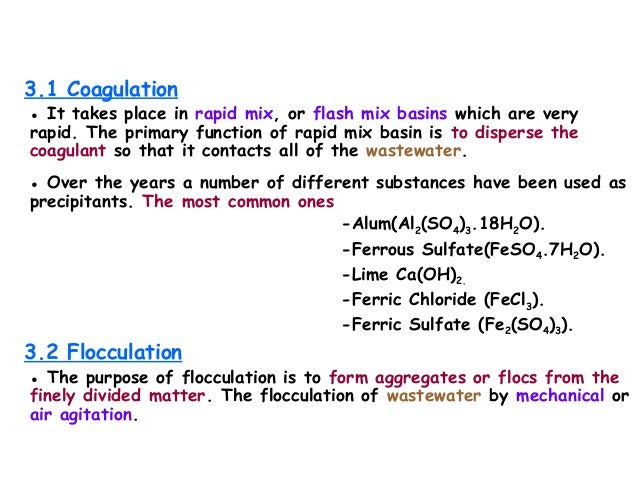
Flocculation
Flocculation, in the field of chemistry, is a process wherein colloids come out of suspension in the form of floc or flake; either spontaneously or due to the addition of a clarifying agent. The action differs from precipitation in that, prior to flocculation, colloids are merely suspended in a liquid and not actually dissolved in a solution.
What is the difference between coagulation and flocculation?
first process in drinking water treatment, coagulation, is to destabilize the particles and allow them the potential to collide and stick together. There are four main mechanisms for coagulation: double layer compression, adsorption and charge neutralization, sweep flocculation, and inter-particle bridging. Sweep flocculation is the primary
What is the goal of flocculation in water treatment?
Coagulation and flocculation are very important steps in a water treatment plant process. Coagulation means a process using coagulant chemicals and mixing by which colloidal and suspended materials are destabilized and agglomerated into flocs.
What is the process of flocculation?
Apr 03, 2018 · Coagulation and flocculation for wastewater treatment represent tested ways to improve efficiency and remove a high volume of particles. Coagulation clumps contaminants together so they are more easily removed. Flocculating agents in wastewater treatment are used to remove contaminants. Get the details here.
What is the difference between flocculation and agglutination?
The primary purpose of the coagulation and flocculation is to destabilize the charged colloidal particles in water and make them to settle so as to remove turbidity from the water. In addition to removing turbidity from the water, coagulation and flocculation process removes many bacteria which are suspended in the water and can be used to remove color from the water.
What is coagulation in water treatment process?
Coagulation is the chemical water treatment process used to remove solids from water, by manipulating electrostatic charges of particles suspended in water. This process introduces small, highly charged molecules into water to destabilize the charges on particles, colloids, or oily materials in suspension.6 days ago
What is flocculation and coagulation in water treatment?
Coagulation and flocculation occur in successive steps intended to overcome the forces stabilising the suspended particles, allowing particle collision and growth of flocs, which then can be settled and removed (by sedimentation) or filtered out of the water.May 24, 2019
What is coagulation and flocculation in the water treatment process quizlet?
Coagulation - chemicals are added that will cause the particles to begin to clump together. Flocculation - the particles gather together to form larger, settleable particles.
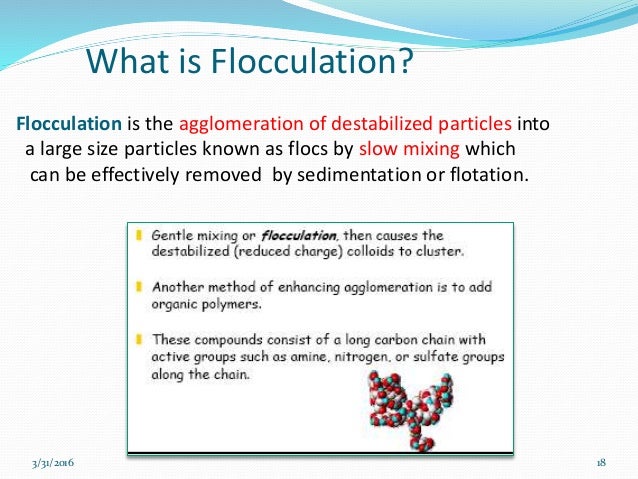
What is the flocculation process?
Flocculation is a process by which a chemical coagulant added to the water acts to facilitate bonding between particles, creating larger aggregates which are easier to separate. The method is widely used in water treatment plants and can also be applied to sample processing for monitoring applications.
What is meant by coagulation and flocculation?
Coagulation is the destabilization of colloidal particles brought about by the addition of a chemical reagent called as coagulant. Flocculation is the agglomeration of destabilized particles into microfloc and after into bulky floccules which can be settled called floc.
Why is coagulation and flocculation necessary?
Coagulation and flocculation are used to separate the suspended solids portion from the water. Suspended particles vary in source, charge, particle size, shape, and density. Correct application of coagulation and flocculation depends upon these factors.
What is the purpose of flocculation during the treatment of drinking water quizlet?
The purpose of coagulation and flocculation is to remove particulate impurities and color from the water being treated.
Which is the most important consideration in coagulation flocculation process control?
The most important consideration in coagulation-flocculation process control is selection of the proper type and amount of coagulant chemical(s) to be added to the water being treated. This decision is made with the help of a jar test.
What are floc particles?
Floc is a small, loosely aggregated mass of flocculent material suspended in or precipitated from a liquid. It consists of finely divided suspended particles in a larger, usually gelatinous particle, the result of physical attraction or adhesion to a coagulant compound.Nov 24, 2016
Why is flocculation important in water treatment?
Coagulation and flocculation are both critical processes to separate and remove suspended solids in water and wastewater treatment. These processes improve the clarity of the water to reduce turbidity.
What is flocculation separation?
flocculation, in physical chemistry, separation of solid particles from a liquid to form loose aggregations or soft flakes. These flocculates are easily disrupted, being held together only by a force analogous to the surface tension of a liquid.
Where is flocculation used?
Flocculation and sedimentation are widely employed in the purification of drinking water as well as in sewage treatment, storm-water treatment and treatment of industrial wastewater streams. Typical treatment processes consist of grates, coagulation, flocculation, sedimentation, granular filtration and disinfection.
What is the chemistry of coagulation and flocculation?
The chemistry of coagulation and flocculation is primarily based on electricity. Electricity is the behavior of negative and positively charged particles due to their attraction and repulsion. Like charges (two negatively charged particles or two positively charged particles) repel each other while opposite charges (a positively charged particle and a negatively charged particle) attract.
Why is coagulation important in water treatment?
It is, however, an important primary step in the water treatment process, because coagulation removes many of the particles, such as dissolved organic carbon, that make water difficult to disinfect. Because coagulation removes some of the dissolved substances, less chlorine must be added to disinfect the water.
What is coagulation reaction?
cationic, anionic, and nonionic) and molecular weight. Coagulation is a reaction caused by adding salts of iron or aluminum to the water.
How does flocculation work?
Flocculation follows coagulation in the conventional water treatment process. Flocculation causes the agglomeration or collection of small particles into larger, more readily settleable floc particles. It is usually a tapered process with two or more units in series. The first unit has a higher mix speed and the mixing speed decreases in subsequent basins to promote the growth of floc particles. The total detention time in the flocculation basin is normally 30 to 60 minutes. Through experience, we see that effective mixing reduces the required amount of chemicals and greatly improves the sedimentation process, which results in longer filter runs and higher quality finished water. The goal of flocculation is to form a uniform, feather-like material similar to snowflakes - a dense, clingy floc that traps the fine, suspended, and colloidal particles and carries them down rapidly in the settling basin. To increase the speed of floc formation and the strength and weight of the floc, polymers are often added.
When operators determine the best coagulant dosage for the current raw water quality conditions based on jar tests and other
When operators determine the best coagulant dosage for the current raw water quality conditions based on jar tests and other lab data, they must be able to set the chemical feeders to apply the proper quantity of coagulant. As part of the routine, an operator must deal with preparing solutions from dry chemicals and for jar tests.
Why are adjustments necessary in water treatment plants?
In a well-run water treatment plant, adjustments are often necessary in order to maximize the coagulation/flocculation process. These adjustments are a reaction to changes in the raw water entering the plant. Coagulation will be affected by changes in the water's pH, alkalinity, temperature, time, velocity and zeta potential.
What is the purpose of coagulation?
The primary purpose of the coagulation/flocculation process is the removal of turbidity from the water. Turbidity is a cloudy appearance of water caused by small particles suspended therein. Water with little or no turbidity will be clear.
What is coagulation in water treatment?
Coagulation water treatment is the first step in chemical wastewater treatment. Instead of passing over particles that would otherwise slip through the filter and fall too slowly to be trapped as sediment, coagulation clumps them together so they are more easily removed. Most of us know coagulation from anatomy class.
Why is flocculation so popular?
Coagulation and flocculation processes have become more and more popular due to the increasingly stringent filtration requirements for industrial and municipal water treatment and wastewater treatment facilities levied by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA.)
What is a flocculant?
Flocculants are lightweight, medium weight and heavy polymers that cause the destabilized clumps of particles to agglomerate and drop out of the solution, removing them from the filtered water. The weight used depends on the type of particle.
Is alum a good coagulant?
It’s the same principle with wastewater treatment. In coagulation treatment, a harmless chemical such as alum causes all of the particles to give off a positive charge and thus clump together, making them easier to filter. Coagulation is especially useful in removing the chemical phosphorus from water. Yet coagulation water treatment is far ...
What is the purpose of coagulation and flocculation?
The primary purpose of the coagulation and flocculation is to destabilize the charged colloidal particles in water and make them to settle so as to remove turbidity from the water. In addition to removing turbidity from the water, coagulation and flocculation process removes many bacteria which are suspended ...
What is the process of adding coagulant to water?
Coagulation is a unit process of addition of coagulant chemicals to water and rapid mixing so as to neutralize the electrical charges of the colloidal particles in the water, and allow them to come closer and form fine clumps or micro flocs. No related topics.
What are the three types of particles that cause turbidity?
In the order from smallest to largest, these particles are chemicals in solution, suspended colloidal solids, and suspended discrete solids. Some discrete particles of sizes bigger than 0.01 mm such as silt and fine sand causing turbidity would settle ...
What is the zeta potential of a coagulant?
The amount of coagulant to be added to the water will depend on the zeta potential, a measurement of the magnitude of electrical charge surrounding the colloidal particles. The zeta potential is the amount of repulsive force or electric charge, which keeps the particles in the water.
Do colloids dissolve in water?
Colloids, also known as non settleable solids, do not dissolve in water although they are electrically charged. Still, the particles are so small that they will not settle out of the water by gravity even after several years of retention and they cannot be removed by filtration alone.
What is the process of coagulation and flocculation?
Coagulation and flocculation are two processes commonly used in water treatment in order to get rid of unwanted suspended material in water. However, they can be commonly adopted for de-stabilizing any suspension system.
What is the difference between flocculation and coagulation?
Coagulation involves the use of a coagulant which has the potential to de-stabilize the previously stabilized charged particles in the suspension. Whereas in flocculation, the de-stabilization is brought about by physical techniques such as mixing of the solution, and also sometimes by the addition of polymers.
What is flocculation in biology?
What is Flocculation. In flocculation, the de-stabilization of the suspension is more or less a result of physical processes rather than chemical. The most common way is to add a flocculant to the suspension, where the flocculant is generally a polymer.
What is the difference between coagulant and flocculant?
Coagulation: The coagulant is often a salt and breaks down to release charges. Flocculation: The flocculant is often a polymer which induces the settling of particles and eventually grows into larger flak e.
What is colloidal suspension?
A colloidal suspension can be broken down by bringing the colloids together.
What is a coagulant?
Coagulation is an important phenomenon in the clotting of blood. Hence, coagulation is commonly known as clotting. The effects of a coagulant can be reversed by the use of an anti-coagulant. These anti-coagulants are often used to ease blood clots to prevent artery blockage. Alum Whilte.
What degree does Melani Maria have?
Melani Maria has a BSc (Hons) degree in Chemistry and doing her Masters, specializing in Perfumery and Business. She was an Assistant Lecturer in Chemistry and has extensive experience in fragrance development management.
What is flocculation in science?
Flocculation: A process wherein colloids come out of suspension in the form of floc, either spontaneously or due to the addition of a clarifying agent. It is used in applications like water purification, sewage treatment, cheese production and brewing, for example. Regarding this, what is the process of flocculation? ...
What is the most common coagulant used for water purification?
Chemicals (coagulants) are added to the water to bring the nonsettling particles together into larger, heavier masses of solids called floc. Aluminum sulfate (alum) is the most common coagulant used for water purification. Other chemicals, such as ferric sulfate or sodium aluminate, may also be used. Herein, what is coagulation and flocculation ...
