When to start anti-aging treatments?
Depending on how a problem the acne has been, you may want to consider starting at around age 20 to 25 for anti-aging therapy, but earlier (even as early as age 9, with your doctor's guidance) for prophylactic anti-acne therapy.
How to prevent aging naturally?
- Global fashion icon Trinny Woodall has launched two skincare products
- It's a world first for Trinny, 58, who's the founder of beauty empire Trinny London
- She launched the Better Off gel cleanser and Be Your Best Enzyme balm cleanser
- It's essential to cleanse your face properly to prevent fine lines and wrinkles
What is the cure for aging?
“The Alliance for Aging Research supports HHS Secretary Becerra’s announcement today ordering Medicare to reconsider its 2022 Part B premium increase after Biogen reduced the list price by 50 percent for Aduhelm, its FDA-approved monoclonal antibody therapy (mAB) targeting amyloid for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease.
What is T6 heat treatment?
T6 Heat Treatment is a two-phase process which is applied to Aluminium, Copper, or Silicon alloys to increase the strength of the alloy by as much as 30%. Phase One – Quenching The alloy is heated to 500⁰C for 9-10 hours which causes the copper to dissolve in the aluminium and form the Single Phase Alloy.

What is ageing in heat treatment process?
Ageing is a process used to increase strength by producing precipitates of the alloying material within the metal structure.
What is aging treatment?
Artificial aging is the treatment of a metal alloy at elevated temperatures so as to accelerate the changes in the properties of an alloy as a result of the casting and forging process. Generally, the chemical properties of newly cast and forged metals naturally change and settle very slowly at room temperature.
What is aging process of metals?
Metal aging is a process used on solution heat-treated metal alloys that can be done artificially or happen naturally. Natural aging occurs throughout the life of the metal alloy. During the natural aging process, super-saturated alloying elements within the metal alloy form what are known as metal precipitates.
What defines aging?
Aging is the sequential or progressive change in an organism that leads to an increased risk of debility, disease, and death. Senescence consists of these manifestations of the aging process.
What is the normal aging process?
What's happening. With age, bones tend to shrink in size and density, weakening them and making them more susceptible to fracture. You might even become a bit shorter. Muscles generally lose strength, endurance and flexibility — factors that can affect your coordination, stability and balance.
What is ageing in material?
Ageing of materials or products implies changes of the original state, but it does not necessarily only comprise deterioration or degradation. Ageing can also mean formation of new substances and stabilisation. In some cases this effect is desirable.
What is the purpose of aging metal?
The basics of metal aging Metal aging is used on solution heat treated alloys in order to increase their strength and hardness, while reducing their ductility. This can be done naturally—simply by letting the metal alloy hang out for years on end—or it can be done artificially.
What is aging in aluminium?
8.6. 4 Thermal ageing of aluminium. Ageing is the process that transforms the supersaturated solid solution to precipitate particles that can greatly enhance the strength properties. It is the formation of precipitates that provide aluminium alloys with the mechanical properties required for aerospace structures.
What is annealing heat treatment process?
annealing, treatment of a metal or alloy by heating to a predetermined temperature, holding for a certain time, and then cooling to room temperature to improve ductility and reduce brittleness.
What happens in the ageing process?
At the biological level, ageing results from the impact of the accumulation of a wide variety of molecular and cellular damage over time. This leads to a gradual decrease in physical and mental capacity, a growing risk of disease and ultimately death.
What are the 3 types of aging?
The 3 Unique Kinds of AgingBiological Aging. This is the type of aging most people are familiar with, since it refers to the various ways the human body naturally changes over time. ... Psychological Aging. ... Social Aging.
What causes aging?
According to this theory, aging is caused by changes in hormones, which are produced by the endocrine system. Immunological theory. Also called the autoimmune theory, this is the idea that the immune response is designed to decline. The result is disease and aging.
How does heat treatment affect aging?
The heat treatment aging process involves elevating the temperature of an alloy to change its properties. The process accelerates changes in an alloy’s properties through a series of heat treatments. When the aging process occurs at room temperature, the chemical properties of newly cast and forged metals will transform and settle very slowly. Artificial heat aging involves much higher temperatures and accelerates the process of changing and settling. This process of aging ensures a high degree of quality and a level of accuracy that can meet the standards of very precise specifications. Benefits include:
What is the aging process used for?
One of these, the aging process, can be used for strengthening alloys and giving them important properties for industrial applications .
What is metal heat treatment?
Metal heat treatments are designed to alter the properties of a metal without changing its shape. Heat treatment in Gastonia, NC is a process that can be applied to a variety of materials and is used for many different reasons. Treating metal with heat can change its physical and chemical properties to alter factors like the strength of the metal, how brittle it is and its softness or hardness. Depending on the industry and the application that a metal component will be used for, different heat treatments might be employed. One of these, the aging process, can be used for strengthening alloys and giving them important properties for industrial applications.
What happens when a metal is aging at room temperature?
When the aging process occurs at room temperature, the chemical properties of newly cast and forged metals will transform and settle very slowly. Artificial heat aging involves much higher temperatures and accelerates the process of changing and settling.
How does aging affect metal?
Aging increases the stability of a metal component. It restores the equilibrium of the metal and eliminates any unstable conditions. Increased properties: In addition to the strength and stability that the aging process offers, it can also add valuable properties to the item that is being treated. Aging can give a piece ...
Does aging increase the strength of a metal?
Strengthening: The aging process can greatly increase the strength of a metal component . This allows your component to be used for a variety of applications that require durability and strength.
Does aging give metal coercivity?
Aging can give a piece of metal high coercivity, which is an important property that can be very beneficial. Speed: Aging heat treatment in Gastonia, NC is a relatively rapid process, which means that you can have your component treated in a short period of time.
What is the aging process?
The aging process is just one of several steps featured in the process of precipitation hardening, with the others being solution treatment and quenching. In precipitation heat treatment, the solution gets heated up to a moderate temperature to induce precipitation. The material then gets held at that temperature for a specific period of time.
How does artificial aging work?
Artificial aging, then, occurs when the metal alloy is treated at elevated temperatures to accelerate the changes in properties you’d find in the natural aging process and as a result of casting and forging. The chemical properties in the cast and forged materials will change quite slowly at room temperature, so this process speeds it up and also allows for more control and higher quality in those property changes. Manufacturers are also able to use artificial aging to make parts ready for machines much faster.
Why is aging important?
Aging is an essential step that ensures that the materials in the alloy do not revert to their original configuration after a time period. Aging is performed under controlled conditions so that the resultant grain structure will create a greater tensile strength in the metal than in its former state.
What are the benefits of aging?
Aging not only helps to enhance high strength of alloys but helps them to acquire other valuable properties such as high coercivity. In addition, aging tends to restore the equilibrium in the metal and to eliminate any unstable conditions brought upon by a prior operation.
How does artificial aging affect the properties of metals?
Artificial aging is the treatment of a metal alloy at elevated temperatures so as to accelerate the changes in the properties of an alloy as a result of the casting and forging process. Generally, the chemical properties of newly cast and forged metals naturally change and settle very slowly at room temperature. Artificial aging will speed up this change more rapidly at higher temperatures. This process ensures quality and accuracy in close tolerance specifications. It also helps manufacturers make machine-ready parts available much more quickly to machinists and distributors.
What are the three criteria for precipitation hardening?
To perform precipitation hardening, there has to be three criteria - appreciable maximum solubility, a solubility curve that reduces quickly with temperature, and composition of the alloy that is less than the maximum solubility.
Why is artificial aging important?
Artificial aging will speed up this change more rapidly at higher temperatures. This process ensures quality and accuracy in close tolerance specifications. It also helps manufacturers make machine-ready parts available much more quickly to machinists and distributors.
What is it called when you age at room temperature?
Aging that occurs at room temperature is referred as natural aging.
Why do metals change over time?
Basic construction metals tend to physically transform over time due to natural environmental conditions. The texture and color of the metal surface changes with an oxide layer forming on it in the initial stages. Soon this layer converts to a hydroxide layer. Later this hydroxide layer combines with other elements in the atmosphere and finally ...
How does ageing increase strength?
Ageing is a process used to increase strength by producing precipitates of the alloying material within the metal structure. Solution treatment is the heating of an alloy to a suitable temperature, holding it at that temperature long enough to cause one or more constituents to enter into a solid solution and then cooling it rapidly enough to hold these constituents in solution. Subsequent precipitation heat treatments allow controlled release of these constituents either naturally (at room temperature) or artificially (at higher temperatures).
What is precipitation hardening?
Precipitation hardening: Stainless steels. Precipitation heat treatments strengthen materials by allowing the controlled release of constituents to form precipitate clusters which significantly enhance the strength of the component. Solution and age. Ageing is a process used to increase strength by producing precipitates ...
What is the process of increasing the strength of an alloy?
Solution and age. Ageing is a process used to increase strength by producing precipitates of the alloying material within the metal structure. Solution treatment is the heating of an alloy to a suitable temperature, holding it at that temperature long enough to cause one or more constituents to enter into a solid solution ...
What are the 12 heat treatment processes?
Annealing, normalizing, quenching, tempering, quenching and tempering … totally 12 heat treatment processes. This article will help you sort out.
When should steel be cold treated?
Application key: (1) Steel parts should be cold treated immediately after quenching, and then tempered at low temperature to eliminate internal stress during low temperature cooling; (2) Cold treatment is mainly applicable to tight tools, measuring tools and tight parts made of alloy steel.
What temperature is steel tempered at?
After heat preservation, quenching is performed, and then tempered at a temperature of 400-720 degrees.
What is normalizing steel?
Normalizing is usually used as a pre-treatment process for forgings, weldments and carburized parts. For low- and medium-carbon carbon layout steels and low-alloy steel parts with low functional requirements can be performed with the final heat treatment.
How long to keep steel in furnace?
Heat the steel to 80 – 200 degrees, keep it for 5 – 20 hours or longer , then take it out of the furnace and cool it in the air.
How hot should carburizing medium be?
Put the steel parts in the carburizing medium, heat it to 900-950 degrees and keep it warm, so that the surface of the steel parts can obtain a carburizing layer with a certain concentration and depth.
What Does Age Hardening Mean?
In metallurgy, age hardening is a heat treatment technique used to increase the hardness of an alloy by a relatively low-temperature heat treatment that causes precipitation of components or phases of the alloy from the supersaturated solid solution.
Why do alloys need to be aged?
Unlike ordinary tempering, alloys must be kept at elevated temperature for hours, or "aged," to allow precipitation to take place. Age hardening creates changes in physical and mechanical properties by producing fine particles of a precipitate phase, which impede the movement of dislocations, or defects in a crystal's lattice.
Is age hardening good for corrosion?
Age hardening gives moderate to good corrosion resistance. For example, age hardening stainless steels are used where high strength and good corrosion resistance are required as well as for applications requiring high fatigue strength, good resistance to galling and stress corrosion resistance. Alloys made by the age-hardening process have many ...
Why is heat treatment important?
It is very important manufacturing process that can not only help the manufacturing process but can also improve the product, its performance, and its characteristics in many ways. By Heat Treatment process, Example: The plain carbon steel. The following changes may be achieved: The hardness of Steel may be increased or decreased.
Why is heat treated steel used?
This heat treatment process is usually carried for low and medium carbon steel as well as alloy steel to make the grain structure more uniform and relieve the internal stresses.
What are the changes in steel?
The following changes may be achieved: The hardness of Steel may be increased or decreased. Internal stresses that are set up due to cold or hot working may be relieved. The machinability of Steel may be enhanced. The mechanical properties like tensile strength the Talati shock resistance toughness etc may be improved.
What is hardening steel?
Hardening is a heat treatment process carried out to increase the hardness of Steel.
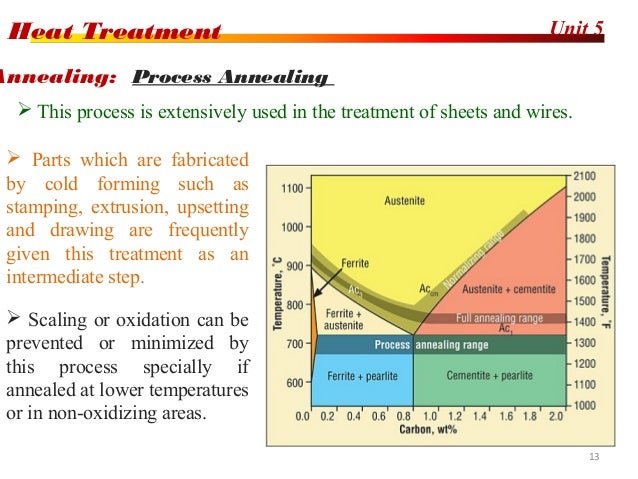
Why is annealing done?
Annealing is carried out for such parts to remove the internal stresses and make them more ductile and less brittle.
What is annealing in metal?
Annealing is carried out for accomplishing one or more of the following: Softening of a metal or alloy. This may be done due to improving machinability. Relieving internal residual stresses caused by the various manufacturing process. Refining the grain size of the metal or alloy.
What is normalizing steel?
Normalizing is a heat treatment process similar to annealing in which the Steel is heated to about 50 degree Celsius above the upper critical temperature followed by air cooling. This results in a softer state which will be lesser soft than that produced by annealing.
What is heat treatment?
Heat treatment is a heating and then cooling process using predefined methods to achieve desired mechanical properties like hardness , ductility, toughness, strength, etc. It is the combination of thermal, industrial, and metalworking processes to alter the mechanical properties and chemical properties of metals.
How does heat treatment change mechanical properties?
During the whole process, the mechanical properties get changed due to changes in microstructure. All metallic metals have grains which are nothing but microstructures of crystals. The nature of those grains determines the behavior of the mechanical properties of a metal. Heat treatment changes that mechanical structure by controlling the rate ...
How does heat treatment help metals?
Heat treatment assist in improving the ductility of metal in the annealing process. Heat treatment helps in hardening metals. Case hardening helps in hardening only the outer surface of the metal piece keeping the rest of the portion soft and ductile. Machinability of metals gets improved.
How is annealing done?
Annealing is done by heating the metals at the above critical temperature , hold them there for some time and then cool it at a very slow rate in the furnace itself. Annealing is usually done on ferrous and non-ferrous metals to reduce hardness after the cold working process.
What is annealing in metals?
Annealing. Annealing is a heat treatment process that is used to soften the metal. In other words, annealing helps to improve ductility, machinability, and toughness. On the flip side, the hardness of metals gets reduced. Annealing does this by changing the microstructure of metals.
How does tampering work?
Tampering is a very common process for machine tools, knives, etc. Tampering is usually done by heating the metal at a relatively low temperature. The temperature depends on the required mechanical properties of metals.
How many types of annealing processes are there?
There are two types of annealing process which are shown below.
