
How does eecp therapy reverse cardiovascular disease?
What Are the Benefits of EECP Treatment? Increased oxygen supply for the heart Decrease in chest pain Improved EKG response to exercise Decrease in nitroglycerin use Increase in energy Increased exercise duration Long term effects up to 2 years
Where to get eecp therapy?
EECP is a non-invasive treatment procedure used for patients that suffer from symptoms of Angina such Chest Pain, Shortness of Breath and Fatigue caused by narrowed or blocked arteries . EECP Therapy is a low risk of any potential complications that are associated with other traditional invasive surgical procedures.
Is eecp therapy right for me?
Enhanced External Counterpulsation (EECP) is a non-invasive, FDA-approved outpatient therapy to reduce the intensity and frequency of angina-related chest pain. EECP treatment is administered through three sets of cuffs that are applied around the calves, thighs, and buttocks.
How beneficial is eecp?
Enhanced external counterpulsation (EECP) is a noninvasive procedure in which a set of inflatable cuffs (similar to blood pressure cuffs) mechanically compress the blood vessels in your lower limbs. This increases the blood flow and oxygen back to the heart, reducing the work that the heart has to do.
How does EECP treatment work?
EECP treatment applies pressure to blood vessels in your lower limbs. The pressure increases blood flow back to your heart, so your heart works better. When your heart pumps better, symptoms ease. This type of therapy can also encourage blood vessels to open new pathways for blood to flow to your heart.Mar 17, 2022
Is EECP therapy effective?
EECP has proven to be a safe, effective and non-invasive therapy for a patient with refractory angina. It has been shown to improve the health-related quality of life in diabetic and non-diabetic patients with CAD.May 6, 2020
How long does EECP last?
“The great majority of participants have more energy and can exercise with much less angina or heart pain,” Rubenfire adds. “For some, the effects of EECP treatment can last up to two years.”Mar 13, 2017
What are the benefits of EECP?
EECP helps grow new collaterals for blood to flow, like a natural bypass around blocked arteries. Increases blood flow. EECP acts like a second heart and improves circulation of oxygenated blood throughout the arterial system and organs of the body when the heart is at rest.
Does EECP hurt?
EECP can be somewhat uncomfortable but is generally not painful. In studies, the large majority of patients have tolerated the procedure quite well.Apr 3, 2022
What is the cost of EECP?
In india usually a center who is providing which matches international standards charge between 80000 Rs - 120000 for 35 sessions of EECP. The overall price can be higher if number of sessions are increased due to any reason.Dec 15, 2019
Is EECP approved in India?
The Government Order in G.O. No. 174 has approved the treatment of Enhanced External Counter Pulsation Therapy (EECP), which is a non-invasive one.Aug 28, 2014
What are the side effects of EECP treatment?
EECP increases blood flow to the heart, while simultaneously stimulating the opening and formation of collaterals (small branches of blood vessels around the heart) to create a natural bypass around narrowed or blocked arteries. Common side effects with EECP: Skin bruising/abrasion. Back and leg pain*
How old is EECP?
EECP treatment originated in China where it has been extensively used since the 1960s. In the past 10 years it has been introduced to the United States, where there are currently around 1200 machines in operation.
Can EECP reduce blood pressure?
Conclusions: EECP therapy leads to a reduction in both systolic and diastolic blood pressure, which is most prominent in patients with baseline hypertension. These results maintain throughout the 35 sessions.Sep 14, 2017
Is EECP therapy FDA approved?
EECP is a non-invasive therapy that has been approved by the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the management of refractory angina and heart failure.
Is EECP an alternative to bypass surgery?
EECP is a US-FDA approved alternative treatment for patients who are advised angioplasty and bypass surgery. How long does the treatment take? EECP is a 35 day's treatment in which patient has to come daily for one hour sessions.Jan 29, 2021
History of EECP Treatment
EECP treatment originated in China where it has been extensively used since the 1960s. In the past 10 years it has been introduced to the United St...
Who Is Eligible For EECP Treatment?
Individuals are eligible for treatment if they have: 1. Had coronary artery bypass (CABG) or stents placed in the coronary arteries with ongoing an...
Who Should Not Seek EECP Treatment?
Patients who should not undergo EECP include those with: 1. Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy 2. Congenital heart disease 3. Valvular disease 4. Enlarged...
What Are The Benefits of EECP Treatment?
1. Increased oxygen supply for the heart 2. Decrease in chest pain 3. Improved EKG response to exercise 4. Decrease in nitroglycerin use 5. Increas...
University of Michigan EECP Program Overview
Before beginning EECP, you should: 1. Get a physician referral 2. Schedule your pre-treatment appointments, which include: 1. Nursing assessment 2....
How does EECP work?
Treatment is administered through three pairs of external inflatable cuffs that are applied around the lower legs, upper legs and buttocks. These cuffs continuously inflate and deflate between the resting period of the heartbeat and increase blood returned to the heart. The basic principle of EECP treatment involves increasing the amount ...
Where did EECP originate?
EECP treatment originated in China where it has been extensively used since the 1960s. In the past 10 years it has been introduced to the United States, where there are currently around 1200 machines in operation. The idea for EECP stemmed from the development of the intra-aortic balloon pump (IABP). IABP resulted in increasing the amount of blood that can get pumped out of the heart by inflating a balloon in the aorta between each heartbeat. Opening up the aorta allows more blood flow and therefore decreases how hard the heart has to work. This same theory is applied to EECP but is taken one step further. EECP Increases the amount of blood going back to the heart, providing more blood for the heart to work with. This also decreases how hard the heart has to work but on a much greater scale, especially for people with damaged heart tissue.
What is the purpose of stress test for EECP?
Individuals will complete a stress test prior to beginning EECP treatment. This will establish their exercise capacity and provide final clearance to begin treatment. More importantly, it will identify the severity, frequency and duration of chest pain with exercise.
How does EECP affect the heart?
EECP Increases the amount of blood going back to the heart, providing more blood for the heart to work with. This also decreases how hard the heart has to work but on a much greater scale, especially for people with damaged heart tissue.
Does Michigan Medicine offer EECP?
Michigan Medicine Preventive Cardiology offers a combination of EECP and cardiac rehabilitation during the same visit to maximize a patient’s time commitment. This has proved to be effective in enhancing wellness as patients are given the opportunity to undergo EECP treatment, exercise and learn about nutrition, stress management and strategies for behavior change.
What is EECP in medical terms?
EECP is a mechanical procedure in which long inflatable cuffs (like blood pressure cuffs) are wrapped around both of the patient’s legs. While the patient lies on a bed, the leg cuffs are inflated and deflated synchronously with each heartbeat.
What is EECP in cardiology?
While several clinical studies appear to show that this treatment can help reduce symptoms of angina in people with coronary artery disease (CAD), EECP has yet to be accepted by most cardiologists and has not entered mainstream cardiology practice.
How is deflation controlled?
The inflation and deflation are controlled by a computer, which uses the patient’s electrocardiogram ( ECG) to trigger inflation early in diastole (when the heart relaxes and is filled with blood), and deflation just as systole (heart contraction) begins.
How long does EECP last?
3 . Other studies have shown that the improvement in symptoms following a course of EECP seems to persist for up to five years (though 1 in 5 patients may require another course of EECP to maintain their improvement).
Does Medicare cover EECP?
Medicare has approved coverage for EECP for patients with angina who have exhausted all their other choices. In 2014, several professional organizations finally agreed in a focused update that EECP ought to be considered for patients with angina that's not helped by other treatments.
Is EECP good for angina?
Several studies suggest that EECP can be quite effective in treating chronic stable angina. 2 . A small randomized trial showed that EECP significantly improved both the symptoms of angina (a subjective measurement) and exercise tolerance (a more objective measurement) in people with CAD.
How does EECP work?
EECP increases blood flow to the heart while stimulating the formation of new collaterals pathways (small branches of blood vessels around the heart) to allow a natural bypass around narrowed or blocked arteries .
How is EECP administered?
EECP treatment is administered through three sets of cuffs that are applied around the calves, thighs, and buttocks. The cuffs inflate and deflate synchronized with the heartbeat using an electrocardiograph (ECG).
What happens when your heart beats?
When your heart beats (systole phase), the cuffs deflate, facilitating cardiac unloading. EECP increases blood flow to the heart, while simultaneously stimulating the opening and formation of collaterals (small branches of blood vessels around the heart) to create a natural bypass around narrowed or blocked arteries.
What is EECP?
Enhanced external counterpulsation (EECP) is a noninvasive procedure in which a set of inflatable cuffs (similar to blood pressure cuffs) mechanically compress the blood vessels in your lower limbs. This increases the blood flow and oxygen back to the heart, reducing the work that the heart has to do.
Preparing for your procedure
Prior to your treatment, you’ll meet with your doctor to discuss your medical history, the medicines you take and any questions you have about the procedure. Wear tight-fitting, seamless cycling pants or athletic tights to prevent chafing, one of the main adverse side effects of this treatment.
After your procedure
Most patients report little or no discomfort during the procedure. Some people may feel tired after the first few treatments, but this loss of energy tends to improve over time. To manage heart disease, you should make several lifestyle changes both before and after the procedure, including:
How long does EECP therapy last?
EECP therapy may also help decrease your chest pain and increase your energy level. The results of EECP therapy may last weeks or years after therapy ends.
What is EECP in cardiology?
Enhanced external counterpulsation (EECP) is a nonsurgical procedure used to increase blood flow to your heart.
What happens if your heart doesn't pump?
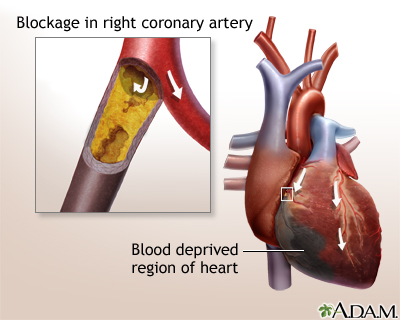
You may also have a blockage from a heart attack. When your heart does not get enough blood and oxygen, it does not pump well. This means less oxygen travels through your body. You may have chest pain, feel more tired than usual, and have trouble breathing.
How long does it take to get EECP?
You may need EECP treatment once a day, 5 days a week. Each treatment will take up to 2 hours. EECP treatment usually takes about 7 weeks to complete. If your symptoms do not improve after the first 7 weeks, you may need up to 12 more treatments.
Can you refuse treatment?
You always have the right to refuse treatment. The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
What does a cuff look like?
Healthcare providers will place large cuffs on your upper and lower legs. The cuffs look like large blood pressure cuffs. The cuffs will fill with air, causing them to squeeze your legs. The cuffs on your lower legs squeeze first, then your upper leg cuffs will squeeze. The cuffs will then release the air.
How to reduce blood pressure?
Ask your healthcare provider about the best exercise plan for you. Exercise makes the heart stronger and lowers blood pressure. Decrease stress. Talk to your healthcare provider about the best ways to manage stress. Deep breathing, meditation, and listening to music may help decrease your stress.

Treatment
Operation
- The inflation and deflation are controlled by a computer, which uses the patients ECG to trigger inflation early in diastole (when the heart relaxes and is filled with blood), and deflation just as systole (heart contraction) begins. The inflation of the cuffs occurs sequentially, from the lower part of the legs to the upper, so that the blood in the legs is milked upwards, toward the heart.
Mechanism of action
- Second, by its deflating action just as the heart begins to beat, EECP creates something like a sudden vacuum in the arteries, which reduces the work the heart muscle has to perform in pumping blood. It is also speculated that EECP may help reduce endothelial dysfunction. The mechanism for the apparent sustained benefits seen with EECP is unknown. There is some evid…
Research
- Several studies suggest that EECP can be quite effective in treating chronic stable angina. A small randomized trial showed that EECP significantly improved both the symptoms of angina (a subjective measurement) and exercise tolerance (a more objective measurement) in patients with CAD. EECP also significantly improved quality of life measures, as compared to placebo therapy…
Benefits
- There is also evidence that EECP may act as a form of passive exercise, leading to the same sorts of persistent beneficial changes in the autonomic nervous system that are seen with real exercise.
Prognosis
- EECP can be somewhat uncomfortable but is generally not painful. In studies, the large majority of patients have tolerated the procedure quite well.
Risks
- But not everyone can have EECP. People probably should not have EECP if they have aortic insufficiency, or if they have had a recent cardiac catheterization, an irregular heart rhythm such as atrial fibrillation, severe hypertension, peripheral artery disease involving the legs, or a history of deep venous thrombosis. For anyone else, however, the procedure appears to be safe.
Contraindications
- Based on what we know today, EECP should be considered in anybody who still has angina despite maximal medical therapy, and in whom stents or bypass surgery are deemed not to be good options. Medicare has approved coverage for EECP for patients with angina who have exhausted all their other choices. In 2014, several professional organizations (the American Coll…
Criticism
- In general, the cardiology community has largely chosen to ignore such an outlandish form of therapy, and many cardiologists fail to even consider offering EECP as a therapeutic option. Consequently, most patients who have angina never hear about it. Indeed, EECP is a little outlandish. It certainly does not look like cardiology. Nobody can really explain how it works. An…