
What is an open fracture?
6 rows · Open fracture with extensive soft-tissue laceration, damage, or loss or an open segmental ...
What to do if you have an open fracture?
Overview of concepts and treatments in open fractures Open fractures are one of the few lower extremity surgical emergencies. These injuries require immediate treatment. If untreated, severe cases of open fracture can be limb threatening. This article is a review of the literature of open fractures and the current treatment guidelines.
What are the treatment options for open fracture wounds?
For this reason, early treatment for an open fracture focuses on preventing infection at the site of the injury. The wound, tissues, and bone must be cleaned out in a surgical procedure as soon as possible. The fractured bone must also be stabilized to allow the wound to heal. Illustration and x-ray show an open fracture.
How is an open fracture stabilized?
Aug 14, 2021 · Open Fracture Management - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf. An open fracture is an injury where the fractured bone and/or fracture hematoma are exposed to the external environment via a traumatic violation of the soft tissue and skin. The skin wound may lie at a site distant to the fracture and not directly over it.
What are the three types of treatment for fractures?
Diagnosis and treatment of bone fracturesSplints – to stop movement of the broken limb.Braces – to support the bone.Plaster cast – to provide support and immobilise the bone.Traction – a less common option.Surgically inserted metal rods or plates – to hold the bone pieces together.Pain relief.
What are the types of open fractures?
Classification of Open FracturesType 1: <1cm wound and clean.Type 2: 1-10cm wound and clean.Type 3A: >10cm wound and high-energy, but with adequate soft tissue coverage.Type 3B: >10cm wound and high-energy, but with inadequate soft tissue coverage.Type 3C: All injuries with vascular injury.
What is the management or treatment for close and open fractures?
Options for wound closure in the treatment of open fractures include primary closure of the skin, split-thickness skin-grafting, and the use of either free or local muscle flaps. The timing of open wound closure has proponents in the immediate, early, and delayed categories.
What is a Type 1 open fracture?
They categorized open injuries into the familiar three categories, based on wound size, level of contamination, and osseous injury, as follows: Type I = an open fracture with a wound less than 1 cm long and clean; Type II = an open fracture with a laceration greater than 1 cm long without extensive soft tissue damage, ...May 9, 2012
What are Type 1 and Type 2 fractures?
Type I: clean wound smaller than 1 cm in diameter, appears clean, simple fracture pattern, no skin crushing. Type II: a laceration larger than 1 cm but without significant soft-tissue crushing, including no flaps, degloving or contusion. Fracture pattern may be more complex.May 21, 2015
What are the 7 types of fractures?
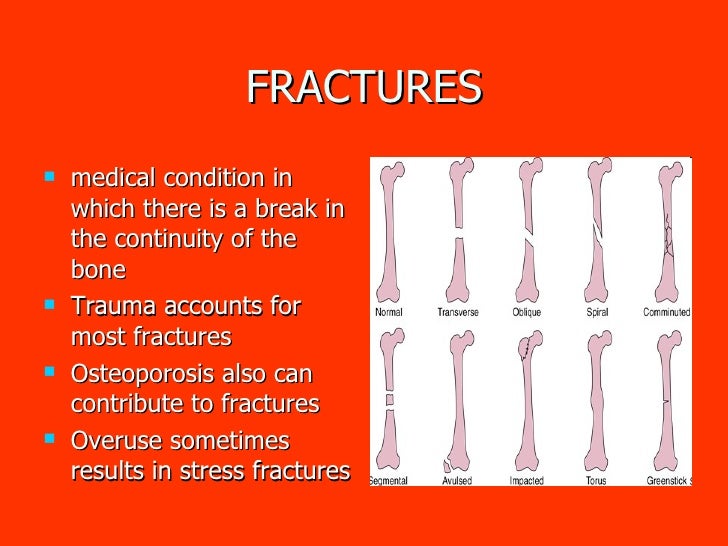
Different types of bone fractures can be open, closed, stable, displaced, partial, or complete.Transverse Fracture. Transverse fractures are breaks that are in a straight line across the bone. ... Spiral Fracture. ... Greenstick Fracture. ... Stress Fracture. ... Compression Fracture. ... Oblique Fracture. ... Impacted Fracture. ... Segmental Fracture.More items...•May 26, 2020
How do you treat a open tibial fracture?
If you fracture your tibia or fibula, you might need ORIF to bring your bones back into place and help them heal. During an “open reduction,” orthopedic surgeons reposition your bone pieces during surgery to put them back into their proper alignment.
What antibiotics are used for open fractures?
For grade 1 and grade 2 open fractures antibiotics should be given to cover gram-positive organisms. Cephalosporins such as cefazolin or cefuroxime can be used. Additional coverage for gram-negative organisms should be administered in grade 3 fractures.
What is open fracture?
Open fracture (compound fracture): The bone pokes through the skin and can be seen. Or a deep wound exposes the bone through the skin. Closed fracture (simple fracture). The bone is broken, but the skin is intact.
What is a Type 3 open fracture?
Grade III Open Fracture Grade IIIA fractures include high-energy fractures, as evidenced by severe bone injury (segmental or highly comminuted fractures) and/or large, often contaminated soft-tissue wounds. 2 Most surgeons classify high-energy fractures as IIIA even if the skin wound is not large.Jun 30, 2021
What is a Type 3 fracture?
A type III fracture (see the images below) is a fracture through the physis and epiphysis. This fracture passes through the hypertrophic layer of the physis and extends to split the epiphysis, inevitably damaging the reproductive layer of the physis.Mar 13, 2019
What is open fracture type IIIA IIIB or IIIC?
Severe type III open fractures were subtyped according to the differences in prognosis for sepsis, amputation, and treatment: IIIA (adequate soft-tissue coverage of bone with extensive soft-tissue laceration or flaps), IIIB (extensive soft-tissue loss with periosteal stripping and bone exposure), and IIIC (arterial ...
How to heal an open fracture?
Successful treatment of an open fracture depends a great deal on your cooperation. Performing specific exercises both during and after the healing process is essential to help restore muscle strength, joint motion, and flexibility. Your doctor or a physical therapist will provide you with a rehabilitation exercise plan.
What causes an open fracture?
Cause. Most open fractures are caused by some type of high-energy event—such as a gunshot or motor vehicle accident. These patients will often have additional injuries to other parts of the body. An open fracture can also result from a lower-energy incident, such as a simple fall at home or an injury playing sports.
What is internal fixation?
Internal fixation can be used to treat open fractures in which: 1 The wound is clean, 2 There is minimal skin or tissue damage, and 3 The broken pieces of bone can be well aligned
Why does an open fracture have difficulty healing?
Some open fractures may have difficulty healing because of damage to the blood supply around the bone at the time of injury. If the bone does not heal, further surgery, including bone grafting to the fracture site and repeat internal fixation, may be necessary.
When is an external fixator removed?
It is then removed during a second procedure when the fracture is healed. This patient's open fracture has been stabilized with external fixation and the wound has been partially closed with antibiotic beads.
What do you do in an emergency room?
In the emergency room, your doctor will do an initial evaluation and check for other injuries. He or she will want to know how your injury occurred and will ask about your medical history. Your doctor will then examine the wound and fracture site, checking for damage to soft tissues, nerves, and circulation. When there is any wound in the same area ...
Can bone infection be cured?
The patient may require long-term antibiotics and multiple surgical procedures. In extreme cases where the infection cannot be cured and the patient's life is threat ened, amputation may even be necessary. For this reason, preventing infection is the focus of early treatment.
Open Fracture Explanation and Definition
Are you a football fan? If so, you might remember a quarterback by the name of Joe Theismann, whose playing days ended after a tackle caused an open fracture to his right leg. The bones were broken so hard and with such force that the snap of the bones could literally be heard during the game.
Treatments of an Open Fracture
Treatment of open fractures usually consists of immediate surgery to prevent the broken bone from causing further damage to the organs, muscles, skin, or any other soft tissue surrounding the fracture site.
How to treat hairline fracture?
Treatment for a Hairline Fracture: The most important thing you can do to heal a stress fracture is rest. Take time off from exercising.
What is an oblique fracture?
An oblique fracture occurs when the bone breaks at an angle. It tends to occur most often on long bones, such as the femur or tibia. This type of injury causes a visible deformity beneath the skin. Treatment for an Oblique Fracture: Treatment varies depending on the severity of the injury.
What is a transverse fracture?
A transverse fracture is one that occurs at a 90-degree angle, straight across the bone. It happens when the impact comes perpendicular to the site of injury. Treatment for a Transverse Fracture: The medical provider will realign the bones through an open reduction internal fixation (ORIF).
What is the most severe injury?
5. Compound Fracture. This is one of the most severe injuries: A compound or open fracture is when the bone pierces the skin when it breaks. Surgery is usually called for due to its severity and the risk of infection. Treatment for a Compound Fracture: This type of injury is an emergency.
What is a greenstick fracture?
Greenstick Fracture. In a Greenstick fracture, a portion of the bone breaks but not completely through. The injured bone may also bend near the broken portion. This type of injury is most common in children. Treatment for a Greenstick Fracture: If the bone is bent, the doctor will manually straighten it.
What is pathological fracture?
Pathological fractures occur when a patient has an illness that has weakened their bones, such as osteoporosis , arthritis , osteomyelitis , osteosarcoma, or metabolic bone disorders. Treatment for a Pathological Fracture: Treatment will depend on the underlying condition that caused the fracture.
Can you hear a bone when it cracks?
In some cases, you even hear the bone when it cracks, which is both shocking and disconcerting. Then the shooting pain sets in and the inability to move the injured body part. Other times, the injury progresses gradually, and you don’t even realize that there’s a problem until you feel the pain of the fracture.
Why do bones break?
What causes broken bones? While bones are very strong, they can break. Most often, breaks happen because the bone runs into a stronger force ( getting thrown forward in a car crash, say). Also, repetitive forces – like from running — can fracture a bone.
What is a broken bone?
Bone fractures, commonly known as broken bones, happen to millions of people across the country each year. Typically caused by sports injuries, car accidents or falls, these painful injuries take time to heal. Your healthcare provider has several options to treat fractures. Appointments 216.444.2606.
How to diagnose a broken bone?
To diagnose a broken bone, your healthcare provider will examine the injury. You will also likely have one or more imaging tests. These tests can include: X-rays: This tool produces a two-dimensional picture of the break. Healthcare providers often turn to this imaging first.
Can you cast a broken toe?
With smaller bones such as fingers and toes, you won’t get a cast. Your healthcare provider might wrap the injury before using a splint. Occasionally, your healthcare provider might need to put you in traction. This treatment uses pulleys and weights to stretch the muscles and tendons around the broken bone.
What does it mean when you break a bone?
When you break a bone, healthcare providers call it a bone fracture. This break changes the shape of the bone. These breaks may happen straight across a bone or along its length. A fracture can split a bone in two or leave it in several pieces. Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center.
What is a closed fracture?
The categories include: Closed or open fractures: If the injury doesn’t break open the skin, it’s called a closed fracture. If the skin does open, it’s called an open fracture or compound fracture.
What is it called when the skin breaks?
If the skin does open, it’s called an open fracture or compound fracture. Complete fractures: The break goes completely through the bone, separating it in two. Displaced fractures: A gap forms where the bone breaks. Often, this injury requires surgery to fix.
How to treat a fractured bone?
Treatment of fractures involves the joining of the broken bones either by immobilizing the area and allowing the bone to heal on its own, or surgically aligning the broken bones and stabilizing it with metal pins, rods or plates. Sometimes, the broken bone fails to re-join and heal even after treatment. This is called non-union. Non-union occurs when the broken bones do not get sufficient nutrition, blood supply or adequate stability (not immobilized enough) to heal. Non-union can be identified by pain after the initial fracture pain is relieved, swelling, tenderness, deformity and difficulty bearing weight.
What is type 1 fracture?
Type I – Fracture through the growth plate. The epiphysis is separated from the metaphysis with the growth plate remaining attached to the epiphysis. The epiphysis is the rounded end of the long bones below the growth plate and the metaphysis is the wider part at the end of the long bones above the growth plate.
Why do bones break?
A bone may get fractured completely or partially and it is caused commonly from trauma due to fall, motor vehicle accident or sports. Thinning of the bone due to osteoporosis in the elderly can cause the bone to break easily. Overuse injury is a common cause of stress fractures in athletes. Types of fractures include:
What are the different types of fractures?
Types of fractures include: Simple fractures in which the fractured pieces of bone are well aligned and stable. Unstable fractures are those in which fragments of the broken bone are misaligned and displaced. Open (compound) fractures are severe fractures in which the broken bones cut through the skin. This type of fracture is more prone ...
How does the body react to a fracture?
Our body reacts to a fracture by protecting the injured area with a blood clot and callus or fibrous tissue. Bone cells begin forming on either side of the fracture line. These cells grow towards each other and thus close the fracture.
Why do my feet get fractured?
When the muscles of the foot are overworked or stressed, they are unable to absorb the stress and when this happens the muscles transfer the stress to the bone which results in stress fracture. Stress fractures are caused by a rapid increase in the intensity of exercise.
What is the purpose of traction?
Traction. Traction method is used for the management of fractures and dislocations that cannot be treated by casting . There are two methods of traction namely, skin traction and skeletal traction. Skin traction involves attachment of traction tapes to the skin of the limb segment below the fracture.
What is the treatment for an open fracture?
The treatment of an open fracture requires urgent exploration and cleaning of the wound, appropriate antibiotic treatment, and stabilization of the fracture.
What is an open fracture?
on September 19, 2020. Open fractures are injuries to the bone that occur when a broken bone is exposed outside the body. Open fractures, sometimes called compound fractures, can occur when there is a small cut to the skin that communicates to a fracture, or they can occur with severe soft-tissue injuries that threaten the survival of the limb.
What are the different grades of fractures?
Grades of Open Fractures 1 Grade I Open Fracture 2 A grade I open fracture occurs when there is a skin wound that communicates with the fracture measuring less than one centimeter.#N##N# Sometimes it is difficult to assess if a fracture is open (meaning the wound connects to the broken bone), but this can be determined by injecting fluid into the fracture site and seeing if the fluid exits from the wound. 3 Grade II Open Fracture 4 Grade II fractures have larger soft-tissue injuries, measuring more than one centimeter.#N##N# 5 Grade III Open Fracture 6 Grade III open fractures represent the most severe injuries and include three specific subtypes of injuries.#N##N# 7 Grade IIIA fractures include high-energy fractures, as evidenced by severe bone injury (segmental or highly comminuted fractures) and/or large, often contaminated soft-tissue wounds. Most surgeons classify high-energy fractures as IIIA even if the skin wound is not large. 8 Grade IIIB fractures have significant soft-tissue damage or loss, such that bone is exposed, and reconstruction may require a soft-tissue transfer (flap) to be performed in order to cover the wound. 9 Grade IIIC fractures specifically require vascular intervention, since the fracture is associated with vascular injury to the extremity.
