What is cryogenic treatment?
What is Cryogenic Treatment? Cryogenic treatment is used to improve the durability of moving steel parts.
What is cryogenic deflashing?
These temperatures cause the flash to become stiff or brittle and to break away cleanly. Cryogenic deflashing is the preferred process when removing excess material from oddly shaped, custom molded products.
What is cryogenic hardening process?
Cryogenic hardening is a cryogenic treatment process where the material is slowly cooled to very low temperatures. By using liquid nitrogen, the temperature can go as low as −196 °C. It can have a profound effect on the mechanical properties of certain materials, such as steels or tungsten carbide.
How does cryogenic treatment alter the crystal structure of steel?
Cryogenic treatment alters the crystal structure of steel by completing the conversion of austenite to martensite making it harder. Now, I recall making a screwdriver in metalwork class at secondary school many years ago.

What is the purpose of cryogenic treatment?
Cryotherapy is the use of extreme cold to freeze and remove abnormal tissue. Doctors use it to treat many skin conditions (including warts and skin tags) and some cancers, including prostate, cervical and liver cancer. This treatment is also called cryoablation.
How long does it take for cryogenic hardening to occur?
Typical cryogenic treatment consists of a slow cool-down of -5 °F per minute (-3°C per minute) from ambient to -320 °F (-196°C), a soak for 24 to 72 hours, and warm up to ambient temperature.
How cold is cryogenic treatment?
What are cryogenic temperatures? The scien- tific community generally defines cryogenic temperatures as temperatures below А150 C (А238 F, or 123 K) (Ref 10). This, admittedly, is an artificial upper limit. Temperatures used presently in cryogenic treatment are generally –185 C (–300 F, or 89 K).
What does cryo treatment do to steel?
Cryogenic hardening is able to make metal objects and workpieces more resistance to wear and tear. Metal doesn't just become harder through cryogenic hardening; it becomes tougher and more resistant to wear. As a result, cryogenic hardening is performed to increase the usable life of metal objects and workpieces.
What do you mean by cryogenic?
Definition of cryogenic 1a : of or relating to the production of very low temperatures. b : being or relating to very low temperatures. 2a : requiring or involving the use of a cryogenic temperature. b : requiring cryogenic storage.
What does cryogenic treatment do for brake rotors?
Cryogenic treatment of rotors or cryo-rotors is the freezing of rotors. It is a special process which involves exposing brake rotors in freezing temperatures in order to add more durability and lengthen its life expectancy.
What are the risks of cryotherapy?
Exposure to extreme cold can cause injuries. There have been reports of people getting frostbite or cold-induced rashes after whole-body cryotherapy....Risks of Whole-Body CryotherapyHigh blood pressure.Heart disease.Lung disease.Poor blood circulation.Allergy symptoms triggered by cold.Neuropathy in the legs or feet.
What happens to your body during cryotherapy?
Cryotherapy warms your core, shrinks pores, and pushes blood to the surface of your skin. Blood and lymph flow, two of the most important things in your body, are greatly affected by cryotherapy. The process also flushes toxins, such as lactic acid, to help stimulate healing.
Is cryosurgery considered surgery?
Cryosurgery is a type of surgery that involves the use of extreme cold to destroy abnormal tissues, such as tumors. The surgery most often involves the use of liquid nitrogen, although carbon dioxide and argon may also be used.
What is cryogenic coating?
Foster® 90-66™ Cryogenic Coating/Adhesive is a two-part black elastomeric coating/adhesive designed for use in cryogenic and specific chemical resistance applications.
Can liquid nitrogen damage metal?
Yes. Cooling just about anything to liquid nitrogen temperatures makes it more brittle than at higher temperatures. At higher temperatures, defects in the crystal lattice of a material are more mobile. Bending a crystal will introduce slippage and cracking.
What is cryo treatment for knives?
Cryogenic treatment is a common process designed to enhance the performance of metal blades. Extreme deep freezing increases the service life of knives by improving their resistance to wear. As a one-time treatment, freezing knife blades makes them more durable and less prone to chipping and fracturing under stress.
How long does cryogenic treatment take?
The turn around time must be calculated into the delivery schedule. Likewise, the cryogenic treatment process itself takes 2 days, so the time needed to send cutters to be treated needs to be calculated into the production schedule.
What temperature does cryogenics take?
Cryogenics simply takes the quench to new lows—minus 300°F. According to cryogenic treatment research done by Dr. Randall Barron from Louisiana State University, there are two primary mechanisms at work in the cryogenic treatment process.
What is cryogenic tool steel?
Alloy tool steels such as those used to make end mills, twist drills, reamers and other cutting tools have been the subject of most of the research of the cryogenic treatment effect . The research has demonstrated that using deep cryogenic treatment results typically in a two- to five-fold improvement over the normal life of these tools.
Why do cryogenic chambers have heaters?
Most cryogenic chambers are equipped with a small heater that raises the temperature to almost 300°F for the final couple of hours to ensure there are no “cold” spots in the material and to provide tempering. Because nitrogen in its gaseous form is used as the cooling agent, parts and tools to be cooled remain dry.
How long does it take to cryo treat a swollen ear?
The cryogenic treatment process is relatively simple albeit time consuming. A typical treatment cycle takes around 48 hours to complete. However, time is the key to a proper cryogenic treatment.
How long does it take for liquid nitrogen to cool down?
The cool-down phase, going from ambient to minus 300-310°F (the temperature of liquid nitrogen) usually runs in a 4- to 6-hour range (1 to 2 degrees per minute). This is followed by a “soak” lasting around 24 hours. Once the parts have soaked, warm up to room temperature is another 4 to 6 hours.
Why is nitrogen used as a cooling agent?
Because nitrogen in its gaseous form is used as the cooling agent, parts and tools to be cooled remain dry. During the cool-down phase any oxygen in the chamber is purged by the nitrogen, so no rust can form. Only arrangement of the parts is needed, no fixtures or racks are required.
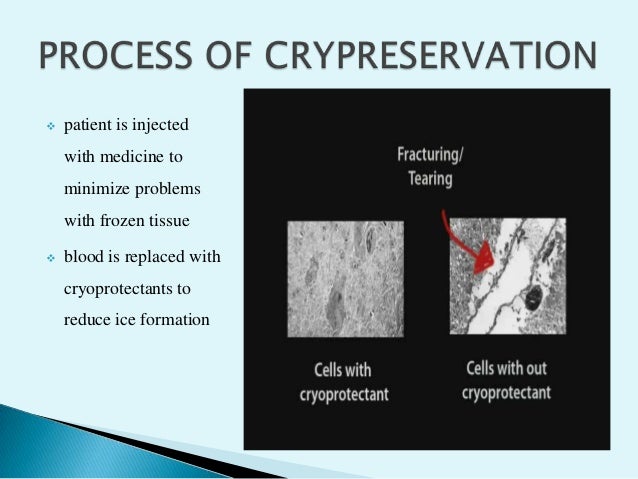
What is cryogenic treatment?
Cryogenic treatment is used to improve the durability of moving steel parts. Cryogenic treatment is a process of cooling steel alloy down to low very temperatures (−190 °C) to increase its surface hardness to improve its resistance to wear, the practical application being to extend the life of cutting tools, gear teeth, moving engine parts, ...
What would be magical if cryogenic treatment were some kind of ‘silver bullet’?
It would be magical if cryogenic treatment were some kind of ‘silver bullet’ that improves the insulation properties of mica spacers, reduces inter-electrode movement and improves the emission of the cathode coatings to reduce noise and microphony.
Does cryogenic treatment work on vacuum tubes?
Effect on Vacuum Tubes? So cryogenic treatment can work to improve the hardness of ferrous metals such as steel, but what about a vacuum tube—a tube is not a lump of steel— like a wristwatch, it’s a delicate and complex mechanism composed of many different parts, which in turn are made from different types of materials.
Can you store electronic components at cryogenic temperatures?
It’s not recommended practice to treat electronic components like this and it’s worth noting that electronics component manufacturers publish datasheets that specify temperature ranges for storing and operating their devices at—none recommend storing their components at cryogenic temperatures.
Can cryogenic treatment be used on Sylvania tubes?
The bottom line is that cryogenic treatment is no remedy for inferior materials or defects in tube construction and it won’t transform a rebranded modern manufacture tube into a genuine N.O.S. Mullard a or Sylvania tube—it just doesn’t work that way.
What is cryogenic treatment?
Cryogenic treatment is a common process designed to enhance the performance of metal blades. Extreme deep freezing increases the service life of knives by improving their resistance to wear. As a one-time treatment, freezing knife blades makes them more durable and less prone to chipping and fracturing under stress.
What temperature is cryogenic treatment?
Cryogenic treatment goes by many other names, including cryogenic tempering, cryogenic hardening and deep cryogenic treatment (DCT), which usually indicates that the process uses temperatures below 300 degrees Fahrenheit.
Why do knives need cryogenic process?
Knives and blades need to undergo and repeated use, often under high-impact and severe conditions. They need to maintain their shape, sharpness or strength. Metal becomes harder through the cryogenic process and can then stand up to significant and repetitive use for much longer .
Why invest in cryogenically treated blades?
By choosing to invest in cryogenically treated blades or knives, you’ll benefit from longer-lasting blades that require less maintenance and cause less downtime to your operations. Here are a few of the many reasons why cryogenically treated industrial knives and blades are a good option for your business. 1.
Why cryogenically freezing knife blades?
1. Increases Resistance to Wear and Tear. The primary benefit of cryogenically freezing knife blades is that it increases the blades’ resistance to wear and tear. In industrial settings, maintaining and improving productivity are the primary goals.
Why is cryogenic treatment important?
It allows an increase in fatigue life, load capacity, and wear resistance of gears without an increase in weight or major modifications to component design .
What is cryogenic process?
Cryogenic processing — the deep chilling of tool steel so that the molecular structure of the metal is brought to “cryogenic stillness” in order ...
What is cryo treatment?
One of the strangest aspects of cryogenic treatment is the thin layer about .0001” thick on the outside of the tool that remains untreated. After this layer is removed by sharpening, the tools will get the added wear resistance.
How to reverse cryo treatment?
The only way to reverse the cryo treatment is if you take the tool back up to a critical temperature, such as heat treating. It creates a denser molecular structure and closes the grains structure, resulting in a larger contact surface area that reduces friction, heat, and wear.
What temperature do you need to cryogenic steel?
Prior to the deep cryogenic step, many tool steels require a preconditioning step consisting of a short temper. Once the temperature reaches -305F the cryogenic process enters the “soak phase,” which maintains this temperature for a period to allow for transformation on a molecular level.
What is dry process?
The dry process means the material is not exposed to any cryogenic liquids, eliminating the risk of thermal shock. A microprocessor is programmed according to size, weight, and configuration of the parts being treated.
Does cryo treating reduce the cost of the product?
Customers have reported a material removal rate of less than half the normal material removed in re-sharpening. Cryo treating reduces the cost of the product by having longer tool life, less scrap, fewer rejections, and above all, less-costly downtime.
What is cryogenic burn?
Cryogenic burns are cold burns, meaning the tissue is damaged from the cold temperature of the liquid . When our cells get too cold, the liquid inside freezes, damaging the structural integrity of the cells. Since the cells are physically damaged, when they thaw from the cold they don't go back to healthy tissue, ...
Why do scientists burn with cryogenic liquids?
A scientist wears special gloves to handle liquid nitrogen. Cryogenic burns can also be caused by touching materials that have come in contact with cryogenic liquids. Metals that hold cryogenic liquids lose heat rapidly and can become cold enough to create cryogenic burns.
Where can you find cryogenic material?
Cryogenic material is found in labs, coolant systems and even pressurized spray bottles like deodorant. Cryogenic burns produce tissue damage through ice crystals and structural changes to cells, which can produce frostbite.
Is it painful to thaw a cryogenic burn?
The wound may not be painful at first, since the nerves may be frozen as well. But as the skin thaws, be prepared for the patient to experience immense pain. Keep calm and continue to warm the skin very slowly. Once professional help arrives, the treatment team has several steps to treat a cryogenic burn.
Can a cryogenic burn be worse?
Improper first aid can make a cryogenic burn worse, so it's important to get emergency medical help right away. Tissue damage can be made worse if the wound is heated too quickly, or is heated and then refrozen. Picture thawing and freezing a piece of chicken, not an appetizing meal.
Do cryogenic burns denature?
In cryogenic burns, proteins do not denature, and unless the burns are severe, they rarely produce significant scarring. Like other burns, cryogenic burns vary in intensity. The extent of the burn depends on how long the skin was exposed and how much surface area came in contact with the cryogenic material.
What is cryotherapy for cancer?
Cryotherapy is the use of extreme cold to freeze and remove abnormal tissue. Doctors use it to treat many skin conditions (including warts and skin tags) and some cancers, including prostate, cervical and liver cancer. This treatment is also called cryoablation.
What happens to cells during cryotherapy?
During cryotherapy, the healthcare provider applies extreme cold to abnormal tissue. Cells can’t survive this severe cold and die after treatment. Your healthcare provider can use a few different substances to create the intense cold used in cryotherapy. These substances can include:
How to use cryoprobe for external cryotherapy?
If you have external cryotherapy, your healthcare provider will apply the cold with a spraying device or cotton swab. Providers usually use liquid nitrogen for this type of treatment. For internal cryotherapy, the cryoprobe is inserted through a small incision in your skin.
Why does cryotherapy cause skin to blister?
External cryotherapy causes frozen skin to blister and peel off so that healthy new skin can grow . When abnormal cells freeze and die during internal cryotherapy, your immune system helps clear the tissue out of the body.
How long does it take for a scab to heal after cryotherapy?
Any mild pain should be gone after about three days. The treated area will form a scab, which usually heals in one to three weeks. After internal cryotherapy, you may have mild pain or soreness in the affected area for up to three days.
Can you cryotherapy without surgery?
Cryotherapy is usually done without open surgery. Most people recover quickly from the procedure and with little pain. Your provider might recommend cryotherapy for: Bone cancer. Cervical cancer, liver cancer or prostate cancer. Precancerous cells in the cervix (lower end of the uterus).
Can you cryosurgery on skin?
Most people don’t need to do anything special to prepare for cryotherapy on the skin. Your healthcare provider will give you instructions before internal cryotherapy to help you prepare. You may have to stop taking certain medications, such as aspirin or blood thinners, a few days before internal cryosurgery.
How does cryosurgery treat cancer?
For tumors on the skin, the doctor applies liquid nitrogen directly to the abnormal area with a cotton swab or spraying device. For tumors inside the body, the doctor may use a device called a cryoprobe to freeze the tumor tissue.
What is cryosurgery used for?
Cryosurgery is used to treat tumors on the skin, as well as certain tumors inside the body.
What are the benefits of cryosurgery?
For tumors inside the body, only a small cut or puncture is usually needed to insert the cryoprobe through the skin. As a result, pain, bleeding, and other problems that come with surgery are reduced.
What is the procedure to place liquid nitrogen on a tumor?
As liquid nitrogen or argon gas flows through the cryoprobe, the doctor places it directly on the tumor. During this procedure, the doctor uses ultrasound or MRI to guide the cryoprobe to the correct spot, which helps limit damage to nearby healthy tissue.
What type of cancer is treated with cryosurgery?
Cancers Treated with Cryosurgery. Cryosurgery can be used to treat the following types of cancer: retinoblastoma. skin cancers, including basal cell and squamous cell carcinomas. skin lesions from AIDS -related Kaposi sarcoma. early-stage prostate cancer. liver cancer that is confined to the liver.
Can cryoprobes be used to freeze tumors?
Sometimes, more than one cryoprobe is used to freeze different parts of the tumor. When the frozen tissue thaws, the cells die. Tumors that were frozen inside the body will be absorbed. Tumors that were frozen on the skin will form a scab that will fall off as the damaged skin heals.
Can cryosurgery cause side effects?
Cryosurgery can cause side effects, although they are likely to be less severe than those from other local treatments, such as surgery or radiation therapy. The side effects that you might have depend mostly on the part of your body that is treated. For instance:
What temperature is cryotherapy?
The cooling treatment, known as cryotherapy, requires spending time in a "cryosauna" that's cooled to -264 degrees. The method is not new, but it is said to reduce inflammation, improve athletic performance and even slow signs of aging.
How long does cryotherapy last?
“After the short cryotherapy stimulation, the effects last from six to eight hours, where the muscle spasticity is being reduced, when you feel endorphins release and adrenaline release.
How often does Famiglietti do cryotherapy?
Recovering from ankle surgery, Famiglietti does cryotherapy three times a week before his physical therapy sessions. "It helps reduce the swelling around the joint, and that's what I’m trying to improve: range of motion and stability,” Famiglietti said.
How long does it take for a cryotherapy machine to cool down?
Liquid nitrogen is used to cool down the sauna, and, after two to three minutes , skin temperature drops to 32 degrees and one can exit the polar chamber.
Why do doctors use ice machines?
Many doctors use ice compacts and ice machines post-op to decrease local inflammation and expedite healing. Powers has never tried whole-body cryotherapy, but she sees the potential for its use in post-surgery care and would be open to recommending it to patients.
Does cryotherapy help with inflammation?
The method is not new , but it is said to reduce inflammation, improve athletic performance and even slow signs of aging. “We always equate cold therapy (ice) with reduction of inflammation, and cryotherapy is used every day in some form or another.
What is cryogenic deflashing?
Cryogenic deflashing is a deflashing process that uses cryogenic temperatures to aid in the removal of flash on cast or molded workpieces. These temperatures cause the flash to become stiff or brittle and to break away cleanly.
What is the size of a cryogen?
A cryogen, such as liquid nitrogen, is used to cool the workpieces; once cooled they are tumbled and blasted with media pellets, ranging size from 0.006 to 0.080 inches (0.15 to 2.03 mm).
Does cryogenic deflashing extend mold life?
Cryogenic deflashing extends mold life. Rather than replace or repair a mold (which typically involves downtime and high cost), the parts can be deflashed.