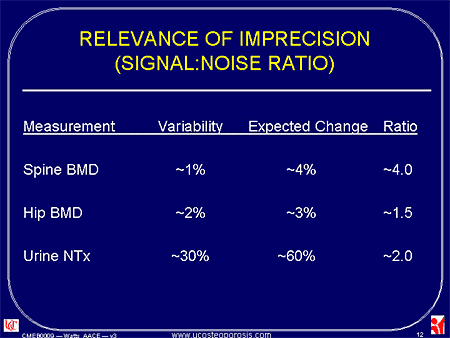
Discussion
- Antiresorptive treatment. Various studies point out that the antiresorptive treatment not only increases bone mineral density in the hip and decreases bone remodelling, but could also protect of osteoporotic fractures ...
- Treatment that acts on the CNS. ...
- Living institutionalised. ...
- Limitations. ...
What is the meaning of antiresorptive?
: slowing or blocking the resorption of bone Since postmenopausal osteoporosis is characterized by bone resorption that exceeds bone formation, antiresorptive agents can help to restore skeletal balance by reducing bone turnover, primarily at the tissue level. — Ernesto Canalis et al. What does 'poke' refer to in the expression 'pig in a poke'?
Which Antiresorptive therapies are used to treat osteoporosis?
Abstract Antiresorptive therapies are used to increase bone strength in individuals with osteoporosis and include five principal classes of agents: bisphosphonates, estrogens, selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs), calcitonin and monoclonal antibodies such as denosumab.
What is the aim of antiresorptive treatment for osteosarcoma?
The aim of antiresorptive treatment is to ensure adequate bone remodeling, reparation of microdamage of bone, and increased bone strength. Ideally, this effect should be maintained long-term.
What is the difference between anabolic and antiresorptive medications?
Anabolic medication builds new bone, increases bone density, and lowers the risk of broken bones. Antiresorptive medications include a class of drugs called bisphosphonates. These medications include: Risedronate (Actonel™, Actonel™ with Calcium, and Atelvia™)
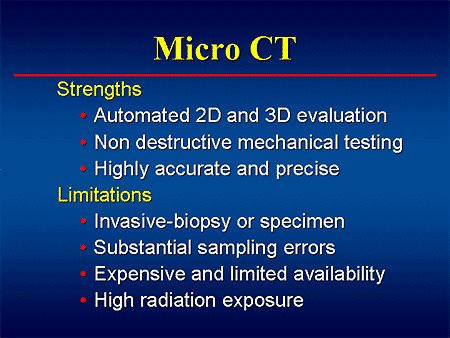
What does antiresorptive therapy mean?
Antiresorptive agents are bone preserving medications which can slow down the bone loss associated with osteoporosis (O'Neil et al. 2004). These reduce bone loss by inhibiting bone degeneration activity and/or promoting bone formation.
How do antiresorptive drugs work?
Antiresorptive drugs work by slowing the resorption or breakdown part of the remodeling cycle. Anabolics work by stimulating the formation part of the remodeling process. More bone is formed than is taken away. The result is stronger bone that is less likely to break.
What is the most popular treatment for osteoporosis?
Bisphosphonates are usually the first choice for osteoporosis treatment. These include: Alendronate (Fosamax), a weekly pill. Risedronate (Actonel), a weekly or monthly pill.
Is estrogen an antiresorptive?
Antiresorptive agents such as estrogens, SERMs (in postmenopausal women) and calcitonin are considered to be second-line agents that are appropriate in special circumstances.
What is the newest treatment for osteoporosis?
Romosozumab (Evenity). This is the newest bone-building medication to treat osteoporosis. It is given as an injection every month at your doctor's office and is limited to one year of treatment.
What are the long term side effects of alendronate?
Serious side effects and their symptoms can include the following:Ulcers or erosions of your esophagus. Symptoms can include: ... Bone death of your jaw. Symptoms can include: ... Unusual bone breaks in your hip and leg bones. ... Hypocalcemia (low calcium levels in your blood). ... Severe bone, joint, or muscle pain.
What foods to avoid if you have osteoporosis?
7 Foods to Avoid When You Have OsteoporosisSalt. ... Caffeine. ... Soda. ... Red Meat. ... Alcohol. ... Wheat Bran. ... Liver and Fish Liver Oil.
Is walking good for osteoporosis?
You can prevent bone loss with regular exercise, such as walking. If you have osteoporosis or fragile bones, regular brisk walking can help to keep your bones strong and reduce the risk of a fracture in the future. How should you walk and how often? You should walk briskly on a regular basis.
What is the life expectancy of a person with osteoporosis?
This excess risk is more pronounced in the first few years on treatment. The average life expectancy of osteoporosis patients is in excess of 15 years in women younger than 75 years and in men younger than 60 years, highlighting the importance of developing tools for long-term management.
What are the side effects of bisphosphonates?
General side effects of bisphosphonates and denosumabFever and flu-like symptoms. ... Low levels of calcium in your blood (hypocalcaemia) ... Bone and joint pain. ... Changes in bowel movements. ... Tiredness and low energy levels. ... Feeling sick. ... Changes to your kidneys. ... Irritation of the food pipe (oesophagus)More items...•
Can estrogen reverse osteoporosis?
Estrogen replacement therapy used to be the only FDA-approved treatment to prevent osteoporosis. There are now many other drugs and medications for osteoporosis, but estrogen remains a fairly common treatment to conserve bone mass and prevent osteoporosis-related fractures in post-menopausal women.
Does progesterone improve bone density?
P4 prevents bone loss in pre- and possibly perimenopausal women; progesterone co-therapy with antiresorptives may increase bone formation and BMD.
What are the antiresorptive agents used for?
Antiresorptive therapies are used to increase bone strength in individuals with osteoporosis and include five principal classes of agents: bisphosphonates, estrogens, selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs), calcitonin and monoclonal antibodies such as denosumab. However, no head-to-head studies have compared different antiresorptive agents ...
What is the best treatment for osteoporosis?
Several antiresorptive agents can safely reduce fracture risk in various high-risk populations. Bisphosphonates or denosumab should be recommended as first-line therapy for patients with osteoporosis. Selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs) are currently not used as first-line therapy except, occasionally, ...
What are the benefits of bisphosphonates?
Bisphosphonates reduce the risk of vertebral fractures in postmenopausal women. 30 In addition, nitrogen-containing bisphosphonates, such as alendronate, risedronate and zoledronate, reduce the risk of hip fracture and nonvertebral fractures ( Table 1 ). 14, 17, 18.
How do bisphosphonates help with osteoporosis?
Bisphosphonates suppress bone resorption by binding to bone at sites of active remodeling and blocking osteoclast activity. 29 These agents have made a major contribution to the management of patients with osteoporosis and are currently the most widely used antiresorptive therapies. Bisphosphonates reduce the risk of vertebral fractures in postmenopausal women. 30 In addition, nitrogen-containing bisphosphonates, such as alendronate, risedronate and zoledronate, reduce the risk of hip fracture and nonvertebral fractures ( Table 1 ). 14, 17, 18
Which estrogen receptor modulator is most commonly used for osteoporosis?
SERMs inhibit bone resorption through the same mechanism as do estrogens. Raloxifene is the most widely used SERM in osteoporosis treatment.
Is Denosumab a first line therapy?
Denosumab, which also has good antifracture efficacy, is another possible first-line therapy, although long-term safety data are lacking. However, no single antiresorptive therapy is currently appropriate for all patients or clearly superior to other therapies.
Does antiresorptive therapy increase BMD?
Antiresorptive therapies suppress bone turnover and also increase BMD; 26, 27 however, the increase in BMD generally accounts for only a modest portion of the antifracture efficacy. 28 For this reason, fracture is the most important clinical end point in efficacy trials of these therapies. Most studies of antiresorptive therapies have, therefore, been carried out in postmenopausal women, who have a high prevalence of osteoporosis and an increased risk of fractures. The Cochrane Collaboration has reviewed the antifracture efficacy of various individual antiresorptive agents in postmenopausal women ( Table 1 ); however, these data do not enable any conclusions to be drawn with regard to which agents are most effective, since no head-to-head studies have compared different antiresorptive agents using fracture as an end point.
What is the FDA approved medication for osteoporosis?
What are the FDA-approved medications for osteoporosis? Antiresorptive medication prevents bone loss, may increase bone density, and lowers the risk of broken bones. Anabolic medication builds new bone, increases bone density, and lowers the risk of broken bones. Antiresorptive medications include a class of drugs called bisphosphonates.
What does FDA approval mean for a syringe?
FDA approval means the medication has been proven to: Slow bone loss. Increase bone density. Reduce fracture risk at the spine or hip.
Can anti-osteoporosis cause bone loss?
While anti-osteoporosis medications can increase bone mineral density, they may also cause excessive suppression of physiologic bone remodeling, leading to the development of atypical femoral fractures and osteonecrosis of the jaw.
Can anti-osteoporosis medication increase bone mineral density?
During the initial management of acute osteoporotic spinal frac ture, different types of anti-osteoporosis medication may result in different clinical and radiologic outcomes, according to study results published in Osteoporosis International. While anti-osteoporosis medications can increase bone mineral density, ...