
What are the functions of the common fibular nerve?
Sep 12, 2013 · Fibular Neurodynamic Test (FNT) This test biases both the common and superficial fibular nerves. Normal responses include stretching and pulling in the anterolateral leg and ankle and the foot dorsum.
What are non surgical treatments for fibular nerve entrapment?
Sep 01, 2013 · A combined treatment protocol of spinal and fibular head manipulation and neurodynamic mobilization including soft tissue work of the psoas and hamstring muscles was performed. Outcome measures were assessed at pretreatment, 1 week posttreatment, and 3-month follow-up and included numeric pain rating scale, range of motion, pressure pain …
What is a normal response to the fibular nerve test?
The first step in treatment for peroneal nerve entrapment is rest. The doctor will splint your ankle in a neutral position, and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs can help to reduce inflammation and swelling. For patients that are overweight, diet and exercise can help to …
What should I do if I have fibular nerve pain?
Jul 01, 2021 · Mobilization of the neurodynamic system, also called neuromobilization or neurodynamics, is an approach to treatment of pain that relies on influencing pain physiology via mechanical treatment of neural tissues and the surrounding non neural structures (Butler and Moseley 2003; Basson et al., 2017).
How is common fibular nerve pain treated?
Nonsurgical treatments, including orthotics, braces or foot splints that fit inside the person's shoe, can bring relief. Physical therapy and gait retraining can help the person improve their mobility. Some injuries may require peripheral nerve surgery, including one or more of these procedures: Decompression surgery.
How do you heal the common fibular nerve?
Treatment of Common Peroneal Nerve Entrapment begins with rest, splinting the ankle in the neutral position, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs to reduce the swelling and inflammation, diet and exercise in obese patients, and strict glucose control in diabetics.
What happens when the common fibular nerve is damaged?
When the nerve is injured and results in dysfunction, symptoms may include: Decreased sensation, numbness, or tingling in the top of the foot or the outer part of the upper or lower leg. Foot that drops (unable to hold the foot up) "Slapping" gait (walking pattern in which each step makes a slapping noise)
How do you release pressure from the peroneal nerve?
3:286:06MSR Peroneal Nerve Release - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo by creating the foot dorsiflexion and inversion through all the fascial connections through theMoreSo by creating the foot dorsiflexion and inversion through all the fascial connections through the peroneus longus and brevis here we're going to affect the nerve.
How long does it take peroneal nerve to heal?
The recovery time after a common peroneal nerve decompression at the knee is usually 3-4 months. For the first 6 weeks, we do not want to encourage the knee to form a lot of scar tissue around the area of the decompression, so we have patients on crutches.
What doctor treats peroneal nerve?
You're likely to start by seeing your family doctor. Depending on the suspected cause of foot drop, you may be referred to a doctor who specializes in brain and nerve disorders (neurologist).Dec 4, 2020
How do you treat nerve damage in the foot?
Various therapies and procedures might help ease the signs and symptoms of peripheral neuropathy.Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS). Electrodes placed on the skin deliver a gentle electric current at varying frequencies. ... Plasma exchange and intravenous immune globulin. ... Physical therapy. ... Surgery.Jul 3, 2021
What helps nerves heal faster at home?
There are a variety of ways a person can relieve the pain of a pinched nerve at home.Extra sleep and rest. Sleep is essential for a healing nerve. ... Change of posture. ... Ergonomic workstation. ... Pain relieving medications. ... Stretching and yoga. ... Massage or physical therapy. ... Splint. ... Elevate the legs.More items...
What are the causes of common fibular nerve injury?
There are numerous traumatic and non-traumatic causes of peroneal nerve injuries, including knee dislocation, direct impact or cut on the fibular neck, fracture of the proximal fibula, compression by use of a tight plaster cast, or compression wrapping, prolonged bed rest, and regular crossing of the legs.Feb 12, 2022
How can I release the peroneal nerve at home?
2:047:29Peroneal Nerve - Flossing and Tensioning - Ask Dr. AbelsonYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipYou can increase decrease tension by working with the head so as Sam's. Doing this she can eitherMoreYou can increase decrease tension by working with the head so as Sam's. Doing this she can either bring her chin up or same motion and then bringing the head back.
Is peroneal nerve same as fibular nerve?
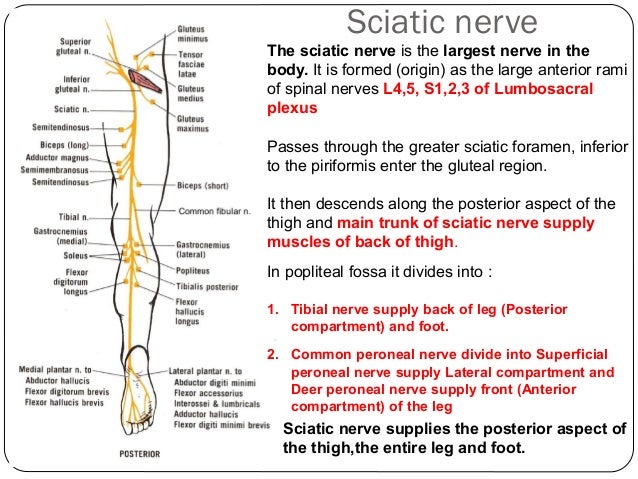
The common peroneal nerve, also known as the common fibular nerve, is a major nerve that innervates the lower extremity. As one of the two major branches off the sciatic nerve, it receives fibers from the posterior divisions of L4 through S2.
Can a peroneal nerve be fixed?
Treatment options involve two main strategies: restoration of peroneal nerve function and tendon transfer to restore muscle function and balance of the foot. Peroneal nerve interventions include neurolysis, neuroplasty, or cable graft nerve repair.Aug 6, 2014
Ulnar Neurodynamic Test (UNT)
This test biases the ulnar nerve, brachial plexus, and potentially the lower cervical nerve roots.
Median Neurodynamic Test 2 (MNT2)
This version biases the lower cervical nerve roots, spinal nerves, brachial plexus, and median nerve.
Radial Neurodynamic Test (RNT)
This test looks predominately at radial nerve, as well as the nerve roots. It is uncertain if this test biases any particular nerve root.
Radial Sensory Neurodynamic Test (RSNT)
This test is used to rule out de Quervain’s disease as a neurodynamic problem.
Straight Leg Raise (SLR)
This test is performed with any posterior symptoms from the heel to the thoracic spine.
Sural Neurodynamic Test (SNT)
This test biases the sural nerve, which can often be involved in a sprained ankle.
Slump Test
This test checks the peripheral and central nervous system, and can encompass symptoms from the head to the foot.
Which nerve has sensory and motor fibers?
The common peroneal nerve and its terminal branches have both motor and sensory fibers, but its motor function is limited. The rest of it is purely sensory, sending information about things like temperature and pressure to and from the brain.
Where does the tibial nerve go?
The tibial nerve continues down the back of the leg while the common peroneal nerve wraps around the outside of the knee to reach the front of your calf. Anatomy of the Sciatic Nerve. Staras/Getty Images.
What nerve is the peroneal nerve?
The common peroneal nerve, also called the common fibular nerve, is a peripheral nerve that branches off from the sciatic nerve. It and its branches supply sensation and some motor function to the lower leg and top of the foot. 1 .
Where does the sciatic nerve run?
The roots they join together and run down through the buttocks and the back of the thigh. As the sciatic nerve reaches the back of your knee, which you might call the "knee pit" but doctors refer to as the popliteal fossa, it separates into two main branches: Tibial nerve. Common peroneal nerve. The tibial nerve continues down the back ...
What nerve sends sensation to the skin of the lower leg?
The common peroneal nerve has a relatively short run. Soon after branching off from the sciatic nerve, it sends off two cutaneous branches. "Cutaneous" means having to do with the skin; these cutaneous branches provide sensation to the skin of your lower leg. They're called the sural communicating nerve and the lateral sural cutaneous nerve.
Which muscle is responsible for knee flexing?
The nerve connects to the short head of the biceps femoris muscle. That is part of the hamstring muscles, which are what allow your knee to flex. That's the only portion of the main nerve that serves a motor function.
Where does the peroneal nerve run?
From its origin just above the popliteal fossa, the common peroneal nerve runs along the inner edge of the biceps femoris muscle, over the head of the gastrocnemius. That's where the two cutaneous branches split off.
Description
The common peroneal nerve is the smaller and terminal branch of the sciatic nerve which is composed of the posterior divisions of L4, 5, S1, 2.
Function
Motor: Innervates the short head of the biceps femoris directly. Also supplies (via branches) the muscles in the lateral and anterior compartments of the leg.
Motor Functions
The common fibular nerve innervates the short head of the biceps femoris muscle (part of the hamstring muscles, which flex at the knee).
Sensory Functions
There are two cutaneous branches that arise directly from the common fibular nerve as it moves over the lateral head of the gastrocnemius. • Sural communicating nerve: This nerve combines with a branch of the tibial nerve to form the sural nerve. The sural nerve innervates the skin over the lower posterolateral leg.
Clinical Relevance
The common peroneal nerve is in a particularly vulnerable position as it winds around the neck of the fibula. It may be damaged at this site by
Common Peroneal Tension Test
A common peroneal nerve stress test ( SLUMP test while biasing the foot and ankle in PF/IN) revealed reproduction of the patient's symptoms. The symptoms met the 3 criteria for positive neural tension:
Causes for Peroneal Nerve Entrapment
Several conditions can be risk factors for peroneal nerve entrapment. Health conditions such as diabetes and arthritis can be a leading factor in developing peroneal nerve entrapment. A history of knee sprains or trauma can also increase your risk.
Symptoms of Peroneal Nerve Entrapment
One common symptom of peroneal nerve entrapment is pain, numbness, or tingling in the top of the foot. When you can’t feel the top of your foot, you can unknowingly injure or damage the foot more.
How Peroneal Nerve Entrapment is Diagnosed
Your doctor will begin with evaluating the length and severity of your condition. The doctor will conduct a physical exam to check for numbness evidence of nerve inflammation. This test is called the Tinel’s test and also a scratch-collapse test.
Treatment for Peroneal Nerve Entrapment
The first step in treatment for peroneal nerve entrapment is rest. The doctor will splint your ankle in a neutral position, and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs can help to reduce inflammation and swelling. For patients that are overweight, diet and exercise can help to relieve the pain.
Aftercare for Peroneal Nerve Entrapment Surgery
A fibular tunnel release surgery takes about one hour. After your surgery, the incision will be wrapped in a dressing, and you can go home a few hours after recovery. You will usually be given some pain relievers, and it is advisable to have someone to drive you to and from the procedure.
Use a Trusted Foot Specialist
Peroneal nerve entrapment can be a painful condition. It can cause you difficulty in walking and keep you from enjoying many activities. Luckily, there is a treatment to help your situation.
Abstract
Different approaches are used in physical therapy when treating patients with peripheral nerve paralysis and pain syndrome, such as neuro-mobilization techniques, manual therapy, muscle strengthening, active mobilization and relaxation techniques.
1. Introduction
Different active and passive approaches such as neuro-mobilization techniques ( Butler 2000; Shacklock 2005 ), manual therapy ( Balthazard et al., 2012 ), muscle strengthening, active mobilization ( Jensen et al., 2012) and relaxation techniques ( Ozsoy et al., 2019 ), are used in physical therapy to treat patients with peripheral nerve paralysis and pain syndrome ( Butler and Moseley 2003 )..
3. Timeline
The timeline of the PNF interventions was running from T0 (baseline) to T1 and consisted of 6 sessions in total over a period of 3 weeks. Each therapy session focused on neuromobilization and lasted 45 min. Follow-up was made at T2, which was 3.5 months later.
4. Patient management
The patient's assessment revealed a clear neurodynamic component. Therefore, a neuromobilization strategy was defined, using clinical reasoning integrating the PNF philosophy, facilitating principles, procedures and specific techniques ( Adler et al., 2014; Smedes et al., 2016 ).
5. Results
The patient's ability to move with less pain improved, as illustrated by different tests.
6. Discussion
The hypothesis for the treatment set-up was that the patient's symptoms were linked to resection of the tumor in the lumbar spine.
7. Conclusion and take-home message
The patient's function, activity and participation level improved to a degree close to or beyond clinical relevance, and the PSC pain disappeared over a period of 3.5 months. His walking pace was slightly quicker.
What is nerve flossing?
Nerve flossing is an exercise technique often used in physical therapy to improve the way your nerves move. Nerve flossing is also known as nerve gliding or neural glides. Occasionally after injury or illness, muscles, joints, and tendons can become tight.
What happens if a nerve is pinched?
If this nerve becomes pinched by a facet joint or herniated disc, slight damage to the membrane of the nerve may occur. This damage may result in a bit of scar tissue developing around the nerve, leading to tightness, pain, or tingling in that area where the nerve courses.
Where is Laura Campedelli?
Laura Campedelli, PT, DPT, is a physical therapist currently working in New York at Morgan Stanley Children’s Hospital , an affiliate of New York Presbyterian. Nerve flossing is an exercise technique often used in physical therapy to improve the way your nerves move.
What exercise can you do if you have a problem with your arm?
If you are having a problem with your arm or arms and your physical therapist determines that you may benefit from upper extremity nerve gliding, then they may prescribe a flossing exercise . These may include:
What are the two parts of the nervous system?
Your nervous system is grossly divided into two parts: The central nervous system, consisting of the brain and spinal cord , and the peripheral nervous system . The peripheral nervous system are the nerves that exit your spinal cord and travel through your body to your arms, trunk, and legs. These nerves communicate information from your body to your brain to tell it what is going on. They sense things like temperature, pain, pressure, and position. The peripheral nerves also communicate information from your brain to your muscles, telling them to move or relax.
Can you floss if you have a pinched nerve?
If you have suffered a pinched nerve or an injury that limits your movement, you may have increased neural tension. In that case, nerve flossing or gliding exercises may be prescribed. Nerve flossing may cause a temporary increase in your pain, but symptoms should abate quickly. These exercises can be useful in helping you return to full mobility. That way, you can quickly and safely get back to your previous level of function and activity.
What is it called when your hand tingles?
A common upper extremity nerve injury is called carpal tunnel syndrome. This often leads to pain, tingling, and weakness in your hand and thumb muscles.
What is the purpose of peroneal nerve palsy?
Advertisement. Peroneal nerve palsy physical therapy exercises help to maintain strength and range of motion. Check with your doctor before performing any exercises for this condition.
Why does my peroneal nerve hurt?
Some causes of peroneal nerve dysfunction include a fractured fibula, knee injury, regularly crossing your legs or wearing high boots or pressure to the knee while asleep, in surgery or in a coma.
How to strengthen ankles and feet?
Here are a few exercises to maintain strength and mobility in the foot and ankle recommended by the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons: 1 Heel Cord Stretch - This stretches the calf muscles. Place your hands on the wall and place your non-affected leg forward with the knee slightly bent. Your affected leg should be back behind you. Keep your heel on the ground to stretch the calf. Repeat this stretch with the back knee bent to target a different part of the calf muscle. 2 Golf Ball Roll - Roll a golf ball on the sole and arch of the affected foot for two minutes. 3 Calf Raises - Hold the back of a chair or the wall for balance and lift your unaffected foot so that your weight is on the affected leg. Raise the heel of the foot and then lower back to the ground to strengthen the calf 4 Ankle Rotations - Sit in a chair or on a bench so that your feet hover in the air without touching the ground. Use your affected foot to write the alphabet in the air.
What is ankle rotation?
She is passionate about all aspects of fitness and maintaining a healthy lifestyle. Ankle rotations are a great exercise to help peroneal nerve dysfunction. Peroneal nerve dysfunction is a form of peripheral neuropathy caused by nerve damage within a branch of the sciatic nerve that leads to the leg.
What causes numbness in the leg?
It may also be seen in individuals with medical conditions such as Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, diabetes, ano rexia, alcoholism and some autoimmune conditions. People suffering from this condition often experience numbness within the leg as well as a loss of muscle tone, muscle mass and even muscle control.
How to stretch calf muscles?
Place your hands on the wall and place your non-affected leg forward with the knee slightly bent. Your affected leg should be back behind you . Keep your heel on the ground to stretch the calf. Repeat this stretch with the back knee bent to target a different part of the calf muscle. Golf Ball Roll - Roll a golf ball on the sole and arch ...
Who is Aubrey Bailey?
Aubrey Bailey is a Doctor of Physical Therapy with an additional degree in psychology and board certification in hand therapy. Dr. Bailey is also an Anatomy and Physiology professor. She is a former American College of Sports Medicine certified personal trainer and currently works as a Level 1 CrossFit coach.
Description
Function
Motor Functions
Sensory Functions
- The first step in treating neuropathy in the common peroneal nerve is to treat the underlying cause, whether it's disease or injury. If that's not enough to relieve symptoms, or if symptoms are severe enough to warrant immediate treatment, you have multiple options.3 1. Physical therapy, to maintain or regain muscle strength 2. Occupational therapy...
Clinical Relevance
Common Peroneal Tension Test