Medication
Bursitis is the painful swelling of a small, fluid-filled sac called a bursa. These sacs cushion areas where bone would otherwise rub on muscle, tendons or skin. By padding these areas, bursae (plural for bursa) decrease friction, rubbing and inflammation. Although you have bursae throughout your body, bursitis most often occurs around the joints.
Procedures
There eight hip bursitis treatments can typically help ease inflammation and get you back in action. As always, follow your doctor’s instructions for recovery and case. 1. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs like ibuprofen and naproxen sodium can ease pain and inflammation at the same time.
Therapy
How is bursitis treated? Home treatment is often enough to reduce pain and let the bursa heal. Your doctor may suggest physical therapy to strengthen the muscles around your joints. Rest the affected area. Avoid any activity or direct pressure that may cause pain. Apply ice or cold packs as soon as you notice pain in your muscles or near a joint.
Self-care
Aug 30, 2021 · How Is Bursitis Treated? Take these steps to treat bursitis: Avoid activities that make it worse. Rest and raise the affected area. Use crutches or a cane if needed. Put a brace, band, or splint on...
Nutrition
Sep 09, 2021 · Bursitis is a very painful condition that affects small fluid filled sacs, normally known as Bursae. The Bursae is the cushion of the bone, muscles and tendons that are very close to your joints. This painful condition occurs when the bursae becomes inflamed, this usually happens when the bursae is irritated by overuse or excessive pressure.
How is bursitis treated?
Jul 31, 2020 · Bursitis (bur-SY-tis) is a painful condition that affects the small, fluid-filled sacs — called bursae (bur-SEE) — that cushion the bones, tendons and muscles near your joints. Bursitis occurs when bursae become inflamed. The most common locations for bursitis are in the shoulder, elbow and hip.
What is the treatment for elbow Bursa?
Septic bursitis is a medical emergency that requires prompt treatment with broad-spectrum antibiotics (e.g., cephalosporins, clindamycin, or vancomycin ). Mild cases of septic bursitis can be treated with oral antibiotics, while severe cases may require intravenous (IV) antibiotics.
What is bursitis (Bursa)?
Treatments for shoulder bursitis focus on reducing inflammation and minimizing symptoms. Most people get symptom relief with these nonsurgical treatments: Bursa (steroid) injections to ease pain and swelling for a couple of months. Corticosteroids, such as Kenalog or Celestone that you take orally for severe pain and inflammation.
How to get a doctor to diagnose bursitis?
First of all, the treatment will focus on pain reduction. Dosed rest and cooling of the sore spot is very important. For the next step in the treatment process, the focus will be on increasing the load capacity. Possible treatment interventions applied by the physiotherapist are massage, stretching, exercise therapy and joint mobilisations.

What is the fastest way to cure bursitis?
Apply ice to reduce swelling for the first 48 hours after symptoms occur. Apply dry or moist heat, such as a heating pad or taking a warm bath. Take an over-the-counter medication, such as ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB, others) or naproxen sodium (Aleve, others), to relieve pain and reduce inflammation.Jul 31, 2020
What is the best anti-inflammatory for bursitis?
Doctors may recommend over-the-counter nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen or naproxen, to reduce inflammation in the bursa and tendon and relieve pain. These medications are typically recommended for a few weeks while the body heals.
How long does it take for bursitis to heal?
Treatment typically involves resting the affected joint and protecting it from further trauma. In most cases, bursitis pain goes away within a few weeks with proper treatment, but recurrent flare-ups of bursitis are common.Jul 31, 2020
What triggers bursitis?
What causes bursitis? Repetitive motions, such as a pitcher throwing a baseball over and over, commonly cause bursitis. Also, spending time in positions that put pressure on part of your body, such as kneeling, can cause a flare-up. Occasionally, a sudden injury or infection can cause bursitis.May 29, 2020
Is bursitis serious?
When a bursa is infected, it is called septic bursitis. Septic bursitis typically affects bursae located at the knee and elbow joints. Unlike aseptic (non-infectious) bursitis, septic bursitis is a potentially serious medical condition and prompt medical attention is advisable.
What do doctors prescribe for bursitis?
What is the best medication for bursitis?Best medications for bursitisMotrin (ibuprofen)NSAIDOralAleve (naproxen)NSAIDOralTylenol (acetaminophen)AnalgesicOralCelebrex (celecoxib)Prescription NSAIDOral6 more rows•Oct 14, 2020
What happens if bursitis is left untreated?
Chronic pain: Untreated bursitis can lead to a permanent thickening or enlargement of the bursa, which can cause chronic inflammation and pain. Muscle atrophy: Long term reduced use of joint can lead to decreased physical activity and loss of surrounding muscle.
Why is bursitis so painful?
Bursitis is the painful swelling of bursae. Bursae are fluid-filled sacs that cushion your tendons, ligaments, and muscles. When they work normally, bursae help the tendons, ligaments, and muscles glide smoothly over bone. But when the bursae are swollen, the area around them becomes very tender and painful.Apr 16, 2020
Is bursitis a form of arthritis?
The key difference between arthritis and bursitis is the anatomical structures that they affect. Arthritis is a chronic condition that irreparably damages bone, cartilage, and joints, whereas bursitis is a temporary condition that involves the painful swelling of bursae for a time. Pain is worst in the morning.
Is walking good for bursitis?
Running and jumping can make hip pain from arthritis and bursitis worse, so it's best to avoid them. Walking is a better choice, advises Humphrey.Jan 17, 2014
What foods should you avoid if you have bursitis?
Eat whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and fatty fish to help reduce inflammation. Avoid processed foods and foods high in sugar and fat.Dec 19, 2015
Can bursitis be cured?
Bursitis is likely to improve in a few days or weeks if you rest and treat the affected area. But it may return if you don't stretch and strengthen the muscles around the joint and change the way you do some activities.
How to prevent bursitis?
To prevent bursitis: Learn proper posture or technique for sports or work activities. Avoid sitting or kneeling too long. These positions put a lot of pressure on joints. Maintain a healthy weight to reduce pressure on joints. Use cushions and pads when you kneel or put weight on your elbows.
What tests are used to diagnose bursitis?
If you have another bursitis flare-up or signs of infection, your provider may recommend: X-rays to rule out other conditions. Ultrasound or MRI (magnetic imaging res onance) imaging tests to detect swollen bursae. A blood test to look for infection.
What is bursitis in a swollen sac?
What is bursitis? Bursitis is the painful swelling of a small, fluid-filled sac called a bursa. These sacs cushion areas where bone would otherwise rub on muscle, tendons or skin. By padding these areas, bursae (plural for bursa) decrease friction, rubbing and inflammation.
What are the risk factors for bursitis?
The main risk factors for bursitis include: Older age. Jobs or hobbies that involve repetitive tasks (such as sports, manual labor, or music). Conditions such as arthritis, diabetes, gout or thyroid disease.
How long does bursitis last?
Bursitis is usually short-lived, lasting a few hours to a few days. If you don’t rest, it can make your recovery longer. When you have chronic bursitis, painful episodes last several days to weeks. Follow your healthcare provider’s recommendations to prevent recurring episodes.
What is the pain in the joints?
Bursitis. Bursitis is a painful swelling, usually around the joints. It’s common in the shoulders, elbows, knees and feet. You’re more likely to get it if you have a job or hobby that puts a lot of stress on your joints. Appointments 216.444.2606. Appointments & Locations. Contact Us. Overview. Symptoms and Causes.
Where do you get bursitis?
You’re most likely to develop bursitis in joints you use over and over in the same way or in places you put a lot of pressure such as: Shoulders (subacromial bursitis). Elbows (olecranon bursitis, sometimes called miner’s or barfly’s elbow). Knees (prepatellar bursitis or housemaid’s knee).
What is hip bursitis?
Hip bursitis is a condition that causes hip pain ranging from moderate, occasional twinges to a nearly-constant, searing ache. Confusingly it is often caused be either too much activity or not enough. The reason for that comes down to the anatomy of the hips.
Types of hip bursitis
There are two types of hip bursitis, both named for the location of the irritated bursa:
What causes hip bursitis?
Hip bursitis can occur naturally as we age due to wear and tear in the hip joint over time. Beyond this, there are six other common causes of hip bursitis, including:
What are common hip bursitis symptoms?
Hip bursitis symptoms have one thing in common—hip pain —but the quality of the pain and where it occurs depends on the type of bursitis, as do other symptoms.
Getting a hip bursitis diagnosis
Most often, a hip bursitis diagnosis starts with a medical history and physical examination.
How to treat hip bursitis: 8 approaches
In the most severe stages of hip bursitis pain, the best treatment is rest. Inflamed and painful bursa need time to recover. An extended rest period may do more harm than good, though.
How to treat bursitis?
How is bursitis treated? 1 Rest the affected area. Avoid any activity or direct pressure that may cause pain. 2 Apply ice or cold packs as soon as you notice pain in your muscles or near a joint. Apply ice 10 to 15 minutes at a time, as often as twice an hour, for 3 days (72 hours). You can try heat, or alternating heat and ice, after the first 72 hours. 3 Use pain relievers. Use nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen or naproxen, to reduce pain and inflammation. NSAIDs come in pills and also in a cream that you rub over the sore area. Acetaminophen (such as Tylenol) can also help with pain. Don't rely on medicine to relieve pain so that you can keep overusing the joint. 4 Do range-of-motion exercises each day. If your bursitis is in or near a joint, gently move the joint through its full range of motion, even during the time that you are resting the joint area. This will prevent stiffness. As the pain goes away, add other exercises to strengthen the muscles around your joint. 5 Avoid tobacco smoke. Smoking delays wound and tissue healing.
How to stop bursitis pain?
If your bursitis is in or near a joint, gently move the joint through its full range of motion, even during the time that you are resting the joint area. This will prevent stiffness. As the pain goes away, add other exercises to strengthen the muscles around your joint. Avoid tobacco smoke.
How to heal a bursa?
Home treatment is often enough to reduce pain and let the bursa heal. Your doctor may suggest physical therapy to strengthen the muscles around your joints. Rest the affected area. Avoid any activity or direct pressure that may cause pain.
What is the best medicine for sores?
NSAIDs come in pills and also in a cream that you rub over the sore area. Acetaminophen (such as Tylenol) can also help with pain.
Does smoking cause bursitis?
Smoking delays wound and tissue healing. If you have severe bursitis, your doctor may use a needle to remove extra fluid from the bursa. You might wear a pressure bandage on the area. Your doctor may also give you a shot of medicine to reduce swelling.
How to prevent bursitis?
You can’t always prevent bursitis, but some steps can lower your risk. Use cushions or pads when you’re resting a joint on a hard surface, like if you’re kneeling or sitting. If you play sports, mix things up so you don’t make the same motions all the time.
What is bursitis in the body?
What Is Bursitis? Bursitis is inflammation or irritation of a bursa sac. You have these sacs all over your body. They’re filled with fluid that helps ease rubbing and friction between tissues like bone, muscle, tendons, and skin. Bursitis is common around major joints like your shoulder, elbow, hip, or knee.
How to stop swollen joints from hurting?
Take breaks often when you’re making the same motions over and over again. Use good posture all day. Keep a healthy body weight. If something hurts, stop doing it and check with your doctor. Bursitis Diagnosis. Your doctor will ask about your symptoms and do a physical exam to see if the joint is swollen.
How to get rid of a swollen thigh?
Take over-the-counter anti-inflammatory medicines. See your doctor if you don’t feel better after a week. They might give you medications like steroids, which work quickly to lower inflammation and pain. Your doctor might prescribe pills to swallow or use a needle to inject them into the irritated area.
How to heal a bursa in the knee?
If you have an infected bursa, your doctor might use a needle to take out fluid. You’ll probably need antibiotics. It’s rare, but you might need surgery if other treatments aren’t helping.
What age do you get bursitis?
Bursitis is common in adults, especially after age 40. It’s usually caused by repeated pressure on an area or by using a joint too much. High-risk activities include gardening, raking, carpentry, shoveling, painting, scrubbing, tennis, golf, skiing, and throwing.
How to build strength in sports?
If you play sports, mix things up so you don’t make the same motions all the time. Warm up and stretch before you play, and always use proper form. Start slowly and easily when you’re trying a new exercise or sport. As you build strength, you can use more force and do the motion more often.
Bursitis Symptoms
When it comes to this condition, pain is usually the most common symptom and it may build up slowly to quite severe – this is usually the result of calcium deposits in the area.
Bursitis Causes
Bursitis is primarily cause by 2 different things: pressure and repetitive motions.
What is Bursitis of the hip?
Bursitis of the hip is called Trochanteric Bursitis - an inflammation or swelling of an area of the hip called the greater trochanter. Hip pain usually happens when the bursa becomes irritated and inflamed. Symptoms of Trochanteric Bursitis is the pain at the point of the hip and this pain usually extends to the outside of the thigh.
What is Bursitis of the Knee?
Knee bursitis is very similar to hip bursitis with the inflammation happening in the knee joint this time round. Bursae are there to help reduce friction but also cushion your pressure points between your tendons, muscles, bones and skin near your knee joint.
What is shoulder bursitis?
Shoulder bursae. Bursae are small fluid-filled sacs that reduce friction between moving parts in your body's joints. Shoulder bursitis is inflammation or irritation of a bursa (shown in blue) in your shoulder. Elbow bursa. Open pop-up dialog box. Close. Elbow bursa.
What are some examples of bursitis?
If your work or hobby requires repetitive motion or pressure on particular bursae, your risk of developing bursitis increases. Examples include carpet laying, tile setting, gardening, painting and playing a musical instrument.
What is the bursae in the knee?
Knee bursae. Bursae are small fluid-filled sacs (shown in blue) that reduce friction between moving parts in your body's joints. Knee bursitis is inflammation or irritation of one or more of the bursae in your knee. Bursitis (bur-SY-tis) is a painful condition that affects the small, fluid-filled sacs — called bursae (bur-SEE) ...
What is the bursa in the shoulder?
Bursae are small fluid-filled sacs that reduce friction between moving parts in your body's joints. Shoulder bursitis is inflammation or irritation of a bursa (shown in blue) in your shoulder. Bursae are small fluid-filled sacs that reduce friction between moving parts in your body's joints.
Why do I throw a baseball over my head?
Throwing a baseball or lifting something over your head repeatedly. Leaning on your elbows for long periods. Extensive kneeling for tasks such as laying carpet or scrubbing floors. Other causes include injury or trauma to the affected area, inflammatory arthritis such as rheumatoid arthritis, gout and infection.
Can being overweight cause bursitis?
Being overweight can increase your risk of developing hip and knee bursitis.
How to treat a bursal infection?
Treatment includes broad-spectrum antibiotics, as well as drainage of the bursal fluid through needle aspiration. In severe cases, surgical drainage or removal of the bursa may be necessary in order to resolve the infection completely.
What is septic bursitis?
Septic bursitis, or infectious bursitis, refers to the infection and subsequent inflammation of a bursa (plural: bursae). Bursae are small, fluid-filled sacs that cushion and lubricate joints, the areas where different tissues (e.g., muscles, tendons, and bone) rub against each other. Bursae provide a smooth gliding surface ...
What is the procedure to remove bursal fluid?
Symptoms of bursitis often resemble those of other medical conditions, so additional laboratory tests, often including bursal aspiration , are usually needed to confirm the diagnosis. Bursal aspiration is a procedure that involves using a thin needle to remove a small amount of bursal fluid for analysis.
What is it called when you have a bursitis in your knee?
Similarly, prepatellar bursitis may occur in people who spend a lot of time kneeling or crawling, like carpet layers, clergy, gardeners, or household cleaners. When bursitis develops in the knee, it is sometimes referred to as “clergyman’s knee” or “housemaid’s knee.”. Less often, septic bursitis can develop in deep bursae located between bone ...
How to tell if you have bursitis?
Diagnosis of septic bursitis generally involves aspiration and analysis of the bursal fluid. Treatment includes broad-spectrum antibiotics, ...
What is the procedure for a bursa infection?
Finally, in the rare cases in which the infection has spread to nearby tissues, treatment may include a bursectomy, the surgical removal of the affected bursa .
Why does my bursa swell?
When bursitis occurs, the synovial membrane becomes thickened and produces excessive fluid, which causes painful swelling of the bursa. The most common causes of bursitis are overuse from a repeated motion, direct injury, infection, and certain types of metabolic or inflammatory joint disorders (e.g., gout or rheumatoid arthritis ). ...
What to take for bursitis?
Physical therapy exercises to strengthen weak muscles and improve range of motion. Antibiotics to clear up bacterial infections that cause bursitis.
What is shoulder bursitis?
Shoulder bursitis is the most common type of bursitis. It occurs when excess fluid builds up in a bursa, the cushioning pad between bones and tissue in joints. Many people with shoulder bursitis also have shoulder tendinitis. The conditions cause pain and can affect arm mobility.
What is the bursae in the shoulder?
In the shoulder, the subacromial bursae cushion the area between the rotator cuff tendons and the acromion (the highest point of the shoulder blade or scapula). Bursae allow the tendons and bones to glide without friction when you move and lift your arms. Injuries or overuse can cause fluid to collect in bursae, causing bursitis.
What is the bursae?
The bursae (bur-SEE) are potential fluid-filled sacs that are part of the skeletal system. They cushion the space between bones and connective tissue, allowing tendons, muscle and bone to move together. In the shoulder, the subacromial bursae cushion the area between the rotator cuff tendons and the acromion ...
What tests are done to check for shoulder pain?
Your healthcare provider will perform a physical exam to assess shoulder pain and range of motion. You may also get these diagnostic tests: X-rays to check for arthritis, bone spurs and other problems that can affect the shoulder. MRI or ultrasound to look for inflammation in bursae.
How do you know if you have bursitis?
Shoulder pain from bursitis can come on suddenly or gradually. You may experience a dull ache, sharp pain or mild tenderness. Other signs of shoulder bursitis include: Shoulder stiffness or a feeling of swelling.
What is the procedure to remove a bursae?
This surgery may take place arthroscopically using small incisions and a tiny camera (arthroscope). Your provider may remove: Damaged tissue that presses on and irritates the bursae.
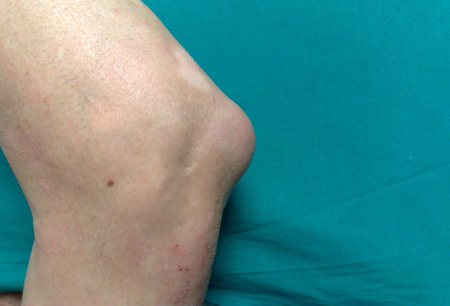
What Is Heel Bursitis?
Where the attachment of the Achilles tendon to the heel bone is located there are two bursas (fluid sacs). A deeper one, located between the heel bone and the Achilles tendon, and a more superficial one between the Achilles tendon and the skin. A bursitis of the heel is an inflammation of one of those two bursas.
How does bursa inflammation of the heel arise?
In most cases heel bursitis will occur gradually. In the superficial bursa an inflammation is often the result of local damage or trauma to the bursa. A good example of this is friction of the shoe rim against the heel, with repeated friction the bursa can become irritated.
Symptoms of bursitis of the heel
With bursitis of the heel there are symptoms such as swelling, heat, redness, (pressure) pain and limitation of movement. In the case of superficial bursitis, a red hump may be visible near the attachment of the Achilles tendon to the heel bone. This hump can feel painful. Wearing closed shoes can also be experienced as painful.
How is heel bursitis diagnosed?
A heel bursitis is generally well diagnosed by a general practitioner or physiotherapist. Additional examinations, such as ultrasound, CT scan or MRI scan, will only be necessary in very few cases to make the diagnosis.
How is heel bursitis treated?
It is important to start treatment on time, preferably under the supervision of the physiotherapist. First of all, the treatment will focus on pain reduction. Dosed rest and cooling of the sore spot is very important.
