
Medication
- Avoid sharing needles, razor blades, or nail clippers.
- Use proper safety precautions if you’ll be exposed to bodily fluids, such as when performing first aid.
- Hepatitis C isn’t usually transmitted through sexual contact, but it’s possible. Limit your exposure by practicing sex with a condom or other barrier method. ...
Procedures
How To Beat Hep C Naturally. There are a number of ways you can combat the symptoms that come with being diagnosed as having chronic fatigue syndrome. Whether it’s through treatments like temping, acupuncture or yoga which have been shown to help alleviate some depression issues along with sleep problems and other common challenges faced by ...
Self-care
The hepatitis C antibody will be permanently positive, but this doesn’t mean you’re reinfected. For some people, hepatitis C can also clear up on its own. This is called spontaneous remission. Infants and young women in particular may have a chance of the virus clearing itself out of their bodies. This is less likely among older patients.
Nutrition
What should a provider do for a patient with confirmed HCV infection?
- medical evaluation (by either a primary-care clinician or specialist [e.g., in hepatology, gastroenterology, or infectious disease]) for chronic liver disease, including treatment and monitoring;
- hepatitis A and hepatitis B vaccination;
- screening and brief intervention for alcohol consumption; and
- HIV risk assessment and testing.
How do you cure Hepatitis C naturally?
How to beat Hep C naturally?
Can hepatitis C be cured on its own?
What should someone do after treatment for hepatitis C?

What is the success rate of Hep C treatment?
Hepatitis C treatment can cure more than 90 percent of hepatitis C cases, but testing is a critical first step. It's estimated 40 percent of people with hepatitis C in the U.S. from 2015-2018 were unaware of their infection.
Which treatment is best for hepatitis?
Several antiviral medications — including entecavir (Baraclude), tenofovir (Viread), lamivudine (Epivir), adefovir (Hepsera) and telbivudine (Tyzeka) — can help fight the virus and slow its ability to damage your liver. These drugs are taken by mouth. Talk to your doctor about which medication might be right for you.
Can your body fight off hep C?
Among those who do have symptoms, the illness is usually so mild that most don't even recognize that they have liver disease. In 15-40% of persons with acute hepatitis C, the immune system successfully fights off the infection, the virus is cleared from the body within 6 months, and the liver heals completely.
What is the first line of treatment in hepatitis?
Currently, pegylated interferon alfa (PEG-IFN-a), entecavir (ETV), and tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (TDF) are the first-line agents in the treatment of hepatitis B disease.
What is hepatitis C?
Hepatitis C, or hep C, is an infection of the liver caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV). The virus is transmitted through the blood, most commonly through contaminated needles, but also through sex. In 75% to 85% of cases, the infection becomes “chronic,” which means the body cannot get rid of it.
What are the new hep C treatments?
The new treatments for hep C type 1 (DAATs or direct-acting antiviral therapies) include drugs like:
How can I be sure my hep C is cured?
12 weeks after your treatment has ended, a blood test can measure how much viral genetic material (viral RNA) is in your blood. If no viral RNA is detected, this is called a “sustained virologic response” (SVR, for short). An SVR is important because studies show us that 99% of all SVRs end in a long-term cure.
How much do the new hep C treatments cost?
The new hep C drugs are expensive. So expensive, that two of them make it onto our list of the 11 Most Expensive Drugs in the U.S.A. This is because they are still patented (although that is due to run out this year for Harvoni and Epclusa—but without any promise of significantly cheaper generics ).
What was the only treatment for hepatitis C?
Before 2014, the only treatment for hepatitis C was called interferon and ribavirin, taken as weekly injections under the skin, plus pills. Interferon treatment caused many unpleasant side effects and was not usually successful. Then a new generation of medications became available.
How to get rid of hepatitis C?
Eat well, drink 8 to 10 glasses of water each day, and try to get a full night's sleep. Learn about the hepatitis C medications you are taking. This includes special risks and warnings. If taking ribavirin, use sunscreen, wear long sleeves and a hat, and limit sun exposure.
How to remove hepatitis C virus?
remove (or clear) all the hepatitis C virus from your body permanently. stop or slow down the damage to your liver. reduce the risk of developing cirrhosis (advanced scarring of the liver) reduce the risk of developing liver cancer (hepatocellular carcinoma) reduce the risk of liver failure and the need for a liver transplant.
How long does it take for a hepatitis C flare to occur?
The flare usually occurs within a few weeks after the patient starts taking medication for hepatitis C.
What are the patients who should be seen by a hepatitis C specialist for treatment?
drink alcohol. are homeless. have other medical problems. Patients who should be seen by a hepatitis C specialist for treatment are patients who: have been previously treated but the treatment failed. have cirrhosis and have been ill from their cirrhosis. have fluid in the abdomen.
How long does it take to cure HCV?
Treatment is usually 8-12 weeks long but can be as much as 16 weeks long in certain situations. Some patients with more damage to their liver may require 24 weeks of treatment, but this is uncommon. The duration depends on the medication, and specific HCV factors in particular patients.
Does hepatitis C affect the liver?
In an untreated state, the hepatitis C virus infects the cells of the liver and then continuously lives there, making copies of itself that circulate in the bloodstream. Antiviral medications can destroy the ability of the virus to reproduce, so the amount of virus in the bloodstream then decreases.
What is the best medication for hepatitis C?
A Full List of Hepatitis C Medications: Epclusa, Harvoni, Zepatier, and More. Hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection causes liver inflammation that can lead to liver problems, including cancer. People who have chronic hepatitis C need medication to treat it. These drugs can help ease symptoms.
Why is it important to treat hepatitis C?
Even if an HCV infection hasn’t caused symptoms yet, it’s still important to treat it. This is because drugs can also lower the risk of complications from hepatitis C, such as dangerous liver problems. HCV has different genetic variations ...
What is the name of the drug that is used to treat cirrhosis?
Epclusa, which contains sofosbuvir and velpatasvir, was approved in 2016. It can be used in combination with ribavirin in people with moderate to severe cirrhosis. Epclusa was the first medication to treat all six HCV genotypes.
What are directed inhibitors used for?
These drugs are used to treat all HCV genotypes. They’re used alone or in combination with other medications. Examples of directed inhibitors include ledipasvir, a component of the combination drug Harvoni and elbasvir, a component of the combination drug Zepatier.
How does ribavirin work?
Ribavirin works by stopping viruses from replicating and spreading. It’s an oral medication that comes as a capsule or tablet and is available in several strengths. It’s always used in combination with other drugs to treat hepatitis C. The most common brand name of ribavirin is Rebetol.
Can interferons be used for hepatitis C?
Interferons. Interferons were the standard treatment for hepatitis C for many years, but now, the newer treatments listed above are typically used instead. This is because interferons can cause a lot of side effects, and they’re not as effective for treating chronic HCV infection.
Does Vosevi work for hepatitis C?
It contains the drugs sofosbuvir, velpatasvir, and voxilaprevir. Vosevi is intended for use in people who’ve been treated with sofosbuvir, which didn’t work to treat hepatitis C.
How rare is hepatitis C?
Now that more advanced screening tests for hepatitis C are used in blood banks, the risk of transmission to recipients of blood or blood products is considered extremely rare, at <1 case per 2 million units transfused.
What is the aseptic technique for HCV?
All health-care personnel, including those who are HCV positive, should follow a strict aseptic technique as described by the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health and the CDC, including appropriate hand hygiene, use of protective barriers, and safe injection practices.
What is the risk of cirrhosis in the following year?
Patients who develop cirrhosis have a 1%–4% annual risk of developing hepatocellular carcinoma and a 3%–6% annual risk of hepatic decompensation; for the latter patients, the risk of death in the following year is 15%–20% ( 7 ).
Can hepatitis C cause liver enzymes to fluctuate?
Yes. It is common for patients with chronic hepatitis C to have fluctuating liver enzyme levels, with periodic returns to normal or near normal levels. Liver enzyme levels can remain normal for over a year despite chronic liver disease ( 28 ).
Does dental surgery spread hepatitis C?
As long as Standard Precautions and other infection-control practices are consistently implemented, medical and dental procedures performed in the United States generally do not pose a risk for the spread of hepatitis C.
Is hepatitis C test complete?
If a person tests positive for HCV antibodies, hepatitis C testing is not considered complete unless the initial positive anti-HCV test is followed by a test for HCV RNA as per CDC guidelines. A positive test for HCV RNA is needed before a patient can be diagnosed with current HCV and begin receiving treatment.
How to prevent hepatitis C?
Hepatitis C can be prevented. 1 Avoid sharing or reusing needles, syringes or any other equipment used to prepare and inject drugs, steroids, hormones, or other substances. 2 Do not use personal items that may have come into contact with an infected person’s blood, even in amounts too small to see, such as glucose monitors, razors, nail clippers, or toothbrushes. 3 Do not get tattoos or body piercings from an unlicensed facility or in an informal setting.
How long does it take to cure hepatitis C?
Treatments are available that can cure most people with hepatitis C in 8 to 12 weeks.
What is hepatitis C?
Hepatitis C is a liver disease caused by the hepatitis C virus. When someone is first infected with the hepatitis C virus, they can have a very mild illness with few or no symptoms or a serious condition requiring hospitalization.
How does hepatitis C spread?
The hepatitis C virus is usually spread when someone comes into contact with blood from an infected person. This can happen through: ► Sharing drug-injection equipment. Today, most people become infected with hepatitis C by sharing needles, syringes, or any other equipment used to prepare and inject drugs. ► Birth.
What happens if you get hepatitis C?
Left untreated, chronic hepatitis C can cause serious health problems including liver disease, liver failure, liver cancer, and even death.
How long does it take for hepatitis C to show up?
If symptoms occur with a new infection, they usually appear within 2 to 12 weeks, but can take up to 6 months to develop. People with chronic hepatitis C can live for years without symptoms or feeling sick. When symptoms appear with chronic hepatitis C, they often are a sign of advanced liver disease.
What causes hepatitis in the liver?
When the liver is inflamed or damaged, its function can be affected. Heavy alcohol use, toxins, some medications, and certain medical conditions can cause hepatitis. Hepatitis is most often caused by a virus. In the United States, the most common types of viral hepatitis are hepatitis A, hepatitis B, and hepatitis C.
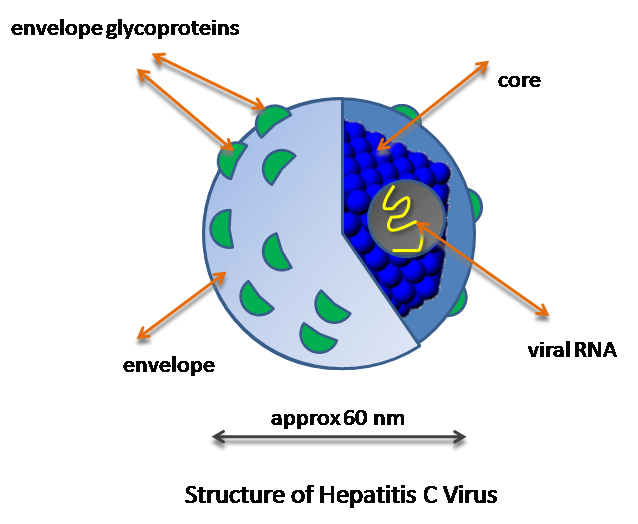
Diagnosis
Clinical Trials
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Preparing For Your Appointment
Specialist to consult
Treatment
- Screening for hepatitis C
The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommends that all adults ages 18 to 79 years be screened for hepatitis C, even those without symptoms or known liver disease. Screening for HCVis especially important if you're at high risk of exposure, including: 1. Anyone who has ever i…
Medical uses
- Explore Mayo Clinic studiestesting new treatments, interventions and tests as a means to prevent, detect, treat or manage this condition.
Mechanism
- If you receive a diagnosis of hepatitis C, your doctor will likely recommend certain lifestyle changes. These measures will help keep you healthy longer and protect the health of others as well: 1. Stop drinking alcohol.Alcohol speeds the progression of liver disease. 2. Avoid medications that may cause liver damage.Review your medications with your doctor, including o…
Prognosis
- If you think you may have a risk of hepatitis C, see your family doctor. Once you've been diagnosed with a hepatitis C infection, your doctor may refer you to a specialist in liver diseases (hepatologist) or infectious diseases.
Symptoms
- Hepatitis C virus is treated with all-oral medications. These pills, called antiviral medications , are usually taken once per day. These antiviral medications are extremely good at attacking the virus and preventing it from multiplying. Antiviral medications were not the original treatment for hepatitis C. Before 2014, the only treatment for hepat...
Results
- Ribavirin (without interferon) is still sometimes prescribed to be taken along with the new antiviral medicines, but it has become more and more uncommon that ribavirin is needed at all. Ribavirin has some mild-moderate side effects. Ribavirin is a pill taken twice per day, as 2 or 3 pills in the morning plus 2 or 3 pills at night, depending on the patient's body weight. Most patients do not n…
Access
- In an untreated state, the hepatitis C virus infects the cells of the liver and then continuously lives there, making copies of itself that circulate in the bloodstream. Antiviral medications can destroy the ability of the virus to reproduce, so the amount of virus in the bloodstream then decreases. The amount of virus in the blood is measured by a viral load (also called HCV RNA).