When to start ADT,?
These include: Salvage surgery or radiation, if your doctor thinks the cancer is still confined to the “prostate bed,” the area around... Immunotherapy; a vaccine such as Provenge, designed to boost your body’s ability to fight off the cancer. Early chemotherapy. A clinical …
How to disable ADT?
Androgen deprivation therapy (ADT) ADT injections. The most common form of ADT involves injecting medicine to block the production of testosterone. The... Intermittent ADT. Occasionally ADT injections are given in cycles and continue until your PSA level is low. Injections... Anti-androgen tablets. ...
When to start ADT with a PSA only recurrence?
Androgen deprivation therapy (ADT) is widely used in the community setting to treat men with clinically localized... The dramatic clinical effects of suppressing serum testosterone levels in men with advanced prostate cancer were first... The monthly depot of …
What is the true cost of ADT pulse?
Types of hormone therapy Treatment to lower testicular androgen levels. Androgen deprivation therapy, also called ADT, uses surgery or medicines... Treatment to lower androgen levels from the adrenal glands. LHRH agonists and antagonists can stop the testicles from... Drugs that stop androgens from ...
How is ADT therapy administered?
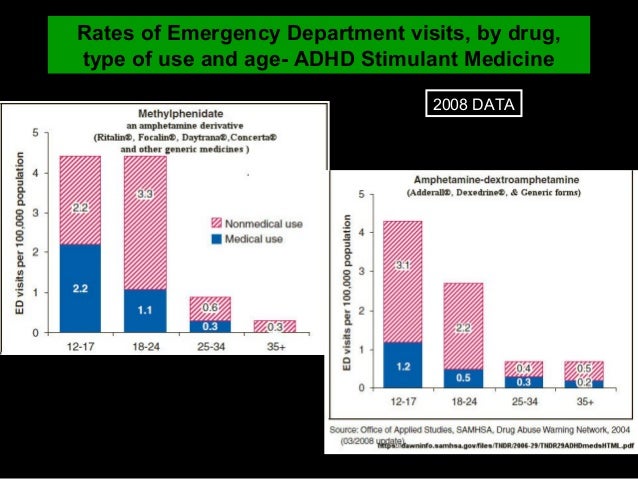
The most common form of ADT involves injecting medicine to block the production of testosterone. The injections can be given by your GP or specialist. How often you have injections depends on the drug – they may be given monthly, every three months or every six months. They can help slow the cancer's growth for years.
What is ADT cancer treatment?
Hormone therapy (also called androgen deprivation therapy or ADT) is part of the standard of care for advanced and metastatic prostate cancer. ADT is designed to either stop testosterone from being produced or to directly block it from acting on prostate cancer cells.
How long does ADT therapy last?
Patients typically receive ADT for two to three years, based on previous clinical trials that established that long-term ADT (28-36 months) is more effective than short term ADT (4-6 months).Mar 14, 2018
Is ADT a form of chemotherapy?
Chemotherapy is now often recommended in combination with ADT as the initial treatment for males whose cancer has already spread outside of the prostate, typically to the bones or other organs.Oct 5, 2021
Is Lupron ADT therapy?
LUPRON DEPOT, an androgen deprivation therapy (ADT), has been a pioneer in the treatment of advanced prostate cancer.
When do ADT side effects start?
ADT impacts both erectile function and libido. These effects are directly linked to testosterone decline and as a result, sexual side effects occur usually within the first year of ADT initiation [19].
Does ADT shrink the prostate?
Generally, reports showed that after 3 to 8 months of ADT, including an LHRH agonist with or without an antiandrogen, results in a prostate size decrease from 20%–50% [16-18].Dec 26, 2016
Will my testosterone come back after hormone therapy?
If you stop your hormone therapy, your testosterone levels will gradually rise again and some side effects will reduce. Your side effects won't stop as soon as you finish hormone therapy – it may take several months. Surgery to remove the testicles (orchidectomy) can't be reversed, so the side effects are permanent.
Is ADT a radiation?
These are the most common: * Intermediate-risk men who are given six months of ADT plus external-beam radiation; * High-risk men who are getting radiation therapy. This is a finite course of ADT, and this combination – two or three years of ADT plus external-beam radiation – has been proven to cure cancer in many men.
Does ADT lower PSA?
The presence of distant metastases at the initiation of ADT, a higher PSA nadir after ADT, a higher velocity of PSA decline, and a time to reach PSA nadir of <9 months are associated with an increased risk of progression to CRPC.
How long do you have hormone treatment before radiotherapy?
You might have hormone therapy before, during and after radiotherapy. Doctors usually recommend that you have the treatment for between 3 months and 3 years. How long depends on the risk of your cancer coming back and how many side effects you get.
Where is brachytherapy done?
Placement may be inside a body cavity or in body tissue: Radiation placed inside a body cavity. During intracavity brachytherapy, a device containing radioactive material is placed in a body opening, such as the windpipe or the vagina. The device may be a tube or cylinder made to fit the specific body opening.Jun 19, 2020
When Is Hormone Therapy used?
Hormone therapy may be used: 1. If the cancer has spread too far to be cured by surgery or radiation, or if you can’t have these treatments for som...
Possible Side Effects of Hormone Therapy
Orchiectomy and LHRH agonists and antagonists can all cause similar side effects from lower levels of hormones such as testosterone. These side eff...
Current Issues in Hormone Therapy
There are many issues around hormone therapy that not all doctors agree on, such as the best time to start and stop it and the best way to give it....
What is ADT therapy?
ADT: What You Really Need to Know. The only people who really like androgen deprivation therapy (also called ADT, or hormonal therapy) are the drug companies that make billions of dollars a year selling the drugs. Doctors don’t like it, and men don’t like being on these drugs. So why do it?
How to get mad at yourself?
You will need to get mad at it. Work hard to take back your life – work doubly hard, because not only will it try to turn you into a tub of butter, but you might get mildly depressed. Your brain will tell you that you’re too tired to exercise. It’s deceiving you. You must not listen to it. Exercise anyway.
What is provenge in cancer?
Immunotherapy; a vaccine such as Provenge, designed to boost your body’s ability to fight off the cancer. Early chemotherapy. A clinical trial testing a promising new drug. Don’t get us wrong; we’re not hating on ADT. If you need it, you need it. But it’s not just like taking a vitamin supplement or getting a flu shot.
Does ADT help with diabetes?
A big gut equals a bigger risk for diabetes, heart attack and stroke. All of this is magnified with ADT. Maybe you already have some of these risk factors; maybe you’ve already had a heart attack, or you’ve got diabetes. If you need ADT, you need it.
What is the fat around your belly called?
Elevated blood pressure; unhealthy levels of blood sugar, cholesterol, and triglycerides; and abdominal fat – a big jelly donut of visceral fat, also known as “heart attack fat,” right around your belly, a cardiac spare tire. A big gut equals a bigger risk for diabetes, heart attack and stroke.
Does exercise help with depression?
Exercise will help with depression, with the cardiac risks, and with the risk to your brain. As University of Colorado radiation oncologist E. David Crawford, M.D., recently put it, “What’s heart healthy is usually prostate-cancer healthy….
Does ADT cause cognitive impairment?
Male hormones including testosterone are called androgens, and ADT basically shuts down all of those hormones. ADT has a lot of side effects, including a higher risk of cognitive impairment, but the biggest elephant in the room is the fact that men on ADT lose their sex drive and ability to have an erection.
What is ADT treatment?
Androgen deprivation therapy (ADT) for prostate cancer. Prostate cancer needs testosterone to grow. Reducing how much testosterone your body makes may slow the cancer’s growth or shrink the cancer temporarily. Testosterone is an androgen (male sex hormone), so this treatment is called androgen deprivation therapy (ADT).
What is ADT injection?
It is also known as hormone therapy. There are different types of ADT that may be used. Learn more about: ADT injections. Intermittent ADT. Anti-androgen tablets. Removing the testicle (orchidectomy) Side effects of ADT. Listen to podcasts on Making Treatment Decisions and Coping with a Cancer Diagnosis.
How often do you give ADT?
The injections can be given by your GP or specialist and are usually given every three months. They can help slow the cancer’s growth for years.
What are the side effects of ADT?
Side effects may include: tiredness (fatigue) reduced sex drive (low libido) erection problems. loss of muscle strength. hot flushes and sweating. weight gain, especially around the middle.
What are the risks of taking vitamin D supplements?
loss of bone density (osteoporosis) – calcium and vitamin D supplements and regular exercise help reduce the risk of osteoporosis. higher risk of diabetes, high cholesterol and heart disease – your doctor will assess these risks with you.
Can you restart ADT injections?
Occasionally ADT injections are given in cycles and continue until your PSA level is low. Injections can be restarted if your PSA rises again. This is known as intermittent ADT. In some cases, this can reduce side effects. It is not suitable for everyone.
What is the goal of hormone therapy?
The goal is to reduce levels of male hormones, called androgens, in the body, or to stop them from fueling prostate cancer cells. Androgens stimulate prostate cancer cells to grow. The main androgens in the body are testosterone ...
What hormones are used to remove testicles?
Estrogens (female hormones) were once the main alternative to removing the testicles (orchiectomy) for men with advanced prostate cancer. Because of their possible side effects (including blood clots and breast enlargement), estrogens have been replaced by other types of hormone therapy.
What are the main androgens in the body?
The main androgens in the body are testosterone and dihydrotestosterone (DHT). Most androgen is made by the testicles, but the adrenal glands (glands that sit above your kidneys) as well as the prostate cancer itself, can also make a fair amount.
Is prostate cancer permanent?
It is probably the least expensive and simplest form of hormone therapy. But unlike some of the other treatments, it is permanent, and many men have trouble accepting the remo val of their testicles.
What is the effect of orchiectomy?
Orchiectomy (surgical castration) Even though this is a type of surgery, its main effect is as a form of hormone therapy. In this operation, the surgeon removes the testicles, where most of the androgens (such as testosterone and DHT) are made. This causes most prostate cancers to stop growing or shrink for a time.
Can LHRH antagonists cause prostate cancer?
LHRH antagonists can be used to treat advanced prostate cancer. These drugs work in a slightly different way from the LHRH agonists, but they lower testosterone levels more quickly and don’t cause tumor flare like the LHRH agonists do. Treatment with these drugs can also be considered a form of medical castration.
What is the receptor that helps prostate cancer cells grow?
For most prostate cancer cells to grow, androgens have to attach to a protein in the prostate cancer cell called an androgen receptor . Anti-androgens are drugs that also connect to these receptors, keeping the androgens from causing tumor growth. Anti-androgens are also sometimes called androgen receptor antagonists.
What is the procedure to remove testicles?
This form of hormone therapy (also called androgen deprivation therapy, or ADT) includes: Orchiectomy, a surgical procedure to remove one or both testicles. Removal of the testicles, called surgical castration , can reduce the level of testosterone in the blood by 90% to 95% ( 5 ).
What is the LHRH agonist?
LHRH agonists are given by injection or are implanted under the skin. Four LHRH agonists are approved to treat prostate cancer in the United States: leuprolide (Lupron), goserelin (Zoladex), triptorelin (Trelstar), and histrelin (Vantas).
What is the most common treatment for prostate cancer?
Treatments that reduce androgen production by the testicles are the most commonly used hormone therapies for prostate cancer and the first type of hormone therapy that most men with prostate cancer receive. This form of hormone therapy (also called androgen deprivation therapy, or ADT) includes:
Which hormone is responsible for the production of testosterone?
Drawing shows that testosterone production is regulated by luteinizing hormone (LH) and luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone (LHRH). The hypothalamus releases LHRH, which stimulates the release of LH from the pituitary gland. LH acts on specific cells in the testes to produce the majority of testosterone in the body.
Does exercise help with bone loss?
However, drugs to treat bone loss are associated with a rare but serious side effect called osteonecrosis of the jaw ( 20 ). Exercise may help reduce some of the side effects of hormone therapy, including bone loss, muscle loss, weight gain, fatigue, and insulin resistance ( 20, 32 ).
What does it mean when your PSA is high?
An increase in PSA level may indicate that a man’s cancer has started growing again. A PSA level that continues to increase while hormone therapy is successfully keeping androgen levels extremely low is an indicator that a man’s prostate cancer has become resistant to the hormone therapy that is currently being used.
Where are androgens produced?
Most of the remaining androgens are produced by the adrenal glands . Androgens are taken up by prostate cells, where they either bind to the androgen receptor directly or are converted to dihydrotestosterone (DHT), which has a greater binding affinity for the androgen receptor than testosterone.
What are the side effects of ADT?
It is associated with numerous side effects that can influence quality of life. Hot flushes, sexual dysfunction, gynecomastia, osteoporosis, metabolic syndrome, and depression are well-described complications of ADT. The implications of ADT use for risks ...
What is the treatment for metastatic prostate cancer?
The standard treatment for men with metastatic prostate cancer is androgen deprivation therapy (ADT). This therapy is associated with a multitude of side effects that can impact quality of life. These include vasomotor complications (in particular, hot flushes), sexual dysfunction and gynecomastia, osteoporosis, metabolic syndrome, and depression.
Does ADT cause weight gain?
A variety of metabolic changes have been observed with ADT, including weight gain, dyslipidemia, hyperglycemia, and sarcopenia. Weight gain, specifically, is a well-recognized side effect of ADT. [20-22] Retrospective studies have found that men on ADT for nonmetastatic prostate cancer had a median weight gain of 1 to 2 kg after 1 year ...
Is ADT associated with CVD?
There are conflicting data on the risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD) with use of ADT. Currently, there are no prospective randomized controlled data assessing the association of ADT use with risk of CVD. In a large retrospective population-based cohort study, multivariate analyses demonstrated that men with newly diagnosed prostate cancer who received ADT had a 20% increased risk of CVD. [41] Somewhat paradoxically, the study found that men receiving treatment for less than 12 months were at higher risk for cardiovascular events compared with men who had been on ADT for longer. A major limitation of this study is that the researchers were unable to control for smoking and obesity, which are two major risk factors for CVD and could confound the results. Additionally, age was a major variable associated with CVD. A meta-analysis of eight large trials found no significant differences in risk of CVD in patients receiving ADT vs controls, nor was duration of ADT significantly associated with increased risk of CVD. [42]
Can men with prostate cancer take ADT?
Currently, no specific recommendation adjustments for men with prostate cancer receiving ADT should be pursued outside of primary prevention, including smoking cessation, and secondary prevention, including glycemic control, lipid-lowering therapy, and aspirin therapy for men with coronary artery disease.
Does ADT cause hot flushes?
Hot flushes are one of the most common and bothersome side effects associated with ADT. Up to 80% of patients undergoing treatment with GnRH agonists will experience hot flushes, with 27% of these patients reporting this symptom as the most significant adverse side effect. [3] .
Does EBRT cause erectile dysfunction?
Several studies have shown that treatment for clinically localized prostate cancer involving either radical prostatectomy, brachytherapy, or external beam radiotherapy (EBRT) can result in long-term erectile dysfunction. [9,10] Patients receiving neoadjuvant ADT with EBRT were found to have decreased frequency of erection, decreased overall sexual function, and an increase in frequency of hot flushes. [11] In addition, loss of libido is a major consequence of ADT. The degree of erectile dysfunction for patients on ADT is impacted by pretreatment sexual function, as well as by changes in libido; in patients previously able to attain an erection, phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitors, intracavernosal injection therapy, vacuum-assisted devices, or other topical agents may be used. Given the complex interplay between physiology, psychology, stress, and emotion involved in sexual function, a referral to a psychology or counseling service with a focus on sexual health is recommended for interested patients and their partners.
What are the side effects of ADT?
Often called chemical castration, the effects mimic those in men who have had both testicles removed (orchiectomies, also known as surgical castration.) Possible side-effects of ADT include: Hot flashes. Decreased libido and erectile dysfunction (not being able to have an erection)Loss of energy, general weakness.
How many modules does Brian Lawenda have?
Did you enjoy this article? Dr. Brian Lawenda has developed a comprehensive 25-module course dedicated to cancer health and prevention. Enroll today for 30 days free access to the first two modules. This includes a personal cancer risk assessment.
What is Xtandi used for?
Xtandi is used effectively in men with (1-10) Newly diagnosed hormone sensitive metastatic prostate cancer. Rising PSA and no other evidence of disease.
How many patients were in the Prosper trial?
PROSPER is a comparative clinical trial that enrolled approximately 1,400 patients with non-metastatic CRPC that had progressed, based on a rising PSA level despite ADT, but who had no symptoms and no prior or present evidence of metastatic disease. The trial directly compared Xtandi plus ADT to ADT alone.
What are the different types of prostate cancer?
by Dr. C.H. Weaver M.D. updated 6/2020 1 Newly diagnosed hormone sensitive metastatic prostate cancer 2 Rising PSA and no other evidence of disease 3 Non-metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (NM-CRPC) 4 Metastatic CRPC. 5 In combination with Keytruda Immunotherapy
What is the treatment for prostate cancer?
This type of treatment is referred to as androgen deprivation therapy (ADT).
How many men die from prostate cancer?
An estimated 220,800 new cases of prostate cancer are diagnosed annually in the U.S., with more than 27,500 men dying from the disease. Prostate cancer is stimulated to grow from exposure to the male hormone, testosterone.
Does ADT cause prostate cancer?
The combination of ADT plus an anti-androgen drug shuts off the supply of testosterone, which is the fuel that drives prostate cancer growth. Traditionally this had been accomplished with ADT + a non-steroidal anti-androgen medication.
Does Xtandi delay chemotherapy?
Results of a phase III trial reported at the 2014 American Society of Clinical Oncology Annual Meeting demonstrated that treatment with Xtandi® significantly delays the need for chemotherapy in metastatic prostate cancer patients previously treated with hormone therapy.
