Explore
Treatment The clinical significance of Blastocystis spp. is controversial. Treatment with metronidazole * at various doses has been reported, for example (adults): 250 mg to 750 mg metronidazole* orally 3 times daily for 10 days 1500 mg metronidazole* orally once daily for …
What is the treatment for Blastocystis hominis?
Dec 14, 2020 · What is the Treatment? So what treatment is recommended for knocking out Blastocystis Hominis? Below are the steps I help my patients take to treat this gut parasite and ultimately their skin conditions: Diet. Diet is an important first step in eliminating this parasite. Most parasites like Blastocystis feed on sugar, grains, and starches.
Is Blastocystis hominis a parasite?
What first-line treatments are available for Blastocystis ‘hominis’ infection? Metronidazole is usually listed as a first-line treatment for Blastocystis. A recent review on e-medicine listed dosages and duration for metronidazole and several other drugs.
Can metronidazole be used as a first-line treatment for Blastocystis?
Mar 12, 2013 · Metronidazole appears to be the most effective drug for Blastocystis chemotherapy despite some evidence for treatment failure. In such circumstances, TMP-SMX and nitazoxanide may be considered as second choice drugs. Treatment should be instituted if the diarrhea is persistent and no other causative pathogen is identified in fecal specimens.
Can Blastocystis go away on its own?
Even though the pathogenicity of Blastocystis Hominis remains controversial, anti-protozoan drugs have been used to treat individuals in whom the parasite is found. The most widely used treatment option is the chemotherapeutic drug Metronidazole which, while effective in some individuals, shows signs of resistance by B. hominis or limited effectiveness in others.
What is the best treatment for blastocystis hominis?
TreatmentAntibiotics, such as metronidazole (Flagyl) or tinidazole (Tindamax)Combination medications, such as sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim (Bactrim, Septra, others)Anti-protozoal medications, such as paromomycin or nitazoxanide (Alinia)Jan 19, 2021
How do I get rid of blastocystis hominis?
Several drugs have been used against Blastocystis infection, the most common still being metronidazole (MTZ), as the first-line treatment, followed by nitazoxanide (NTZ), trimethoprim–sulfamethoxazole (TMP-SMX), ketoconazole, and tinidazole as secondary treatments.Mar 22, 2017
Does blastocystis hominis need treatment?
Those with Blastocystis in the stool who have an associated skin eruption should be considered for treatment in the absence of other causes, but this recommendation is based on scant data. When treatment is given, we usually use metronidazole as first-line treatment, based on the available clinical trial data.Nov 10, 2011
Is blastocystis hominis serious?
Many protozoans normally live in the digestive tract and are harmless or even helpful, but some cause disease. Blastocystis is a microscopic single-celled organism (protozoan). Many parasitic protozoans normally live in your digestive tract and are harmless or even helpful; others cause disease.Jan 19, 2021
What disease does Blastocystis cause?
Blastocystis is a prevalent enteric protozoan that infects a variety of vertebrates. Infection with Blastocystis in humans has been associated with abdominal pain, diarrhea, constipation, fatigue, skin rash, and other symptoms.Oct 21, 2008
What are the symptoms of blastocystis hominis?
Many people with Blastocystis hominis in their stools have no symptoms at all. However, in those that do report symptoms, the most common ones are diarrhoea, abdominal pain and vomiting. Other reported symptoms are anal itching, weight loss, constipation and excess gas.Nov 1, 2015
Can you live with Blastocystis hominis?
Once a person or animal has been infected with Blastocystis 'hominis', the parasite lives in the intestine and is passed in feces. Because the parasite is protected by an outer shell, it can survive outside the body and in the environment for long periods in some cases.
What is Blastocystis hominis cysts?
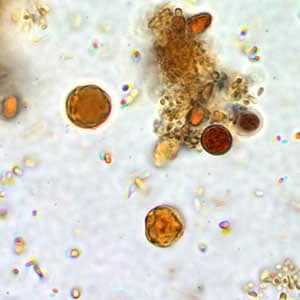
Blastocystis is a genetically diverse unicellular parasite of unclear pathogenic potential that colonizes the intestines of humans and a wide range of non-human animals.Oct 21, 2019
What is the life cycle of Blastocystis hominis?
The life cycle of Blastocystis sp. is not yet understood, including the infectious stage and whether (and which of the) various morphologic forms of this polymorphic organism that have been identified in stool or culture constitute distinct biologic stages of the parasite in the intestinal tract of hosts.Oct 22, 2019
Why is blastocystis sp. considered more appropriate?
However, because of extensive genetic diversity (even among organisms isolated from humans) and low host specificity, the designation Blastocystis sp. is considered more appropriate. If genetic typing is performed, the subtype (ST) also should be noted in accordance with consensus terminology.*.
What are some examples of stramenopiles?
On the basis of molecular data, the organism has been classified as a stramenopile. Organisms such as diatoms, chrysophytes, water molds, and slime nets are other examples of stramenopiles. Blastocystis organisms isolated from humans have commonly been referred to as B. hominis.
How many STs are there in humans?
Among the nine STs found to date in humans, the four most prevalent STs are ST1, ST2, ST3, and ST4; other STs occur sporadically and may be related to zoonotic transmission. * Stensvold, C.R., Suresh, G.K., Tan, K.S., Thompson, R.A., Traub, R.J., Viscogliosi, E., Yoshikawa, H. and Clark, C.G., 2007.
Is Blastocystis sp. an infectious organism?
The life cycle of Blastocystis sp. is not yet understood, including the infectious stage and whether (and which of the) various morphologic forms of this polymorphic organism that have been identified in stool or culture constitute distinct biologic stages of the parasite in the intestinal tract of hosts. The cyst form (3–5 µm) is postulated to be an infectious stage, but not confirmed. The predominant form found in human stool specimens is referred to as the vacuolar (or central body) form and is of variable size (5–40 µm, occasionally much larger). Replication appears to occur via binary fission. Other morphologic forms (e.g., ameboid and granular forms) also have been noted in stool samples and/or culture; their biological role and eventual developmental fate require further investigation.
Can blastocystis cause gastrointestinal disease?
Whether Blastocystis sp. (or particular subtypes thereof or particular strains of certain subtypes) can cause gastrointestinal disease ( symptomatic infection) in humans continues to be debated and investigated. Blastocystis sp. has been detected in both symptomatic and asymptomatic persons.
How long does metronidazole last?
Treatment with metronidazole * at various doses has been reported, for example (adults): 1 250 mg to 750 mg metronidazole* orally 3 times daily for 10 days 2 1500 mg metronidazole* orally once daily for 10 days
How long does nitazoxanide last?
Treatment with nitazoxanide * has been shown to be effective in clearing organisms and improving symptoms at the following doses: Adults, 500 mg nitazoxanide* orally twice daily for 3 days. Children, 200 mg nitazoxanide* orally twice daily for 3 days in patients aged 4–11 years, and 100 mg nitazoxanide* orally twice daily for 3 days in patients ...
Is nitazoxanide safe for pregnancy?
Nitazoxanide is in pregnancy category B. Data on the use of nitazoxanide in pregnant women are limited, and risk to the embryo-fetus is un known. Nitazoxanide should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
Is metronidazole excreted in breast milk?
Metronidazole is excreted in breast milk. The American Academy of Pediatrics classifies metronidazole as a drug for which the effect on nursing infants is unknown but may be of concern. The World Health Organization (WHO) advises to avoid metronidazole treatment in lactating women.
Is metronidazole safe for pregnancy?
Metronidazole is in pregnancy category B. Data on the use of metronidazole in pregnant women are conflicting. The available evidence suggests use during pregnancy has a low risk of congenital anomalies. Metronidazole may be used during pregnancy in those patients who will clearly benefit from the drug, although its use should be weighed against any potential risks.
Is paromomycin safe for pregnant women?
Oral paromomycin has not been assigned to a pregnancy category by the Food and Drug Administration. Data on the use of oral paromomycin in pregnant women are limited, and the risk to the embryo-fetus probably is low. Oral paromomycin generally is poorly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, with minimal, if any, systemic availability.
Is iodoquinol safe for pregnancy?
Oral iodoquinol has not been assigned a pregnancy category by the Food and Drug Administration. Data on the use of iodoquinol in pregnant women are limited, and risk to the embryo-fetus is unknown. Iodoquinol should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
How to get rid of parasites?
Diet. Diet is an important first step in eliminating this parasite. Most parasites like Blastocystis feed on sugar, grains, and starches. So, even if someone is taking a natural product or medication, eating a bunch of sugar (which is standard to a typical diet), can prevent them from working.
What is the name of the protozoa that causes diarrhea?
Blastocystis Hominis is a single cell protozoa amoeba that can cause all sorts of issues. Apart from the usual symptoms of diarrhea, constipation, and IBS, it can cause nausea, abdominal cramps, skin problems, aches and pains, fatigue, and thyroid issues.
Can a dermatologist diagnose eczema?
While most doctors and dermatologists would diagnose this condition as eczema, dermatitis, psoriasis, or chronic hives I was able to look internally and get to the root cause of her problem. Instead of prescribing lotions, internal steroids, or steroid creams, I could prescribe a treatment that truly resolved it.
Where does Blastocystis live?
Blastocystis is a microscopic single-cell organism (protozoan) that lives in the digestive tract. Many protozoans normally live in the digestive tract and are harmless or even helpful, but some cause disease.
What is the scientific name for Blastocystis?
Researchers have found several variations — either different species or different strains within a species. The scientific name used now is Blastocystis spp, an abbreviation that means "multiple species.".
What is the name of the parasite that lives in the digestive tract?
Blastocystis is a microscopic parasite that can live in your digestive tract. Researchers don't fully understand the role blastocystis plays, if any, in causing disease. Some people experiencing diarrhea, abdominal pain or other gastrointestinal problems have blastocystis organisms in their stool.
How does blastocystis spread?
Blastocystis may be transmitted through food or water or by contact with human or animal feces. Blastocystis infection is generally more common among people who live in or travel to developing countries and among people who work ...
Can you boil and peel blastocystis?
When you travel, you can take steps to lower your risk of exposure to blastocystis. A general guideline is to avoid eating what you can't boil, cook or peel. More specifically, avoid:
Do protozoans cause disease?
Many parasitic protozoans normally live in your digestive tract and are harmless or even helpful; others cause disease. It's not clear whether blastocystis causes disease. Most people who carry the organism have no signs or symptoms, but it's also found in people who have diarrhea and other digestive problems.
What is the first line of treatment for blastocystis?
What first-line treatments are available for Blastocystis ‘hominis’ infection? Metronidazole is usually listed as a first-line treatment for Blastocystis. A recent review on e-medicine listed dosages and duration for metronidazole and several other drugs.
What drugs were used to treat blastocystis?
Drugs included TMP-SMX, rifaximin, Nitazoxanide, and others. However the review noted that those studies did not use reliable methods for detecting Blastocystis infection to establish eradication of the organism.
Why do antimicrobials fail to work?
Antimicrobials may fail to work against specific microbes if they do not have sufficient activity against the organism, or because the inhibition provided by the antimicrobial is insufficient to allow the host to clear the organism. There is a remarkably lack of in-vitro study of Blastocystis.
Is there a cure for blastocystis hominis?
There is no known eradication strategy for Blastocystis hominis. Regardless of what any supplement company or practitioner has claimed. If anyone is claiming that you need no further investigation and just need to take a round of antibiotics/herbs and you’ll be fine, find a new physician.
Can blastocystis be fixed?
Most people make the mistake of fixating on Blastocystis as the cause of all their health issues, and typically go straight in with heavy antibiotic and herbal treatments, which typically leaves people with even more chronic gut issues that makes complete resolution harder to achieve in the long term.
How to prevent infection in children?
avoid uncooked foods washed with unboiled tap water and avoid drinking unboiled tap water when you are traveling in countries where the water supply may be contaminated; teach children the importance of washing hands to prevent any type of infection;
What is the health benefit of black walnuts?
Health benefits of black walnut include its capacity to reduce inflammation, improve heart health, and stimulate circulation.
How does a parasite spread?
It can be spread by: traveling to countries where the organism is common; having contact with someone who is ill with this parasite; eating uncooked food contaminated with this parasite;
What is the best medicine for a swollen ear?
Medications for treating this infection include: antiprotozoal medications, like – nitazoxanide (Alinia) or paromomycin; combination medications, like – trimethoprim (Septra, Bactrim) and sulfamethoxazole; antibiotics, like – tinida zole (Tindamax) or metronidazole (Flagyl).
Is Goldenseal good for parasites?
Goldenseal (scientifical name – Hydrastis Canadensis) is an excellent ingredient to look for in eyewash and mouthwash recipes and formulas. Moreover, it is a natural remedy for numerous internal parasites because of its content of berberine, a plant natural compound that works against intestinal parasites, like – Entamoeba histolytica, Giardia lamblia, blastocystis hominis, and pinworms.
Does essential oil kill worms?
This essential oil has potent antiviral, antibacterial, and anti-fungal qualities. It kills internal parasites by destroying the eggs which worms lay in the intestinal tract. It is even more effective when combined with wormwood and black walnuts.
Can pumpkin seeds cure intestinal worms?
According to the University of Maryland Medical Center, pumpkin seeds are an effective cure for intestinal worms. Additionally, eating only a small amount of pumpkin seeds can provide you with a notable quantity of magnesium, healthy fats, calcium, and zinc.

Overview
Symptoms
- If you have a blastocystis infection without signs or symptoms, then you don't need treatment. Mild signs and symptoms might improve on their own within a few days. Potential medications for eliminating a blastocystis infection and improving symptoms include: 1. Antibiotics, such as metronidazole (Flagyl) or tinidazole (Tindamax) 2. Combination med...
Causes
Risk Factors
Complications
Prevention