What is the importance of BOD in water quality management?
The main advantages of this method compared to the dilution method are:
- simplicity: no dilution of sample required, no seeding, no blank sample.
- direct reading of BOD value.
- continuous display of BOD value at the current incubation time.
What is the best water treatment?
List of the Leading Companies Profiled in the Global Market are:
- Veolia (Aubervilliers, France)
- Acciona (Alcobendas, Spain)
- Pt. Amrita Enviro Energi (Banten, Indonesia)
- Hydro International (Clevedon, United Kingdom)
- Orenco Systems (Oregon, The U.S.)
- ASIO, spol. s r.o. ...
- Aquatech International LLC (Maharashtra, India)
- Trojan Technologies (London, UK)
- BioMicrobics Inc. (Kansas, UK)
- Kurita Water Industries Ltd. ...
What does BOD stand for water?
Biological Oxygen Demand (BOD) and Water. Biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) represents the amount of oxygen consumed by bacteria and other microorganisms while they decompose organic matter under aerobic (oxygen is present) conditions at a specified temperature. When you look at water in a lake the one thing you don't see is oxygen.
What are the benefits of water treatment?
Wastewater Treatment Process and its Benefits
- Wastewater Treatment Process. The wastewater treatment process must be divided into different treatment stages to ensure good water and sanitation quality.
- Benefits of Wastewater Treatment. The wastewater treatment process does not only produce clean reusable water, but also has the potential to produce various other benefits.
- Conclusion. ...
What is a good level of BOD in water?
1-2 ppmA BOD level of 1-2 ppm is considered very good. There will not be much organic waste present in the water supply. A water supply with a BOD level of 3-5 ppm is considered moderately clean.
What is BOD and COD of water?
The biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) represents the amount of dissolved oxygen (DO) consumed by biological organisms when they decompose organic matter in water. The chemical oxygen demand (COD) is the amount of oxygen consumed when the water sample is chemically oxidised.
Why is BOD value important in wastewater treatment?
The BOD is an important parameter for assessing water quality. It deals with the amount of oxygen consumption (mg O2 L− 1) by aerobic biological organisms to oxidize organic compounds. Sewage with high BOD can cause a decrease in oxygen of receiving waters, which in turn can cause the death of some organism.
What causes high BOD?
High biochemical oxygen demand can be caused by: high levels of organic pollution, caused usually by poorly treated wastewater; high nitrate levels, which trigger high plant growth.
Which is better COD or BOD?
COD is always higher than BOD because chemical oxidation is easier than biological oxidation.
Why is BOD done for 5 days?
BOD occurs in 2 general stages. While calculating the oxygen demand, the carbonaceous stage is taken into account. This stage is almost completed in 5 days, which means that most of the organic content of the sewage is oxidized under aerobic conditions in 5 days. Hence ,BOD for 5 days is calculated.
What happen if BOD is high?
The greater the BOD, the more rapidly oxygen is depleted in the stream. This means less oxygen is available to higher forms of aquatic life. The consequences of high BOD are the same as those for low dissolved oxygen: aquatic organisms become stressed, suffocate, and die.
What happens when BOD is low?
Inversely, low BOD means less oxygen is being removed from water, so water is generally purer. Cold water retains oxygen better than warmer water, so in summer months, dissolved oxygen is usually lower from the start.
Does BOD affect pH?
presented in Table 2, the pH correlated negatively with the BOD (r = -0.418) and negatively with the COD (r = -0.347) ... ... presented in Table 2, the pH correlated negatively with the BOD (r = -0.418) and negatively with the COD (r = -0.347) ...
How do you reduce BOD in water?
These are the best practices for reducing BOD and TSS that facility managers should know:Focus on removing TSS from wastewater first. ... Get a properly sized EQ tank. ... Control the pH of the waste stream. ... Install a modern plate pack DAF made of stainless steel or plastic. ... Use a regenerative turbine air dissolution pump.More items...•
What is BOD value?
The BOD value is most commonly expressed in milligrams of oxygen consumed per liter of sample during 5 days of incubation at 20°C and is often used as a surrogate for the degree of organic pollution of water (Armiento, 2016). Most pristine rivers will have a 5-day carbonaceous BOD below 1 mg/L.
What does negative BOD mean?
BOD blanks too low or negative. The blank must be below 0.20 mg/L, so "too low" means values that are negative. There are three possible causes for this: Micro-sized bubbles in the BOD bottle: Micro-sized bubbles can be difficult to see when the bottle is initially set.
What is BOD in wastewater?
Industries that discharge wastewater into municipal sanitary sewers or waterways are facing strict regulations on levels of biological or biochemical oxygen demand (BOD). Solid materials in wastewater can consist of organic and/or inorganic materials and organisms.
What is BOD discharge?
Worldwide commercial and industrial manufacturing operations require the best available wastewater technology methods to achieve biological oxygen demand (BOD) discharge compliance. Worldwide expansion of commercial production and manufacturing increases the levels of industrial liquid waste byproducts. Industries that discharge wastewater into municipal sanitary sewers or waterways are facing strict regulations on levels of biological or biochemical oxygen demand (BOD).
What is the purpose of a biological oxygen demand test?
Biological Oxygen Demand (BOD) is a chemical procedure for determining the amount of dissolved oxygen needed by aerobic biological organisms “bio-bugs” in a body of water to break down organic material present in a given water sample at a certain temperature over a specific time period. It is not a precise quantitative test, although it is widely used as an indication of the quality of water.
Does ALAR water treatment increase BOD?
ALAR Water Treatment provides these industries with cost effective wastewater equipment solutions in order to help achieve BOD discharge compliance.
How is BOD used in wastewater treatment plants?
Biological oxygen demand is often used in wastewater treatment plants as an index of the degree of organic pollution in water.
How is BOD determined?
There are a few methods approved for determining biological oxygen demand, although one of them is used overwhelmingly by the analytical community. It is known as Standard Methods 5210B.
What is biochemical oxygen demand?
Biochemical oxygen demand is the amount of oxygen consumed by bacteria and other microorganisms while they decompose organic matter under aerobic conditions.
What does a low BOD mean?
Higher BOD indicates more oxygen is required, signifying lower water quality. Low BOD means less oxygen is being removed from water, so the water is usually more pure.
What is dissolved oxygen?
Dissolved oxygen is a crucial component of natural water bodies, maintaining the aquatic life and quality aesthetic of streams and lakes. The decay of organic matter in water is measured as biochemical oxygen demand. Environmental stresses and other human-induced factors can lessen the amount of dissolved oxygen in a water body, however.
What is a BOD in wastewater?
Biological Oxygen Demand (BOD) is a chemical procedure for determining the amount of dissolved oxygen needed by microorganisms to break down organic matter.
What is a BOD tank?
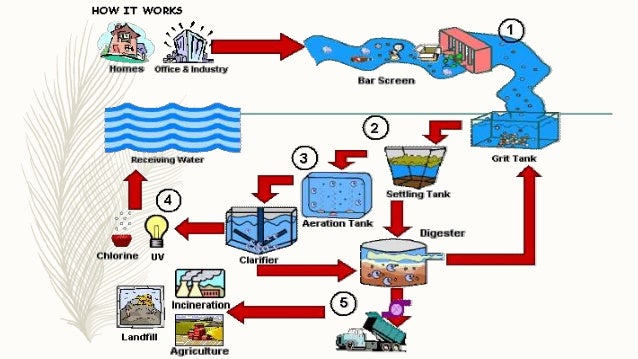
BOD - Aeration Tank Process. In a conventional BOD Wastewater Treatment process, microorganisms use oxygen to break down organic compounds. The microorganisms essentially consume the organic matter, but there must be enough oxygen in the water. If there isn’t enough oxygen in the water, the microorganisms will die.
How does a sludge thickener work?
When there is enough wastewater in the sludge thickener, the slurry from the tank is pumped into the Filter Press. The filter press separates the liquids and solids using pressure filtration. Sludge Cake will form between the filter plates, where it can be safely removed and easily discarded. The excess water is returned to the Initial Settling Tank.
How is wastewater collected?
Wastewater is collected in the Initial Settling Tank or the Primary Clarifier . The main function and purpose of the Initial Settling Tank is to make the wastewater homogeneous, and it allows for solids to settle to bottom of the tank forming sludge. The sludge collect is removed and piped over to the Sludge Thickening Tank. While the Setting Tank will remove much of the initial solids, there are organic compounds will not settle, and it will need to be treated in the Aeration Tank or a DAF Clarifier, depending on the specific application.
What is Met Chem wastewater?
There are various types of wastewater that require specific treatment. Met-Chem will engineer and design a custom system to fit your specific wastewater treatment needs.
Where is the waste activated sludge collected?
The Waste Activated Sludge from the clarifier is collected in the Sludge Thickener. The thickening tank will provide additional solid-liquid separation. Any liquid overflow will be returned to the settling rank. The thickened sludge will be processed by the Filter Press .
Who manufactures wastewater treatment systems?
Met-Chem manufactures wastewater treatment systems. Each wastewater treatment system will be custom designed for your specific needs. As your business grows, we can expand your current system, reducing the need to purchase a new costly system
What is the BOD of wastewater?
The BOD is a pollution parameter mainly to asses the quality of effluent or wastewater. Untreated wastewater has usually a high oxygen demand. Are the impurities organic material or aerobic organism, the wastewater has a biological oxygen demand, BOD.
How to measure BOD?
How to measure the BOD level? 1 Method I: A sample of the water is kept at a constant temperature of 20°C in the dark. After a period of five days, the oxygen content is measured. In comparison to the original value, the oxygen consumption during the measurement period indicates the oxygen demand in the water. 2 Method II: If a very high BOD is to be expected or if other toxic or inhibitory substances are present in the water, the sample can be diluted at the beginning. In this way it can be prevented that too little oxygen is present to break down the organic substances. This would falsify the measurement result. As with method 1, a comparison of the before and after values now serves as a measure of oxygen consumption during the measurement period.
Who demands this oxygen?
The biochemical decomposition of organic substrates is carried out by microorganism. For this work the bacteria need energy. Aerobic bacteria, that do this work, need dissolved oxygen to produce energy. This oxygen is consumed in this process and the amount of dissolved oxygen in the water gets less. If there is a lot of organic material present in the water, the oxygen demand is correspondingly high to carry out the decomposition. This oxygen is then lacking the plants and animals that also live in this water.
What is the indicator of BOD?
An alternative indicator to BOD is COD – Chemical Oxygen Demand. Anaerobic bacteria, such as SRB, don't need dissolved oxygen in the water to survive. Such microorganism is living on sulfur instead of oxygen, hence they can't be detected by measuring the biochemical oxygen demand.
Why is industrial wastewater a COD?
Industrial wastewater tends to a higher chemical oxygen demand, COD caused by dissolved chemicals or pollutants from washing processes. Both BOD or COD requires a lot of dissolved oxygen from the water. The significance of BOD is very clear. If oxygen is used from organic impurities, it cant be used by other creatures living in the water.
Why is it important to have a low BOD level in the water?
It is very important for every government to ensure a low BOD level in the effluent water leaving a sewage plant. As it is in public interest to have rivers, lakes and seas with a high level of dissolved oxygen. A low biochemical oxygen demand ensures that the dissolved oxygen is not only consumed by organisms from the wastewater.
What does a high BOD level mean?
A high BOD level can indicate the existence of faecal contamination. Or particulate and dissolved organic carbon from various sources, neither from human nor from animal. This kind of contamination can seriously affect human health and cause problems to the industry.
BOD Compliance
High concentrations of BOD in wastewater can lead to regulatory issues. By implementing a system to effectively reduce the BOD in the wastewater stream your company will have the ability to remain in compliance and reduce risk. This will save your company regulatory costs.
COD Compliance
Effluent with high concentrations of COD can lead to compliance issues. Our wastewater systems can significantly reduce the Chemical Oxygen Demand in your wastewater. We have saved our customers surcharges and headaches by reducing their COD wastewater.
Visit Our Blog
bioprocessH2O offers innovative wastewater and water reuse treatment technologies to serve a wide variety of industrial and decentralized markets.
