What is anaerobic wastewater treatment and how does it work?
How do aerobic wastewater treatment systems work?
- Activated sludge. Used widely used in municipal applications, activated sludge processes occur when wastewaters from the primary treatment phase enter an aeration tank.
- Fixed-bed bioreactors, or FBBRs. ...
- Moving bed bioreactors, or MBBRs. ...
- Membrane bioreactors, or MBRs. ...
- Biological trickling filters. ...
What are the different types of anaerobic treatment?
WRRF digesters vary in a number of ways including:
- size and shape;
- processing rate,
- number of stages to the process,
- operating temperature,
- extent of pre-digestion processing; and
- types of mixing strategies.
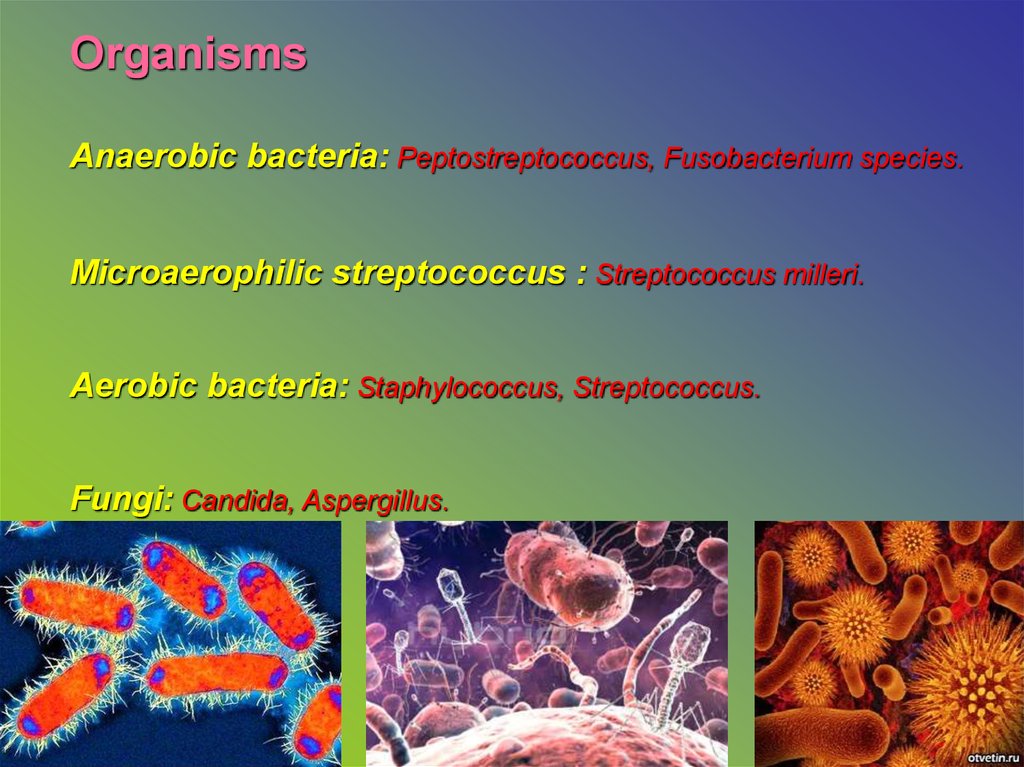
Which antibiotics have anaerobic coverage?
- No cephalosporin covers Enterococcus (except Ceftaroline).
- Only Ceftazidime and Cefepime cover Pseudomonas.
- Only Cefoxitin and Cefotetan have good anaerobic coverage.
What is the primary benefit of anaerobic exercise?
What Are the Pros of Anaerobic Respiration?
- Muscles can respire even when they don’t have oxygen available. When you’re working out, the amount of oxygen the body needs to aerobically respire increases. ...
- It assists aerobic respiration. A unique component of anaerobic respiration is the fact that it can metabolize pyruvic acid. ...
- The body can adapt the energy more quickly. ...

What is anaerobic treatment process?
Anaerobic treatment is a proven and energy-efficient method for treating industrial wastewater. It uses anaerobic bacteria (biomass) to convert organic pollutants or COD (chemical oxygen demand) into biogas in an oxygen-free environment.
What is aerobic and anaerobic treatment?
Aerobic treatment is typically applied to efficiently treat low strength wastewater (COD <1000 mg/L) when the treatment requires the presence of oxygen. Whereas, anaerobic treatment is typically applied to treat wastewater with higher organic loading (COD >4000 mg/L).
What are aerobic treatments?
Aerobic treatment is a biological wastewater treatment process that takes place in the presence of oxygen. Aerobic biomass converts organics in the wastewater into carbon dioxide and new biomass.
Which is better aerobic or anaerobic wastewater treatment?
Since anaerobic treatment is preferred when the dissolved organic concentrations of untreated wastewater are high, aerobic treatment is often used as a secondary treatment process and follows an anaerobic stage.
What's the difference between aerobic and anaerobic?
Aerobic means 'with air' and refers to the body producing energy with the use of oxygen. This typically involves any exercise that lasts longer than two minutes in duration. Continuous 'steady state' exercise is performed aerobically. Anaerobic means 'without air' and refers to the body producing energy without oxygen.
What is the difference between anaerobic and aerobic processes?
There are two types of Respiration: Aerobic Respiration — Takes place in the presence of oxygen. Anaerobic Respiration –Takes place in the absence of oxygen.
What is the difference between aerobic and anaerobic water treatment?
While both rely on a process of microbial decomposition to treat wastewater, the key difference between anaerobic and aerobic treatment is that aerobic systems require oxygen, while anaerobic systems do not. This is a function of the types of microbes used in each type of system.
What is anaerobic system?
The anaerobic energy system (also called the lactic acid system) is the body's way of creating energy in the form of ATP quickly. Primarily using glucose as fuel, this energy system powers the muscles anywhere from ten to thirty seconds for intense efforts.
What is the difference between aerobic and anaerobic septic systems?
Aerobic bacteria need oxygen to live, and anaerobic do not. Both, however, are essential for breaking down waste in septic treatment systems.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of anaerobic treatment of wastewater?
Up-flow or down-flow anaerobic filters: suited to treating wastes containing organic matter in soluble form, which excludes many forms of municipal waste. It is more widely applied to treating industrial wastes. The main disadvantage of the anaerobic filter reactor is the high cost of the filter material.
Is septic tank aerobic or anaerobic?
anaerobic bacterialThe term "septic" refers to the anaerobic bacterial environment that develops in the tank that decomposes or mineralizes the waste discharged into the tank. Septic tanks can be coupled with other onsite wastewater treatment units such as biofilters or aerobic systems involving artificially forced aeration.
What is BOD and COD?
Biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) is the amount of oxygen required by the microorganisms to break down the organic materials, whereas chemical oxygen demand (COD) is the amount of oxygen required to break down the organic material via oxidation.
What are the advantages of anaerobic treatment?
3.5.4.6.1 Advantages of anaerobic treatment processes. Anaerobic treatment processes have several advantages over the aerobic treatment processes. Anaerobic treatment processes require less energy for its operation than the aerobic treatment process. The biomass generation in anaerobic process is six- to eightfolds lower than ...
What is anaerobic digestion?
Anaerobic digestion as a unit process in municipal wastewater treatment has been in use for many years now. It is employed for stabilization of sludge solids from primary and secondary sedimentation tanks either in closed digesters or open lagoons. Anaerobic lagoons are also used for treatment of industrial wastes.
How does anaerobic pool affect COD?
The anaerobic pool can degrade the organic matter and reduce the COD concentration. Under the anaerobic conditions, the refractory organics are hydrolyzed to degradable organic matter easily. At the same time, it can weaken microbial inhibition and toxic effects of some toxic substances.
What pH is toxic to anaerobic?
3.4.5.7 pH and Toxicity. Anaerobic treatment is very sensitive to pH. The process thrives well in the pH range 6.5–7.8, with an optimum pH near neutral. At pH values below 6.0, the reaction rate drops off rapidly, and the resulting acidity can become quite toxic to the methanogens.
Where is the influent zone in anaerobic pool?
The anaerobic pool contains the influent zone, the reaction zone, and the effluent zone. Anaerobic pool influent is located at the pool bottom. The use of perforated pipe or other flowing method requires uniform distribution of leachate. They cannot have dead ends and are easy to maintain management.
Can reactors have dead ends?
They cannot have dead ends and are easy to maintain management. The reactor is a major part of the anaerobic pool. To avoid clogging, there is no filler in the reaction zone. The sludge in the reaction area is generally suspended anaerobic activated sludge and contains a certain amount of granular sludge.
Is wastewater aerobic or anaerobic?
Anaerobic treatment of wastewaters has a number of advantages over aerobic treatment process, namely, the energy input of the system is low, as no energy is required for oxygenation, lower production of excess sludge (biological synthesis) per unit mass of organic matter stabilized, lower nutrient requirement due to lower biological synthesis, and the degradation of waste organic material leads to the production of biogas, which is a valuable source of energy.
What is the role of antimicrobials in anaerobic infection?
The primary role of antimicrobials is to limit the local and systemic spread ...
What is the role of anaerobic bacteria in the body?
The isolation of anaerobes requires appropriate methods of collection, transportation and cultivation of specimens. The lack of use of any of these methods can lead to inadequate recovery of anaerobes and inappropriate therapy. Treatment of anaerobic infection is complicated by the slow growth of these organisms and the growing resistance of anaerobic bacteria to antimicrobials. The primary role of antimicrobials is to limit the local and systemic spread of infection. Surgical drainage is of primary importance. This includes debriding of necrotic tissue, draining the pus, improving circulation, alleviating obstruction and increasing tissue oxygenation. The most effective antimicrobials against anaerobic organisms are metronidazole, the carbapenems (imipenem, meropenem and ertapenem), chloramphenicol, the combinations of a penicillin and a beta-lactamase inhibitor (ampicillin or ticarcillin plus clavulanate, amoxicillin plus sulbactam, and piperacillin plus tazobactam), tigecycline and clindamycin.
What is the role of antimicrobials in a patient's drainage?
The primary role of antimicrobials is to limit the local and systemic spread of infection. Surgical drainage is of primary importance. This includes debriding of necrotic tissue, draining the pus, improving circulation, alleviating obstruction and increasing tissue oxygenation.
What is anaerobic digestion?
Anaerobic digestion is a process in which microorganisms convert organic matter into biogas in the absence of oxygen. Anaerobic treatment is typically utilized to treat warm, high-strength industrial wastewater containing high concentrations of biodegradable organic matter. This energy-efficient process reliably removes biochemical oxygen demand ...
What is the process of removing organics from wastewater?
As organics are removed from the wastewater during the anaerobic digestion process , methane-rich biogas is produced. Anaerobic digestion produces very little excess sludge & with treatment the agriculturally-beneficial sludge can safely be applied to land as fertilizer.
What is anaerobic treatment?
Anaerobic treatment of wastewater may be used to treat industrial wastewater. This type of wastewater often contains high levels of organic matter in warmer temperatures. Anaerobic treatment systems may be used in areas where a central treatment plant is not possible.
What is aerobic bacteria?
The aerobic bacteria in sewage treatment feed on the water, which is mixed with air. The bacteria reproduce and continue to attack the waste, with some waste settling on the bottom of water as sludge. This sludge may be pumped out of the system so that the system is not clogged.
What are the two types of wastewater treatment?
Two primary types of wastewater treatment processes are aerobic and anaerobic. Aerobic and anaerobic wastewater treatment help prevent waterborne diseases and improve the biological water quality, which is necessary for a population’s overall health.
What is biogas used for?
The biogas can be used to produce electricity and heat and serve as a renewable energy source that effectively replaces fossil fuels . However, the anaerobic wastewater treatment process provides some oversight to ensure that the methane-rich biogases are properly released.
Why is air circulated throughout wastewater treatment?
In the aerobic process, air is circulated throughout a treatment in order to cause bacteria that break down waste within the wastewater. Electricity is used throughout the process. Some systems may use a pre-treatment process that reduces solids that aerobic bacteria may have difficulty compressing.
Is aerobic treatment more expensive than alternative treatment?
Aerobic treatment units are typically more expensive to operate than alternative processes. The operation requires continued use of electricity, and solids must be pumped out of the system frequently. Additionally, professionals must inspect and maintain electrical and mechanical components. The septic tanks must also be maintained.
Is anaerobic wastewater treatment more efficient than aerobic?
In comparison, the anaerobic wastewater treatment process is typically more economically friendly for the following reasons: The anaerobic treatment of wastewater generates much less sludge than the aerobic treatment does. The sludge produced in anaerobic wastewater treatment can be used for soil enrichment.