
How Does Flocculation Work in Water Treatment Plant?
- First Stage: Solid Granules Suspended in Wastewater are Negatively Charged. ...
- Second Stage: Mixers Must be Utilized to Stir the Effluent. ...
- Third Stage: A polymer chemical is added to the wastewater after floc begins to develop. ...
- Fourth Stage: After the completion of flocculation, the huge solid masses in the wastewater stream are removed. ...
What do flocculants do in water treatment?
Flocculation is a water treatment technique in which particles combine to create bigger clusters, or flocs, which are then removed from the water. This process might happen naturally or with the help of chemical agents. It is a widespread method of wastewater treatment, stormwater treatment, & purification of drinking water.
What happens during the process of flocculation?
Sep 13, 2021 · Flocculation is the water purification process to remove contaminants from the water. It is the most common process to treat wastewater management, stormwater, and drinking water, making it clean and disinfected to use. The process of flocculation is separating the solution from the sediment and debris mixed in it.
What is added to water to cause flocculation?
Flocculation is a process by which a chemical coagulant added to the water acts to facilitate bonding between particles, creating larger aggregates which are easier to separate. The method is widely used in water treatment plants and can also be applied to sample processing for monitoring applications.
What is difference between flocculation and precipitation?
Jun 11, 2020 · Coagulation-flocculation is a chemical water treatment technique typically applied prior to sedimentation and filtration (e.g. rapid sand filtration) to enhance the ability of a treatment process to remove particles. Why do water treatment plants bother performing a flocculation procedure?
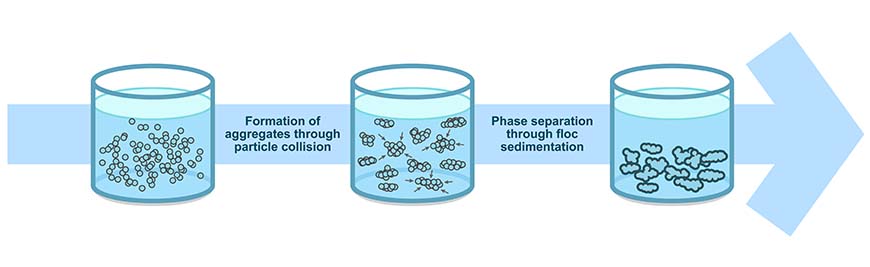
What is the flocculation process?
Flocculation is a process by which a chemical coagulant added to the water acts to facilitate bonding between particles, creating larger aggregates which are easier to separate. The method is widely used in water treatment plants and can also be applied to sample processing for monitoring applications.
Why is flocculation important in water treatment?
Coagulation and flocculation are both critical processes to separate and remove suspended solids in water and wastewater treatment. These processes improve the clarity of the water to reduce turbidity.
What flocculants are used in water treatment?
Types of coagulants and flocculantsKlarAid* coagulants – highly charged inorganic, organic and blended coagulants for clarification of industrial water and wastewater. ... Novus* flocculants – high molecular weight polymers for use as clarification, flotation and dewatering aids.More items...
What is the purpose of flocculant?
Flocculants are substances that promote the agglomeration of fine particles present in a solution, creating a floc, which then floats to the surface (flotation) or settles to the bottom (sedimentation). This can then be more easily removed from the liquid.
Why is flocculation important?
Applying flocculation ensures a high flux over filtration units as well as efficient and cost effective separation of cell material from supernatant. Used water can contain significant amounts of suspended particulate matter, which often takes long to sediment.
What is flocculation and sedimentation?
When this reaction occurs, the particles bind together, or coagulate (this process is sometimes also called flocculation). The larger particles, or floc, are heavy and quickly settle to the bottom of the water supply. This settling process is called sedimentation.Jan 23, 2017
What is coagulation and flocculation in water treatment?
Coagulation and flocculation are two separate processes, used in succession, to overcome the forces stabilising the suspended particles. While coagulation neutralises the charges on the particles, flocculation enables them to bind together, making them bigger, so that they can be more easily separated from the liquid.
What chemicals are used in flocculation?
Aluminum sulfate or alum (Al2(SO4)3), ferric chloride (FeCl3) and ferric sulfate (Fe(SO4)3) are the most widely used flocculants [1, 70]. These flocculants have a long history of use in removing colloidal particles from water and wastewater [15, 17].
What is the role of flocculins in S. cerevisiae?
Flocculation in S. cerevisiae is thought to be mediated by the binding of specific extracellular proteins, termed flocc ulins, to the high-mannose side chains of cell wall-associated glycoproteins (77). Flocculins are encoded by a small gene family consisting of at least four functional genes, FLO1, FLO5, FLO9, and FLO10, as well as three pseudogenes, all of which have a subtelomeric location analogous to that of the SUC, MAL, and MEL gene families (78). Recent work indicates that FLO gene expression is negatively regulated by the Tup1/Ssn6 complex, a general transcriptional repressor involved in repression of mating type-specific genes, glucose-repressible genes, and oxygen-sensitive genes, among others (79). Ssn6 serves as an adapter to link the complex to targeting factors specific for each class of genes, where-as Tup1 is responsible for repression per se. Repression is believed to involve a change in chromatin structure because it is accompanied by the induction of strong nucleosome phasing for long distances away from the site of initial recruitment of the complex. Consistent with this notion, the repression domain of Tup1 interacts directly with the N-terminal arms of histones H3 and H4 (80). Not surprisingly, loss-of-function mutations in either TUP1 or SSN6 result in derepression of genes regulated by the Tup1/Ssn6 complex. Such mutations also cause gross flocculation of S. cerevisiae (81,82), and recent data confirm that flocculation results from derepression of FLO gene expression (83). The relevant cis-acting element (s) and targeting factor (s) in this case have not been identified.
What is the most common secondary concentration method?
Organic flocculation is the most common secondary concentration method when a protein solution such as beef extract or skimmed milk is used as the eluant. This method was first described by Katzenelson et al.85 and involves lowering the pH of the eluant to 3.5 in order to produce protein precipitates. The virus-containing floc can subsequently be collected by centrifugation and dissolved in a small volume of buffer. Although good recoveries of enteric viruses have been reported, organic flocculation still suffers from some limitations. The low pH used in this method may compromise the viability of some viruses, especially rotaviruses.86 In addition, the residual of beef extract remaining after organic flocculation may interfere with molecular detection methods. 17
What is the ability of yeast cells to flocculate?
The ability of yeast cells to flocculate is under metabolic control; energy generation and protein synthesis are required for flocculation (Baker and Kirsop, 1972) and flocs can be dispersed by sugars, notably mannose (Taylor and Orton, 1978), although glucose and maltose are also effective (Eddy, 1955a; Mill, 1964 ).
What are the differences in the flocculation characteristics of yeast cultures?
There is no doubt that the differences in the flocculation characteristics of various yeast cultures are primarily a manifestation of the culture's cell wall structure. Several mechanisms for flocculation have been proposed. One hypothesis is that anionic groups of cell wall components are linked by Ca2+ ions.
What is flocculation in yeast culture?
The flocculation property, or conversely, lack of flocculation, of a particular yeast culture is one of the major factors when considering important characteristics during brewing and other ethanol fermentations. Unfortunately, a certain degree of confusion has arisen by the use of the term flocculation in the scientific literature to describe different phenomena in yeast cell behavior. Specifically, flocculation, as it applies to brewer's yeast, is “the phenomenon wherein yeast cells adhere in clumps and either sediment from the medium in which they are suspended or rise to the medium's surface.” This definition excludes other forms of aggregation, particularly that of ‘clumpy-growth’ and ‘chain formation’. This nonsegregation of daughter and mother cells during growth has sometimes erroneously been referred to as flocculation. The term ‘nonflocculation’ therefore applies to the lack of cell aggregation, and consequently, a much slower separation of (dispersed) yeast cells from the liquid medium. Flocculation usually occurs in the absence of cell division, but not always, during late logarithmic and stationary growth phase and only under rather circumscribed environmental conditions involving specific yeast cell surface components (proteins and carbohydrate components) and an interaction of calcium ions. Although yeast separation often occurs by sedimentation, it may also be by flotation because of cell aggregates entrapping bubbles of CO2 as in the case of ‘top-cropping’ ale brewing yeast strains.
Why is beer liable to biological instability?
Beers of this nature, because of the presence of fermentable sugars, are liable to biological instability.
What is the mechanism of destabilization of colloidal sols?
A general mechanism for the destabilization of colloidal sols by high-molecular-weight synthetic polymers, termed polyelectrolytes, is described by the theory of bridging. The polyelectrolyte is adsorbed at several sites, not covering the whole area of the colloidal particles. As the polyelectrolyte molecules are relatively long, ...
What is the most common coagulant used for water purification?
Chemicals (coagulants) are added to the water to bring the nonsettling particles together into larger, heavier masses of solids called floc. Aluminum sulfate (alum) is the most common coagulant used for water purification. Other chemicals, such as ferric sulfate or sodium aluminate, may also be used. Herein, what is coagulation and flocculation ...
What is flocculation in brewing?
Flocculation: A process wherein colloids come out of suspension in the form of floc, either spontaneously or due to the addition of a clarifying agent. It is used in applications like water purification, sewage treatment, cheese production and brewing, for example. Click to see full answer. Regarding this, what is the process of flocculation?
What is floculation in water?
Flocculation is a water treatment process where solids form larger clusters, or flocs, to be removed from water. This process can happen spontaneously, or with the help of chemical agents. It is a common method of stormwater treatment, wastewater treatment, and in the purification of drinking water. One of the requirements for treated water leaving ...
What is Cleanawater's solution?
Cleanawater offers a number of solutions for the wastewater industry to help keep wastewater within specification: Chemical dosing, in particular pH dosing, is a common method of wastewater treatment. Regulations require treated wastewater to be in a neutral pH range when discharged into the environment.
What is the charge of suspended solid particles in wastewater?
Suspended solid particles in wastewater are negatively charged. In the first stage of flocculation, a coagulant like aluminium sulphate is added to the wastewater. The positively charged coagulant molecules neutralize the negatively charged solid particles suspended in the water.
What is Cleanawater wastewater?
Cleanawater is an Australian company that specialises in wastewater treatment equipment and solutions. Our track record and experience over more than 20 years means that we have the expertise to help you solve your wastewater problems. Our technical experts can help you evaluate your application and advise you on the optimum solutions for your needs.
Why is Cleanawater important?
Cleanawater uses a chlorine-based system to achieve a high level of disinfection. This protects workers and the general public from potential health hazards associated with unwanted bacteria in the wastewater system. It is particularly important where water is recycled for use.
Why is high energy mixing required in wastewater?
The wastewater must be agitated with mixers. High energy mixing is required initially to ensure that the coagulant spreads throughout the water. When flocculation is in progress the mixing energy is reduced to prevent the mass of particles from separating again.
What is a flocculant?
Flocculants are lightweight, medium weight and heavy polymers that cause the destabilized clumps of particles to agglomerate and drop out of the solution, removing them from the filtered water. The weight used depends on the type of particle.
What percentage of giardia is removed?
The U.S. EPA surface water treatment rule requires 99.9 percent (3-log) Giardia removal or inactivation, and at least 99 percent (2-log) removal of Cryptosporidium. The combination of coagulation and flocculation is particularly useful at exceeding these guidelines.
Why is flocculation so popular?
Coagulation and flocculation processes have become more and more popular due to the increasingly stringent filtration requirements for industrial and municipal water treatment and wastewater treatment facilities levied by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA.)
What is coagulation in water treatment?
Coagulation water treatment is the first step in chemical wastewater treatment. Instead of passing over particles that would otherwise slip through the filter and fall too slowly to be trapped as sediment, coagulation clumps them together so they are more easily removed. Most of us know coagulation from anatomy class.
When was coagulation water used?
Yet coagulation water treatment is far from being a new process. In fact, it was in use by the Egyptians as early as 2,000 B.C. Later the Romans used the coagulation process in water treatment, as did the English in the 18th century.
Is alum a good coagulant?
It’s the same principle with wastewater treatment. In coagulation treatment, a harmless chemical such as alum causes all of the particles to give off a positive charge and thus clump together, making them easier to filter. Coagulation is especially useful in removing the chemical phosphorus from water. Yet coagulation water treatment is far ...
What is the last process to the first barrier against water contamination?
The last process to the first barrier against water contamination is sedimentation . During sedimentation, the flow of the water is slowed to resemble a calm environment. As the water is calmed, the large flocs that have been formed settle to the bottom of the sedimentation basin, sometimes called a clarifier. As the flocs are settling to the bottom, the relatively particle free water passes over a system of weirs and moves to the filtration process.
What is the job of an environmental engineer?
Civil and specifically environmental engineers take water from the environment that is hazardous to human health and treating it so that it is safe to drink. Students will learn and understand the challenges faced by engineers when designing the first three processes of a conventional surface water treatment plant. They will learn to think about not just the science behind engineering, but the practicalities such as cost and feasibility.
What are the three processes of treatment?
The first three processes of treatment make up the first barrier against contaminants. The main goal of coagulation, flocculation and sedimentation is to remove the particles, which could be harmful to human health, from the water. If done correctly, a majority of the incoming particles formed flocs and settled out in the sedimentation basin, yet there inevitably will be smaller particles or flocs that remain suspended in the water as it leaves. Although the probability of contaminates in the water leaving the sedimentation basin has been greatly reduced, to remove the remaining particles or flocs the water must be first passed through a media filter, which is the second barrier between potential pathogens and the consumer.
What are the steps of surface water treatment?
In this lesson students learn about the first three steps of a conventional surface water treatment plant: coagulation, flocculation and sedimentation. They learn the basic chemistry behind destabilizing natural water particles and the physics behind encouraging the collision of those particles to form flocs that will settle out of solution. Students acquire knowledge about the specifics of the three processes, while enforcing an understanding of how each process works within the overall design of water treatment.
Why are particles in water considered stable?
The cause of this stability is static electricity. Particles in natural waters are coated with macromolecules called ‘natural organic matter,’ which are produced by the decomposition of organic matter such as leaves, living organisms, aquatic plants, etc. Natural organic matter has functional groups that at neutral pH’s are negatively charged, giving the overall charge of the particles. Because all of the particles are negatively charge, they are repelled by one another so that the particles cannot collide and stick together to form larger and larger particles. Therefore, the goal of the first process in drinking water treatment, coagulation, is to destabilize the particles and allow them the potential to collide and stick together.
What is clarification aid?
In influent water and effluent wastewater treatment, clarification aids like coagulants and flocculants help remove suspended solids, including oil, organics (TOC and color) and hardness. In turn, this allows our customers to prepare their influent raw water for efficient use as process water, meet wastewater discharge regulations reliably, ...
What is Klaraid used for?
They are designed to function in a variety of industrial water and wastewater treatment applications , including use as a primary coagulant for removal of colloidal turbidity and color for raw water clarification, as a demulsifier to facilitate liquid solids separation in dissolved gas flotation units for primary wastewater treatment, and settling and filter aids used separately or in conjunction with organic flocculants.
What is Novus water soluble?
Novus products are cationic, high molecular weight water-soluble polymers provided as liquid emulsions, providing the right balance of ease of use and cost-effectiveness. They are designed to function in a variety of industrial water and wastewater treatment applications.
What is the process of destabilization of water?
Coagulation water treatment is the process of particle destabilization by charge neutralization. Once neutralized, the particles no longer repel each other and can be brought together. Coagulation is necessary for the removal of the colloidal-sized suspended matter in wastewater.
What is poly floc?
PolyFloc products are high molecular weight water-soluble polymers. They are designed to function in a variety of industrial water and wastewater treatment applications. Depending on customer preference, they are available in concentrated powder form, cost-effective emulsion liquids and convenient, easy-to-feed liquid solutions.
What is suspended matter?
Suspended matter in raw water supplies is removed by various methods to provide water suitable for domestic purposes and most industrial requirements. The suspended matter can consist of large solids, settleable by gravity alone without any external aids, and nonsettleable material, often colloidal in nature.
Does coagulation affect ionization?
Coagulation can also be affected by the addition of water-soluble organic polymers with numerous ionized sites for particle charge neutralization. Flocculation can be enhanced by the addition of high-molecular-weight, water-soluble organic polymers.
How to remove turbidity from water?
In addition to removing turbidity from the water, coagulation and flocculation is beneficial in other ways. The process removes many bacteria which are suspended in the water and can be used to remove color from the water. Turbidity and color are much more common in surface water than in groundwater.
How does flocculation work?
Flocculation follows coagulation in the conventional water treatment process. Flocculation causes the agglomeration or collection of small particles into larger, more readily settleable floc particles. It is usually a tapered process with two or more units in series. The first unit has a higher mix speed and the mixing speed decreases in subsequent basins to promote the growth of floc particles. The total detention time in the flocculation basin is normally 30 to 60 minutes. Through experience, we see that effective mixing reduces the required amount of chemicals and greatly improves the sedimentation process, which results in longer filter runs and higher quality finished water. The goal of flocculation is to form a uniform, feather-like material similar to snowflakes - a dense, clingy floc that traps the fine, suspended, and colloidal particles and carries them down rapidly in the settling basin. To increase the speed of floc formation and the strength and weight of the floc, polymers are often added.
What is coagulation reaction?
cationic, anionic, and nonionic) and molecular weight. Coagulation is a reaction caused by adding salts of iron or aluminum to the water.
Why is coagulation important in water treatment?
It is, however, an important primary step in the water treatment process, because coagulation removes many of the particles, such as dissolved organic carbon, that make water difficult to disinfect. Because coagulation removes some of the dissolved substances, less chlorine must be added to disinfect the water.
What is the purpose of coagulation?
The primary purpose of the coagulation/flocculation process is the removal of turbidity from the water. Turbidity is a cloudy appearance of water caused by small particles suspended therein. Water with little or no turbidity will be clear.
What happens when water flows over the ground?
As surface water flows over the ground to streams, through streams, and then through rivers, the water picks up a large quantity of particles. As a result, while aeration is more commonly required for groundwater, treatment involving coagulation and flocculation is typical of surface water.
How long does it take for a water mixer to shear?
However, if the water is mixed for more than sixty seconds, then the mixer blades will shear the newly forming floc back into small particles. After flash mixing, coagulation occurs.
What is coagulation and how is it used in water treatment?
Coagulation is the process of adding specific chemicals to untreated water in order to destabilize the particles within the water. In most cases, aluminum sulfate or ferric chloride is added to achieve this. These particles have positive charges that are opposite to the negative charges of suspended particles within the water.
What is flocculation and how is it used in water treatment?
Flocculation is the process of encouraging the formation of flocs, or small clumps, from solids in the water. The water is mixed and activated slowly, allowing movement of particles and micro solid throughout the waste water treatment chamber.
Deploying coagulation and flocculation together in sequence
Where coagulation is found to be lacking — i.e., in creating large macro flocs that can be easily filtered and removed — flocculation can help. In areas where flocculation is inadequate by itself — for example, in targeting the particles that are suspended within the untreated water — coagulation is useful.
