
Medication
Cervical cancer is treated in several ways. It depends on the kind of cervical cancer and how far it has spread. Treatments include surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy. Page last reviewed: December 14, 2021. Content source: Division of Cancer Prevention and Control, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Procedures
“This study provides a proof of concept of immunotherapeutic checkpoint inhibition in cervical cancer. If cemiplimab is approved, it will provide a second-line treatment option for women with recurrent cervical cancer,” Tewari said.
Therapy
The cervical cancer guidelines ... and exploring other methods of control—such as immunotherapy—for advanced cancers. Prevention remains key While the new patient guidelines focus primarily on cancer treatment rather than prevention, NCCN continues ...
Nutrition
Gynecologists use several tests to diagnose cervical cancer, including:
- Pelvic exam: a visual and physical assessment of the external and internal female pelvic organs
- Pap smear: a screening that collects cells from the cervix
- HPV test: an STI test involving a sample of cervical cells
- Endocervical curettage: collection and examination of cervical tissue
- Colposcopy: examination of the cervix with a magnifying instrument
What is cervical cancer and how is it treated?
How do you cure cervical cancer?
What are some common methods of cervical cancer treatment?
How is cervical cancer diagnosed and treated?
See more
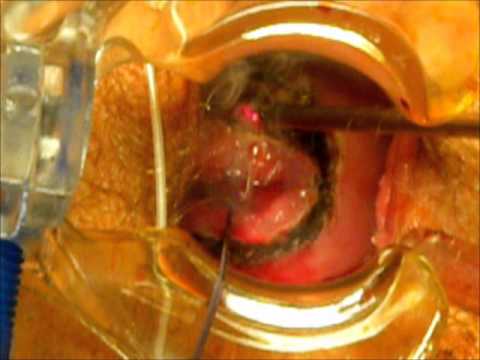
Can cervical cancer be cured completely?
Cervical cancer is curable, but it is difficult for doctors to know for sure that it will never come back following treatment. Therefore, doctors often use the term “remission” to describe cancer that has gone away and is no longer causing symptoms.
How do they remove cervical cancer?
The procedure can be done in different ways: Using a surgical blade (cold knife cone biopsy) Using a laser beam (laser conization) Using a thin wire heated by electricity (the loop electrosurgical excision procedure, LEEP or LEETZ procedure).
What is the first line of treatment for cervical cancer?
Palliative platinum-based chemotherapy (CT) is the standard first-line treatment for metastatic/recurrent cervical cancer.
How long does treatment for cervical cancer last?
As with surgery, the radiation affects cancer cells only in the treated area. Your treatments might be external, internal, or both. External radiation comes from a large machine that aims a beam of radiation at your pelvis. You'll probably get treatments, which take only a few minutes, 5 days a week for 5 to 6 weeks.
What is the main cause of cervical cancer?
Nearly all cervical cancers are caused by an infection with certain high-risk types of human papillomavirus (HPV). You can get HPV from: any skin-to-skin contact of the genital area. vaginal, anal or oral sex.
What happens when a woman's cervix is removed?
After the trachelectomy, you can expect: vaginal bleeding for two or more weeks. pain (you'll be prescribed pain medication) a urinary catheter (a thin tube inserted into the bladder to release urine) in place for one to two weeks postsurgery.
What are the symptoms of Stage 1 cervical cancer?
Signs and symptoms of stage 1 cervical cancer can include:Watery or bloody vaginal discharge that may be heavy and can have a foul odor.Vaginal bleeding after intercourse, between menstrual periods or after menopause.Menstrual periods may be heavier and last longer than normal.
What is the most common treatment for cervical cancer?
Common treatment approaches For the earliest stages of cervical cancer, either surgery or radiation combined with chemo may be used. For later stages, radiation combined with chemo is usually the main treatment. Chemo (by itself) is often used to treat advanced cervical cancer.
Does cervical cancer spread fast?
Usually, cervical cancer grows slowly, but sometimes it can develop and spread quickly. Cervical cancer is one of the cancers that can occur in young women.
Can you live a normal life after cervical cancer?
This is very common if you've had cancer. For other women, the cancer may never go away completely. These women may get regular treatments with chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or other therapies to try to control the cancer for as long as possible.
Is cervical cancer serious?
Cervical cancer is a slow-growing, but life-threatening disease. Today's screening techniques mean you're more likely to discover precancerous cells that can be removed before they get the chance to develop into cancer. With early diagnosis and treatment, the outlook is very good.
Does cervical cancer come back after treatment?
Approximately a third of women treated for cervical cancer will have recurrence during follow-up (11), with most relapses occurring in the first two to three years after treatment (7, 12).
How to treat cervical cancer during pregnancy?
Treatment of cervical cancer during pregnancy depends on the stage of the cancer and how long the patient has been pregnant. A biopsy and imaging tests may be done to determine the stage of the disease. To avoid exposing the fetus to radiation, MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) is used.
Where does cervical cancer form?
Cervical cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the cervix. The cervix is the lower, narrow end of the uterus (the hollow, pear-shaped organ where a fetus grows). The cervix leads from the uterus to the vagina (birth canal). Anatomy of the female reproductive system.
How big is stage 2 cervical cancer?
Stage II cervical cancer. In stages IIA1 and IIA2, cancer has spread from the cervix to the upper two-thirds of the vagina but has not spread to the tissue around the uterus. In stage IIA1, the cancer is 4 centimeters or smaller. In stage IIA2, the cancer is larger than 4 centimeters.
What is the purpose of DNA and RNA in a cervical Pap test?
Cells are collected from the cervix and DNA or RNA from the cells is checked to find out if an infection is caused by a type of HPV that is linked to cervical cancer. This test may be done using the sample of cells removed during a Pap test.
What is the risk factor for cervical cancer?
Human papillomavirus (HPV) infection is the major risk factor for cervical cancer. Anything that increases your chance of getting a disease is called a risk factor. Having a risk factor does not mean that you will get cancer; not having risk factors doesn't mean that you will not get cancer.
What is the procedure to remove abnormal cells from a Pap test?
Biopsy: If abnormal cells are found in a Pap test, the doctor may do a biopsy. A sample of tissue is cut from the cervix and viewed under a microscope by a pathologist to check for signs of cancer. A biopsy that removes only a small amount of tissue is usually done in the doctor’s office.
How does chemo work?
When chemotherapy is taken by mouth or injected into a vein or muscle , the drugs enter the bloodstream and can reach cancer cells throughout the body ( systemic chemotherapy ). When chemotherapy is placed directly into the cerebrospinal fluid, an organ, or a body cavity such as the abdomen, the drugs mainly affect cancer cells in those areas ( regional chemotherapy ). The way the chemotherapy is given depends on the type and stage of the cancer being treated.
What is the test for cervical cancer?
A Pap test can detect abnormal cells in the cervix, including cancer cells and cells that show changes that increase the risk of cervical cancer. HPV DNA test.
What tests are done to determine if you have cervical cancer?
Your cancer's stage is a key factor in deciding on your treatment. Staging exams include: Imaging tests.
What is palliative care?
Palliative care is specialized medical care that focuses on providing relief from pain and other symptoms of a serious illness. Palliative care specialists work with you, your family and your other doctors to provide an extra layer of support that complements your ongoing care.
What tests can be done to check if you have cancer?
Tests such as X-ray, CT, MRI and positron emission tomography (PET) help your doctor determine whether your cancer has spread beyond your cervix. Visual examination of your bladder and rectum. Your doctor may use special scopes to see inside your bladder and rectum.
Can you remove cancer from a small cervix?
Surgery to cut away the cancer only. For a very small cervical cancer, it might be possible to remove the cancer entirely with a cone biopsy. This procedure involves cutting away a cone-shaped piece of cervical tissue, but leaving the rest of the cervix intact.
Can you use chemotherapy for cervical cancer?
Sometimes both methods are used. For locally advanced cervical cancer, low doses of chemotherapy are often combined with radiation therapy, since chemotherapy may enhance the effects of the radiation . Higher doses of chemotherapy might be recommended to help control symptoms of very advanced cancer.
Can you be prepared for cancer?
No one can be prepared for a cancer diagnosis. You can, however, try to manage the shock and fear you're feeling by taking steps to control what you can about your situation.
What is the treatment for cervical cancer?
Cervical cancer treatments include surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy. If your doctor says that you have cervical cancer, ask to be referred to a gynecologic oncologist —a doctor who has been trained to treat cancers of a woman’s reproductive system.
What is the purpose of information about cancer?
Doctors use this information to plan treatment and to monitor progress.
What is the difference between a gynecologic oncologist and a radiation oncologist
Different treatments may be provided by different doctors on your medical team. Gynecologic oncologists are doctors who have been trained to treat cancers of a woman’s reproductive system. Surgeons are doctors who perform operations. Medical oncologists are doctors who treat cancer with medicine. Radi ation oncologists are doctors who treat cancer ...
What is the treatment for a swollen vein?
Surgery: Doctors remove cancer tissue in an operation. Chemotherapy: Using special medicines to shrink or kill the cancer. The drugs can be pills you take or medicines given in your veins, or sometimes both.
Surgery
Surgery is the main treatment for cervical cancers. Sometimes you'll get chemotherapy or radiation to shrink the tumor before surgery, or to kill cancer cells that remain afterward. The type of surgery you have depends on how large the cancer has grown and whether it has spread.
Radiation
Radiation uses high-energy X-rays to kill cancer cells and stop their growth. You might get radiation before or after surgery, or if your cancer has spread beyond your cervix.
Chemotherapy
In “chemo,” drugs are used to kill or slow the growth of cervical cancer cells. You'll usually get chemo through an IV.
Targeted Therapy
Targeted therapy uses drugs that kill cancer cells but spare healthy cells. For example, bevacizumab ( Avastin) is a drug that stops new blood vessels from forming. This can slow down tumor growth in advanced cervical cancer, because tumors need new blood vessels for nourishment. Doctors often use targeted therapy with chemotherapy.
Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy is the use of medicines to stimulate a person’s own immune system to recognize and destroy cancer cells more effectively. Immunotherapy can be used to treat cervical cancer that has spread or come back (recurred).
Clinical Trials
If you've tried a few treatments and they didn't work, or the cancer has spread, ask your doctor about a clinical trial. These test new treatments to see if they’re safe and if they work. They’re often ways for people to try new medicines or therapies that aren’t available to everyone.
How Can I Feel Better During Cervical Cancer Treatment?
You’re probably so focused on getting well, you hardly have time to think about how to ease the side effects from your treatments like hair loss or changes in your appetite. But there are things you can do that can help you feel better.
What is cervical cancer?
Most of the other cervical cancers are adenocarcinomas. Adenocarcinomas are cancers that develop from glandular cells. Cervical adenocarcinoma develops from the mucus-producing gland cells of the endocervix. Less commonly, cervical cancers have features of both squamous cell carcinomas and adenocarcinomas.
What is the goal of cervical cancer screening?
The goal of cervical cancer screening is to find pre-cancer or cancer early when it is more treatable and curable. Regular screening can prevent cervical cancers and save lives. The tests for cervical cancer screening are the HPV test and the Pap test.
What is the endocervix?
The endocervix is the opening of the cervix that leads into the uterus. It is covered with glandular cells. The exocervix (or ectocervix) is the outer part of the cervix that can be seen by the doctor during a speculum exam. It is covered in squamous cells.
How are cervical cancers classified?
Cervical cancers and cervical pre-cancers are classified by how they look in the lab s with a microscope. The main types of cervical cancers are squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma. Most (up to 9 out of 10) cervical cancers are squamous cell carcinomas. These cancers develop from cells in the exocervix.
What is the name of the cancer that can be found in the cervix?
These are called adenosquamous carcinomas or mixed carcinomas. Although almost all cervical cancers are either squamous cell carcinomas or adenocarcinomas , other types of cancer also can develop in the cervix. These other types, such as melanoma, sarcoma, and lymphoma, occur more commonly in other parts of the body.
What is the term for abnormal changes in the cervix?
Instead, the normal cells of the cervix first gradually develop abnormal changes that are called pre-cancerous. Doctors use several terms to describe these pre-cancerous changes, including cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN), squamous intraepithelial lesion (SIL), and dysplasia. When the pre-cancers are checked in the lab, ...
Where does cervical cancer start?
Cervical cancer starts in the cells lining the cervix -- the lower part of the uterus (womb). The cervix connects the body of the uterus (the upper part where a fetus grows) to the vagina (birth canal). Cancer starts when cells in the body begin to grow out of control.
What is the best treatment for cervical cancer?
Surgery for Cervical Cancer. Many women with cervical cancer will have some type of surgery. Surgery can be used to: Help diagnose cervical cancer. Help determine how far the cancer has spread. Help treat the cancer (especially for early-stage cancers)
What is the procedure to remove pre-cancer cervix?
Two types of procedures can be used to treat pre-cancers of the cervix: Ablation destroys cervical tissue with cold temperatures or with a laser rather than removing it. Excisional surgery (conization) cuts out and removes the pre-cancer.
How to treat cervical intraepithelial neoplasia?
Another way to treat cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) is with excisional surgery called conization. The doctor removes a cone-shaped piece of tissue from the cervix. The tissue removed in the cone includes the transformation zone where cervical pre-cancers and cancers are most likely to start.
What is cryosurgery used for?
Cryosurgery is a type of ablation where a very cold metal probe is placed directly on the cervix. This kills the abnormal cells by freezing them. It is used to treat cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN). This can be done in a doctor’s office or clinic. After cryosurgery, you may have a watery brown discharge for a few weeks.
/iStock-667825020-5b37ff19c9e77c003782ecf0.jpg)
Diagnosis
Treatment
Clinical Trials
Coping and Support
Specialist to consult
Preparing For Your Appointment