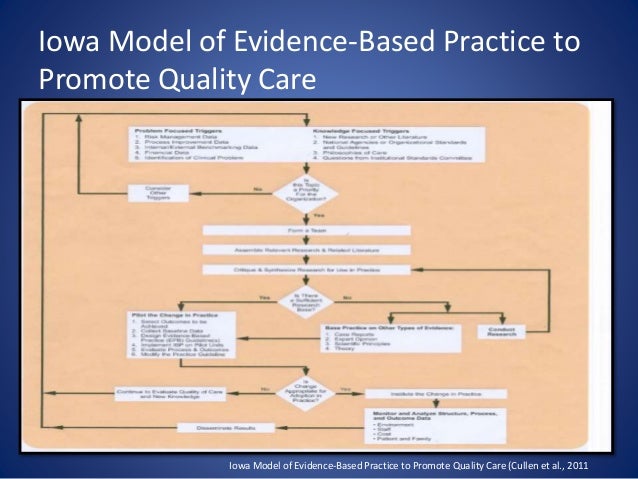
Evidence-Based Practices: Practices that integrate the best research evidence with clinical expertise and patient values. Practice-Based Evidence: A range of treatment approaches and supports that are derived from, and supportive of, the positive cultural of the local society and traditions. Click to see full answer.
Full Answer
What is the difference between research and evidence based practice?
· Answer Historically, EBM primarily involved physicians and concentrated on the“treatment” aspect of medicine. EBP takes a more multidisciplinary (nurses, clinicians, NPs, PAs, Physical & Occupational Therapists and Hospital Administration) approach and includs many facets of health including etiology, prevention, diagnosis, treatment, and more.
Does evidence based medicine does more good than harm?
· Therapists who use treatments based on science engage in what is called “evidence-based practice” (EBP). If the treatments they use have scientific evidence supporting the effectiveness of the treatments, they are called evidence-based treatments (EBTs).
What are the disadvantages of evidence based practice?
Here’s the difference: Evidence-based practice is research-based practice that has been shown effective through rigorous scientific evaluation. Best practice typically does not undergo the same scientific evaluation—those processes used in research to validate the assessment or effectiveness of practice.
What are the principles of evidence based practice?
Evidence-Based Practices: Practices that integrate the best research evidence with clinical expertise and patient values. Practice-Based Evidence: A range of treatment approaches and supports that are derived from, and supportive of, the …
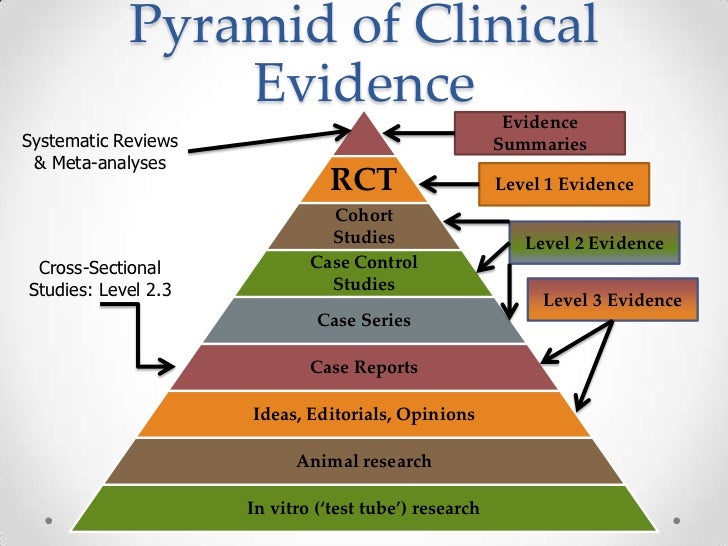
What is the difference between evidence-based treatment and Evidence-Based Practice?
Therapists who use treatments based on science engage in what is called “evidence-based practice” (EBP). If the treatments they use have scientific evidence supporting the effectiveness of the treatments, they are called evidence-based treatments (EBTs).
What is an evidence-based treatment?
Evidence-based treatment (EBT) refers to treatment that is backed by scientific evidence. That is, studies have been conducted and extensive research has been documented on a particular treatment, and it has proven to be successful.
What are examples of evidence-based treatments?
Evidence-based TherapiesApplied Behavior Analysis.Behavior therapy.Cognitive behavioral therapy.Cognitive therapy.Family therapy.Dialectical behavior therapy.Interpersonal psychotherapy.Organizational Skills Training.
What is the difference between research based practice and Evidence-Based Practice?
The main difference between Research and Evidence-Based Practice is that Research-based practice is a systematic process and is planned to carry out an investigation. While in Evidence-Based Practice, there is no systematic and planned way and all the propositions are carried out based on evidence.
Is CBT an evidence-based treatment?
CBT is an effective, evidence-based treatment plan for a wide range of disorders, so making it accessible as possible should be a priority.
What is EBP based?
'Evidence-Based Practice (EBP) requires that decisions about health care are based on the best available, current, valid and relevant evidence. These decisions should be made by those receiving care, informed by the tacit and explicit knowledge of those providing care, within the context of available resources'[3].
What is evidence-based treatment in mental health?
The Evidence-Based Treatment Practices (EBP) Evidence-based practices, or EBPs, are therapies that have been studied academically or clinically, proved successful, and replicated by more than one investigation or review, according to the National Alliance on Mental Illness.
What does CBT focus on?
Cognitive behavioral therapy focuses on changing the automatic negative thoughts that can contribute to and worsen emotional difficulties, depression, and anxiety. These spontaneous negative thoughts have a detrimental influence on mood.
What makes Qi different from research?
The QI process involves evaluating and learning from experience. Research: A systematic investigation, including research development, testing, and evaluation, designed to develop or contribute to generalizable knowledge.
Is there a difference between evidence-based and research-based?
Research-based - Parts or components of the program or method are based on practices demonstrated effective through Research. Evidence-based - The entire program or method has been demonstrated through Research to be effective.
What is research based?
Evidence-Informed (or Research-Based) Practices are practices that were developed based on the best research available in the field. This means that users can feel confident that the strategies and activities included in the program or practice have a strong scientific basis for their use.
What is a practice based research?
Practice-based Research is an original investigation undertaken in order to gain new knowledge partly by means of practice and the outcomes of that practice.
What is research based instruction?
Research-based teaching means that students carry out research in their courses independently and with an open outcome. This helps to internalize and practice research conducts and methods, skills such as formulating a precise question and processing and monitoring a research process.
Why is research important for evidence based practice?
Using EBP in clinical settings requires a working knowledge of research terms and methods. It allows nurses to implement the latest research methods in real-world scenarios, like direct patient care.
What is evidence based practice?
Here’s the difference: Evidence-based practice is research-based practice that has been shown effective through rigorous scientific evaluation. Best practice typically does not undergo the same scientific evaluation—those processes used in research to validate the assessment or effectiveness of practice.
Is best practice a clinical study?
It’s important to keep in mind that what is regarded as a best practice can blossom into a full clinical study. It then has the potential of growing and expanding into evidence-based practice.
What is the National Registry for Evidence-Based Programs and Practices?
The National Registry for Evidence-Based Programs and Practices (NREPP), which is maintained by the United States’ Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA), lists all evidence-based programs and practices. To be listed in NREPP, a practice must be determined, after extensive research, to have significant impact on ...
What is EBT in psychotherapy?
The Use of EBT in Evidence-Based Practice (EBP) Evidence-based treatments play a significant role in evidence-based practices in psychotherapy and general health care. EBP evolved from evidence-based medicine (EBM), which was established in 1992 for the same reasons: to encourage the use of safe, effective medicine as opposed to poorly studied, ...
What is effectiveness model?
Effectiveness models are associated with real-world research, in which treatments are observed in clinical settings with mental health professionals and the people who regularly come to see them. Practical clinical trials (PCTs) measure effectiveness. Many believe the ideal research situation would somehow combine the two (Nathan, 2004).
Is EBT effective in two studies?
A strong EBT will be proven effective in several studies—not one or two. It is also important to look at who is funding the research, as well as how and where the studies are conducted; ideally, multiple independent and unbiased studies will be conducted that verify the safety and effectiveness of a treatment.
Is EBM a problem?
EBM is now the problem, fueling overdiagnosis and overtreatment.”. Along these lines, there is also the argument that all forms of treatment in psychotherapy offer some benefit, regardless of the quantity or quality of supporting evidence.
Is EBT based on scientific evidence?
EBT in Child and Adolescent Therapy. Since they are presumably based on scientific evidence, evidence- based treatments are encouraged in coping with issues faced by children and adolescents. However, it is important to note that when choosing a treatment for a minor, parents, guardians, and practitioners should always examine ...
Is EBT evidence based?
Of course, the incorpora tion of EBT is just one facet of evidence-based practice ; EBP also stresses the importance of informed decision-making when determining how to approach a person’s health situation. This requires a physician or mental health professional to be aware of current discoveries and dialogue in the research field, thereby enabling him or her to examine all possible approaches to treatment.
What is the need for improvement in EBP?
Findings demonstrate a compelling need for improvement in knowledge and implementation of EBP in CNs, compared with the better attitudes. Except education, knowledge translating into implementation needs more coordination with authorities to magnify the facilitators and overcome the barriers. Further studies need to concentrate on deficient knowledge and implementation of EBP among CNs. Policy makers can use the facilitators and barriers found by this review to modify nursing education, current scientific resources supplement, practice supports for care improving.
What is EBP in nursing?
WHO has suggested that health improving in communities is dependent upon nursing services underpinned by evidence-based practice (EBP).[2] EBP refers to using the best available evidence for decision-making and providing efficient and effective care for patients on a scientific basis.[6] Systematic implementation of EBP can enhance healthcare safety and improve patient outcomes. [7,8]Although EBP is equally important to CNs as it is to clinical nurses, EBP in community nursing is still in the initial stage. [5]
What are the limitations of systematically electronic databases?
One of the limitations is that though systematically electronic databases searching has been down, some relevant literatures may be missed as in any reviews.[ 61] To avoid this, the articles were independently searched by 2 researchers and all eligible articles were saved with maximum degree. Language and publication bias were possible despite that our review scope was increased to worldwide.
What are the barriers to EBP?
Barriers of EBP among CNs were mostly gathered in an environment scale. Time and resources were referred mostly.[58] When workload is too heavy, nurses are less likely to search and apply evidence. [55,58]Nurses who have access to more available resources, such as electronic databases, libraries, and professional guidelines, tend to rely more on scientific evidence. [59,30]Four articles referred inadequate knowledge as a barrier, and indicated that the current academic education programs did not adequately prepared for EBP implementation. [23,15,28,59,60]Barriers distributed evidence was relatively less, and these can be overcome by providing more evidence resources, peer supports, and literature screening skills. All cited barriers can be ascribed to 3 possible factors ultimately: inadequate supports of time and resources, inadequate knowledge and training, inadequate encouragement, and assistance from organizations. Barriers were recognized by researchers; however, workable and comprehensive approaches to overcome these barriers are lacking. Measures reported in studies were educational programs generally, which are effective in knowledge improving. More concerns should be focused on EBP implementation. Barriers must be settled, not just in education and training, but also in objective barriers and comprehensive elimination. Policy support and institutional protection is not a choice, but a necessity. More investment in resource supplement, nursing workforce, nursing guidance, and EBP approaches is needed for well EBP implementation, and therefore CNs can get abundant research time and resources, better EBP operating environment, and additional supports from working stuff and managements.
How many facilitators are there in EBP?
Fourteen facilitators and 21 barriers of CNs’ EBP application were identified and were divided into 3 themes: characters of the evidence (e.g., the presentation, quantity, and quality of the studies); characters of the environment, that is, facilitators and barriers perceived in the work settings; characters of the nurses, that is, the nurses’ values, skills, and awareness about EBP (Table (Table22).
What are the attitudes of CNs about EBP?
Contrary to the lacking of knowledge, CNs consistently expressed satisfactory attitudes and beliefs about EBP. They agreed that primary care needed to keep up with current scientific base and best evidence. [23,27,28]This positive attitude toward EBP may be associated with evidence-based intervention experience, working years in nursing,[37]the role of leader (having more authority and influences),[15]EBP experiences,[24]job satisfaction and group cohesion, organizational culture, and, readiness for system-wide integration of EBP.[33] However, positive attitudes toward EBP did not mean the implementation of EBP.[51] Rutledge and Skelton[15]found that after 1-year training program focusing on EBP facilitation skills, almost all participants have more confidence in EBP, whereas they had not implement EBP into daily job. Other researchers[51]also supported that despite familiarity with EBP, nurses seldom participated in EBP.
Why was no study excluded in the quality assessment stage?
No study was excluded in the quality assessment stage because potential valuable insights may be presented even in lower quality researches.[ 47] The bias caused by researchers should be noted because no cross-sectional study explained unified training and education for the data collectors in the use of measuring tools, and the dealing of confounding factors within the study design or in data analysis was not shown. No author stated the influences of researcher on the study of qualitative designs, nor specified clear philosophical perspective. With regards to quasi-experimental studies, there was a lack of report about confounding variables on whether participants were involved in other similar studies contemporarily. The designs of randomized controlled trial's (RCT) randomization and concealment were insufficient and needed to be improved in blind design.[48] Comprehensive application of mixed methods studies was satisfied, but the interview context description and controlling of confounding variables were deficient. [49]
What is evidence based practice?
APA's definition of evidence-based practice includes the clinician, or more precisely the role of “clinical expertise.” Clinical expertise encompasses the assessment of clients and the provision of appropriate services. A therapist must ultimately use a decision-making process (i.e., clinical judgment) to determine if an intervention, based on the latest research, is likely to be effective for a particular client given his or her unique circumstance. This component of the definition acknowledges the inherent limitation of research findings—that the individual application of research is constrained by myriad client and environmental factors that could potentially influence the effectiveness of a type of treatment. Practitioners must use their clinical judgment and expertise to determine how to implement, and if necessary, modify a given approach for a particular client, in a particular circumstance, at a particular time.
What is the difference between EBP and EBT?
The clinical expertise component of EBP also distinguishes the two different approaches to evidence. EBP tends to appeal to those who value clinicians' autonomy and individualized treatment decisions while EBT tends to appeal to those who believe that more structure and consistency is needed to ensure positive outcomes (Littell, 2010 ). As noted, EBTs focus on the treatment, intervention, or program itself and not on who is delivering or receiving it. This is perhaps the biggest difference between EBT and EBP.
What is the best available research?
Consisting of both researchers and practitioners, the APA Task Force defined “the best available research” as “results related to intervention strategies, assessment, clinical problems, and patient populations in laboratory and field settings as well as to clinically relevant results of basic research in psychology and related fields” ( 2006, p. 274). In contrast to the efforts of Division 12 and others that delineate the RCT as the gold standard of research, the Task Force did not identify one research methodology to be superior, maintaining that different methodologies are required to answer different research questions, including effectiveness studies, process research, single-subject designs, case studies, and qualitative methodologies.
What is the raison d'être of empirically supported treatment?
Accountability via the application of research to practice is the raison d'être of the empirically supported treatment (EST), evidence-based treatment (EBT), and evidence-based practice (EBP) movements. Although basing practice on empirical findings seems only reasonable, application becomes complex when unfurled in the various social, political, economic, and other ideological contexts that influence the delivery of mental health services (Norcross, Beutler, & Levant, 2006). This chapter describes two different approaches to defining and disseminating evidence (Littell, 2010)—one that seeks to improve clinical practice via the dissemination of treatments meeting a minimum standard of empirical support (EBT) and another that describes a process of research application to practice that includes clinical judgment and client preferences (EBP). We unfold the controversy by addressing the nature of evidence, how it is transported to real-world settings, and ultimately, whether such evidence improves client outcomes. To further inform the debate surrounding the two approaches, this chapter also discusses the randomized clinical trial (RCT), its specificity assumption, and the connection of the RCT to a medical model way of understanding psychotherapy. Finally, we strike at the heart of the controversy by tackling the thorny question of whether EBTs should be mandated.
Is EBT limited to racial minority?
For example, EBT research of racial/ethnic minority, sexual minority, or economically disadvantaged populations is limited, and therefore it is unknown if the efficacy of EBTs extend to such groups.