What does a balloon pump do for the heart?
The balloon pump is a short term device, useful for periods of a few hours up to two weeks 5. It decreases the workload of the heart, thus decreasing the oxygen demand or MVO2, and increases the circulation of the coronary arteries, thus increasing oxygen delivery to all cardiac cells.
What happens when you put a balloon in Your Heart?
When the heart contracts, it sends blood out to the body. As it relaxes, blood flows into the coronary arteries to bring oxygen to the heart. An IABP allows blood to flow more easily into your coronary arteries. It also helps your heart pump more blood with each contraction. The balloon is inserted into your aorta.
What is balloon angioplasty used to treat?
Although this topic deals with the coronary arteries in the heart, balloon angioplasty can also be used to open narrowed vessels in many other parts of your body. For example, doctors can perform carotid angioplasty to open narrowed carotid arteries, which are the arteries that supply blood to the brain.
How is a deflating balloon placed in the heart?
When the heart pumps, the balloon deflates (not pulsing). The device is inserted percutaneously, using the femoral artery as the entry point and the proximal descending aorta as the destination. The balloon tip sits just beneath the exit of the left subclavian artery.

How long does balloon heart surgery take?
The procedure usually takes about 1-1/2 to 2-1/2 hours, and most patients will spend the night in the hospital. You may feel a little sleepy until the sedative has worn off. Nurses will watch you during the night to see that your heart rate and blood pressure are normal.
Is a stent and balloon the same thing?
A balloon catheter is a long, thin plastic tube with a tiny balloon at its tip. A stent is a small, metal mesh tube. Balloons and stents come in different sizes to match the size of the diseased artery.
What is balloon therapy for heart?
Coronary angioplasty is a medical procedure in which a balloon is used to open a blockage in a coronary (heart) artery narrowed by atherosclerosis. This procedure improves blood flow to the heart. Atherosclerosis is a condition in which a material called plaque builds up on the inner walls of the arteries.
Is balloon same as angioplasty?
The angioplasty stenting procedure uses a small stent to help support your coronary artery. The balloon catheter is used to place the stent into the clogged coronary artery.
How long can a balloon pump stay in?
The catheter connects to a computer that controls the rate of inflation and deflation. While most patients only use the IABP for a few days, it can stay in place for up to a month.
How long does a balloon stent last?
How long will a stent last? It is permanent. There is just a 2–3 per cent risk of narrowing coming back, and if that happens it is usually within 6–9 months. If it does, it can potentially be treated with another stent.
How is the balloon procedure done?
The intragastric balloon procedure is done in the endoscopy unit as an outpatient procedure. You'll be sedated for the procedure. During the procedure, the doctor advances a thin tube (catheter) loaded with the intragastric balloon down your throat into your stomach.
When do you put a balloon in your heart?
Overview. Coronary angioplasty (AN-jee-o-plas-tee), also called percutaneous coronary intervention, is a procedure used to open clogged heart arteries. Angioplasty uses a tiny balloon catheter that is inserted in a blocked blood vessel to help widen it and improve blood flow to the heart.
How is balloon surgery done?
Overview. Balloon angioplasty is a procedure used to open narrowed or blocked arteries. It uses a balloon attached to a catheter that's inserted into an artery. At the place where deposits of plaque have closed off or narrowed the channel for blood flow, the balloon is inflated.
What is the success rate of balloon angioplasty?
Coronary balloon angioplasty and stents facts Angioplasty is successful in opening coronary arteries in well over 90% of patients. Up to 30% to 40% of patients with successful coronary angioplasty will develop recurrent narrowing at the site of balloon inflation.
How safe is balloon angioplasty?
Angioplasty is very safe. You may get a bruise, feel sore, or have some bleeding where the tubes were inserted. More serious problems don't happen very often, but they are possible. They can include serious bleeding, blood clots, and narrowing of the artery again.
What are some potential complications of balloon dilation?
Risks of the ProcedureBleeding at the catheter insertion site.Blood clot or damage to the blood vessel at the insertion site.Infection at the catheter insertion site Cardiac dysrhythmias/arrhythmias (abnormal heart rhythms)Stroke.Rupture of the valve, requiring open-heart surgery.
What Is Balloon Angioplasty?
Interventional cardiologists perform angioplasty, which opens narrowed arteries. They use a long, thin tube called a catheter that has a small ball...
What Can I Expect During A Balloon Angioplasty Or Stent Procedure?
The procedures are performed in the cardiac catheterization laboratory (also called the cath lab).Patients are usually told not to eat or drink any...
What Happens After The Procedure?
After you leave the hospital, you should drink plenty of fluids and avoid driving, bathing, and smoking for 1 or 2 days after the procedure. You sh...
Can Restenosis Be Prevented?
Doctors are always trying to come up with new ways to prevent arteries from re-closing after an angioplasty or stent procedure. In recent years, do...
How long do you have to take antiplatelet therapy after balloon angioplasty?
If you had a stent placed, you will need to take a blood-thinning medicine or antiplatelet therapy for a year or longer. Your doctor will tell you how and when to take these medicines. About 35% to 40% of patients who have balloon angioplasty are at risk of more blockages in the treated area. This is called restenosis.
What is the procedure that opens a narrowed artery?
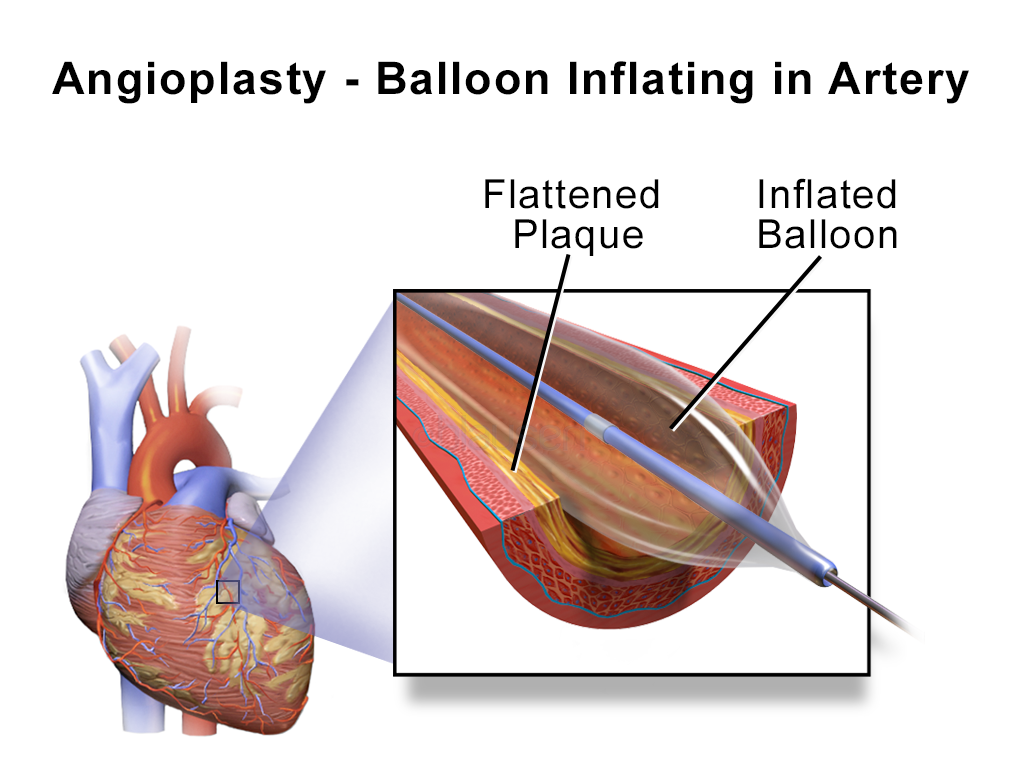
Interventional cardiologists perform angioplasty, which opens narrowed arteries. They use a long, thin tube called a catheter that has a small balloon on its tip. They inflate the balloon at the blockage site in the artery to flatten or compress the plaque against the artery wall.
What happens when a stent is deflated?
Once the stent is open, the balloon is deflated. The catheter, guidewire, and deflated balloon are then removed, leaving the stent behind to hold the artery open. Firm pressure will be applied to the site where the catheter was inserted to stop any bleeding. You will also be bandaged.
Why do you need a stent for angina?
By keeping the vessel open, the stent helps to improve blood flow to the heart muscle and reduce the pain of angina. Stent procedures are usually used along with balloon angioplasty. In fact, about 80% of patients who have balloon angioplasty will have a stent placed as well.
What is the most common form of heart disease?
Coronary artery disease (CAD) affects more than 15 million Americans, making it the most common form of heart disease. CAD most often results from a condition known as atherosclerosis, which happens when a waxy substance forms inside the arteries that supply blood to your heart. As the plaque builds up, the artery narrows, ...
What happens when a plaque builds up in the heart?
As the plaque builds up, the artery narrows, making it more difficult for blood to flow to the heart. As the blockage gets worse, blood flow to the heart slows and a condition called angina may develop. In time, the narrowed or blocked artery can lead to a heart attack.
Where is the stent placed in the artery?
If doctors are placing a stent in the artery, the stent is put at the tip of the catheter, over the balloon. When the catheter is positioned at the blockage, the balloon is inflated, expanding the stent. Once the stent is open, the balloon is deflated.
What is balloon angioplasty?
Balloon angioplasty, also known as percutaneous transluminal angioplasty (PTA), is a minimally invasive procedure done to widen narrowed or obstructed blood vessels. The procedure accesses a blood vessel via a catheter inserted through an incision in the skin.
What are the conditions that balloon angioplasty is used for?
Among the conditions balloon angioplasty may be used for are: Heart attack: Also known as myocardial infarction. Peri pheral ischemia: Impaired blood flow in part of the body other than the heart or brain due to peripheral artery disease.
Why is balloon angioplasty not performed?
Because balloon angioplasty is used to correct severely impaired blood flow, the benefits of treatment usually outweigh the risks. With that said, the procedure is not performed on vessels that are structurally unsound. 3
How long does it take for a balloon to deflate?
As the balloon expands, it coats the walls of the vessel with medications that reduce the risk of restenosis. After several minutes, the balloon is deflated. If a stent is needed, another catheter mounted with a stent is fed along the guidewire into the newly opened passageway.
What is the tube that is inserted into the blood vessel called?
A hollow tube , called an introducer sheath, is inserted into the blood vessel. Under the guidance of the live video feed, a thin guidewire is fed through the introducer sheath to the site of the obstruction. Following the path of the guidewire, the balloon catheter is gently eased into the center of the obstruction.
How long before a cardiologist can you stop taking anticoagulants?
These include anticoagulants, which are stopped 48 hours before the procedure, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), which are stopped four days beforehand.
Can you feel discomfort after a balloon catheter is deflated?
Once in place, the catheter is inflated. It is not uncommon to feel discomfort when this happens, although it usually disappears once the balloon is deflated. In some cases, the cardiologist may repeat steps 4 and 5, using a drug-coated balloon catheter for the second pass.
What is balloon angioplasty?
Balloon angioplasty is a minimally invasive cardiac catheterization procedure used to open narrow and blocked arteries. Heart stents are tiny lattice-shaped metal tubes that serve as scaffolding to keep the artery open. Because UT Southwestern cardiologists are active in heart research and national-level work, we are at the vanguard ...
What is the surgeon's job prior to balloon angioplasty?
The surgeon provides specific instructions to the patient prior to the balloon angioplasty – and possible stenting – and explains risks such as bleeding, infection, or adverse reaction to anesthesia. Patients also meet with the anesthesiologist prior to the surgery to review their medical history.
How does a balloon affect blood pressure?
The balloon inflates just as the aortic valve closes, which increases the blood pressure above the balloon long enough to push more blood through the coronary arteries , thus increasing delivery of needed oxygen and nutrients to the cardiac muscle.
What is the function of a balloon pump?
Cardiac balloon pump function. If heart muscle is severely damaged or diseased it may be unable to generate an adequate ejection fraction. One example is a heart attack. A large myocardial infarct (MI) can result in enough dead, dying and injured cardiac muscle cells that the heart cannot maintain adequate pump action.
What is a circulatory assist device?
Circulatory assist devices offer mechanical support for a failing heart and can be used in either the short or long term, depending on the type of machine and patient variables such as disease process, coexisting illnesses, age, or transplantation considerations.
What is cardiac assist?
Cardiac assist device provides mechanical support for a heart in crisis. During an average life span, the heart beats 2.5 billion times and pumps 1 million barrels of blood into circulation [1]. This amazing cardiac output is dependent on the heart rate and the stroke volume, which is the amount of blood ejected with each heartbeat, ...
Where is the balloon inserted?
The device is inserted percutaneously, using the femoral artery as the entry point and the proximal descending aorta as the destination. The balloon tip sits just beneath the exit of the left subclavian artery.
Does a circulatory assist pump blood?
The most commonly used circulatory assist device doesn’t actually “pump” blood. The intra-aortic balloon pump (IABP) targets those patients who need mechanical support over a short period of time to allow their heart to repair itself and resume normal function.
Can paramedics transport IABP?
Properly trained paramedics can safely transport IABP patients [6]. Of course, this requires a working knowledge of the particular pump model in use and how to troubleshoot any problems. Fortunately, pump difficulties during transport are uncommon; some reported examples include issues with the timing of inflation or deflation, loss of power, and cable malfunction [6,7]. You are more likely to have a transport complication with the patient’s underlying medical condition than with the IABP. And like a vent transfer, document your placement confirmation of the tube and balloon prior to transport, preferably in writing.
Special permission
Mr Reach, a builder from Kent, suffered severe heart failure after a heart attack - leaving him extremely unwell and short of breath.
How it works
The balloon - the size of a small chilli pepper - is inserted using a keyhole technique - without the need for major surgery
What is balloon valvuloplasty?
Balloon valvuloplasty is a procedure performed in the cardiac catheterization laboratory to treat stenotic or narrowed heart valves. Normal valves (aortic, mitral, tricuspid and pulmonic) comprise two or three pliable tissue leaflets which open and close to modulate blood flow through the heart. Valves may become narrowed because ...
How is a balloon valve deemed successful?
The procedure is deemed successful when the pressure difference across the valve is reduced by an acceptable degree, without causing the valve to become too leaky . Sometimes multiple inflations of the balloon or larger balloon sizes are required to adequately open the valve.
How does valvuloplasty improve blood flow?
The goal of valvuloplasty is to improve blood flow through the valve by separating points of fusion of the valve leaflets to one another , which improves valve opening and unloads the heart and ultimately improves symptoms.
Where is a balloon valvuloplasty catheter inserted?
In balloon valvuloplasty, catheters are usually inserted via the femoral artery and femoral vein, which are used as the pathways to the heart. Pressures are measured in the heart chambers to confirm the degree of narrowing. A balloon catheter is advanced into the heart and guided to the narrowed valve. The balloon on the catheter is inflated and ...
Is valvuloplasty a permanent procedure?
Valvuloplasty is usually not a permanent solution for valve stenosis, but may be the preferred treatment for certain forms of valve disease or for patients who are not candidates for valve replacement. Beaumont’s heart team will determine which procedure will be best for you after a thorough evaluation.
Can a balloon be removed from the body?
Once an acceptable result is achieved, the balloon and catheters are removed from the body. The femoral artery and femoral vein may be sutured closed or compressed manually to stop bleeding from the groin at the end of the procedure. No prosthetic or artificial material is left within the heart.
What is the best treatment for atrial fibrillation?
One of the most effective treatments for atrial fibrillation (AFib) is cryoablation, which uses extreme cold to freeze heart cells that cause an irregular heartbeat. At Stanford, our arrhythmia team has led research in this treatment from its inception through the latest clinical trials.
What is balloon cryoablation?
Balloon cryoablation is a minimally invasive procedure that helps restore a regular heartbeat by disrupting the abnormal electrical pathways in the heart that cause atrial fibrillation.
How does cryoablation work?
Catheter cryoablation works by using a special gas that travels through a thin tube called a catheter, which is inserted into the body and positioned at the site of the heart rhythm problem. Learn more about what to expect with cryoablation.
Can cryoballoons be used after a procedure?
After the Procedure. After the procedure, we remove the catheters and take patients to a monitored unit for observation. In most cases, we observe the patient’s heart monitor overnight.
Can cryoballoons treat atrial arrhythmia?
They then inflate a tiny balloon at the end of the catheter with a special gas coolant to freeze the atrial tissue triggering the arrhythmia. During one application, the cryoballoon is able to treat a large surface of atrial tissue. The director of the Stanford Cardiac Arrhythmia Service, Paul J. Wang, MD, is a co-inventor of cryoballoon ablation.
