
ENZYME TREATMENT
- COCOA ENZYME. This is a delightful treatment with soothing and calming properties. The enticing aroma of the pure cocoa makes it appealing as well as relaxing and effective.
- RASBERRY ENZYME. This raspberry enhanced enzyme with a light and refreshing berry scent has multiple benefits. ...
- ZYMASE ENZYME. This enzyme is appropriate for use on most skin types. ...
Full Answer
What enzyme breaks down enzymes?
Jan 01, 2022 · Skin Care & Beauty Written by Laurel Enright February 1st, 2021 Enzyme peels are composed of fruit enzymes and have many of the same results as chemical peels without the harshness and downtime. Similar to a chemical peel, enzyme peels exfoliate the skin by removing dead skin cells while nourishing the new layer of skin it leaves behind.
What to do when you have elevated liver enzymes?
Enzymatic treatment involves the use of lytic enzymes that attack and degrade the cell wall to allow release of proteins (Middelberg, 1995 ). The use of enzymes to degrade cell wall polysaccharides is considered a gentler alternative method to alkaline or acidic approaches to protein solubilization and extraction.
What does enzyme replacement therapy mean?
enzyme treatment The “Lunchtime” facial, safe for pregnant or nursing, 30 minute treatment time (if no add-ons). An enzyme peel is a non-abrasive skin therapy for patients looking to rejuvenate the skin while being too sensitive for a chemical peel.
What medications can cause liver enzymes to be elevated?
Apr 12, 2022 · Laundry enzyme presoaks are a pre-washing stain removal treatment used to break down protein stains like grass, blood, and baby formula so they can be more efficiently removed during the regular wash cycle. A presoak is necessary when clothes are heavily soiled or stained with oil, protein or tannin stains. >> Click to read more <<
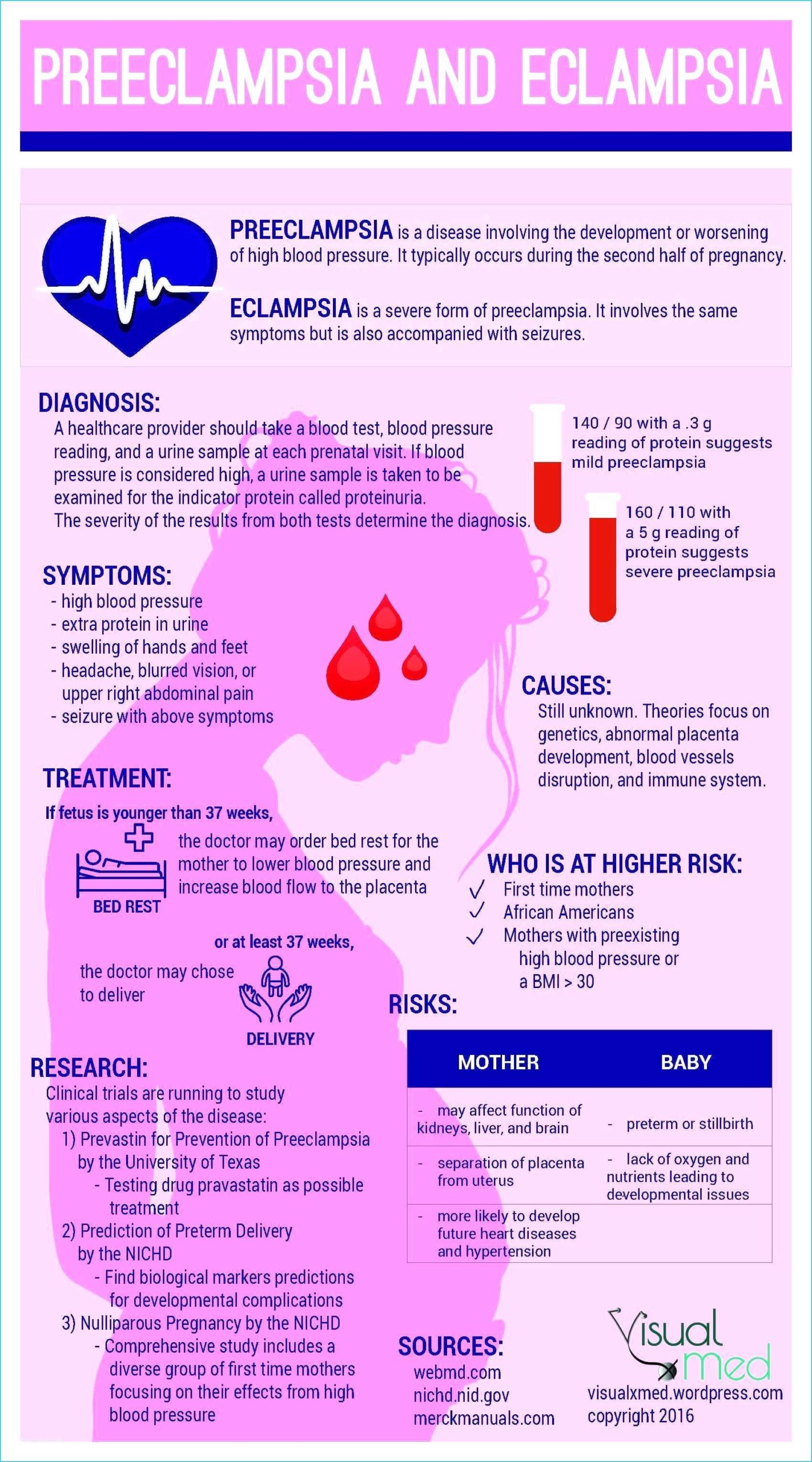
What does enzyme treatment do?
Enzyme Therapy is a facial treatment that stimulates your capillaries by dilating the channels to allow fresh oxygen & blood flow to the face. It exfoliates dead skin cells into a weak acid & flushes them from the skin.
Which diseases can be treated by enzyme therapy?
Medical usesDiseaseEnzymeGaucher diseaseVelaglucerase alfaGaucher disease type IAlgluceraseLysosomal acid lipase deficiency (Wolman disease/CESD)Sebelipase alphaMPS ILaronidase9 more rows
How long does enzyme treatment last?
The smooth results and hydrated feeling can last up to a week or more. One treatment per month will help you keep improving the appearance of fine lines, wrinkles, brown spots, and oily or congested skin.
What is a facial enzyme treatment?
Enzyme peels are composed of fruit enzymes and have many of the same results as chemical peels without the harshness and downtime. Similar to a chemical peel, enzyme peels exfoliate the skin by removing dead skin cells while nourishing the new layer of skin it leaves behind.Oct 29, 2020
What are the symptoms of enzyme deficiency?
Symptoms may include lack of muscle coordination, brain degeneration, learning problems, loss of muscle tone, increased sensitivity to touch, spasticity, feeding and swallowing difficulties, slurred speech and an enlarged liver and spleen.
What are the symptoms of low enzymes?
Symptoms of Digestive Enzyme InsufficiencyBelly pain or cramps.Bloating.Diarrhea.Gas.Oily stools (bowel movements)Unexplained weight loss.
Is there a cure for enzymes?
Not a cure. Lifelong treatments are necessary with any ERT, sometimes even when adverse effects occur.Sep 24, 2020
What are the side effects of enzyme replacement therapy?
The most frequent of the infusion-related symptoms were rigors, flushing, pyrexia, dyspnoea, headache and nausea. These reactions occurred initially within the first 1–4 months of the start of treatment.
What causes enzyme deficiency?
Enzyme deficiency is thought to be genetically inherited almost always in a recessive fashion, as it is mainly the result of “loss-of-function” mutations [4].
How much is an enzyme treatment?
Enzyme Therapy is 1.5 hour treatment & costs between $139 for basic to $229 for advanced. The more advanced treatments, include a pre-exfoliation which is done before your Enzyme Therapy to target your concerns & increase the benefits of each treatment.
Do enzyme peels hurt?
Do enzyme peels hurt? Depending on the product, you might feel some tingling sensation (this is from fruit acids doing their work). This sensation should be comfortable and by no means burning.
Is enzyme good for your face?
Enzymes help break down the keratin protein in the upper layer of the skin, which sticks dead skin cells together. Without this, the dead skin can gently go away. This results in smooth, healthy-looking skin and also helps reduce blemishes and pigmentation.
How does enzyme replacement therapy work?
What Is Enzyme Replacement Therapy and How Does it Work? The cells of your body are always working to carry out complex tasks, most of which go completely unnoticed. But when there is a problem at the cellular level, the effects can be both serious and extensive.
What are enzymes responsible for?
They’re responsible for interacting with other chemicals inside the body to bring about certain reactions, such as converting complex sugars into usable energy. ...
What is ERT therapy?
Enzyme replacement therapy (ERT) is a medical treatment whereby replacement enzymes are given to patients who suffer from chronic conditions resulting from enzyme deficiencies or malfunction. The most common method of ERT is through IV infusions, in which the replacement enzyme is administered directly into the bloodstream through ...
What is the role of lysosomes in the body?
Lysosomes are what break down proteins and other macromolecules in the body, so when they are unable to do so, various symptoms and conditions develop, often with serious consequences on a person’s daily life. Read: Enzyme Replacement Therapy for Lysosomal Diseases.
How does ERT affect the immune system?
ERT can trigger immune responses based on how the body reacts to the infused enzyme. These effects will vary from person to person. Development of resistance to enzymes. The effectiveness of some ERTs can decrease over time if the body develops a resistance to the replacement enzymes. Not a cure.
What is the name of the enzyme that breaks down fat?
Fabry disease occurs when the body is unable to make the enzyme necessary to break down a fat called globotriaosylceramide (Gb3 or GL-3). The lack of this enzyme, alpha-galactosidase A, causes buildup within the cells, which damages them and leads to serious symptoms throughout the body.
What is ERT for Fabry disease?
ERT for Fabry disease seeks to replace the deficient enzyme, alpha-galactosidase A . The two primary replacement enzymes used for Fabry disease are agalsidase alfa and agalsidase beta, which mimic the behavior of the enzyme they’re replacing. Infusions of these and other alternative ERTs must be given every two weeks, ...
What is enzymatic treatment?
Enzymatic treatment involves the use of lytic enzymes that attack and degrade the cell wall to allow release of proteins (Middelberg, 1995 ). The use of enzymes to degrade cell wall polysaccharides is considered a gentler alternative method to alkaline or acidic approaches to protein solubilization and extraction. This is in contrast to most chemical-based protocols that often result in protein denaturation, which restricts further evaluation of the biochemical and biological characteristics ( Fleurence, 1999 ). However, it is difficult to compare with other enzymatic studies because of the differences in the type and concentration of enzymes used, with several investigations focusing specifically on the improvement of protein availability and in vitro digestibility of macroalgae P. palmata ( Galland-Irmouli et al., 1999; Marrion et al., 2003, 2005; Goñi et al., 2002 ). There is also limited information on cell disruption efficiency on algal samples. While enzymatic treatment is deemed highly promising in increased utilization of seaweed proteins, disruption and protein extraction can be further enhanced in combination with other methods ( Combined Extraction Process Using Traditional and Emerging Techniques section).
What enzymes are used in EAE?
EAE normally uses hydrolytic enzymes in plant extraction such as pectinase and cellulase. These enzymes are used to break down the structure of the cell wall for allowing efficient extraction and the release of bioactive compounds (Saini & Keum, 2018 ).
Why are alpha-galactosidase important?
Alpha-galactosidases are an important group of enzymes used in food processing; the most important use of this group of enzymes is in soy-based foods which have great nutritional relevance all over the world because of their high protein concentration . Not only proteins but also other compounds of soybean are responsible for its great nutritional value, such as oligosaccharides including raffinose and stachyose. However, these oligosaccharides limit the consumption of soy products as food and feed. They are classified as antinutritional factors due to their high indigestibility by humans and other monogastric animals, whose intestinal mucosa does not secrete alpha-galactosidases. In this way, the consumption of soybean products has become possible due to alpha-galactosidases ( Singh and Vij, 2018; Vandenberghe et al., 2019 ). In fact, to avoid gastrointestinal disorders, alpha-galactosidases can be applied during processing to eliminate these oligosaccharides or they can be administered orally to enhance food digestion ( Bhatia et al., 2020 ). These enzymes can also be employed in the sugar industry to improve the sucrose crystallization through the hydrolysis of raffinose from sugar beet and increase the process yield ( Meguro et al., 1975 ). In the healthcare industry, alpha-galactosidase has been used in the treatment of Fabry disease, caused by the human deficiency in this enzyme ( Rosa Neto et al., 2020 ).
What is the most commonly used enzyme in decellularization?
Enzymatic treatments, involving proteases and nucleases, are incorporated into the decellularization strategy to aid in the removal of cellular proteins and nucleic remnants. Trypsin is one of the most commonly used proteolytic enzymes in decellularization methodologies, and is typically used in combination with the calcium chelating agent, ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA).11,119 EDTA is used to inactivate intracellular proteases that are released by the trypsinized cells and are capable of degrading the ECM constituents. Trypsin is a serine protease that cleaves proteins at the carboxyl side of lysine and arginine residues except when followed by proline, as is the case with collagen. It is predominantly used in decellularization protocols to aid in the detachment of cells from the surrounding ECM proteins by disrupting protein interactions, resulting in a more open matrix that can facilitate the removal of cellular debris. 11,119 Trypsin has been part of enzymatic treatments for decellularization of a number of tissues including heart valves, 13,19,70,76 vascular grafts, 12,14 and pericardium. 82 Nonetheless, variable cell loss has been reported in the literature following trypsin treatment. 13,19,76 Schenke-Layland and colleagues reported insufficient cell removal from pulmonary valves but preservation of ECM components (GAG, collagen, and elastin) following shorter trypsin-EDTA incubation times (5 and 8 h). At a longer incubation period (24 h), complete cellular removal was reported. However, the ECM biochemical composition (especially in terms of o -sulfated GAGs as well as acid and salt soluble collagens) and ECM integrity were negatively impacted in a time-dependent manner. 19 On the other hand, complete cellular removal and well-conserved and arranged collagen and elastin fibers were found by Teebken et al. who used a multistep enzymatic extraction method with trypsin-EDTA, deoxyribonuclease (DNase), and ribonuclease (RNase) to decellularize thoracic aortas. 14 Therefore, the nature of the tissue as well as the duration of enzymatic digestion must be taken into consideration when incorporating trypsin-EDTA into a decellularization strategy. 11,12,76
What is biological degradation?
Biological degradation can include enzymatic treatments derived from microorganisms, or the direct use of microorganisms. In most cases, activity of specific microorganisms to degrade mycotoxins can be traced to specific enzymatic activity, blurring the distinction between biological and chemical degradation of mycotoxins. Microbial degradation of mycotoxins has been studied for many years. A strain of Flavobacterium aurantiacum capable of degrading aflatoxins was identified only a few years after the discovery of aflatoxins. There have been many reports of mycotoxin-degrading microorganisms; in some cases, the degradation products are still toxic, but in other cases there seems to be true detoxification. Some studies report inactivation of mycotoxins with microbial cocktails in which specific organisms were not identified. For example, incubating feed with intestinal microflora of chickens was shown to improve feed intake, feed efficiency, and weight gain of pigs and reduced the concentration of deoxynivalenol by 54%–56% ( Charmley and Prelusky, 1994 ). On the other hand, at least one specific microorganism has been identified that can degrade each of the major mycotoxins in corn through enzymatic activity ( Zhu et al., 2016 ). This activity derives from a range of microorganisms, but the majority are bacteria, especially Bacillus spp. The most promising developments related to biological detoxification are likely to be the expression of microbial genes in transgenic plants. This aspect is covered elsewhere in this chapter.
What is the primary cell wall?
The primary cell wall consists of cellulose, pectin compounds, hemicellulose, and glycoproteins ( Choudhari & Ananthanarayan, 2007 ). Pectinase breaks down the pectin found in the plant primary cell walls and the middle lamella.
