soluble in water?
Sodium fluoride, NaF, is also dry, but is easier to feed than other powdered fluoridation chemicals because it is more soluble in water.
What are the requirements for water fluoridation?
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention developed recommendations for water fluoridation that specify requirements for personnel, reporting, training, inspection, monitoring, surveillance, and actions in case of overfeed, along with technical requirements for each major compound used.
What is fluoride in water?
Water fluoridation is the controlled adjustment of fluoride to a public water supply solely to reduce tooth decay. Fluoridated water contains fluoride at a level that is effective for preventing cavities; this can occur naturally or by adding fluoride.
How many countries have fluoridated water?
As of 2012, 25 countries have artificial water fluoridation to varying degrees, 11 of them have more than 50% of their population drinking fluoridated water. A further 28 countries have water that is naturally fluoridated, though in many of them the fluoride is above the optimal level. As of 2012, about 435 million people worldwide received water ...
What is the best way to get rid of tooth decay?
Drinking water is typically the largest source; other methods of fluoride therapy include fluoridation of toothpaste, salt, and milk. The views on the most efficient method for community prevention of tooth decay are mixed. The Australian government states that water fluoridation is the most effective way to achieve fluoride exposure ...
Does fluoride reduce cavities?
Water fluoridation reduces cavities in children, while efficacy in adults is less clear. A Cochrane review estimates a reduction in cavities when water fluoridation was used by children who had no access to other sources of fluoride to be 35% in baby teeth and 26% in permanent teeth.
Does fluoride cause dental fluorosis?
Although fluoridation can cause dental fluorosis, which can alter the appearance of developing teeth or enamel fluorosis, the differences are mild and usually not an aesthetic or public health concern. There is no clear evidence of other adverse effects from water fluoridation.
What is the best level of fluoride in water?
Higher concentrations of fluorine are found in alkaline volcanic, hydrothermal, sedimentary, and other rocks derived from highly evolved magmas and hydrothermal solutions, and this fluorine dissolves into nearby water as fluoride. In most drinking waters, over 95% of total fluoride is the F − ion, with the magnesium –fluoride complex (MgF +) being the next most common. Because fluoride levels in water are usually controlled by the solubility of fluorite (CaF 2 ), high natural fluoride levels are associated with calcium -deficient, alkaline, and soft waters. Defluoridation is needed when the naturally occurring fluoride level exceeds recommended limits. It can be accomplished by percolating water through granular beds of activated alumina, bone meal, bone char, or tricalcium phosphate; by coagulation with alum; or by precipitation with lime.
What is water fluoridation?
Water fluoridation is the water adjustment process that rises or reduces the natural fluoride concentration in drinking water to an optimum level that’s effective for reducing tooth decay and promoting good dental health. It’s done to aid in both dental and skeletal health or more specifically, to reduce and prevent the prevalence ...
What is the primary medium used for fluoride removal?
Adsorption involves filtering of water down through an adsorptive media that’s packed in a column. Many adsorptions or fluoride filters use activated alumina as the primary medium for fluoride removal.
Why is fluoride in water good for teeth?
The fluoride in the water helps strengthen teeth and makes them more resistant to acid attacks. Moreover, it helps with repairing damage caused by early decay, slowing down, or ultimately stopping the decay process.
How long does fluoride last?
The symptoms start 30 minutes after ingestion and often can last up to 24 hours. However, acute over-exposure to fluoride is very rare and it usually stems from accidental contamination of drinking water or as a result of fires or explosion.
Where does fluoride come from?
Fluoride is common in our tap water as well as in many sources of drinking water. It’s a natural mineral that exists in the earth’s upper crust and occurs naturally in surface waters and groundwater around most parts of the world. In surface waters, it occurs naturally from the weathering of rocks and soils containing fluoride compounds ...
Why is fluoride important for dental?
Fluoridated water helps conserve the natural tooth structure hence reducing the need for fillings as well as other subsequent dental treatments. It saves money especially considering that most people around the world can’t afford the cost of having regular dental checks.
What is the maximum amount of fluoride in water?
Less than 1mg/L in areas with a warm climate. Less than (up to) 1.2 mg/L in cooler climates. The maximum upper limit for fluoride in drinking water at 1.5 mg/L. These WHO standards are however not universal, especially in parts of the world where the levels of fluoride might be excessive.
What is fluoride in dentistry?
INTRODUCTION. Fluoride is the ionic form of fluorine, the thirteenth most abundant element in the earth’s crust. It is released into the environment naturally in both water and air. Its concentration in water is variable (1).
Which countries have fluoridated water?
Some of these countries include the US, Brazil, Australia, Canada, Spain, Argentina, South Korea, and New Zealand (17). Over the past 60 years, research studies conducted in several countries were remarkably consistent in demonstrating substantial reductions in caries prevalence as a result of water fluoridation.
How much fluoride is toxic to children?
In children, as little as 8.4 mg/kg may produce symptoms (30). Chronic fluoride toxicity is usually caused by high fluoride concentrations in drinking water or the use of fluoride supplements. Chronic ingestion of high doses leads to dental fluorosis, a cosmetic disorder where the teeth become mottled (1).
Where is fluoride found in the body?
About 99% of total body fluoride is contained in bones and teeth (3) , and the amount steadily increases during life.
What is the source of fluoride?
Water is the major dietary source of fluoride. The variability in water content explains much of the variability in total fluoride intake. Other important sources of fluoride are tea, seafood that contains edible bones or shells, medicinal supplements, and fluoridated toothpastes (2).
Does fluoride help with caries?
Dental caries is an infectious and multifactorial disease afflicting most people in industrialized and developing countries. Fluoride reduces the incidence of dental caries and slows or reverses the progression of existing lesions (10).
Does fluoride increase bone density?
Once taken up into bone, fluoride appears to increase osteoblast activity and bone density, especially in the lumbar spine (7). Fluoride has been suggested as a therapy for osteoporosis since the 1960s, but despite producing denser bone, fracture risk is not reduced.

Overview
Alternatives
The views on the most effective method for community prevention of tooth decay are mixed. The Australian government review states that water fluoridation is the most effective means of achieving fluoride exposure that is community-wide. The European Commissionreview states "No obvious advantage appears in favour of water fluoridation compared with topical preve…
Goal
The goal of water fluoridation is to prevent tooth decay by adjusting the concentration of fluoride in public water supplies. Tooth decay (dental caries) is one of the most prevalent chronic diseasesworldwide. Although it is rarely life-threatening, tooth decay can cause pain and impair eating, speaking, facial appearance, and acceptance into society, and it greatly affects the quality of lif…
Implementation
Fluoridation does not affect the appearance, taste, or smell of drinking water. It is normally accomplished by adding one of three compounds to the water: sodium fluoride, fluorosilicic acid, or sodium fluorosilicate.
• Sodium fluoride (NaF) was the first compound used and is the reference standard. It is a white, odorless powder or crystal; the crystalline form is pref…
Evidence
Existing evidence suggests that water fluoridation reduces tooth decay. Consistent evidence also suggests that it causes dental fluorosis, most of which is mild and not usually of aesthetic concern. No clear evidence of other adverse effects exists, though almost all research thereof has been of poor quality.
Reviews have shown that water fluoridation reduces cavities in children. A con…
Mechanism
Fluoride exerts its major effect by interfering with the demineralization mechanism of tooth decay. Tooth decay is an infectious disease, the key feature of which is an increase within dental plaque of bacteria such as Streptococcus mutans and Lactobacillus. These produce organic acids when carbohydrates, especially sugar, are eaten. When enough acid is produced to lower the pHbelo…
Worldwide prevalence
As of November 2012, a total of about 378 million people worldwide received artificially fluoridated water. The majority of those were in the United States. About 40 million worldwide received water that was naturally fluoridated to recommended levels.
Much of the early work on establishing the connection between fluoride and d…
History
The history of water fluoridation can be divided into three periods. The first (c. 1801–1933) was research into the cause of a form of mottled tooth enamel called the Colorado brown stain. The second (c. 1933–1945) focused on the relationship between fluoride concentrations, fluorosis, and tooth decay, and established that moderate levels of fluoride prevent cavities. The third period, f…