What type of Doctor would treat myasthenia gravis?
Steroid-sparing agents such as azathioprine and mycophenolate may also have a role in treating ocular MG. Other treatments for MG include plasmapheresis, intravenous immunoglobulin, and other immunosuppressive agents, but these are rarely required for ocular MG. Patients should also be evaluated for thymoma. Thymoma should be resected surgically.
Does myasthenia gravis have a cure?
This can be used for ptosis and may be preferable to drug therapy that alters the immune system: using agents such as glucocorticoids (prednisone or similar agents), azathioprine (Imuran®), cyclosporine or mycophenolate mofetil (CellCept®). Applying a patch to one eye. This permits people with double vision to see one image.
Can you be cured of myasthenia gravis?
One of the medications that is commonly used to treat myasthenia gravis is called pyridostigmine (Mestinon®). This medication helps build higher levels of the chemical acetylcholine, which is the signal that tells a muscle to move. The side effects of pyridostigmine can include diarrhea, abdominal cramps, nausea, and vomiting.
Is there any cure for myasthenia gravis?
Because ocular myasthenia gravis is a well-described condition, there are several treatment avenues open to patients. Depending on the type and severity of the symptoms, treatment can include eyeglasses (with or without eyelid crutches) and surgery. Myasthenia gravis is usually treated by team of physicians, and ocular symptoms in particular are generally treated by a …
What can be done for ocular myasthenia gravis?
Like generalized myasthenia gravis, there are a variety of treatments available that include pyridostigmine, immunosuppression, intravenous immunoglobulin, plasmapheresis, thymectomy, lid crutches, ptosis surgery, and extraocular muscle surgery.
Is ocular myasthenia gravis curable?
There's no cure for myasthenia gravis, but treatment can help relieve signs and symptoms, such as weakness of arm or leg muscles, double vision, drooping eyelids, and difficulties with speech, chewing, swallowing and breathing.
How serious is ocular myasthenia gravis?
Myasthenia gravis (MG) is a potentially serious, but treatable autoimmune disease affecting the neuro-muscular junction (NMJ) of the skeletal muscle. Ocular myasthenia gravis (OMG) can mimic isolated cranial nerve palsies, gaze palsies, internuclear ophthalmoplegia, blepharospasm, and even a stroke.
What is the first line treatment of myasthenia gravis?
Pyridostigmine. The first medicine used for myasthenia gravis is usually a tablet called pyridostigmine, which helps electrical signals travel between the nerves and muscles. It can reduce muscle weakness, but the effect only lasts a few hours so you'll need to take it several times a day.
What foods should I avoid with myasthenia gravis?
If your MG medication causes diarrhea or stomach upset, avoid foods that are fatty, spicy or high in fiber. Avoid dairy foods, except for yogurt which can sooth digestive problems. Good choices include mild foods like bananas, white rice, eggs and chicken. Diarrhea can lower potassium levels.
What natural treatment is good for myasthenia gravis?
Natural Remedies and Alternative Medicine for Myasthenia GravisMagnesium.CBD oil.Acupuncture.Chinese herbal medicine.Elderberry.Frankincense.Homeopathic remedies.Ayurvedic treatment.
How can I strengthen my eye muscles?
This is another very simple exercise which can help in strengthening the weakened eye muscles. To start, focus on a nearby object for about 5 seconds. Then move on to distant objects and focus on it for another 5 seconds. This sporadic shifting gives strength to the eye muscles and refreshes them too.
Can ocular myasthenia gravis progress?
Fifty percent of ocular myasthenia gravis (OMG) patients will progress to generalized myasthenia, 90% within 3 years from the onset of ocular symptoms.
What triggers myasthenia gravis?
Myasthenia crisis may be caused by a lack of medicine or by other factors, such as a respiratory infection, emotional stress, surgery, or some other type of stress. In severe crisis, a person may have to be placed on a ventilator to help with breathing until muscle strength returns with treatment.
What are the long term effects of taking Mestinon?
extreme muscle weakness; loss of movement in any part of your body; weak or shallow breathing; slurred speech, vision problems; or.
Can you take pyridostigmine long term?
Pyridostigmine has been used as a treatment for MG for over 50 years and is generally considered safe. It is suitable as a long-term treatment in patients with generalized non-progressive milder disease, and as an adjunctive therapy in patients with severe disease who are also receiving immunotherapy.
How long do you take PredniSONE for myasthenia gravis?
The high-dose regimen consists of prednisone 1.0 to 1.5 mg/kg/d (but usually not >100 mg/d) for 2 to 4 weeks. After this period, a decision is made to immediately switch to every other day or to continue daily high-dose therapy.
How long does ocular myasthenia gravis last?
This is known as "ocular myasthenia". But for most people, the weakness spreads to other parts of the body over a few weeks, months or years. If you've had symptoms affecting your eyes for 2 years or more, it's unusual for other parts of your body to be affected later on.
Can ocular myasthenia gravis progress?
Fifty percent of ocular myasthenia gravis (OMG) patients will progress to generalized myasthenia, 90% within 3 years from the onset of ocular symptoms.
What is the life expectancy of someone with myasthenia gravis?
There is no cure for MG, but most people with the condition have a normal life span. Only 3 to 4 out of every 100 people with MG die because of MG. Years ago, early death occurred in over a third of people with MG. Today, if someone dies of MG, death is usually due to a myasthenic crisis or a thymoma.
Does myasthenia gravis always progress?
Abstract. Background: The natural history of myasthenia gravis [MG] is unpredictable: In the first few years the disease course is worst with subsequent gradual disease stabilization. However, some patients tend to have continued disease activity or resurgence of the disease many years into the illness.
How Does Myasthenia Gravis Affect Me?
Myasthenia gravis is an autoimmune disease that affects the muscles, causing muscle weakness. The disease can affect various muscle groups in the b...
Symptoms of Ocular Myasthenia Gravis
With ocular myasthenia gravis, the symptoms typically include ptosis and diplopia.Ptosis: A drooping eyelid can be seen in either eye or in both ey...
Who Is at Risk For Myasthenia Gravis?
Myasthenia gravis tends to appear mainly in young women and men over the age of 50. Young people diagnosed with myasthenia gravis have a better cha...
Treatments Options For Ocular Myasthenia Gravis
Because ocular myasthenia gravis is a well-described condition, there are several treatment avenues open to patients. Depending on the type and sev...
Surgery For Ocular Myasthenia Gravis
Most often, two different forms of surgery are used to treat ocular myasthenia gravis:Strabismus surgery: This surgery is done on the muscles of th...
What is ocular myasthenia gravis?
What is ocular myasthenia gravis? Ocular myasthenia gravis is a form of myasthenia gravis (MG) in which the muscles that move the eyes and control the eyelids are easily fatigued and...
What is the best way to hold your eyelids open during ptosis?
Using eyelid crutches (clever devices attached to glasses to hold the eyelids open) for ptosis.
How do you know if you have MG?
Problems with double vision and drooping eyelids are often the first symptoms of MG. Although most people have eye problems at the onset of MG, they may have other muscle weakness or develop other muscle weakness in the first two years after MG symptoms begin. About 15% of people with MG will have only ocular problems (ocular MG). If weakness of other muscles develops over time, the MG changes from ocular MG to generalized MG. About half of all people with ocular issues related to MG in the first year will develop generalized MG. People that have had only ocular MG symptoms for five years or more will most likely not develop generalized MG.
What is the best way to hold your eyelids open?
Using eyelid tape (a special type of tape used to hold the eyelids open without injuring the eyelids). This can be used for ptosis and may be preferable to drug therapy that alters the immune system: using agents such as glucocorticoids (prednisone or similar agents), azathioprine (Imuran®), cyclosporine or mycophenolate mofetil (CellCept®).
Why is it important to alternate the patch from one eye to the other?
If the same eye is consistently patched, vision in that eye might decrease. Therefore, it is important to alternate the patch from one eye to the other to avoid permanent vision loss.
Can you have eyelid surgery with MG?
Eyelid or eye muscle surgery is generally not recommended for people with MG
Can MG cause eye muscle weakness?
One hypothesis is that people with MG may simply notice eye weakness more often than mild weakness in other muscle groups in the body. Another hypothesis is that the eye and eyelid muscles are structurally different from muscles in the trunk and limbs. For example, these parts of the body have fewer acetylcholine (AChR) receptors, which is where the defect occurs in autoimmune MG. Eye muscles contract much more rapidly than other muscles and may be more likely to fatigue.
How is ocular myasthenia gravis different from generalized myasthenia gravis?
Ocular myasthenia gravis only affects the muscles that move the eyes and eyelids. The symptoms of ocular myasthenia gravis include double vision (seeing two images instead of one), trouble focusing, and drooping eyelids. On the other hand, generalized myasthenia gravis affects muscles throughout the body.
Why does myasthenia gravis typically cause double vision?
The brain finely controls the eye muscles in order to keep the eyes aligned properly. Weakness of the eye muscles leads to misalignment of the eyes, which causes the eyes to perceive the same object in two different locations.
How often does myasthenia gravis only affect the eyes?
For about one half of patients with myasthenia gravis, the first symptoms are visual. About 15% of these patients will remain only having visual symptoms, even years after their diagnosis. In the other 85% of patients, however, symptoms of weakness will develop in another part of the body, usually within the next three years.
How is myasthenia gravis diagnosed?
Your doctor will begin by asking about your symptoms and performing a physical examination. It will be important to carefully test the eyelids and eye movements, and to see what happens to the muscles when they are fatigued and when they have rested.
What are the treatments for myasthenia gravis?
One of the medications that is commonly used to treat myasthenia gravis is called pyridostigmine (Mestinon®). This medication helps build higher levels of the chemical acetylcholine, which is the signal that tells a muscle to move. The side effects of pyridostigmine can include diarrhea, abdominal cramps, nausea, and vomiting.
How can double vision be treated?
Double vision that results from myasthenia gravis is most often treated by blocking the vision from one eye. Either an eye patch can be worn or scotch tape can be placed over one lens in the eyeglasses. If one eyelid is very droopy and blocks the vision in that eye, the double vision will not require a separate treatment.
What medications should be avoided?
Certain medications can worsen the symptoms of myasthenia and should be avoided. These medications include specific antibiotics (called aminoglycosides and quinolones), beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers, and phenytoin (Dilantin®).
How Does Myasthenia Gravis Affect Me?
Myasthenia gravis is an autoimmune disease that affects the muscles, causing muscle weakness. The disease can affect various muscle groups in the body, and muscles in the face, the neck, and the limbs can exhibit symptoms of weakness and immobility.
Ocular Myasthenia Gravis
In approximately 15 percent of people with myasthenia gravis, the only muscles affected are those in the eyes, in which case the condition is called ocular myasthenia gravis. Some of the first signs of ocular myasthenia gravis include a dropping eyelid and double vision.
Symptoms Of Ocular Myasthenia Gravis
With ocular myasthenia gravis, the symptoms typically include ptosis and diplopia.
Who Is At Risk For Myasthenia Gravis?
Myasthenia gravis tends to appear mainly in young women and men over the age of 50. Young people diagnosed with myasthenia gravis have a better chance at achieving remission than older patients.
Treatments Options For Ocular Myasthenia Gravis
Because ocular myasthenia gravis is a well-described condition, there are several treatment avenues open to patients. Depending on the type and severity of the symptoms, treatment can include eyeglasses (with or without eyelid crutches) and surgery.
Surgery For Ocular Myasthenia Gravis
Most often, two different forms of surgery are used to treat ocular myasthenia gravis:
What is myasthenia gravis?
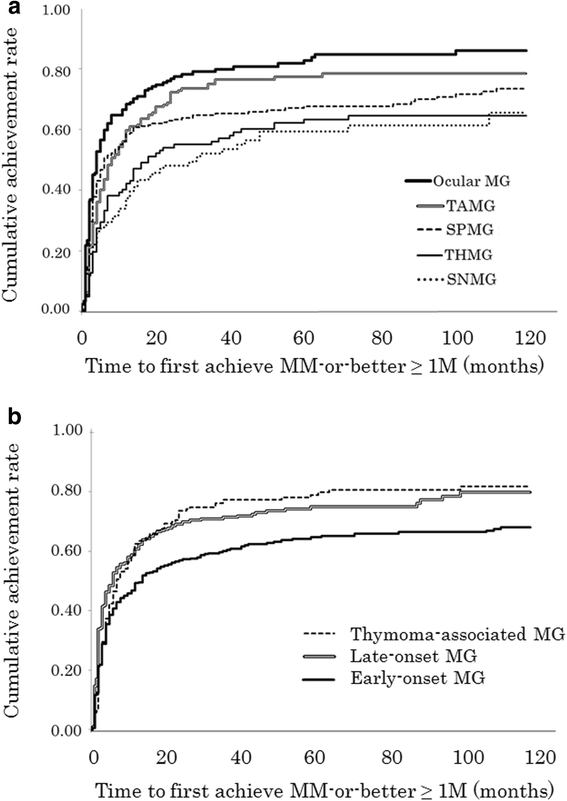
Myasthenia gravis is characterized by a variable weakness of skeletal muscles, which improves on resting. Weakness is exacerbated by repetitive contraction.[5] Generalized myasthenia involves the bulbar, limb, and respiratory muscles; OMG is a subtype of MG where the weakness is clinically isolated to the EOMs, levator, and orbicularis oculi.[5] Expectedly, due to variable involvement of different EOMs, motility patterns are not characteristic of lesions of one or more nerves.[6] Ptosis and diplopia are the initial signs of the disease in over 50% of MG patients;[8] 50-80% of these patients go on to develop generalized disease.[7] In the majority of cases (90%), progression of OMG to its generalized form will occur within the first 2 years after ocular symptoms begin.[9]
How common is myasthenia gravis?
Myasthenia may affect any age group and shows no geographic predilection.[3,4] Onset of symptoms in the first decade or after the age of 70 years is less common.[2] The incidence ranges from 0.04 to 5/100 000/year and prevalence estimates of 0.5-12.5/100 000/year.[2] Generalized and OMG differ with respect to the demographics of the affected population; whilst the ratio of affected females: males is 3:2 or higher in generalized myasthenia gravis (GMG), more males are affected by purely OMG, more so over the age of 40.[5,6] Onset occurs at an earlier age in women (mean age 28 years) than in men (mean age 42 years).[3]
What is MG in ophthalmology?
Myasthenia gravis (MG) is a disease that affects the neuro-muscular junction resulting in classical symptoms of variable muscle weakness and fatigability. It is called the great masquerader owing to its varied clinical presentations. Very often, a patient of MG may present to the ophthalmologist given that a large proportion of patients with systemic myasthenia have ocular involvement either at presentation or during the later course of the disease. The treatment of ocular MG involves both the neurologist and ophthalmologist. Thus, the aim of this review was to highlight the current diagnosis, investigations, and treatment of ocular MG.
How many patients with myasthenia have thymoma?
As many as 70% of patients with myasthenia may have thymic hyperplasia, and 10-15% may harbor a thymoma.[36] Computerized tomography (CT) of the chest is advised in patients diagnosed with myasthenia to detect this association.
How to test for MG?
The Ice test is a simple, but effective clinical test that can be used to confirm the diagnosis of MG. An icepack is placed over the patient's closed eyelids for a period of 2 min (for ptosis) to 5 min (for ophthalmoparesis) [Fig. 1].[5] The ocular motility deficits and ptosis must be measured before and after the test. Although there are no strict guidelines regarding the interpretation of this test,[1] it is, usually, considered positive when the upper eyelid elevates by at least 2 mm following ice application.[5] Cooling may reduce anticholinesterase (AChE) activity, which increases the amount of available ACh at the neuro-muscular junction.[14] There is thus an increase in the efficiency of ACh in eliciting depolarization at the motor end plate.[18]
Can thyroid disease be diagnosed with myasthenia?
Additional testing for thyroid dysfunction may also be considered in patients with myasthenia, since about 4-5% of patients with MG may have concurrent autoimmune thyroid disease .[37]
Is myasthenia gravis a autoimmune disease?
Myasthenia gravis (MG) is a potentially serious, but treatable autoimmune disease affecting the neuro-muscular junction (NMJ) of the skeletal muscle. Ocular myasthenia gravis (OMG) can mimic isolated cranial nerve palsies, gaze palsies, internuclear ophthalmoplegia, blepharospasm, and even a stroke.
What is the treatment for ocular disabling?
When ocular symptoms are severe or disabling, treatment with immune system modulating therapy may be considered.
Why is it important to alternate the patch from one eye to the other?
If the same eye is consistently patched, vision in that eye might decrease. Therefore, it is important to alternate the patch from one eye to the other to avoid permanent vision loss.
How do you know if you have MG?
Problems with double vision and drooping eyelids are often the first symptoms of MG. Although most people have eye problems at the onset of MG, they may have other muscle weakness or develop other muscle weakness in the first two years after MG symptoms begin. About 15% of people with MG will have only ocular problems (ocular MG). If weakness of other muscles develops over time, the MG changes from ocular MG to generalized MG. About half of all people with ocular issues related to MG in the first year will develop generalized MG. People that have had only ocular MG symptoms for five years or more will most likely not develop generalized MG.
Can a thymectomy be done for MG?
Thymectomy is usually not considered for people with ocular MG unless the manifestations are severe or disabling.
Can MG cause eye muscle weakness?
One hypothesis is that people with MG may simply notice eye weakness more often than mild weakness in other muscle groups in the body. Another hypothesis is that the eye and eyelid muscles are structurally different from muscles in the trunk and limbs. For example, these parts of the body have fewer acetylcholine (AChR) receptors, which is where the defect occurs in autoimmune MG. Eye muscles contract much more rapidly than other muscles and may be more likely to fatigue.
Can ocular MG cause weakness?
People with ocular MG do not have difficulty swallowing, speaking or breathing, nor do they have weakness of the arms or legs. Descriptions of the symptoms that people with ocular MG may have include:

Diagnosis
Treatment
- Various treatments, alone or in combination, can relieve symptoms of myasthenia gravis. Your treatment will depend on your age, how severe your disease is and how fast it's progressing.
Clinical Trials
- Explore Mayo Clinic studiestesting new treatments, interventions and tests as a means to prevent, detect, treat or manage this condition.
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
- To help you make the most of your energy and cope with the symptoms of myasthenia gravis: 1. Adjust your eating routine.Try to eat when you have good muscle strength. Take your time chewing your food, and take a break between bites of food. You might find it easier to eat small meals several times a day. Also, try eating mainly soft foods and avoid...
Coping and Support
- Coping with myasthenia gravis can be difficult for you and your loved ones. Stress can worsen your condition, so find ways to relax. Ask for help when you need it. Learn all you can about your condition, and have your loved ones learn about it as well. You all might benefit from a support group, where you can meet people who understand what you and your family members are goin…
Preparing For Your Appointment
- You're likely to first see your family doctor, who will then refer you to a doctor trained in nervous system conditions (neurologist) for further evaluation. Here's information to help you get ready for your appointment.