What does DNA have to do with cancer?
Or they can happen because of other factors such as:
- tobacco smoke
- high energy (ionising) radiation, such as x-rays
- ultraviolet radiation from the sun
- some substances in food
- chemicals in our environment
What is the relationship between cancer and DNA?
Other types of cancer that may be more likely to develop in people with HIV infection include:
- Anal cancer
- Hodgkin disease
- Lung cancer
- Cancers of the mouth and throat
- Some types of skin cancer
- Liver cancer
How does damaged DNA lead to cancer?
Self-Assessment Review Questions
- True or false? Hereditary defects in DNA repair genes are common in cancer.
- DNA mismatch repair targets which lesions?
- Lynch syndrome is associated with enhanced risk for which of the following malignancies?
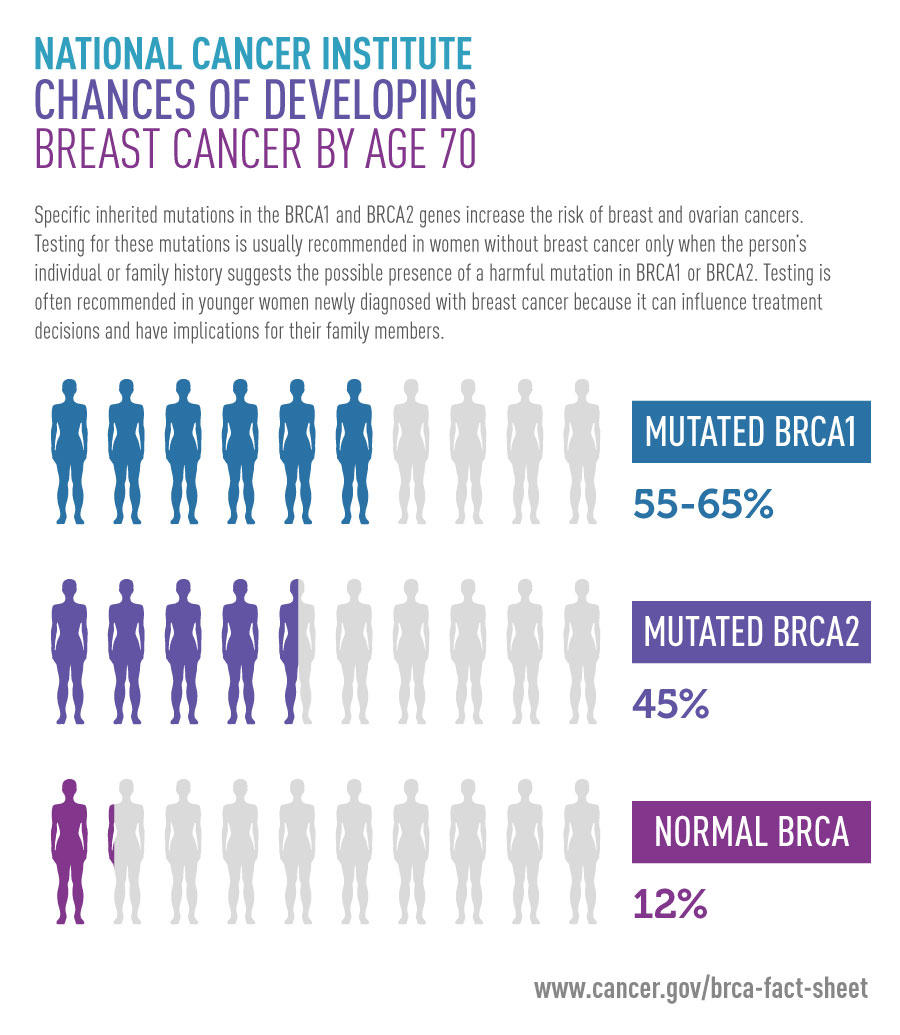
- How common are BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations in the general population?
- Microsatellite instability is a feature of which malignancies?
Does cancer change your DNA?
The results showed that these cancer treatments may damage the DNA within healthy cells in your body as well as damaging the cancer cells they are meant to fight, which can affect mental abilities afterwards. The researchers believe the result of this damage has an actual impact on the aging process.

What is the difference between cancer and DNA?
Cancer is caused by changes to DNA. Most cancer-causing DNA changes occur in sections of DNA called genes. These changes are also called genetic changes. A DNA change can cause genes involved in normal cell growth to become oncogenes.
How do you get DNA cancer?
If a person has an error in a DNA repair gene, mistakes remain uncorrected. Then, the mistakes become mutations. These mutations may eventually lead to cancer, particularly mutations in tumor suppressor genes or oncogenes. Mutations in DNA repair genes may be inherited or acquired.
Is gene therapy better than chemotherapy?
Relatively gene therapy has better safety with tolerable adverse effects than chemotherapy for the treatment of cancer. In the future, tumor genomic analysis, assessment of host humoral and cellular immunity will facilitate a better selection of the most appropriate patient for gene therapy.
What cancers can be treated with gene therapy?
Cancer types, which have been targeted with gene therapy, include brain, lung, breast, pancreatic, liver, colorectal, prostate, bladder, head and neck, skin, ovarian, and renal cancer. Currently, two cancer gene therapy products have received market approval, both of which are in China.
Can DNA repair itself?
Most damage to DNA is repaired by removal of the damaged bases followed by resynthesis of the excised region. Some lesions in DNA, however, can be repaired by direct reversal of the damage, which may be a more efficient way of dealing with specific types of DNA damage that occur frequently.
What causes DNA damage?
DNA damage can be subdivided into two types: (1) endogenous damage caused by reactive oxygen species (ROS) that are derived from metabolic byproducts and (2) exogenous damage caused by radiation (UV, X-ray, gamma), hydrolysis, plant toxins, and viruses.
What are the dangers of gene therapy?
Gene therapy has some potential risks. A gene can't easily be inserted directly into your cells....RisksUnwanted immune system reaction. Your body's immune system may see the newly introduced viruses as intruders and attack them. ... Targeting the wrong cells. ... Infection caused by the virus. ... Possibility of causing a tumor.
How successful is gene therapy?
Through 2020, the remission rate among ALL patients treated with Kymriah was about 85 percent. More than half had no relapses after a year. Novartis plans to track outcomes of all patients who received the therapy for 15 years to better understand how long it remains effective.
How much does gene therapy cost?
A one-time treatment of the life-saving drug for a young child costs US$2.1 million. While Zolgensma's exorbitant price is an outlier today, by the end of the decade there'll be dozens of cell and gene therapies, costing hundreds of thousands to millions of dollars for a single dose.
What are pros and cons of gene therapy?
Gene therapy is a cutting edge medical treatment that has pros and cons. Gene therapy can be life-saving for some people with specific medical conditions, but it's expensive and can cause side effects....ConsExpensive. ... Experimental. ... Potentially dangerous. ... Ethical issues. ... May cause infection.
How is gene therapy performed?
Gene therapy can be used to modify cells inside or outside the body. When it's done inside the body, a doctor will inject the vector carrying the gene directly into the part of the body that has defective cells.
What are the three steps involved in gene therapy?
The basics of the process are the identification of the gene in question, duplication of that gene, and insertion of the gene into the human genome needing the gene (CIS) .
What is the function of CRISPR on T cells?
Then CRISPR is used to remove three genes: two that can interfere with the NY-ESO-1 receptor and another that limits the cells’ cancer-killing abilities.
What was the first trial of CRISPR?
The first trial of CRISPR for patients with cancer tested T cells that were modified to better "see" and kill cancer. CRISPR was used to remove three genes: two that can interfere with the NY-ESO-1 receptor and another that limits the cells’ cancer-killing abilities.
What is the CRISPR enzyme?
CRISPR consists of a guide RNA (RNA-targeting device, purple) and the Cas enzyme (blue). When the guide RNA matches up with the target DNA (orange), Cas cuts the DNA. A new segment of DNA (green) can then be added. Credit: National Institute of General Medical Sciences, National Institutes of Health.
Is CRISPR used in cancer research?
The new tool has taken the research world by storm, markedly shifting the line between possible and impossible. As soon as CRISPR made its way onto the shelves and freezers of labs around the world, cancer researchers jumped at the chance to use it. “CRISPR is becoming a mainstream methodology used in many cancer biology studies because ...
Is CRISPR good for cancer?
There’s also hope that it will have a place in treating cancer, too. But CRISPR isn’t perfect, and its downsides have made many scientists cautious about its use in people. A major pitfall is that CRISPR sometimes cuts DNA outside of the target gene—what’s known as “off-target” editing.
What happens to DNA as a tumor grows?
As a tumor grows, cells die and are replaced by new ones. The dead cells get broken down and their contents, including DNA, are released into the bloodstream. ctDNA are small pieces of DNA, usually comprising fewer than 200 building blocks (nucleotides) in length. The quantity of ctDNA varies among individuals and depends on the type of tumor, ...
What does it mean when a tumor doesn't have ctDNA?
A lack of ctDNA in the bloodstream indicates that the cancer has not returned. Scientists have discovered that dying tumor cells release small pieces of their DNA into the bloodstream. These pieces are called cell-free circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA). Credit: Jonathan Bailey, NHGRI.
How to detect ctDNA?
Detection of ctDNA can be helpful in the following cases: 1 Detecting and diagnosing a tumor. Because tumor DNA has acquired multiple genetic mutations, leading to tumor development, ctDNA is not an exact match to the individual’s DNA. Finding DNA with genetic differences aids in tumor detection. Diagnosing the type of tumor using ctDNA can reduce the need for getting a sample of the tumor tissue (tumor biopsy), which can be challenging when a tumor is difficult to access, such as a tumor in the brain or lung. 2 Guiding tumor-specific treatment. Analyzing the genome of tumor cells using ctDNA can help doctors determine which treatment will be most effective. Currently, however, approval from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for ctDNA testing to personalize cancer treatment is limited. 3 Monitoring treatment. A decrease in the quantity of ctDNA suggests the tumor is shrinking and treatment is successful. 4 Monitoring periods with no symptoms (remission of cancer). A lack of ctDNA in the bloodstream indicates that the cancer has not returned.
Why is ctDNA useful?
Detection of ctDNA can be helpful in the following cases: Detecting and diagnosing a tumor. Because tumor DNA has acquired multiple genetic mutations, leading to tumor development, ctDNA is not an exact match to the individual’s DNA. Finding DNA with genetic differences aids in tumor detection. Diagnosing the type of tumor using ctDNA can reduce ...
Can ctDNA be used to diagnose tumors?
Diagnosing the type of tumor using ctDNA can reduce the need for getting a sample of the tumor tissue (tumor biopsy), which can be challenging when a tumor is difficult to access, such as a tumor in the brain or lung. Guiding tumor-specific treatment.
What is the FDA testing for cancer?
FDA Approves Two Genomic Profiling Tests for Cancer. Tests can identify different cancer-associated genetic alterations. Some tests, called whole-exome sequencing, look at all the genes in your cancer. Others, called whole-genome sequencing, look at all the DNA (both genes and outside of genes) in your cancer.
What type of cancer is a biomarker?
Biomarker testing is also done routinely to select treatment for people who are diagnosed with certain types of cancer—including non-small cell lung cancer, breast cancer, and colorectal cancer.
What are biomarkers used for?
Most biomarker tests used to select cancer treatment look for genetic markers. But some look for proteins or other kinds of markers. Some tests check for one certain biomarker. Others check for many biomarkers at the same time and may be called multigene test s or panel tests.
Why are biomarkers not helpful?
One other reason biomarker tests might not help is because the biomarkers in your cancer can change over time.
What is biomarker testing?
Biomarker testing is a way to look for genes, proteins, and other substances (called biomarkers or tumor markers) that can provide information about cancer. Each person’s cancer has a unique pattern of biomarkers. Some biomarkers affect how certain cancer treatments work. Biomarker testing may help you and your doctor choose a cancer treatment ...
Why isn't my cancer test working?
There could be several different reasons why they may not help you. One reason is that the test might not find a biomarker in your cancer that matches with an available therapy. Even if your cancer has a biomarker that matches an available treatment , the therapy may not work for you.
Can EGFR be used to treat cancer?
For example, people with cancer that has certain genetic changes in the EGFR gene can get treatments that targets those changes, called EGFR inhibitor. In this case, biomarker testing can find out whether someone’s cancer has an EGFR gene change that can be treated with an EGFR inhibitor. Biomarker testing could also help you find a study ...
How does nanotechnology help cancer?
The traditional use of nanotechnology in cancer therapeutics has been to improve the pharmacokinetics and reduce the systemic toxicities of chemotherapies through the selective targeting and delivery of these anticancer drugs to tumor tissues.
What is immunotherapy for cancer?
Immunotherapy is a promising new front in cancer treatment encompassing a number of approaches, including checkpoint inhibition and cellular therapies. Although results for some patients have been spectacular, only a minority of patients being treated for just a subset of cancers experience durable responses to these therapies. Expanding the benefits of immunotherapy requires a greater understanding of tumor-host immune system interactions. New technologies for molecular and functional analysis of single cells are being used to interrogate tumor and immune cells and elucidate molecular indicators and functional immune responses to therapy. To this end, nano-enabled devices and materials are being leveraged to sort, image, and characterize T cells in the Alliance’s NanoSystems Biology Cancer Center.
What is nanotechnology used for?
Additional uses of nanotechnology for immunotherapy include immune depots placed in or near tumors for in situ vaccination and artificial antigen presenting cells. These and other approaches will advance and be refined as our understanding of cancer immunotherapy deepens.
What is the treatment for superficial tumors?
Another type of therapy that relies upon external electromagnetic radiation is photodynamic therapy (PDT). It is an effective anticancer procedure for superficial tumor that relies on tumor localization of a photosensitizer followed by light activation to generate cytotoxic reactive oxygen species (ROS).
Why are nanocarriers used in cancer treatment?
These therapeutics are used in many cases to target ‘undruggable’ cancer proteins. Additionally, the increased stability of genetic therapies delivered by nanocarriers, and often combined with controlled release, has been shown to prolong their effects.
How does radiation affect DNA?
Radiation therapy can either damage DNA directly or create charged particles (atoms with an odd or unpaired number of electrons) within the cells that can in turn damage the DNA. Most types of radiation used for cancer treatment utilize X-rays, gamma rays, and charged particles.
How does radiation therapy work?
Roughly half of all cancer patients receive some form of radiation therapy over the course of their treatment. Radiation therapy uses high-energy radiation to shrink tumors and kill cancer cells. Radiation therapy kills cancer cells by damaging their DNA inducing cellular apoptosis. Radiation therapy can either damage DNA directly ...
Why do tumour suppressor genes stop cells from growing?
It is usual for cells to repair faults in their genes. When the damage is very bad , tumour suppressor genes may stop the cell growing and dividing. Mutations in tumour suppressor genes mean that a cell no longer understands the instruction to stop growing. The cell can then start to multiply out of control.
How much DNA does a human have?
You have more than 2 metres of DNA inside every cell. But is very tightly coiled up so it all fits. DNA is like a code containing all the instructions that tell a cell what to do. It is made up of genes. Humans have around 25,000 genes in total. You inherit half your DNA from your mother and half from your father.
What are the genes that encourage cells to multiply?
Genes that encourage the cell to multiply (oncogenes) Oncogenes are genes that, under normal circumstances, tell cells to multiply and divide. In adults this doesn't happen very often. We can think of oncogenes as being a bit like the accelerator pedal in a car.
Why do cells die?
It is a very complex and important process. Cells usually die whenever something goes wrong, to prevent a cancer forming. There are many different genes and proteins involved in apoptosis. If these genes get damaged, a faulty cell can survive rather than die and it becomes cancerous.
Does cancer repair itself?
It doesn't repair itself properly , and it doesn't die when it should. This can lead to cancer. There are 4 main types of genes involved in cell division. Most tumours have faulty copies of more than 1 of these types.
Can DNA repair cause cancer?
But if the DNA damage occurs to a gene that makes a DNA repair protein, a cell has less ability to repair itself. So errors will build up in other genes over time and allow a cancer to form. Scientists have found damaged DNA repair genes in some cancers, including bowel cancer.
What is cancer therapy?
Cancer therapy is increasingly aimed at the fundamental abnormalities within cancer cells – the genes and proteins that normally keep cell division under control, but are damaged or faulty in tumor cells.
How does sequencing help cancer?
Sequencing can also help researchers track how cancers change their genomic stripes over time. By sequencing the DNA in a tumor before and after treatment, for example, researchers hope to learn how cancer adapts to treatment and potentially becomes resistant to it. An example of this use of sequencing is the PCROWD study at ...
Why is sequencing important in cancer research?
Projects such as The Cancer Genome Atlas are sequencing thousands of tumor tissue samples to help uncover which genetic irregularities drive the growth of various types of cancer. Sequencing can also help researchers track how cancers change their genomic stripes over time. By sequencing the DNA in a tumor before and after treatment, for example, researchers hope to learn how cancer adapts to treatment and potentially becomes resistant to it.
What is DNA sequencing?
DNA sequencing explores the fundamental abnormalities within cancer cells. Since DNA constitutes the “operating manual” of cells, errors in the arrangement of bases can cause a cell to malfunction in a variety of ways. Nowhere is that more evident than in cancer, the disease most associated with wayward genes. ...
What is the purpose of sequencing DNA?
Sequencing DNA involves determining the precise order of the four chemical building blocks, or “bases,” that make up the DNA molecule. The bases – designated A, C, T, and G for the first letters of their chemical names – spell out the genetic code for each cell and each organism.
Can cancer be caused by genetic abnormalities?
Not every genetic misspelling or abnormality results in cancer. Many have no discernible effect on a cell’s function. But certain abnormalities are hallmarks of certain kinds of cancer. Doctors know, for example, that many non-small cell lung cancers (NSCLCs) have mutations in the gene EGFR.