
‘Secondary Treatment’ septic systems like Aerated Wastewater Treatment Systems (AWTS) and sand filter septic systems treat the wastewater from your home to a much higher quality, before the water can be dispersed to your land and used to water your gardens and lawns.
How does secondary wastewater treatment work?
The secondary wastewater treatment process utilises aerobic microorganisms to both breakdown and remove the remaining waste and other small particles. The waste and the microorganisms are both located within the sludge, and remove both the remaining solids and nutrients through bacterial composition.
What is a secondary treatment septic system?
‘Secondary Treatment’ septic systems like Aerated Wastewater Treatment Systems (AWTS) and sand filter septic systems treat the wastewater from your home to a much higher quality, before the water can be dispersed to your land and used to water your gardens and lawns.
What is the difference between secondary treatment and secondary settling?
The secondary treatment is designed to remove soluble organics from the wastewater. Secondary treatment consists of a biological process and secondary settling is designed to substantially degrade the biological content of the sewage such as are derived from human waste, food waste, soaps and detergent.
What is the main purpose of secondary treatment?
Purpose: •The main purpose of secondary treatment is to remove BOD which does not benefit as much as SS from primary settling. •It is a process which is capable of biodegrading the organic matter into non-polluting end products ,e.g. Water,CO
What is secondary treatment of sewage?
Secondary treatment is the removal of biodegradable organic matter (in solution or suspension) from sewage or similar kinds of wastewater. The aim is to achieve a certain degree of effluent quality in a sewage treatment plant suitable for the intended disposal or reuse option.
What is primary and secondary treatment for sewage?
Primary treatment works on sedimentation, where solids separate from the water through several different tanks. In contrast, secondary treatment uses aeration, biofiltration and the interaction of waste throughout its process.
What is secondary treatment?
Secondary treatment removes the soluble organic matter that escapes primary treatment. It also removes more of the suspended solids. Removal is usually accomplished by biological processes in which microbes consume the organic impurities as food, converting them into carbon dioxide, water, and energy…
What is secondary treatment in water treatment?
Secondary treatment involves the removal of biodegradable organic matter (BOD) and suspended solids (TSS) through the processes of aeration and filtration. Secondary treatment is typically characterized as producing a treated wastewater effluent with a BOD of 25 mg/L or less and TSS of 30 mg/L or less.
What are the 3 types of sewage treatment?
Sewage treatment is done in three stages: primary, secondary and tertiary treatment.
What is the difference between primary treatment and secondary treatment?
There are two basic stages in the treat- ment of wastes, primary and secondary, which are outlined here. In the primary stage, solids are allowed to settle and removed from wastewater. The secondary stage uses biological processes to further purify wastewater. Sometimes, these stages are combined into one operation.
What is the main goal of secondary wastewater treatment?
The objective of secondary treatment is the further treatment of the effluent from primary treatment to remove the residual organics and suspended solids.
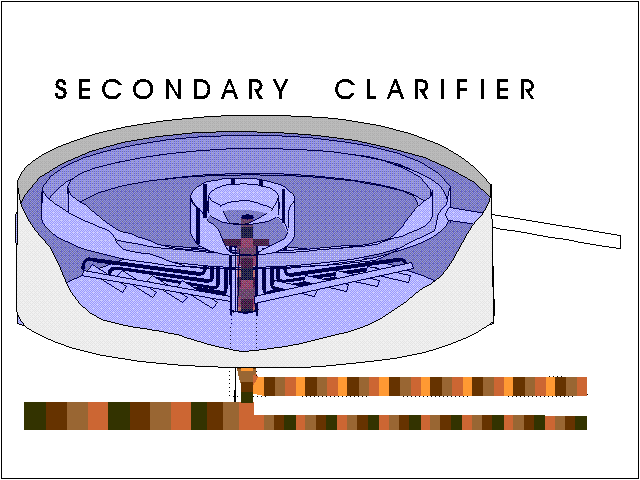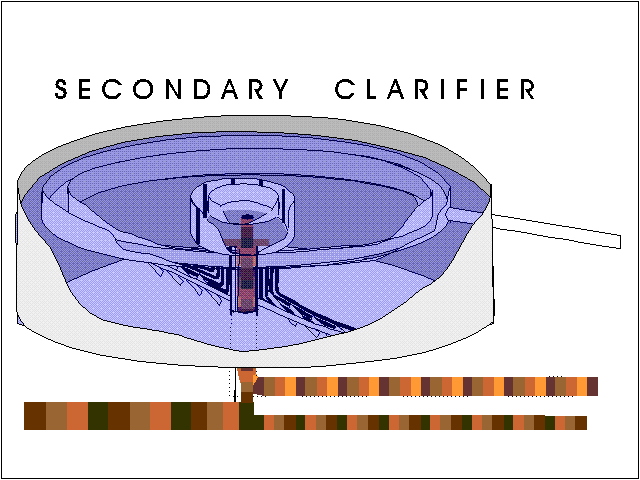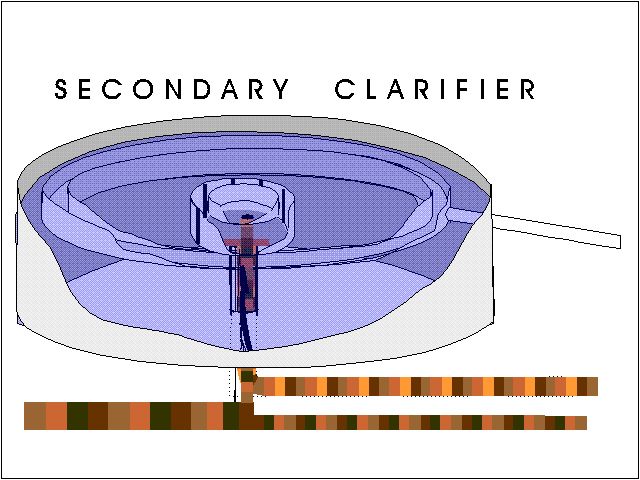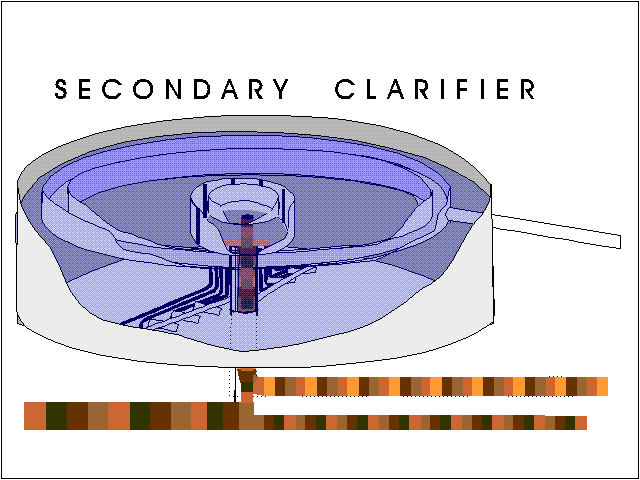
What is the difference between primary and secondary clarifiers?
Primary clarifiers are located downstream of the plant's screening and grit chambers to separate settleable solids from the raw wastewater influent, while secondary clarifiers are constructed downstream of the biological treatment or activated sludge facility to separate the treated wastewater from the biological mass ...
What is meant by secondary treatment?
Secondary treatment is the second step in most waste treatment systems during which bacteria consume the organic parts of the wastes. This is accom...
What is secondary sewage treatment class 12?
Secondary treatment of wastewater works on a deeper level than primary level. It is called as biological treatment because it is designed to substa...
What is primary and secondary treatment for sewage?
In the primary stage, solids are allowed to settle and removed from wastewater. The secondary stage uses biological processes to further purify was...
Secondary Treatment Definition
Secondary treatment of wastewater is a process that follows the primary treatment of sewage.
Objectives of Secondary Treatment
The objectives of secondary treatment are to remove the remaining suspended solids, BOD, and COD from the wastewater. It is done to reduce the primary clarifier load and improve the quality of the effluent discharged from the treatment plant.
What are the Stages of Wastewater Treatment?
The stages of wastewater treatment are collection, pre-treatment, primary treatment, secondary treatment, tertiary treatment, disposal, and reuse.
What is The Secondary Treatment of Wastewater?
This article will tell you about the second stage in the wastewater treatment process.
How Does Secondary Treatment Work
Secondary treatment is treating wastewater in a municipal water system that removes most contaminants from wastewater by reducing their levels to acceptably low levels.
What are The Alternative Types of Secondary Biological Processes?
There are a few different types of alternative secondary biological processes, and these include aerobic and anaerobic processes.
Conclusion
The secondary wastewater treatment process is more complicated than the primary wastewater treatment process. It is necessary to remove the remaining pollutants from the wastewater. The method includes various other activities that can remove the remaining impurities.
What is secondary treatment?
The secondary treatment is designed to remove soluble organics from the wastewater. Secondary treatment consists of a biological process and secondary settling is designed to substantially degrade the biological content of the sewage such as are derived from human waste, food waste, soaps and detergent.
What are the two types of solids in sewage?
SOLIDS IN SEWAGE. The solids present in the sewage are of two types viz., Organic solids, and. Inorganic solids. Organic solids are the substances derived from living things like produces from plant and animal. Examples of organic solids are carbohydrate, protein, and fat.
What is a UASB reactor?
UASB reactor is an anaerobic treatment system. In a UASB-reactor, the accumulation of influent suspended solids and bacterial activity and growth lead to the formation of a sludge blanket near the reactor bottom, where all biological processes take place. Two main features influencing the treatment performance are the distribution of the wastewater in the reactor and the “three-phase- separation” of sludge, gas and water.
How is dissolved carbonaceous organic matter removed from wastewater?
The removal of dissolved and suspended carbonaceous BOD and the stabilization of organic matter found in wastewater is accomplished using a v ariety of microorganisms, principally bacteria. Microorganisms are used to oxidize the dissolved and suspended carbonaceous organic matter into simple end products and additional biomass. This is achieved by providing the favourable environment to microorganisms with food, DO, pH, temperature etc. The organic solids present in the wastewater serve as food for the aerobic microorganisms. The only thing to be provided is the DO, which is essential for the respiration of the aerobic organisms. In the biological treatment processes the DO is supplied either through natural means or by mechanical means by agitation.
What is activated sludge?
The activated sludge process (ASP) is an aerobic biological wastewater treatment process that uses microorganisms, including bacteria, fungi, and protozoa, to speed up decomposition of organic matter requiring oxygen for treatment.
What is a membrane biological reactor?
Membrane Biological Reactors (MBR) includes a semi-permeable membrane barrier system either submerged or in conjunction with an activated sludge process. This technology guarantees removal of all suspended and some dissolved pollutants. The limitation of MBR systems is directly proportional to nutrient reduction efficiency of the activated sludge process. The cost of building and operating a MBR is usually higher than conventional wastewater treatment.
What is an oxydation ditch?
Oxidation ditch is an extended aeration ASP. It is a large holding tank in a continuous ditch with oval shape similar to that of a race-track. The ditch is built on the surface of the ground and is lined with an impermeable lining. With a detention time of more than 24 hours, the wastewater has plenty of exposure to the open air for the diffusion of oxygen. The liquid depth in the ditches is very shallow, 0.9 to 1.5 in, which helps to prevent anaerobic conditions from occurring at the bottom of the ditch.
What is secondary wastewater treatment?
The secondary wastewater treatment process utilises aerobic microorganisms to both breakdown and remove the remaining waste and other small particles. The waste and the microorganisms are both located within the sludge, and remove both the remaining solids and nutrients through bacterial composition. Secondary treatment utilises naturally occurring ...
What is a secondary treatment system?
The secondary treatment chamber (s), known as the aeration chamber (s), takes partially treated wastewater and distributes air through it. This injects gaseous oxygen into the water, becoming dissolved oxygen, which then allows aerobic bacteria to get involved.
What is the difference between a sand filter and a septic tank?
The difference between the sand filter and the septic tank is the conditions - a septic tank works in anaerobic conditions (no oxygen) whereas a sand filter works in aerobic conditions (oxygen present). The effluent is transported into the sand, which acts as a highly effective and naturally absorptive material.
How is water treated in Australia?
Wastewater can be treated in a variety of ways, with septic tanks and home sewage treatment plants offering some of the most common arrangements across Australia. They also offer different levels of treatment, which many people are unaware of.
How many stages of sewage treatment?
Wastewater treatment can have up to three stages - primary, secondary and tertiary. We are discussing the first two stages here, but head to our What are the stages of sewage treatment? information page to learn more about the third stage.
How is effluent transported?
The effluent is transported into the sand, which acts as a highly effective and naturally absorptive material. This in turn can treat effluent to a very high standard which can then be used in irrigation systems.
What is the number to call Express Wastewater?
If you have any questions about primary or secondary wastewater treatment, or feel it may be time to have a wastewater treatment plant installed in your home or business, give the friendly team at Express Wastewater a call on 1300 770 594 or complete an online job booking form today.
What is a primary septic system?
When we talk about a “primary” system, what we really mean is a conventional septic tank with an absorption trench and no other supplementary systems. The effluent flows from the house into the Septic Tank via gravity, and then to the trenches via gravity (or if gravity can’t be achieved, then in some cases it is pumped). The effluent is distributed along the length of the trench through pipes with holes in them. Trenches are filled with gravel and sand, which helps to filter out the pathogens, toxins and other contaminants before it disperses through the soil. Vegetation (typically grass) is planted on top of trenches to allow the take up of nutrients and to help remove excess water through evapotranspiration. Absorption trenches are excavated underground so that the effluent doesn’t come into contact with humans and animals because the quality of the effluent is generally poor.
What is an aerated wastewater treatment system?
An Aerated Wastewater Treatment System (AWTS) is the most versatile installation type as it can be used on all types of properties, including steep, rocky or sandy, or sites with limited space or high water table areas, and even commercial premises. With regular maintenance and care, these systems will last a long while, and, like the Sand Filter, you’re able to use the final effluent to water your grass and plants, via any irrigation type, but most typically subsurface irrigation.
How does effluent flow into a septic tank?
The effluent flows from the house into the Septic Tank via gravity, and then to the trenches via gravity (or if gravity can’t be achieved, then in some cases it is pumped). The effluent is distributed along the length of the trench through pipes with holes in them.
Why do people prefer sand filter septic systems?
Many people prefer these systems because they are environmentally beneficial and contribute water back to the earth, while reducing the risk of contamination on your land and of local waterways. Sand Filter Septic System.
Can a septic system be used on a block?
Generally, ‘primary’ septic systems are not allowed to be used on: blocks smaller than two acres; in environmentally sensitive areas (especially near waterways that lead to potable drinking reserves) or on commercial premises due to the poor quality of the final effluent.
Can you use a sand filter to water grass?
With regular maintenance and care, these systems will last a long while, and, like the Sand Filter, you’re able to use the final effluent to water your grass and plants, via any irrigation type, but most typically subsurface irrigation.
Can you install a septic system without an electrical pump?
And, if your land has a significant slope to it and you can achieve gravity, you may be able to install the septic tank and trenches without an electrical pump, which can save on power too.
What is package sewage treatment?
Commonly known as package sewage treatment plants, these units are commercially available and come in a prefabricated form for use to treat the wastewater flows from individual residences or small rural businesses.
What is a biofiltration system?
Biofiltration systems involve the use of peat or synthetic media to treat the wastewater. A peat fiber biofiltration system functions much like a conventional system with the exception that the wastewater is filtered through a layer of peat before being discharged to the disposal field. Several designs of peat filters are on the market; however the most common system installed in Manitoba is the modular system. The modules contain pre-compacted peat. This is a passive system whereby the effluent slowly trickles through the peat and drains directly to the disposal field. Peat treats the wastewater through physical filtration, adsorption and microbial activity.
