Medication
Treatment and Complications. Legionnaires’ disease requires treatment with antibiotics and most cases of this illness can be treated successfully. Healthy people usually get better after being sick with Legionnaires’ disease, but they often need care in the hospital. Possible complications of Legionnaires’ disease include. Lung failure; Death
Nutrition
How is Legionnaires' disease treated? Many antibiotics are highly effective against Legionella bacteria. The two most potent classes of antibiotic are the macrolides (azithromycin), and the quinolones (ciprofloxacin, levofloxacin, moxifloxacin, gemifloxacin, trovofloxacin).
Can Legionnaires disease kill you?
While historically initial treatment was always with erythromycin, current case series and treatment recommendations suggest that outpatients receive immediate treatment with one of the following antibacterials: azithromycin, erythromycin, clarithromycin, telithromycin, doxycycline or an extended-spectrum fluoroquinolone.
Is there any natural treatment for Legionnaires' disease?
Jul 18, 2016 · Legionnaires’ disease is treated with antibiotics (drugs that kill bacteria in the body). Most people who get sick need care in a hospital but make a full recovery. However, about 1 out of 10 people who get Legionnaires’ disease will die from the infection. Certain People Are at Increased Risk for Legionnaires’ Disease
How to prevent and treat Legionnaires' disease?
45 rows · Jul 19, 2018 · Legionnaires' disease is diagnosed when one of the species of Legionella is found to be the cause of the pneumonia by testing a urine sample ( urine culture) or a sample of saliva and mucus that is coughed up ( sputum culture ). [8] …
Does Legionnaires' disease have a cure?
Apr 10, 2020 · How Legionnaires’ Disease Is Treated Legionnaires' disease is a bacterial infection most commonly treated with antibiotics. Some people will get very sick and will require hospitalization. The sooner treatment begins the less likely you are to develop serious complications such as respiratory failure, septic shock or kidney failure.
See more
May 24, 2021 · When not treated promptly, Legionnaires' disease can be fatal. Prevention. Outbreaks of Legionnaires' disease are preventable, but prevention requires water management systems in buildings that ensure that water is monitored and cleaned regularly. To lower your personal risk, avoid smoking.

Can Legionnaires disease be cured?
Legionnaires' disease requires treatment with antibiotics and most cases of this illness can be treated successfully. Healthy people usually get better after being sick with Legionnaires' disease, but they often need care in the hospital.
What antibiotic kills Legionnaires disease?
Infected individuals usually require hospitalization and may be treated with a number of antibiotics including azithromycin, levofloxacin, or doxycycline.Apr 14, 2016
How long is treatment for Legionnaires disease?
Duration of therapy: The minimum duration of therapy is 5 days for patients who have been afebrile and clinically stable for 48 hours. Patients with mild infection generally require 5 to 7 days of therapy. Patients with severe infection or chronic comorbidities generally require 7 to 10 days of therapy.
How do you recover from Legionnaires disease?
Antibiotic treatment is usually effective in treating Legionnaires' disease. Around 90% of people with the condition make a full recovery. However, while you may start to feel better after a few days, it can be weeks until you are completely back to normal. During this period, it is common to feel tired.
Which medication is the drug of choice for Legionnaires disease?
Macrolides and fluoroquinolones should be the drugs of choice for the treatment of established Legionellosis. Oral macrolides should be prefered in patients with mild to moderate pneumonia; within the macrolides, azithromycin has the most favourable profile of activity.
What's the symptoms of Legionnaires disease?
The symptoms of Legionnaires' disease are similar to the symptoms of the flu:high temperature, feverishness and chills;cough;muscle pains;headache; and leading on to.pneumonia, very occasionally.diarrhoea and signs of mental confusion.Aug 12, 2014
How serious is Legionnaires disease?
Legionnaires' disease is a serious, life-threatening illness that requires prompt treatment. Legionella may also cause a milder condition referred to as Pontiac fever. Pontiac fever doesn't cause pneumonia and isn't life-threatening. It has symptoms similar to those of a mild flu, and it usually goes away on its own.
What are three facts about Legionnaires disease?
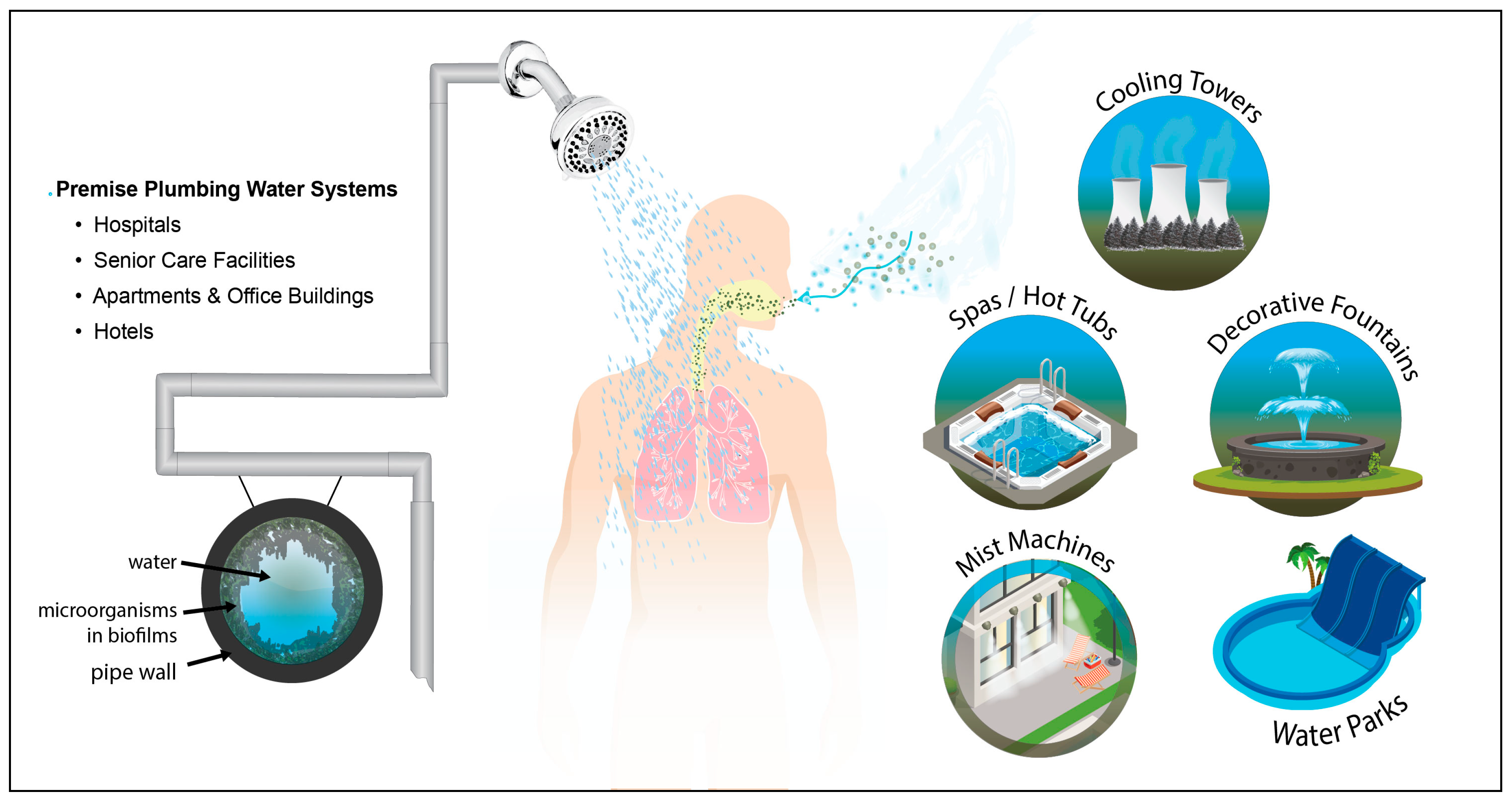
2) Legionella bacteria is commonly found in rivers, lakes and ponds in numbers so low that they're considered harmless. 3) The bacteria can multiply rapidly if present in HVAC systems, condensers or spas, which can be problematic for hotels, hospitals and office blocks.
What is the most common way of contracting Legionnaires disease?
People can get Legionnaires' disease or Pontiac fever when they breathe in small droplets of water in the air that contain the bacteria. Less commonly, people can get sick by aspiration of drinking water containing Legionella. This happens when water accidently goes into the lungs while drinking.
Can Legionnaires cause brain damage?
Cerebral and cerebellar symptoms are frequently associated with Legionnaires' disease. However, corresponding brain lesions are difficult to demonstrate using either computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).Jun 13, 2016
Can Legionnaires be fatal?
Legionnaires' disease is a potentially fatal form of pneumonia and everyone is susceptible to infection. The risk increases with age but some people are at higher risk including: people over 45 years of age.Jan 15, 2021
How long does it take to get over Legionnaires pneumonia?
Antibiotic treatment usually lasts 1 to 3 weeks. Most people make a full recovery, but it might take a few weeks to feel back to normal.
What is Legionnaires disease?
Legionnaires' disease is a severe, often lethal, form of pneumonia. It's caused by the bacterium Legionella pneumophila found in both potable and nonpotable water systems.
What antibiotics are effective against Legionella?
Many antibiotics are highly effective against Legionella bacteria. The two most potent classes of antibiotic are the macrolides (azithromycin), and the quinolones (ciprofloxacin, levofloxacin, moxifloxacin, gemifloxacin, trovofloxacin).
Can Legionnaires disease be admitted to intensive care?
It is not uncommon for patients with Legionnaires' disease to be admitted to the intensive care unit. Some will suffer long-term impaired health-related quality of life. A study of outbreak survivors showed persistence of fatigue (75%), neurologic symptoms (66%) and neuromuscular symptoms (63%) in months after an outbreak.
How to avoid getting sicker?
To avoid making your condition worse, follow these tips: Don't smoke or be around smoke. Don't drink alcohol. Stay out of work or school, and rest as much as you can. Drink plenty of fluids. If you get sicker before you see a doctor, go to an emergency room. By Mayo Clinic Staff.
Does Legionnaires disease go away on its own?
In many cases, treatment requires hospitalization. Pontiac fever goes away on its own without treatment and causes no lingering problems.
How do you treat Legionnaires disease?
Legionnaires’ disease is treated with antibiotics (drugs that kill bacteria in the body). Most people who get sick need care in a hospital but make a full recovery. However, about 1 out of 10 people who get Legionnaires’ disease will die from the infection.
Can you get Legionella if you are 50?
Most healthy people do not get Legionnaires’ disease after being exposed to Legionella. Being 50 years or older or having certain risk factors can increase your chances of getting sick. These risk factors include:
Can Legionella grow in water?
In nature, Legionella live in fresh water and rarely cause illness. In man-made settings, Legionella can grow if water is not properly maintained. These man-made water sources become a health problem when small droplets of water that contain the bacteria get into the air and people breathe them in. In rare cases, someone breathes in Legionella while they are drinking water and it “goes down the wrong pipe” into the lungs. In general, people do not spread Legionnaires’ disease to other people.
What is Legionnaires disease?
Listen. Legionnaires’ disease is a severe type of pneumonia caused by the bacteria Legionella. [1] . The species Legionella pneumophila causes most cases, but other species of Legionella can also cause the disease. It is named Legionnaires’ disease because it was first discovered after a pneumonia outbreak among people who attended an American ...
How many people with Legionnaires disease will not survive?
People with the disease who are otherwise healthy usually recover with antibiotics, although they may need to be cared for in a hospital. About 1 in 10 people with Legionnaires’ disease will not survive due to complications such as respiratory failure, kidney failure, or septic shock. [1] [8]
What is the HPO database?
People with the same disease may not have all the symptoms listed. This information comes from a database called the Human Phenotype Ontology (HPO) . The HPO collects information on symptoms that have been described in medical resources.
How is Legionella diagnosed?
Legionnaires' disease is diagnosed when one of the species of Legionella is found to be the cause of the pneumonia by testing a urine sample ( urine culture) or a sample of saliva and mucus that is coughed up ( sputum culture ). [8] . Without treatment, the disease can be fatal. [1] . People with the disease who are otherwise healthy usually ...
Why is Legionella called Legionella?
It is named Legionnaires’ disease because it was first discovered after a pneumonia outbreak among people who attended an American Legion Convention in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania in 1976. [2] Most people exposed to Legionella do not become sick with Legionnaires' disease. [3] .
What is an orphanet?
Orphanet is a European reference portal for information on rare diseases and orphan drugs. Access to this database is free of charge. PubMed is a searchable database of medical literature and lists journal articles that discuss Legionnaires’ disease. Click on the link to view a sample search on this topic.
What is MedlinePlus?
MedlinePlus was designed by the National Library of Medicine to help you research your health questions, and it provides more information about this topic. The National Organization for Rare Disorders (NORD) has a report for patients and families about this condition.
How to diagnose Legionella?
To diagnose Legionnaires’ disease among other types of pneumonia, your doctor may order urine tests and a sputum culture to determine the presence of the Legionella bacteria.
How long does it take for Legionnaires to set in?
Legionnaires’ disease usually begins with flu-like symptoms similar to other types of bacterial pneumonia. These include: Within two or three days, the illness will have fully set in and patients typically experience more severe cough and difficulty breathing.
What is the number to call for lung cancer?
If you have questions about your diagnosis and what to expect, you can call the Lung Association's Lung HelpLine at 1-800-LUNGUSA to talk to a trained respiratory professional who can help answer your questions and connect you with support.
What are the next steps for a doctor to diagnose pneumonia?
If they suspect pneumonia, the next steps include a chest X-ray and blood tests.
Can Legionnaires disease be fatal?
Legionnaires’ disease can be fatal, so it is important to get prompt medical attention. Your doctor may determine that you have contracted a less severe version of the same disease, called Pontiac fever. This milder condition will clear up on its own without treatment and cause no lingering problems.
What is Legionnaires disease?
Overview. Legionnaires' disease is a severe form of pneumonia — lung inflammation usually caused by infection. It's caused by a bacterium known as legionella. Most people catch Legionnaires' disease by inhaling the bacteria from water or soil. Older adults, smokers and people with weakened immune systems are particularly susceptible ...
What happens if you don't treat Legionnaires?
Acute kidney failure. This is the sudden loss of your kidneys' ability to filter waste from your blood. When your kidneys fail, dangerous levels of fluid and waste accumulate in your body. When not treated promptly, Legionnaires' disease can be fatal.
How does Legionella spread?
How the infection spreads. Most people become infected when they inhale microscopic water droplets containing legionella bacteria. This might be from the spray from a shower, faucet or whirlpool, or water from the ventilation system in a large building . Outbreaks have been linked to:
How long does it take for Legionella to show symptoms?
Symptoms. Legionnaires' disease usually develops two to 10 days after exposure to legionella bacteria. It frequently begins with the following signs and symptoms: Headache. Muscle aches.
What are the ways that a person can get a syphilis infection?
Hot tubs and whirlpools. Cooling towers in air conditioning systems. Hot water tanks and heaters. Decorative fountains. Swimming pools. Birthing pools. Drinking water. Besides by breathing in water droplets, the infection can be transmitted in other ways, including: Aspiration.
What are the symptoms of a symtom?
By the second or third day, you'll develop other signs and symptoms that can include: Cough, which might bring up mucus and sometimes blood. Shortness of breath. Chest pain. Gastrointestinal symptoms, such as nausea, vomiting and diarrhea. Confusion or other mental changes.
What age can you get Legionnaires?
This includes emphysema, diabetes, kidney disease or cancer. Are 50 years of age or older. Legionnaires' disease can be a problem in hospitals and nursing homes, where germs can spread easily and people are vulnerable to infection.
What is Legionella disease?
What is Legionnaires’ disease? Legionnaires’ disease, or legionellosis, is a common type of bacterial pneumonia (lung infection) that can be very serious and sometimes life-threatening. A particular strain of bacteria called Legionella causes the illness.
How many people die from Legionnaires disease?
Because of the potentially serious nature of this disease, many people who get Legionnaires’ disease need to be treated in a hospital. About 1 in 10 people who get the disease die from complications of their illness.
Where do Legionella bacteria live?
Legionella bacteria live best in warm water. They are found in some freshwater lakes and streams. When certain man-made water structures aren’t maintained with proper disinfectants, the bacteria can grow and cause a health risk. But it has also been found in natural water and even soil.
Can you test for Legionella on a chest X-ray?
Legionnaires’ disease can look similar to regular pneumonia on a chest X-ray. Your doctor may test a sample of your urine or phlegm (mucus) to confirm you have Legionnaires’ disease. A blood test can also check for antibodies to Legionella.
Can Legionnaires disease be spread by drinking water?
This is when water “goes down the wrong pipe,” sending liquid down the windpipe and into your lungs instead of down your esophagus and into your stomach. Legionnaires’ disease cannot be spread from person to person.
Is Legionnaires disease a lung infection?
Legionnaires' Disease. Legionnaires’ disease, or legionellosis, is a common type of bacterial pneumonia (lung infection) that can be very serious and sometimes life-threatening. Most cases of Legionnaires’ disease are successfully treated with antibiotics.
Can Legionnaires disease be treated with antibiotics?
Most cases of Legionnaires’ disease are successfully treated with antibiotics. Sometimes, however, Legionnaires’ disease can lead to lung failure or other complications. These complications can be hard to treat. They can even be life-threatening for some people.