Top10homeremedies.com
What are the types of biologic therapy drugs for treating asthma? Xolair is a medication for patients with poorly controlled asthma and allergies to year-round allergens like dust mites,... Xolair is given as one or two subcutaneous injections (shots given under the skin), depending on …
Allremedies.com
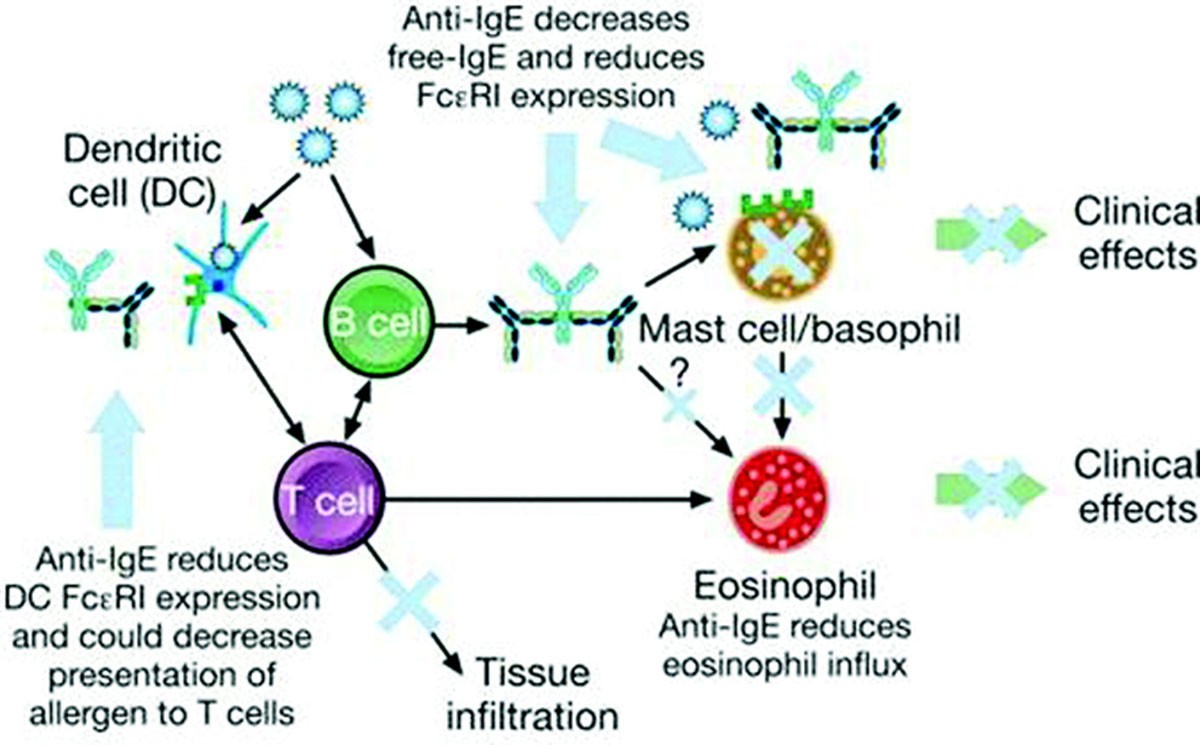
In this review, treatment of severe asthma with monoclonal antibodies, i.e. biologics, which are directed against these inflammation generated pathways are reviewed. The available monoclonal antibodies include omalizumab (anti-IgE); mepolizumab, reslizumab and benralizumab (anti-IL-5 pathways), and dupilumab (anti-IL-4/IL-13).
What are biologic therapies for asthma?
Biological therapy is administered using an IV or via an injection. Because it’s not taken orally, biologics can provide relief sooner. Biological therapy treatment targets the parts of the lungs that are triggering inflammation and causing damages. The most common biologic agents for severe asthma are: XOLAIR® (omalizumab) NUCALA (mepolizumab)
What is severe asthma and how is it treated?
Currently there are five approved biologics for asthma – omalizumab, mepolizumab, reslizumab, benralizumab, and dupilumab – with several others currently in development. Omalizumab targets allergy antibodies known as IgE. Mepolizumab, reslizumab, and benralizumab all target pathways that affect eosinophils, a cell involved in allergic inflammation.
How many biologics are there for severe asthma?
Feb 10, 2020 · There are currently five approved biologics for the treatment of severe asthma. Xolair targets allergy antibodies known as immunoglobulin E (IgE), and the other four biologics (Dupixent, Nucala, Fasenra and Cinqair) target pathways that affect eosinophils, a cell involved in allergic inflammation.
What's new in Asthma Immunology?
Jul 20, 2020 · How Do Biologics Treat Severe Asthma? Biologic therapy drugs. Several others are currently in development. The type of biologic your doctor will prescribe... Side effects. Rarely, these drugs can cause a severe allergic reaction called anaphylaxis. ... Takeaway. Biologics don’t work for everyone — ...

Can biologics be used for asthma?
Biologics can be used to treat severe asthma. They’re a newer case of disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs that are capable of relieving symptoms — especially for cases of severe asthma. They’re a different kind of medication that can be extremely effective when used intravenously.
How to treat severe asthma?
If you or a loved one have severe asthma, the first step is to modify your lifestyle. Limit exposure to allergens when possible, work with your doctor to develop a weight loss plan if you’re obese, avoid known triggers, and quit smoking and avoid secondhand smoke when possible.
How to tell if you have asthma?
Asthma is categorized by how well the condition responds to treatment. That means severe asthma is resistant to treatments and is persistent throughout the day. If you have severe asthma, you may also wake up multiple times during the night, being significantly limited in your regular activities, and have an FEV 1 measurement of less than 60% of usual. Severe asthma may cause: 1 Difficulty breathing 2 Coughing 3 Wheezing 4 Pain in the chest 5 Shortness of breath 6 Chest tightness 7 Asthma attacks
How is asthma categorized?
Asthma is categorized by how well the condition responds to treatment. That means severe asthma is resistant to treatments and is persistent throughout the day. If you have severe asthma, you may also wake up multiple times during the night, being significantly limited in your regular activities, and have an FEV 1 measurement of less than 60% ...
Can corticosteroids be used for asthma?
Oral corticosteroids. In some cases, medications aren’t effective enough, or they come with life-threatening side effects. Biologics can be used to treat severe asthma. They’re a newer case of disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs that are capable of relieving symptoms — especially for cases of severe asthma.
How does biologic therapy work?
How Biological Treatment Works. Biologic infusion therapy treatment is the administration of the medication in an IV that is placed in your arm. Injectable biologic therapy is where the medication is administered as an injection in the arm or abdomen. Your treatment time varies depending on the medication you’ve been given.
What are the biologics for asthma?
What biologics are available for asthma? Currently there are five approved biologics for asthma – omalizumab, mepolizumab, reslizumab, benralizumab, ...
Can biologics help with asthma?
For some patients though, these medications are not enough to control their asthma. Recently, several new medications, known collectively as “biologics,” have been approved for the treatment of moderate-to-severe asthma. Biologics are unique in that they target a specific antibody, molecule, or cell involved in asthma.
How to control asthma?
For many patients with asthma, their asthma is controlled by identifying and avoiding triggers, taking a daily inhaled or oral controller medication, and using a quick-relief inhaler when symptoms develop. For some patients though, these medications are not enough to control their asthma.
What are the targets of asthma?
For asthma, the targets are antibodies, inflammatory molecules, or cell receptors. By targeting these molecules, biologics work to disrupt the pathways that lead to inflammation that causes asthma symptoms.
What are the symptoms of asthma?
Symptoms of poorly controlled asthma include frequent coughing, wheezing, or shortness of breath; waking up at night with difficulty breathing; requiring a fast-acting reliever medication, such as albuterol, several times a day or week; and recurrent hospital admissions, emergency room visits, or need for oral steroids for exacerbations.
What is biologic therapy?
What is a biologic? A biologic is a medication made from the cells of a living organism, such as bacteria or mice, that is then modified to target specific molecules in humans.
What are the benefits of biologics?
The primary benefit of biologics has been a decrease in the frequency of asthma exacerbations, including emergency room visits, hospitalizations, and need for oral steroids. Other benefits include reduced asthma symptoms, reduced dosage of other controller medication, and less missed school and work days. Biologics have been shown ...
What biologics are used for asthma?
There are currently five approved biologics for the treatment of severe asthma. Xolair targets allergy antibodies known as immunoglobulin E (IgE), and the other four biologics (Dupixent, Nucala, Fasenra and Cinqair) target pathways that affect eosinophils, a cell involved in allergic inflammation. IgE is a substance that occurs naturally in ...
Does biologic therapy work for asthma?
Biologic therapy may not work for everyone and it may require the use of other treatments as well. It is likely your doctor will initially introduce a biologic to treat your asthma as part of your treatment plan to see if it helps manage symptoms. If you are able to find a biologic that works for you, this may cut down the number of asthma attacks you experience. It is also possible that you may eventually be able to cut back on the number of other treatments you take, including corticosteroids.
What are the side effects of biologics?
While rare, some biologic drugs can cause allergic reactions called anaphylaxis, which may include: 1 Hives or a rash 2 Swelling in the face, mouth, or tongue 3 Shortness of breath 4 Low blood pressure 5 Wheezing 6 Problems with swallowing 7 Dizziness and/or fainting
What is the best treatment for asthma?
Doctors will prescribe biologics for people with severe asthma whose symptoms aren’t being controlled by inhaled corticosteroids, short-acting beta agonists, and other standard asthma medications. A biologic drug can help to manage shortness of breath and coughing.
How many biologics are there for asthma?
There are currently five approved biologics for the treatment of severe asthma. Xolair targets allergy antibodies known as immunoglobulin E (IgE), and the other four biologics (Dupixent, Nucala, Fasenra and Cinqair) target pathways that affect eosinophils, a cell involved in allergic inflammation.
What are the different types of biologics for asthma?
There are currently five approved biologics for the treatment of severe asthma. Xolair targets allergy antibodies known as immunoglobulin E (IgE), and the other four biologics (Dupixent, Nucala, Fasenra and Cinqair) target pathways that affect eosinophils, a cell involved in allergic inflammation.
What are biologics made of?
Biologics are powerful medicines made of tiny components, including sugars, proteins, DNA, whole tissues, or cells. 2 They come from all sorts of living sources—mammals, insects, plants, bacteria, and more. Biologic drugs are the latest and most advanced treatments available today for the treatment of numerous diseases and conditions.
What is the best treatment for asthma?
Doctors prescribe biologics for certain people with severe asthma whose symptoms haven’t improved with inhaled corticosteroids, short-acting beta-agonists, and other standard treatments. Biologics help to manage symptoms like shortness of breath, wheezing, and coughing when other medications have failed.
Do biologics work for asthma?
Biologics don’t work for everyone — and they might not work alone . At first, your healthcare provider will add a biologic to your regular asthma treatment plan to see if it helps control your symptoms. If biologics work for you, they may reduce the number of attacks you get.
How do biologics work?
Biologics work differently from other asthma medications. Instead of treating symptoms, they target the underlying molecular causes of asthma. Keep reading to find out if biologic drugs are right for you.
What is a biologic drug?
Biologic drugs are genetically engineered proteins. They’re designed to target specific substances in your immune system that cause inflammation. Doctors prescribe biologics for certain people with severe asthma whose symptoms haven’t improved with inhaled corticosteroids, short-acting beta-agonists, and other standard treatments.
What happens when you have an allergic reaction?
These chemicals trigger symptoms like: coughing. shortness of breath.
Is Xolair safe for asthma?
Xolair is approved to treat severe asthma in people ages 6 and over whose asthma isn’t well managed with inhaled corticosteroids. Before getting this treatment, your healthcare provider will confirm you have environment allergies with a positive skin test or blood test.
How do eosinophils work?
They work by triggering inflammation in your body. Eosinophils are helpful in preventing disease. However, when there are too many of them, they can cause too much inflammation and swelling. If that swelling is in the airways of your lungs, it can be hard to breathe.
Is Benralizumab approved for asthma?
It was approved by the FDA for severe asthma with an eosinophilic phenotype in 2015. Examples of eosinophilic phenotypes include eosinophilic asthma and Churg Strauss Syndrome. It’s administered as a subcutaneous injection once a month in your upper arm, thigh, or abdomen. 10. Benralizumab (Fesenra).
What is the immune response to asthma?
Asthma is an abnormal immune response. During this response, immune cells recognize harmless proteins you inhale as harmful. One example of a harmless protein is allergens, like dust mites. Many asthma subgroups are regulated by a type of white blood cell (leucocyte) called T-helper 2 (Th2) cells.
Can eosinophils cause asthma?
Eosinophilic inflammation is usually more severe and difficult to control. 3 Normally, eosinophil levels rise during asthma attacks and decline after. But, in some with severe asthma, they may stay elevated. In this way, they may be responsible for severe asthma. So, biologics block the effects of these chemicals.
How often do you need to inject biologics?
This must be done by a medical professional such as a nurse. This must occur 2-3 times a month, depending on the biologic used. And, unfortunately, due to the complex nature of making them, biologics tend to be very expensive. Still, they are neat options when needed.
Is biologics expensive?
And, unfortunately, due to the complex nature of making them, biologics tend to be very expensive. Still, they are neat options when needed. They are another neat option in the ongoing quest to help every asthmatic obtain ideal asthma control. By providing your email address, you are agreeing to our privacy policy.
Where are fungi kept?
So, they are kept in environments that contain living tissues from animals, bacteria, or yeast. They are allowed to replicate until they exist in large quantities. They also must be stored in solutions in vials. So, they must be given by subcutaneous injections, or just under the surface of the skin.
Does Benralizumab help with asthma?
Similar to the other anti–IL-5 biologics, benralizumab has been shown to reduce asthma exacerbation rates and improve lung function in patients with uncontrolled eos inophilic asthma ( 52 – 54 ). A 2017 Cochrane review demonstrated a significant reduction in asthma exacerbations in patients treated with benralizumab regardless of their AEC. However, the effect of benralizumab was greatest in patients with AEC greater than or equal to 300 cells/μl. Furthermore, improvements in lung function and QOL were only significant in the higher eosinophil group ( 51 ). In the ZONDA trial, benralizumab was shown to significantly reduce OCS use by 75% in patients on long-term OCS with AEC greater than or equal to 150 cells/μl, while reducing annualized asthma exacerbations by 70% ( 55) ( Figure 5 ). Benralizumab appears to be equally effective independent of atopy ( 56 ).
What is severe asthma?
Severe asthma is defined by the European Respiratory Society/American Thoracic Society as asthma that requires treatment with high-dose ICS plus a second controller with or without systemic corticosteroids to maintain control of the disease or , despite this therapy, have suboptimally controlled disease ( 3 ).
Is asthma a high morbidity?
Patients with severe uncontrolled asthma have disproportionally high morbidity and healthcare utilization as compared with their peers with well- controlled disease. Although treatment options for these patients were previously limited, with unacceptable side effects, the emergence of biologic therapies for the treatment ...
Does asthma affect quality of life?
Specifically, patients with severe asthma have increased hospitalizations, detrimental side effects of oral corticosteroids (OCS), poor quality of life (QOL), and impaired lifestyle as compared with patients with well-controlled disease ( 5 ).
What is T2 low asthma?
T2-low asthma, which includes neutrophilic, mixed, or paucigranulocytic asthma, has a comparatively poorly understood pathophysiology and may be influenced by the concomitant use of corticosteroids suppressing underlying eosinophilia. T2-low asthma is caused by neutrophilic or paucigranulocytic inflammation that results in activation of both T1 and T17 cells, and high IL-17A mRNA levels have been found in patients with moderate to severe asthma ( 15 ). These patients are generally less responsive to corticosteroids, have fewer allergic symptoms, and are older at the time of diagnosis. Currently, there is no approved biologic for T2-low asthma, and thus therapy in this group relies on standard treatment with controller medications and possible bronchial thermoplasty ( 14 ). However, one recent trial suggests macrolide therapy with azithromycin may have a role in reducing exacerbations in patients with T2-low asthma ( 16 ).
Is mepolizumab approved for asthma?
Mepolizumab is currently approved for patients 12 years of age and older with severe asthma with an eosinophilic phenotype. Although the FDA has not set an AEC required for use, RCTs have suggested a benefit for patients with a count as low as 150 cells/μl, particularly in patients on chronic OCS ( 45 ).
What is T2 inflammation?
T2 inflammation occurs in approximately half of patients with asthma and may be slightly more common in patients with severe asthma ( 11 ). In T2-high asthma, inhaled allergens, microbes, and pollutants interact with the airway epithelium, which subsequently leads to activation of mediators such as thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP), IL-25, and IL-33 ( Figure 1 ). This process leads to activation of IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13, which can result in attraction and activation of basophils, eosinophils, and mast cells; secretion of IgE by B cells; and activation of innate cells such as the airway epithelium and smooth muscle, resulting in bronchoconstriction, airway hyperresponsiveness, mucus production, and airway remodeling ( 12, 13 ). T2-high asthma encompasses both allergic and nonallergic eosinophilic asthma. Although an allergen-specific, IgE-dependent process plays a significant role in allergic asthma, T2 cytokines play a dominant role in inflammation in nonallergic eosinophilic asthma. Sputum and blood absolute eosinophil counts (AECs), serum IgE, exhaled nitric oxide, and serum periostin are all important biomarkers of T2 inflammation that can help predict response to biologics ( 14 ).
