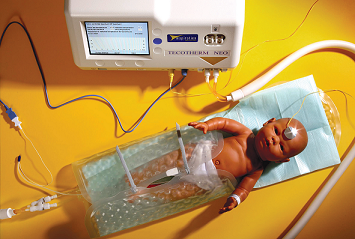
What is cooling therapy for babies?
Neonatal Whole Body Cooling Procedure. Some newborns experience hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy (HIE) at birth. This abnormal neurological state results from reduced levels of oxygen (hypoxia) or blood flow (ischemia) to the baby's brain or body. Over the past several years, therapeutic hypothermia, or whole body cooling, has been used to treat HIE.
How do you cool a newborn in the womb?
Aug 16, 2017 · Neonatal Therapeutic Hypothermia, also known as “Cooling Therapy” is a treatment for newborns that lack oxygen due to birth complications. Infants sometimes lack sufficient oxygen at birth due to blood loss or other complications during delivery.
Can cooling treatment reduce baby's brain damage?
Jul 10, 2014 · But a 2009 study of more than 300 newborns showed cooling treatment - known as therapeutic hypothermia - could help reduce brain damage at 18 months. Researchers think the therapy works by slowing...
What is hypothermia therapy for infants?
COOLING PROCEDURE Within 6 h of birth, eligible infants will undergo whole body cooling therapy to achieve and maintain Core body temperature between 33.5°C and 34.5°C. (Core temperature is monitored continuously using esophageal or rectal temperature probe) [ Figure 1 ]. Figure 1 Flow chart for commencing therapeutic hypothermia

Why would a newborn need to be cooled?
Total body cooling (or whole-body hypothermia) is a process where the baby's temperature is carefully lowered after a traumatic labor experience. Essentially, we're protecting the brain by minimizing the production of toxic substances that can cause brain injury.Jul 23, 2019
Why do babies get cooled in NICU?
Neonatal body cooling, also called newborn therapeutic hypothermia, lowers your baby's body temperature to treat hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy (HIE). HIE is a neonatal brain injury that occurs if your baby's brain doesn't receive enough oxygen.
What does cooling mean for a baby?
Cooling therapy, also called neonatal or therapeutic hypothermia, is one of the most effective treatments for HIE when administered properly. Cooling the baby's body and brain temperature in a controlled environment alters chemical processes in the brain, thus reducing the risk of permanent brain damage.Jul 20, 2021
What is cooling therapy used for?
Once the heart starts beating again, healthcare providers use cooling devices to lower your body temperature for a short time. It's lowered to around 89°F to 93°F (32°C to 34°C). The treatment usually lasts about 24 hours. The heart has an electrical signal that helps coordinate the heartbeat.
When should I start cooling therapy?
According to the Academic Medical Center Patient Safety Organization (AMC PSO), hypothermia therapy should ideally be commenced within six hours of birth (under certain circumstances, this may be done within 12 hours) (2).
How effective is HIE cooling?
There is now good scientific evidence that cooling a baby with moderate or severe HIE to a temperature of 33-34°C, can help to reduce the severity of the injury to the brain and improve the longer term outcome for the baby. There is also some evidence that the faster the baby is treated, the better the outcome.
What is head cooling in newborns?
Neonatal head cooling is a somewhat new treatment through which doctors cool a newborn's head immediately after a traumatic delivery. If a baby experienced a lack of oxygen during birth, otherwise known as hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy (HIE) caused by asphyxia, the brain can experience irreversible damage.
Do babies recover from HIE?
Most babies with mild HIE recover quickly. If your baby has mild HIE, doctors will monitor them closely to check that they are stable and do not need any more treatment. If your baby has moderate to severe HIE, there is a risk of death or long-lasting damage to the brain.
What is HIE newborn?
Hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy (HIE) is a type of brain dysfunction that occurs when the brain doesn't receive enough oxygen or blood flow for a period of time. Hypoxic means not enough oxygen; ischemic means not enough blood flow; and encephalopathy means brain disorder.
What is the reason for body cooling?
A brain region called the hypothalamus is responsible for regulating body temperature. It checks the body's current temperature against its normal temperature and then regulates it. When the body is too hot, regulation occurs through sweating to cool it down.
How long does it take for a baby to cool down?
We continuously monitor your baby during the body cooling process to ensure that he or she receives excellent care. After three days of cooling, your baby will be slowly warmed to normal body temperature. Procedures your baby may need during treatment include:
What to do after NICU discharge?
Once discharged from the NICU, your baby will need careful follow-up with your pediatrician. Additional appointments may be needed with specialists such as a developmental psychologist or neurologist. Call 703-776-6020 for more information about the neonatal whole body cooling procedure at Inova Children's Hospital.
What tests are used to diagnose a baby with HIE?
Procedures your baby may need during treatment include: MRI – brain imaging study that looks for brain injury caused by HIE. EEG – test that measures electrical activity of the brain. Intubation – placing a tube in the windpipe to help with breathing.
What is the term for a newborn's brain that is affected by oxygen?
Some newborns experience hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy (HIE) at birth. This abnormal neurological state results from reduced levels of oxygen (hypoxia) or blood flow (ischemia) to the baby's brain or body. Over the past several years, therapeutic hypothermia, or whole body cooling, has been used to treat HIE.
How long does it take for a baby to get a temperature of 92 degrees Fahrenheit?
Your baby's temperature will be lowered, slowly and safely, to 92 degrees Fahrenheit (33.5 degrees Celsius). By maintaining this temperature for three days, your baby's metabolic processes slow. This decreases the severity and extent of potential brain injury from HIE.
How long does it take for a baby to be treated for encephalopathy?
To be most effective, treatment should begin within six hours of birth. Call 703-776-6020 for more information.
Does cooling help with encephalopathy?
Neonatologists at Inova Children's Hospital recommend this cooling treatment to help protect your baby's brain. By slowing the metabolism, there is evidence the procedure may reduce death and disability in babies with encephalopathy.
What temperature does a baby need to be cool?
Cooling therapy generally cools the baby to a moderate 32-34 degrees Celsius (92-94 degrees Fahrenheit), which is thought to do the following: Reduce energy depletion and metabolism. Decrease excitatory transmitter action in the brain. Reduce ion flux alterations.
How long does cooling therapy last?
More severe injuries may require longer durations of cooling therapy. In general, cooling therapy lasts for 2-3 days, after which doctors gradually warm the baby and make further assessments of his or her condition.
What is a HIE?
Before answering questions about treatment, it is important that you understand your child’s diagnosis. Hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy (HIE) is a form of brain damage occurring in infants who experience lack of oxygen in the brain. HIE generally occurs around the time of birth ...
What is the best treatment for HIE?
Cooling therapy , also called neonatal or therapeutic hypothermia, is one of the most effective treatments for HIE when administered properly. Cooling the baby’s body and brain temperature in a controlled environment alters chemical processes in the brain, thus reducing the risk of permanent brain damage.
What causes a newborn to have a HIE?
HIE can result from negligent healthcare during the labor and delivery process, including: If you have suffered from any of these, or other, circumstances and your newborn was diagnosed with HIE, you may be the victim of a birth injury caused by negligence or medical malpractice .
What causes a birth injury?
There are numerous causes for birth injuries. An unfortunate reality is that negligent healthcare is one of the most devastating. HIE can result from negligent healthcare during the labor and delivery process, including: 1 Issues with the umbilical cord 2 Complications associated with the baby’s position or size 3 Delayed delivery or failure to order a cesarean section 4 Mismanagement of maternal health conditions or complications 5 Failure to monitor and address fetal vital signs 6 Failure to recognize signs of anoxia or hypoxia
What to expect after cooling therapy?
After cooling therapy, your baby will need further assessment and monitoring to make sure he or she can eat, digest, and function healthily. You can expect tests or monitoring like MRIs, EEGs, and heart monitors to make sure there is no abnormal brain, electrical, or heart activity.
How much temperature should a newborn be after hypothermia?
The AMC PSO suggests that the baby’s temperature should be increased by 0.2 – 0.5 degrees Celsius, until it reaches 36.5 degrees Celsius.
When should a baby get hypothermia?
When should my baby get hypothermia therapy? If your baby was diagnosed with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE), doctors have to begin hypothermia therapy very shortly after the oxygen deprivation occurred.
What is the AMC PSO?
Additionally, one or both of the following: The baby had seizures. The baby was showing clinical signs of brain damage. The AMC PSO also describes situations in which hypothermia therapy may be considered .
What is the treatment for hypothermia?
This treatment is known as hypothermia therapy, but it has many other names, such as “therapeutic hypothermia,” “cooling therapy,” and “neonatal cooling.”. Hypothermia therapy involves cooling the baby down to a temperature below homeostasis to allow the brain to recover from a hypoxic-ischemic injury. Typically, the target temperature is about ...
How soon after birth can you give hypothermia?
However, it must be given very shortly after birth/the oxygen-depriving incident in order to be effective (ideally within six hours). This treatment is known as hypothermia therapy, but it has many other names, ...
How long does it take for a baby to get hypothermia?
According to the Academic Medical Center Patient Safety Organization (AMC PSO), hypothermia therapy should ideally be commenced within six hours of birth (under certain circumstances, this may be done within 12 hours) (2). The sooner hypothermia therapy begins, the greater the chance that the baby’s potential disabilities will be minimized.
What is the job of a blood gas test?
Conducting blood gas tests and managing acidosis (excessive acid in the blood) Maintaining normal glucose and electrolyte levels. Providing respiratory and cardiovascular support as needed. Testing for and treating infections. Maintaining sedation at an appropriate level.
Why is it important to cool a baby?
Cooling babies 'helps reduce longer-term brain damage'. Cooling babies deprived of oxygen at birth improves their chances of growing up without disabilities such as cerebral palsy, research suggests. The New England Journal of Medicine study showed newborns given the treatment were more likely to have higher IQs at school age.
How does cooling help the brain?
Researchers think the therapy works by slowing the production of harmful substances in the brain and the rate of brain cell death.
Why are babies put on a mat?
Babies were placed on a special mat and cooled at 33C for three days to help reduce brain injury. Experts say the study confirms the therapy has long-lasting effects. Around one in 500 newborns in the UK suffer from asphyxia - a lack of oxygen around the time of birth.
What percentage of children have no brain abnormalities?
About 45% of cooled children had no brain abnormalities, compared with 28% of those who had had standard treatment. And some 21% in the cooling group had cerebral palsy, compared with 36% in the control group. Babies in the hypothermia group were also more likely to have IQ scores above 85.
What is the IQ of a baby with hypothermia?
Babies in the hypothermia group were also more likely to have IQ scores above 85 . Lead author Prof David Edwards, of King's College London, told the BBC: "What is remarkable about this study is that 20 years ago people thought nothing could be done for this group of patients who can suffer devastating brain damage.
Does cooling help with survival?
The cooling treatment showed no influence on survival rates though - a similar proportion (about 30%) of babies in both groups did not survive to school age. Researchers say the next steps will be to look at therapies that can work in conjunction with therapeutic hypothermia and increase the chances of normal survival.
Does cooling babies help them grow up?
Cooling babies deprived of oxygen at birth improves their chances of growing up without disabilities such as cerebral palsy, research suggests. The New England Journal of Medicine study showed newborns given the treatment were more likely to have higher IQs at school age.
How long does it take for a baby to cool down?
The goal is to start cooling within six hours of birth – the sooner the better. We place the baby on a special blanket that circulates water through it, which cools and eventually warms the baby. Then we place a small temperature probe in the baby’s esophagus to track his or her core temperature.
What does a neonatologist do after stabilizing a newborn?
After stabilizing the infant, the NICU doctor (neonatologist) examines the newborn for signs of possible brain injury or HIE , such as: Too much acid in the blood (a typical body response to low oxygen) Bloodwork that indicates kidney, heart, or liver injury. Low Apgar scores that persist longer than 10 minutes.
What happens if the umbilical cord breaks during labor?
Umbilical cord prolapse : When the bag of water breaks at the onset of labor, the umbilical cord can slip through the partially dilated cervix. If the cord is squeezed between the baby’s and mother’s bodies, the baby might not receive enough blood and oxygen. In spontaneous labor, we can’t plan for the water breaking.
How many deliveries does umbilical cord prolapse?
Umbilical cord prolapse occurs in 1 to 6 of 1,000 deliveries. Amniotic fluid embolism : If amniotic fluid enters a patient’s bloodstream, she can go into shock, essentially causing respiratory failure, cardiovascular collapse, and heavy bleeding.
What are some examples of rare birth events that usually result in emergency delivery and the potential for total body cooling?
Here are some examples of rare birth events that usually result in emergency delivery and the potential for total body cooling: Placental abruption : The placenta pulls away from the uterine wall before delivery, depriving the baby of blood, nutrients, and oxygen.
How long does a baby stay at 33.5 degrees Celsius?
We slowly lower the baby’s body temperature to 33.5 degrees Celsius (92.3 degrees Fahrenheit). The baby will stay at that temperature for 72 hours, a standard based on a 2012 study published in the Journal of Clinical Neonatology.
How many pregnancies are caused by placental abruption?
Placental abruption occurs in approximately 7 to 12 of 1,000 pregnancies in North America and is more prevalent in women with high blood pressure and in those who use drugs such as cocaine that cause spasms in the blood vessels.