Monoclonal antibodies have been used to treat the following conditions:
- Cancer.
- Organ transplant rejection.
- Inflammatory and autoimmune disorders, including allergies.
- Infections, including COVID-19.
- Osteoporosis.
- Eye conditions.
- Migraines.
- High cholesterol.
- Nervous system disorders.
Common question
What are monoclonal antibodies used for in COVID-19?
They are a type of medical treatment. Scientists make monoclonal antibodies, or mAbs, in a lab. They work like the natural antibodies your body makes to fight illness. They go out into your body to identify and attack germs like the coronavirus that causes COVID-19.
What are the dangers of monoclonal antibodies?
Jan 06, 2022 · Monoclonal antibody therapy is a way of treating COVID-19 for people who have tested positive, have had mild symptoms for seven days or less, and are at high risk for developing more serious symptoms. The goal of this therapy is to help prevent hospitalizations, reduce viral loads, and lessen symptom severity.
How soon should you get monoclonal antibodies?
Monoclonal antibodies have been used to treat the following conditions: Cancer. Organ transplant rejection. Inflammatory and autoimmune disorders, including allergies. Infections, including COVID-19. Osteoporosis. Eye conditions. Migraines. High …
What do you know about monoclonal antibody therapy?
Monoclonal antibodies are carefully designed to recognize a single target (for example, a specific part of a specific virus). Sometimes two monoclonal antibodies, targeting different parts of a virus, are given in combination to increase the effectiveness of the treatment; these combinations are called monoclonal antibody cocktails.
How effective is the monoclonal treatment?
Monoclonal antibodies, or mAbs, are made in a laboratory to fight a particular infection (in this case, SARS-CoV-2) and are given to you directly in an infusion. So the mAb treatment may help if you are at high risk for serious symptoms or a hospital stay.
How many types of monoclonal antibody COVID-19 treatments are there in the US?
What is the difference between monoclonal antibodies and the COVID-19 vaccine?
Is there a monoclonal antibody therapy for post COVID-19 exposure?
FDA authorizes bamlanivimab and etesevimab monoclonal antibody therapy for post-exposure prophylaxis (prevention) for COVID-19 | FDA.
Should you still get the COVID-19 vaccine if you were treated with monoclonal antibodies?
If you were treated for COVID-19 with monoclonal antibodies or convalescent plasma, there is no need to delay getting a COVID-19 vaccine.
What is a monoclonal antibody for COVID-19?
Can I get COVID-19 again after having the vaccine?
Getting COVID-19 after you've been vaccinated or recovered is still possible. But having some immunity -- whether from infection or vaccination -- really drops the odds of this happening to you.
Is there an antibody cocktail for COVID-19?
The treatment, bamlanivimab and etesevimab administered together, was granted FDA emergency use authorization in February. Eli Lilly and the FDA stipulated that the antibody cocktail is authorized as a COVID-19 prophylaxis only for individuals who have been exposed to the virus.
Should I get the COVID-19 vaccine if I had COVID-19?
Should post-exposure prophylaxis be used for people who may have been exposed to a person with the coronavirus disease?
There is currently no FDA-approved post-exposure prophylaxis for people who may have been exposed to COVID-19. For information about registered clinical trials of investigational therapeutics for pre or post exposure prophylaxis of SARS-CoV-2 infection, visit ClinicalTrials.gov.
For more information on movement restrictions, monitoring for symptoms, and evaluation after possible exposure to COVID-19, see Interim US Guidance for Risk Assessment and Public Health Management of Persons with Potential Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Exposure in Travel-associated or Community Settings and Interim U.S Guidance for Risk Assessment and Public Health Management of Healthcare Personnel with Potential Exposure in a Healthcare Setting to Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19).
Can you get the Covid vaccine if you were treated with convalescent plasma?
What medication is not recommended before vaccinations for COVID-19?
Should you get the Covid vaccine if you have an autoimmune disease?
How do monoclonal antibodies work against cancer?
Monoclonal antibodies are immune system proteins that are created in the lab. Antibodies are produced naturally by your body and help the immune sy...
Which cancers are treated with monoclonal antibodies?
Many monoclonal antibodies have been approved to treat a wide variety of cancers. To learn about specific treatments for your cancer, see the PDQ®...
What are the side effects of monoclonal antibodies?
Monoclonal antibodies can cause side effects, which can differ from person to person. The ones you may have and how they make you feel will depend...
What is monoclonal antibody?
Monoclonal antibodies are immune system proteins that are created in the lab. Antibodies are produced naturally by your body and help the immune system recognize germs that cause disease, such as bacteria and viruses, and mark them for destruction.
Why are monoclonal antibodies used in immunotherapy?
Some monoclonal antibodies are also immunotherapy because they help turn the immune system against cancer. For example, some monoclonal antibodies mark cancer cells so that the immune system will better recognize and destroy them.
Can monoclonal antibodies cause side effects?
Monoclonal antibodies can cause side effects, which can differ from person to person. The ones you may have and how they make you feel will depend on many factors, such as how healthy you are before treatment, your type of cancer, how advanced it is, the type of monoclonal antibody you are receiving, and the dose.
What antibodies kill cancer cells?
Other monoclonal antibodies bring T cells close to cancer cells, helping the immune cells kill the cancer cells. An example is blinatumomab (Blincyto®), which binds to both CD19, a protein found on the surface of leukemia cells, and CD3, a protein on the surface of T cells. This process helps the T cells get close enough to ...
What is the purpose of monoclonal antibodies?
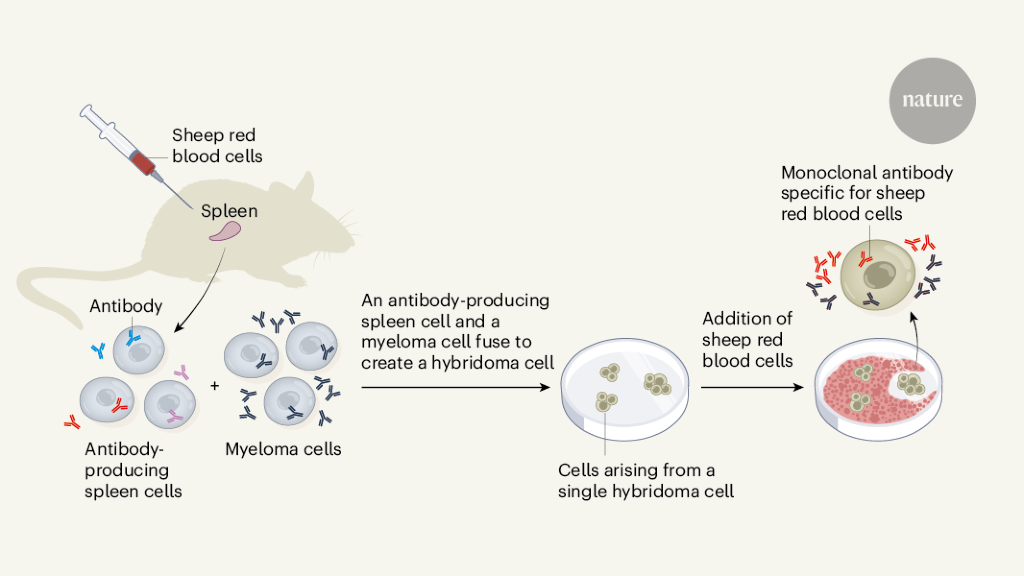
These are known as monoclonal antibodies (mAbs or Moabs). Monoclonal antibodies are used to treat many diseases, including some types of cancer. To make a monoclonal antibody, researchers first have to identify the right antigen to attack.
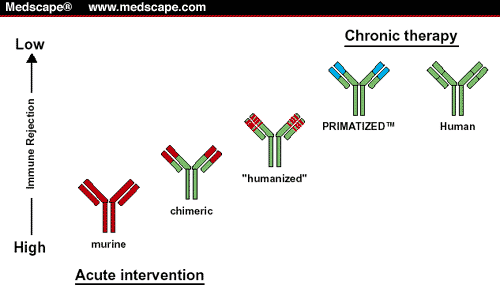
What are monoclonal antibodies made of?
There are 4 different ways they can be made and are named based on what they are made of. Murine: These are made from mouse proteins and the names of the treatments end in -omab. Chimeric: These proteins are a combination of part mouse ...
What are the side effects of mAbs?
It can cause side effects such as high blood pressure, bleeding, poor wound healing, blood clots, and kidney damage.
How does the immune system attack foreign substances?
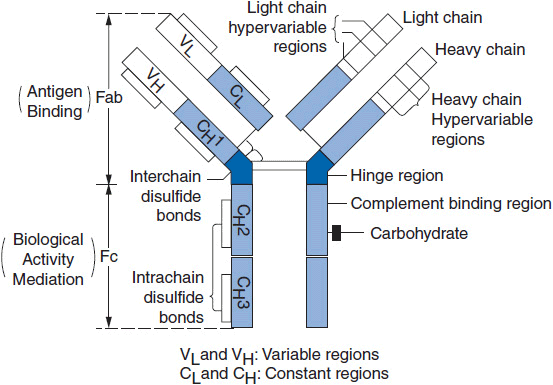
One way the body's immune system attacks foreign substances is by making large numbers of antibodies. An antibody is a protein that sticks to a specific protein called an antigen. Antibodies circulate throughout the body until they find and attach to the antigen. Once attached, they can force other parts of the immune system to destroy ...
What is an antibody?
An antibody is a protein that sticks to a specific protein called an antigen. Antibodies circulate throughout the body until they find and attach to the antigen. Once attached, they can force other parts of the immune system to destroy the cells containing the antigen. Researchers can design antibodies that specifically target a certain antigen, ...
How do antibodies work?
Antibodies circulate throughout the body until they find and attach to the antigen. Once attached, they can force other parts of the immune system to destroy the cells containing the antigen. Researchers can design antibodies that specifically target a certain antigen, such as one found on cancer cells.
What are mAbs made of?
There are 4 different ways they can be made and are named based on what they are made of. Murine: These are made from mouse proteins and the names of the treatments end in -omab.