Is endovascular therapy effective in the treatment of ischemic stroke?
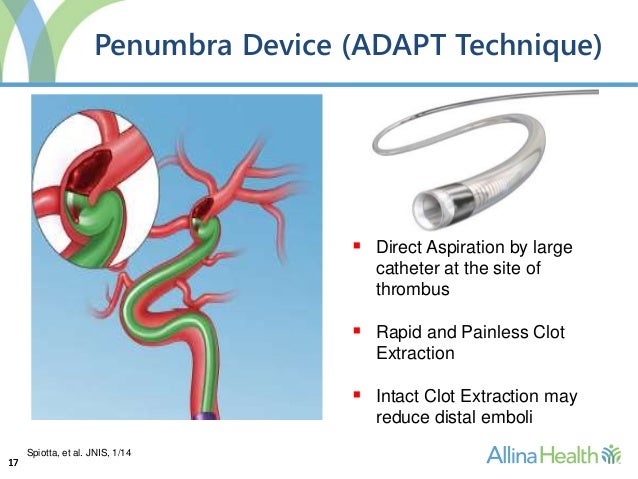
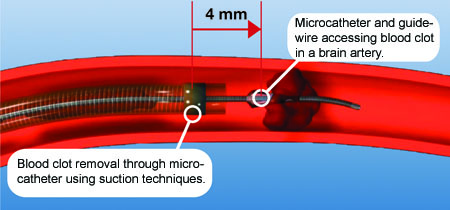
Endovascular treatment of stroke is the non-surgical treatment for the sudden loss of brain function due to blood clots. The treatment uses microcatheters (thin tubes visible under X-rays) which are inserted into the blood clot from the groin or the arm. The blood clot is removed from the blood vessel – this procedure is called a thrombectomy.
What is the treatment for ischemic stroke due to anterior circulation occlusion?
Sep 18, 2015 · The MR CLEAN study (Multicenter Randomized Clinical Trial of Endovascular Treatment for Acute Ischemic Stroke in the Netherlands) is the first randomized controlled trial that proved the efficacy of mechanical thrombectomy . MR CLEAN avoided the drawbacks of previous trials by only including proven large artery occlusion within 6 h of anterior stroke, …
What are the risks of endovascular treatment after a stroke?
Endovascular treatment for acute ischemic stroke. The results of this trial in patients with acute ischemic stroke indicate that endovascular therapy is not superior to standard treatment with intravenous t-PA. (Funded by the Italian Medicines Agency, ClinicalTrials.gov number, NCT00640367.). The results of this trial in patients with acute ischemic stroke indicate that …
Is endovascular treatment for large arterial occlusion safe and effective?
May 15, 2013 · Methods: The SYNTHESIS Expansion trial investigators randomly assigned 362 patients with acute ischemic stroke, within 4.5 hours after onset, to endovascular therapy (intra-arterial thrombolysis with recombinant tissue plasminogen activator [t-PA], mechanical clot disruption or retrieval, or a combination of these approaches) or intravenous t-PA. The …
What is endovascular therapy for ischemic stroke?
What is an endovascular treatment?
What is the primary treatment for acute ischemic stroke?
What is an endovascular thrombectomy?
What is the difference between endovascular and vascular surgery?
Is Angioplasty an endovascular procedure?
What is the treatment for ischemic?
What are 3 possible treatments of an ischemic stroke?
- Thrombolysis – "clot buster" medicine. ...
- Thrombectomy. ...
- Aspirin and other antiplatelets. ...
- Anticoagulants. ...
- Blood pressure medicines. ...
- Statins. ...
- Carotid endarterectomy.
Which drug class is the recommended treatment for a patient with ischemic stroke not caused by a cardiac embolism?
How is endovascular thrombectomy performed?
A balloon catheter guide is inserted into the femoral artery in the groin and advanced to the carotid artery using angiography, a medical imaging technique that allows the neurosurgeon to see inside of blood vessels. A micro-catheter and micro-wire are inserted into the brain beyond the clot.
What are the steps of an endovascular thrombectomy?
What is CTA CTP?
Study Questions
What is the clinical benefit of endovascular therapy for treatment of acute ischemic stroke?
Methods
The SYNTHESIS Expansion trial investigators randomly assigned 362 patients with acute ischemic stroke, within 4.5 hours after onset, to endovascular therapy (intra-arterial thrombolysis with recombinant tissue plasminogen activator [t-PA], mechanical clot disruption or retrieval, or a combination of these approaches) or intravenous t-PA.
Results
A total of 181 patients were assigned to each arm. The median time from stroke onset to the start of treatment was 3.75 hours for endovascular therapy and 2.75 hours for intravenous t-PA (p < 0.001). At 3 months, there was no difference in the patients alive without disability in each arm (30.4% vs. 34.8%).
Conclusions
The investigators concluded that endovascular therapy is not superior to standard treatment with intravenous t-PA.
Perspective
Endovascular therapy for stroke is associated with better recanalization rates compared with fibrinolytics, although the clinical impact of this approach has been questionable. This study suggests that endovascular therapy was not associated with a meaningful clinical benefit.
How effective is mechanical thrombectomy?
Now that the effective treatment for AIS in patients with LVO has been established, we need effective protocols to ensure patients are brought, in timely fashion, to comprehensive stroke centers and thrombectomy-ready centers. It will also be necessary to have sufficient numbers of well-trained hospital staff including stroke neurologists and endovascular experts to deal with an increase in patients with stroke who require screening and treatment. Systems of care for people who have had a stroke need to be adapted so that optimal treatments are available to all patients. It is of paramount importance that we educate not only our colleagues, but also the general population, about the advancement and treatment options for patients with stroke so they can receive the treatment they deserve.
What is a mechanical embolus removal device?
The mechanical embolus removal in cerebral ischemia (Merci) device (Stryker, Kalamazoo, MI) was the first endovascular clot retrieval device investigated in a new era of mechanical thrombectomy, and recanalization was achieved in 48% of patients treated. 6 Neurologic improvement, measured as an increase of ≥ 10 points on the National Institutes for Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS), was seen in approximately 32% of patients, and the symptomatic intracranial hemorrhage rate was low (7.8%). 6 Endovascular clot removal with the second-generation Merci device resulted in a recanalization rate of 69.5% when combined with IA-rTPA. 7
Lessons From Current Evidence
The 4 pillars of successful revascularization with endovascular therapy to achieve a good clinical outcome are the following:
Exploring the Edges of Evidence and Special Populations
As in other fields of medicine, randomized controlled trials results need to be judiciously applied to individual patients. Although some cases represent natural extrapolation of the evidence, other situations are more distinct ( Table ). We discuss 4 situations where the evidence is not entirely clear.
Implementation of the Current Evidence
We are faced with multiple implementation challenges. 32 First, effectively organized systems of care are essential to provide this treatment to eligible stroke patients as quickly as possible. Second, future technological innovations will affect the evolution of care.
Disclosures
Dr Goyal has received research grants from Covidien for design and conduct of SWIFT PRIME trial. Also, Covidien provided partial funding of the ESCAPE trial to the University of Calgary. Dr Goyal has received honoraria from Covidien (significant) and Stryker (modest) for speaking engagements.
Footnotes
The opinions expressed in the article are not necessarily those of the editors or of the American Heart Association.

Introduction
Early Trials 1999-2004
- The early belief was that direct intra-arterial (IA) thrombolytic administration to the occluded vessel would provide improved rates of recanalization superior to that of IV-rTPA. Although efficacy of IA prourokinase (IA-r-proUK) for thrombolysis was demonstrated for patients with middle cerebral artery (MCA) occlusion in a randomized controlled trial,5the bleeding rate was s…
Second-Generation Trials 2005-2012
- The mechanical embolus removal in cerebral ischemia (Merci) device (Stryker, Kalamazoo, MI) was the first endovascular clot retrieval device investigated in a new era of mechanical thrombectomy, and recanalization was achieved in 48% of patients treated.6 Neurologic improvement, measured as an increase of ≥10 points on the National Institutes for Health Strok…
Next-Generation Trials 2015
- The next generation of trials demonstrated the clear efficacy of EVT combined with IV-rTPA versus IV-rTPA alone. The MR CLEAN trial showed clear benefit in outcomes for patients who had EVT.12 Second-generation thrombectomy devices—stent retrievers (also called stentrievers)—were used in the majority of patients undergoing EVT. There was no upper-limit a…
Role of Imaging in Patient Selection
- Initial imaging for patients presenting with suspected LVO typically includes a noncontrast head CT and a head and neck CTA. These studies provide adequate information to identify patients who would benefit most from EVT within 6 hours of symptom onset. The Alberta stroke program early CT (ASPECT) score, a 10-point grading system used to detect early ischemic changes on h…
Recent Trials Extend Time Window For Intervention
- The DAWN trial demonstrated an increased rate of functional independence in patients treated with thrombectomy plus CMM (49%) compared to CMM alone (13%).21 The DEFUSE 3 trial was terminated early because on interim analysis it showed improved functional outcomes with thrombectomy plus CMM alone when treatment occurred from 6 to 16 hours after ischemic stro…
Recommendations
- There has been a revolution in treatment of AIS in recent years extending the treatment window to 24 hours and beyond. When done in a timely fashion and for the right patient population, mechanical thrombectomy is a highly effective therapy. Now that the effective treatment for AIS in patients with LVO has been established, we need effective protocols to ensure patients are br…